Abstract
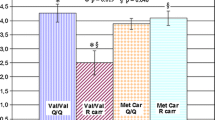
There is an inconsistent finding about the relationship of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) with dementia susceptibility, as well as with cognitive impairment. To substantiate this, we examined COMT genotype effects in certain cognitive domains in dementia. To evaluate the effects of COMT Val158Met on cognitive performance, we used The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), the cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive (ADAS-cog) and the Syndrome Kurz Test (SKT). The results show COMT Val/Met, Val/Val genotype polymorphisms had a significant effect on cognition performance (OR = 1.75 (95 %CI 1.22–2.54) and (OR = 2.76 (95 %CI 1.78–4.26), p < 0.001), and with adjustment for all cognitive test scores together, Val/Val (OR = 4.98 (95 % CI 1.47–16.86) and Val/Met (OR = 3.62 (95 % CI 1.37–9.56) had effect. Our study allows us to understand the role of COMT in cognitive performance in dementia, as well as interaction with other known risk factors for this pathology. This data might help in developing new therapeutic targets for cognitive impairment, main symptom of dementia. Other risk genotypes or haplotypes should be evaluated to determine the association with cognitive decline in dementia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used for this study are available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
American Psychiatric Association, DSM-5 Task Force (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5™, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Barnett JH, Scoriels L, Munafo MR (2008) Meta-analysis of the cognitive effects of the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene Val158/108Met polymorphism. Biol Psychiatry 64(2):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.01.005
Bellander M, Backman L, Liu T, Schjeide BM, Bertram L, Schmiedek F, Lindenberger U, Lovden M (2015) Lower baseline performance but greater plasticity of working memory for carriers of the val allele of the COMT Val(1)(5)(8)Met polymorphism. Neuropsychology 29(2):247–254. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00013a008
Blanchard MM, Chamberlain SR, Roiser J, Robbins TW, Muller U (2011) Effects of two dopamine-modulating genes (DAT1 9/10 and COMT Val/Met) on n-back working memory performance in healthy volunteers. Psychol Med 41(3):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003329171000098X
Bruder GE, Keilp JG, Xu H, Shikhman M, Schori E, Gorman JM, Gilliam TC (2005) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) genotypes and working memory: associations with differing cognitive operations. Biol Psychiatry 58(11):901–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.05.010
Caldú X, Vendrell P, Bartrés-Faz D, Clemente I, Bargalló N, Jurado MA, Serra-Grabulosa JM, Junqué C (2007) Impact of the COMT Val108/158 Met and DAT genotypes on prefrontal function in healthy subjects. NeuroImage 37(4):1437–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.06.021
Chen J, Lipska BK, Halim N, Ma QD, Matsumoto M, Melhem S, Kolachana BS, Hyde TM, Herman MM, Apud J, Egan MF, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR (2004) Functional analysis of genetic variation in catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): effects on mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity in postmortem human brain. Am J Hum Genet 75(5):807–821. https://doi.org/10.1086/425589
de Frias CM, Annerbrink K, Westberg L, Eriksson E, Adolfsson R, Nilsson LG (2004) COMT gene polymorphism is associated with declarative memory in adulthood and old age. Behav Genet 34:533–539
de Frias CM, Marklund P, Eriksson E, Larsson A, Oman L, Annerbrink K, Backman L, Nilsson LG, Nyberg L (2010) Influence of COMT gene polymorphism on fMRI-assessed sustained and transient activity during a working memory task. J Cogn Neurosci 22(7):1614–1622. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21318
Dickerson FB, Boronow JJ, Stallings C, Origoni AE, Sullens A, Yolken RH (2007) The catechol O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism is not associated with broad-based cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 96(1–3):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2007.05.021
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Dekosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Cummings J, Delacourte A, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Jicha G, Meguro K, O’brien J, Pasquier F, Robert P, Rossor M, Salloway S, Stern Y, Visser PJ, Scheltens P (2007) Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol 6(8):734–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70178-3
Dumontheil I, Roggeman C, Ziermans T, Peyrard-Janvid M, Matsson H, Kere J, Klingberg T (2011) Influence of the COMT genotype on working memory and brain activity changes during development. Biol Psychiatry 70(3):222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.027
Erickson KI, Kim JS, Suever BL, Voss MW, Francis BM, Kramer AF (2008) Genetic contributions to age-related decline in executive function: a 10-year longitudinal study of COMT and BDNF polymorphisms. Front Hum Neurosci 2:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.09.011.2008
Fiocco AJ, Lindquist K, Ferrell R, Li R, Simonsick EM, Nalls M, Harris TB, Yaffe K, Health ABC Study (2010) COMT genotype and cognitive function: an 8-year longitudinal study in white and black elders. Neurology 74(16):1296–1302. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d9edba
