Abstract
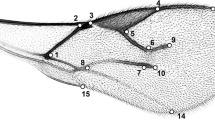
We explored evolutionary changes in wing venation and wing size and shape in Aphidiinae, one of the well-known groups of parasitic wasps from the family Braconidae. Forewings of 53 species from 12 genera were examined, for which a molecular phylogeny was constructed on the basis of the mitochondrial barcoding gene COI. By covering all types of wing venation within the subfamily Aphidiinae and by using landmark-based geometric morphometrics and phylogenetic comparative methods, we tested whether evolutionary changes in wing shape correlate to the changes in wing venation and if both changes relate to wing size. The relationship between wing morphology and host specificity has been also investigated. We found that six types of wing venation, with different degree of vein reduction, could be recognized. Wing venation type is largely genus specific, except in the case of maximal reduction of wing venation which could be found across examined Aphidiinae taxa. The reconstruction of evolutionary changes in wing venation indicates that evolutionary changes in wing shape are related to the changes in wing size, indicating that miniaturization play a role in evolution of wing morphology while host specialization does not affect the wing shape within the subfamily Aphidiinae.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Achterberg, C. (1991). Revision of the genera of Afrotropical and W. Palaearctic Rogadinae Foester (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Zoologische Verhandelingen, 273(1), 1–101.
Belshaw, R., & Quicke, D. L. J. (1997). A molecular phylogeny of the Aphidiinae (hymenoptera: Braconidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 7(3), 281–293.
Belshaw, R., Dowton, M., Quicke, D. L. J., & Austin, A. D. (2000). Estimating ancestral geographical distributions: a Gondwanan origin for aphid parasitoids? Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 267(1442), 491–496.
Chaubet, B., Derocles, S. A. P., Huilé, M., Le Ralec, A., Outreman, Y., Simon, J. C., & Tomanović, Ž. (2013). Two new species of aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera, Braconidae, Aphidiinae) from the high Arctic (Spitsbergen, Svalbard). Zoologischer Anzeiger, 252(1), 34–40.
Derocles, S. A., Plantegenest, M., Simon, J. C., Taberlet, P., & Le Ralec, A. (2012). A universal method for the detection and identification of Aphidiinae parasitoids within their aphid hosts. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12(4), 634–645.
Dowton, M., Belshaw, R., Austin, A. D., & Quicke, D. L. (2002). Simultaneous molecular and morphological analysis of braconid relationships (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Braconidae) indicates independent mt-tRNA gene inversions within a single wasp family. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 54(2), 210–226.
Dryden, I. L., & Mardia, K. M. (1998). Statistical shape analysis. New York: Wiley.
Dudley, R. (2002). The biomechanics of insect flight: form, function, evolution (p. 496). Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Eberle, J., Myburgh, R., & Ahrens, D. (2014). The evolution of Morphospace in Phytophagous scarab chafers: no competition–no divergence? PloS One, 9(5), e98536. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098536.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Phylogenies and the comparative method. The American Naturalist, 125, 1–15.
Finlayson, T. (1990). The systematics and taxonomy of final instar larvae of the family Aphidiidae. Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 152, 3–74.
Gagić, V., Petrović-Obradović, O., Fründ, J., Kavallieratos, N. G., Athanassiou, C., Starý, P., & Tomanović, Ž. (2016). The effects of aphid traits on parasitoid host use and specialist advantage. PloS One, 11(6), e0157674. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157674.
Gärdenfors, U. (1986). Taxonomic and biological revision of Palaearctic Ephedrus(Haliday) (Hymenoptera, Braconidae, Aphidiinae). Entomologica Scandinavica, Supplements, 27, 1–95.
Gärdenfors, U. (1990). Trioxys apterus sp. n. from Ecuador, a new wingless species of Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Insect Systematics & Evolution, 21(1), 67–69.
Gómez-Robles, A., Olejniczak, A. J., Martinón-Torres, M., Prado-Simón, L., & Bermúdez de Castro, J. M. (2011). Evolutionary novelties and losses in geometric morphometrics: a practical approach through hominin molar morphology. Evolution, 65(6), 1772–1790.
