Abstract
Vascular risk factors have been linked to cognitive decline and dementia in the elderly. Microvascular inflammation, especially of the endothelium, may contribute to the progression of neurodegenerative events in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Memantine, an uncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, is a licensed drug used for the treatment of moderate to severe AD. However, little information is available regarding its anti-inflammatory effects on the endothelium. In this study, we investigated the effects of memantine on human brain microvascular endothelial dysfunction induced by the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Our results show that memantine prevents the attachment of monocyte THP-1 cells to human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEs). An in vitro BBB model experiment displayed that memantine could rescue TNF-α-induced disruption of the in vitro BBB model. In addition, memantine also interferes with monocyte transmigration across the BBB model. Our results indicate that TNF-α significantly increased the expression of cell adhesion molecules, such as ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin, which was prevented by pretreatment with memantine. Mechanistically, memantine reversed activation of the transcription factor NF-κB by preventing the phosphorylation and degradation of its inhibitor IκBα. Our data is the first to describe a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism driven by the endothelial cell-mediated neuroprotective effects of memantine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andjelkovic AV, Pachter JS (1998) Central nervous system endothelium in neuroinflammatory, neuroinfectious, and neurodegenerative disease. J Neurosci Res 51:423–430
Bevilacqua MP, Gimbrone MA Jr (1987) Inducible endothelial functions in inflammation and coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost 13:425–433
Chen SL, Tao PL, Chu CH, Chen SH, Wu HE, Tseng LF et al (2012) Low-dose memantine through its anti-inflammation and neurotrophic effects in rats. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 7:444–453
Chengye Z, Daixing Z, Qiang Z, Shusheng L (2013) PGC-1-related coactivator (PRC) negatively regulates endothelial adhesion of monocytes via inhibition of NF κB activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 439:121–125
Cho GS, Lee JC, Ju C, Kim C, Kim WK (2013) N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists memantine and MK-801 attenuate the cerebral infarct accelerated by intracorpus callosum injection of lipopolysaccharides. Neurosci Lett 538:9–14
Cristante E, McArthur S, Mauro C, Maggioli E, Romero IA, Wylezinska-Arridge M et al (2013) Identification of an essential endogenous regulator of blood-brain barrier integrity, and its pathological and therapeutic implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:832–841
Frijns CJ, Kappelle LJ (2002) Inflammatory cell adhesion molecules in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 33:2115–2122
Fukami K, Yamagishi S, Okuda S (2014) Role of AGEs-RAGE system in cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm 20:2395–2402
Grammas P, Ovase R (2001) Inflammatory factors are elevated in brain microvessels in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:837–842
Granger DN, Senchenkova E (2010) Inflammation and the microcirculation. In: integrated systems physiology: from molecule to function, vol. 2. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences Publishers, San Rafael, pp 21–87
Hayden MS, West AP, Ghosh S (2006) NF-kappaB and the immune response. Oncogene 25:758–780
Larochelle C, Alvarez JI, Prat A (2011) How do immune cells overcome the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis? FEBS Lett 585:3770–3780
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Kim J, Kim EH, Kim SJ et al (2006) Memantine reduces hematoma expansion in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage, resulting in functional improvement. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:536–544
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, Jaillon S (2011) Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 11:519–531
Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Paul IA, Wanzo V, Banerjee PK (2012) Memantine prevents cognitive impairment and reduces Bcl-2 and caspase 8 immunoreactivity in rats injected with amyloid beta1-40. Eur J Pharmacol 692:38–45
Mount C, Downton C (2006) Alzheimer disease: progress or profit? Nat Med 12:780–784
Murta V, Farías MI, Pitossi FJ, Ferrari CC (2015) Chronic systemic IL-1β exacerbates central neuroinflammation independently of the blood-brain barrier integrity. J Neuroimmunol 278:30–43
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Quack G (1999) Memantine is a clinically well tolerated N-methyl-d aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist—a review of preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 38:735–767
Perez-de-Puig I, Miró-Mur F, Ferrer-Ferrer M, Gelpi E, Pedragosa J, Justicia C et al (2015) Neutrophil recruitment to the brain in mouse and human ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol 129:239–257
Rao RM, Yang L, Garcia-Cardena G, Luscinskas FW (2007) Endothelial-dependent mechanisms of monocyte recruitment to the vascular wall. Circ Res 101:234–247
Reisberg B, Doody R, Stöffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Möbius HJ (2003) Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 348:1333–1341
Salvador E, Shityakov S, Forster C (2014) Glucocorticoids and endothelial cell barrier function. Cell Tissue Res 355:597–605
Schweingruber N, Reichardt SD, Lühder F, Reichardt HM (2012) Mechanisms of glucocorticoids in the control of neuroinflammation. J Neuroendocrinol 24:174–182
Serra G, Demontis F, Serra F, De Chiara L, Spoto A, Girardi P, Vidotto G, Serra G (2014) Memantine: new prospective in bipolar disorder treatment. World J Psychiatry 4:80–90
Srinivasan M, Lahiri DK (2015) Significance of NF-κB as a pivotal therapeutic target in the neurodegenerative pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19:471–487
Sulkowski G, Dąbrowska-Bouta B, Chalimoniuk M, Strużyńska L (2013) Effects of antagonists of glutamate receptors on pro-inflammatory cytokines in the brain cortex of rats subjected to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 261:67–76
Verma S, Kumar M, Gurjav U, Lum S, Nerurkar VR (2010) Reversal of West Nile virus-induced blood-brain barrier disruption and tight junction proteins degradation by matrix metalloproteinases inhibitor. Virology 397:130–138
Woehrl B, Klein M, Rupprecht T, Schmetzer H, Angele B, Häcker H et al (2010) CXCL16 contributes to neutrophil recruitment to cerebrospinal fluid in pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis 202:1389–1396
Wu HM, Tzeng NS, Qian L, Wei SJ, Hu X, Chen SH et al (2009a) Novel neuroprotective mechanisms of memantine: increase in neurotrophic factor release from astroglia and anti-inflammation by preventing microglial activation. Eur Secur 34:2344–2357
Zuliani G, Cavalieri M, Galvani M et al (2008) Markers of endothelial dysfunction in older subjects with late onset Alzheimer’s disease or vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 272:164–170
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81260182, 81560206) and Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (No. FB2016121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
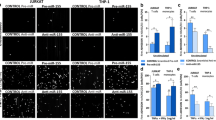
Memantine inhibits the adhesion of monocytes to human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEs). Human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEs) were pretreated with 10 μM or 20 μM memantine for 24 h, followed by incubation with TNF-α (5 ng/ml) for another 24 h. Quantitative data for THP-1 cells attached to HBMVEs was shown (#, P < 0.01 vs. untreated control group; *, P < 0.01 vs. TNF-α treated group). (GIF 3754 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zou, Z., Gong, Y. et al. Regulation of Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Barrier Functions by Memantine. J Mol Neurosci 62, 123–129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0917-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0917-x