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh P (1975) Minimental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patientes for clinician. J Psychiat Res 12:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6
Govoni S, Ranzani GN, Racchi M (2012) Influence of COMT Val158Met polymorphism on Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment in Italian patients. J Alzheimers Dis 32(4):919–926
Grossman MH, Emanuel BS, Budarf ML (1992) Chromosomal mapping of the human catechol-O-methyltransferase gene to 22q11.1 q11.2. Genomics 12(4):822–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/0888-7543(92)90316-k
Gruber O (2012) Genetic polymorphisms of 5-HTT and DAT but not COMT differentially affect verbal and visuospatial working memory functioning. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262(8):667–676
Harris AH, Thoresen CE (2005) Volunteering is associated with delayed mortality in older people: analysis of the longitudinal study of aging. J Health Psychol 10:739 – 752. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105305057310
Hoogland J, de Bie RM, Williams-Gray CH, Muslimovic D, Schmand B, Post B (2010) Catechol-O-methyltransferase val158met and cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(15):2550–2554. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23319
IBM Corp. Released (2020) IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 27.0. Armonk, NY
Juarez-Cedillo T, Sanchez-Arenas R, Sanchez-Garcia S, Garcia-Peña C, Hsiung GY, Sepehry AA, Beattie BL, Jacova C (2012) Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment and its subtypes in the Mexican population. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 34(5–6):271–281. https://doi.org/10.1159/000345251
Kennedy BP, Bottiglieri T, Arning E, Ziegler MG, Hansen LA, Masliah E (2004) Elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine in Alzheimer brain: influence on methyltransferases and cognitive function. J Neural Transm 111:547–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0096-5
Lachman HM, Papolos DF, Saito T, Yu YM, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM (1996) Human catechol-O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: description of a functional polymorphism and its potential application to neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacogenetics 6:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1097/00008571-199606000-00007
Lahiri DK, Nurnberger JI (1991) A rapid non-enzymatic method for the preparation of HMW DNA from blood for RFLP studies. Nucleic Acids Res 19(19):5444. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/19.19.5444
Lanni C, Garbin G, Lisa A, Biundo F, Ranzenigo A, Sinforiani E, Cuzzoni G, Liu J et al (2014) Association between maternal COMT gene polymorphisms and fetal neural tube defects risk in a Chinese population Birth defects research Part A. Clin Mol Teratol 100:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdra.23208
Liu ME, Huang CC, Yang AC, Tu PC, Yeh HL, Hong CJ, Liou YJ, Chen JF, Chou KH, Lin CP, Tsai SJ (2014) Catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism on the relationship between white matter hyperintensity and cognition in healthy people. PLoS One 9(2):e88749. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088749
Lotta T, Vidgren J, Tilgmann C, Ulmanen I, Melen K, Julkunen I, Taskinen J (1995) Kinetics of human soluble and membrane-bound catechol O-methyltransferase: a revised mechanism and description of the thermolabile variant of the enzyme. Biochemistry 34(13):4202–4210. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00013a008
Monllau A, Pena-Casanova J, Blesa R, Aguilar M, Bohm P, Sol JM, Hernandez G (2007) Valor diagnóstico y correlaciones funcionales de la escala ADAS-Cog en la enfermedad de Alzheimer: datos del proyecto NORMACODEM [Diagnostic value and functional correlations of the ADAS-Cog scale in Alzheimer’s disease: data on NORMACODEM project]. Neurologia 22(8):493–501
Nagel IE, Chicherio C, Li SC, von Oertzen T, Sander T, Villringer A, Heekeren HR, Backman L, Lindenberger U (2008) Human aging magnifies genetic effects on executive functioning and working memory. Front Hum Neurosci 2:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.09.001.2008
Opmeer EM, Kortekaas R, van Tol MJ, van der Wee NJ, Woudstra S, van Buchem MA, Penninx BW, Veltman DJ, Aleman A (2013) Influence of COMT val158met genotype on the depressed brain during emotional processing and working memory. PLoS One 8(9):e73290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073290
Pan X, Kaminga AC, Wen SW, Wu X, Acheampong K, Liu A (2019) Dopamine and dopamine receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease: a systematic review and network meta analysis. Front Aging Neurosci 11:175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00175
Papenberg G, Backman L, Nagel IE, Nietfeld W, Schroder J, Bertram L, Heekeren HR, Lindenberger U, Li SC (2014) COMT polymorphism and memory dedifferentiation in old age. Psychol Aging 29(2):374–383. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033225
Potter GG, Taylor WD, McQuoid DR, Steffens DC, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Krishnan KR (2009) The COMT Val158Met polymorphism and cognition in depressed and nondepressed older adults. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 24(10):1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.2235