Gould, S. J. (1966). Allometry and size in ontogeny and phylogeny. Biological Reviews, 41, 587–640.
Henry, L. M., Roitberg, B. D., & Gillespie, D. R. (2006). Covariance of phenotypically plastic traits induces an adaptive shift in host selection behaviour. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 273(1603), 2893–2899.
Hipsley, C. A., Miles, D. B., & Müller, J. (2014). Morphological disparity opposes latitudinal diversity gradient in lacertid lizards. Biology Letters, 10(5), 20140101. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2014.0101.
Kambhampati, S., Völkl, W., & Mackauer, M. (2000). Phylogenetic relationships among genera of Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) based on DNA sequence of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene. Systematic Entomology, 25(4), 437–445.
Kavallieratos, N. G., Tomanović, Ž., Starý, P., Athanassiou, C. G., Sarlis, G. P., Petrović, O., Niketić, M., & Anagnou-Veroniki, M. (2004). A survey of aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) of southeastern Europe and their aphid—plant associations. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 39, 527–563.
Klingenberg, C. P. (2008). Novelty and “homology-free” morphometrics: What’s in a name? Evolutionary Biology, 35, 186–190.
Klingenberg, C. P. (2011). MorphoJ: an integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 353–357.
Klingenberg, C. P. (2016). Size, shape, and form: concepts of allometry in geometric morphometrics. Development Genes and Evolution, 226(3), 113–137.
Klingenberg, C. P., & Gidaszewski, N. A. (2010). Testing and quantifying phylogenetic signals and homoplasy in morphometric data. Systematic Biology, 59, 245–261.
Klingenberg, C. P., & Marugán-Lobón, J. (2013). Evolutionary covariation in geometric morphometric data: analyzing integration, modularity and allometry in a phylogenetic context. Systematic Biology, 62, 591–610.
Kos, K., Petrović, A., Starý, P., Kavallieratos, N. G., Ivanović, A., Toševski, I., & Tomanović, Ž. (2011). On the identity of cereal aphid parasitoid wasps Aphidius uzbekistanicus, Aphidius rhopalosiphi, and Aphidius avenaphis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) by examination of COI mitochondrial gene, geometric morphometrics, and morphology. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 104(6), 1221–1232.
Larsson, S. G. (1978). Baltic amber—a paleobiological study. Entomograph, 1, 1–192.
Laurin, M. (2004). The evolution of body size, Cope’s rule and the origin of amniotes. Systematic Biology, 53, 594–622.
Mackauer, M. (1958). Zur Kenntnis der paläarktischen Aphidiinae (Hym., Braconidae). Zeitschrift für Angewandte Entomologie, 43(3), 282–285.
Mackauer, M. (1961). Die Gattungen der Familie Aphidiidae und ihre verwandtschaftliche Zuordnung (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonoidea). Beitraege zur Entomologie, 11, 792–803.
Mackauer, M. (1968). Insect parasites of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae Sulz., and their control potential. Entomophaga, 13(2), 91–106.
Mackauer, M., & Finlayson, T. (2012). Choreopraon totarae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae), a new parasitoid of Neophyllaphis totarae (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea: Drepanosiphidae) in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 39(1), 77–84.
Maddison, W. P. (1991). Squared-change parsimony reconstructions of ancestral states for continuous-valued characters on a phylogenetic tree. Systematic Zoology, 40, 304–314.
Maddison, W. P., & Maddison, D. R. (2016). Mesquite: a modular system for evolutionary analysis. Version 3.10. http://mesquiteproject.org.
Mitrovski-Bogdanović, A., Petrović, A., Mitrović, M., Ivanović, A., Žikić, V., Starý, P., Vorburger, C., & Tomanović, Ž. (2013). Identification of two cryptic species within the Praon abjectum group (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) using molecular markers and geometric morphometrics. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 106(2), 170–180.
Monteiro, L., & Nogueira, M. (2011). Evolutionary patterns and processes in the radiation of phyllostomid bats. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 11(1), 137.
O’Donnell, D. J. (1989). A morphological and taxonomic study of first instar larvae of Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Systematic Entomology, 14, 197–219.
Ortega-Blanco, J., Bennett, D. J., Delclòs, X., & Engel, M. S. (2009). A primitive aphidiine wasp in Albian amber from Spain and a northern hemisphere origin for the subfamily (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae). Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society, 82(4), 273–282.
Pélabon, C., Firmat, C., Bolstad, H. G., Voje, L. K., Houle, D., Cassara, J., Rouzic, L. A., & Hansen, F. T. (2014). Evolution of morphological allometry. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1320, 58–75.
Petrović, A., Mitrović, M., Starý, P., Petrović-Obradović, O., Žikić, V., Tomanović, Ž., & Vorburger, C. (2013). Lysiphlebus orientalis (Hymenoptera, Braconidae), a new invasive aphid parasitoid in Europe—evidence from molecular markers. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 103, 451–457.
Petrović, A., Mitrović, M., Ivanović, A., Žikić, V., Kavallieratos, N. G., Starý, P., Mitrovski-Bogdanović, A., Tomanović, Ž., & Vorburger, C. (2015). Genetic and morphological variation in sexual and asexual parasitoids of the genus Lysiphlebus—an apparent link between wing shape and reproductive mode. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 15(5), 1–12.
Pie, M. R., & Tschá, M. K. (2013). Size and shape in the evolution of ant worker morphology. PeerJ, 1(1), e205. doi:10.7717/peerj.205.
Polly, P. D. (2008). Developmental dynamics and G-matrices: can morphometric spaces be used to model phenotypic evolution? Evolutionary Biology, 35, 83–96.
Prevosti, F. J., Turazzini, G. F., Ercoli, M. D., & Hingst-Zaher, E. (2012). Mandible shape in marsupial and placental carnivorous mammals: a morphological comparative study using geometric morphometrics. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 164, 836–855.
Quicke, D. L. J., & van Achterberg, C. (1990). Phylogeny of the subfamilies of Braconidae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonoidea). Zoologische Verhandelingen, 258, 1–95.
Ree, R. H., & Donoghue, M. J. (1998). Step matrices and the interpretation of homoplasy. Systematic Biology, 47(4), 582–588.
Rehman, A., & Powell, W. (2010). Host selection behaviour of aphid parasitoids (Aphidiidae: Hymenoptera). Journal of Plant Breeding and Crop Science, 2(10), 299–311.
Riegel, G. T. (1948). The wings of Braconidae (Hymenoptera). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 41(4), 439–449.
Rohlf, F. J. (2001). Comparative methods for the analysis of continuous variables: geometric interpretations. Evolution, 55, 2143–2160.
Rohlf, F. J. (2005). tpsDig program, version 2.04, ecology and evolution, SUNY at Stony Brook. See http://life.bio.sunysb.edu/morph.
Rohlf, F. J., & Slice, D. (1990). Extensions of the Procrustes method for the optimal superimposition of landmarks. Systematic Biology, 39(1), 40–59.
Sanchis, A., Latorre, A., González-Candelas, F., & Michelena, J. M. (2000). An 18S rDNA-based molecular phylogeny of Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Molecular phylogenetics and Evolution, 14(2), 180–194.
Schlinger, E. (1974). Continental drift, Nothofagus, and some ecologically associated insects. Annual Review of Entomology, 19, 323–343.
Sharkey, M. J., & Roy, A. (2002). Phylogeny of the Hymenoptera: a reanalysis of the Ronquist et al. 1999 analysis, emphasizing wing venation and apocritan relationships. Zoologica Scripta, 31(1), 57–66.
Sherratt, E., Gower, D. J., Klingenberg, C. P., & Wilkinson, M. (2014). Evolution of cranial shape in caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona). Evolutionary Biology, 41(4), 528–545.
Smith, P., Kambhampati, S., Völkl, W., & Mackauer, M. (1999). A phylogeny of aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) inferred from mitochondrial NADH 1 dehydrogenase gene sequence. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 11, 236–245.