Radloff L (1977) The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1:385–401. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662167700100306
Roostaei T, Nazeri A, Felsky D, De Jager PL, Schneider JA et al (2017) Genome-wide interaction study of brain beta-amyloid burden and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 22:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.35
Rosa A, Peralta V, Cuesta MJ, Zarzuela A, Serrano F, Martinez-Larrea A, Fananas L (2004) New evidence of association between COMT gene and prefrontal neurocognitive function in healthy individuals from sibling pairs discordant for psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 161(6):1110–1112. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.6.1110
Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL (1984) A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 141:1356–1364. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.141.11.1356
Schaie KW, Willis SL, Caskie GI (2004) The Seattle longitudinal study: relationship between personality and cognition. Neuropsychol Dev Cogn B Aging Neuropsychol Cogn 11:304 – 324. https://doi.org/10.1080/13825580490511134
Sheldrick AJ, Krug A, Markov V, Leube D, Michel TM, Zerres K, Eggermann T, Kircher T (2008) Effect of COMT val158met genotype on cognition and personality. Eur Psychiatry 23(6):385–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.05.002
Sinoff G, Ore L, Zlotogorsky D, Tamir A (1999) Short anxiety screening test-a brief instrument for detecting anxiety in the elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 14:1062–1071. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1099-1166(199912)14:12<1062::aid-gps67>3.0.co;2-q
Starr JM, Fox H, Harris SE, Deary IJ, Whalley LJ (2007) COMT genotype and cognitive ability: a longitudinal aging study. Neurosci Lett 421:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.05.023
Stefanis NC, van Os J, Avramopoulos D, Smyrnis N, Evdokimidis I, Stefanis CN (2005) Effect of COMT Val158Met polymorphism on the continuous performance test, identical pairs version: tuning rather than improving performance. Am J Psychiatry 162(9):1752–1754. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.9.1752
Stuart K, Summers MJ, Valenzuela MJ, Vickers JC (2014) BDNF and COMT polymorphisms have a limited association with episodic memory performance or engagement in complex cognitive activity in healthy older adults. Neurobiol Learn Mem 110:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2014.01.013
Vargas-Alarcón G, Juárez-Cedillo E, Martínez-Rodríguez N, Fragoso JM, García-Hernández N, Juárez-Cedillo T (2016) Association of interleukin-10 polymorphisms with risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias (SADEM study). Immunol Lett 177:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.07.011
Wang X, Wang Z, Wu Y, Yuan Y, Hou Z, Hou G (2014) Association analysis of the catechol-O-methyltransferase/methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genes and cognition in late-onset depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 68(5):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12133
Wardle MC, de Wit H, Penton-Voak I, Lewis G, Munafo MR (2013) Lack of association between COMT and working memory in a population-based cohort of healthy young adults. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(7):1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.24
Willmott C, Withiel T, Ponsford J, Burke R (2014) COMT Val158Met and cognitive and functional outcomes after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 31(17):1507–1514. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.3308
Yan W, Zhao C, Sun L, Tang B (2016) Association between polymorphism of COMT gene (Val158Met) with Alzheimer’s disease: an updated analysis. J Neurol Sci 361:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.01.014
Zilles D, Meyer J, Schneider-Axmann T, Ekawardhani S, Gruber E, Falkai P, Gruber O (2012) Genetic polymorphisms of 5-HTT and DAT but not COMT differentially affect verbal and visuospatial working memory functioning. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin NeuroSci 262(8):667–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-012-0312-0
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Valle Medina Antonio, for his valuable participation in capturing the genetic information used in this study, and Ms. Susan Drier-Jonas for her help with the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from SSA/IMSS/ISSSTE-CONACYT (Mexico) SALUD- 233065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TJC: main investigator, idea of the study, participated in coordination, and drafted the manuscript. EGF: analyzed and interpreted the cognitive tests the patients and coordinate the study. NMR: participated in the coordination and drafted the manuscript. JMF: participated in its design and coordination and drafted the manuscript. OGA: participated in its design and coordination. GVA: participated in genetic analysis and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juárez-Cedillo, T., González-Figueroa, E., Martínez-Rodríguez, N. et al. Influence of COMT polymorphism in cognitive performance on dementia in community-dwelling elderly Mexican (SADEM study). Metab Brain Dis 36, 1223–1229 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00740-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00740-5