Stary, P. (1966). Aphid parasites (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) and their relationship to aphid attending ants, with respect to biological control. Insectes Sociaux, 13, 185–202.
Starý, P. (1970). Biology of aphid parasites (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) with respect to integrated control. Series Entomologica, 6 (p. 643). The Hague: Dr. W. Junk Publishers.
Starý, P. (1972). New aphid parasites (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) from Cuba. Annales Zoologici, 29(9), 317–322.
Starý, P. (1976). Two new Pseudephedrus Starý aphid parasites (Hymenoptera, Aphidiidae) associated with Nothofagus in South America. With notes on the continental drift. Entomologica Scandinavica, 7, 24–30.
Starý, P. (1981). On the strategy, tactics and trends of host specificity evolution in aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera, Aphidiidae). Acta Entomologica BohemoSVNvaca, 78, 65–75.
Stayton, C. T. (2005). Morphological evolution of the lizard skull: a geometric morphometrics survey. Journal of Morphology, 263, 47–59.
Stigenberg, J., Boring, C. A., & Ronquist, F. (2015). Phylogeny of the parasitic wasp subfamily Euphorinae (Braconidae) and evolution of its host preferences. Systematic Entomology, 40, 570–591.
Tremblay, E., & Calvert, D. (1971). Embryosystematics in the aphidiines (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Bolletino del Laboratorio di Entomologia Agraria ‘Filippo Silvestri’, 29, 223–249.
Wharton, R. (1980). Review of the Nearctic Alysiini (Hymenoptera, Braconidae): with discussion of generic relationship within the tribe. Entomology University of California Publication, 88, 1–112.
Wharton, R., Shaw, S., Sharkey, M., Wahl, D., Woolley, J., Whitfield, J., Marsh, P., & Johnson, W. (1992). Phylogeny of the subfamilies of the family Braconidae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonoidea): a reassessment. Cladistics, 8, 199–235.
Wharton, R. A., Marsh, P. M., & Sharkey, M. J. (1997). Manuel of the new world genera of the family Braconidae (Hymenoptera). Washington: International Society of Hymenopterists.
Willemstein, S. C. (1987). An evolutionary basis for pollination ecology. Leiden Botanical Series, 10, 425.
Yu, D. S. K., van Achterberg, C., & Horstmann, K. (2012). Taxapad 2012, Ichneumonoidea 2011. Database on flash-drive.
Žikić, V., Tomanović, Ž., Ivanović, A., Kavallieratos, N. G., Starý, P., Stanisavljević, L. Ž., & Rakhshani, E. (2009). Morphological characterization of Ephedrus persicae biotypes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) in the Palaearctic. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 102(1), 1–11.
Žikić, V., Ilić Milošević, M., Stanković, S., Petrović, O., Petrović-Obradović, O., Kavallieratos, N., Starý, P., & Tomanović, Ž. (2012). Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) of Serbia and Montenegro-tritrophic interactions. Acta Entomologica Serbica, 17, 83–105.
Žikić, V., Lazarević, M., & Milošević, D. (2017). Host range patterning of parasitoid wasps Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Zoologischer Anzeiger – A Journal of Comparative Zoology, 268, 75–83.
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments and suggestions. This research was supported by the Grant III43001 (The Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia). We thank to Dr. Lydia Mitits from the Democritus University of Thrace, Komotiní, Greece and Antonis Mylonopoulos, Komotiní, Greece for the English language proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplement 1
The data and parameters used for the analysis of selected parasitoids. Country’s abbreviations: BEL = Belgium, CHE = Switzerland, CHL = Chile, CHN = China, CZE = Czech Republic, FRA = France, GRC = Greece, IND = India, IRN = Iran, JPN = Japan, MNE = Montenegro, NLD = Netherlands, SLO = Slovenia, SRB = Serbia. Legator’s abbreviations: AM = A. Mitrovski-Bogdanović, AP = A. Petrović, BL = B. Lavandero, CV = C. Vorburger, ER = E. Rakhshani, HT = H. Takada, KK = K. Kos, MB = M. Brajković, MD = M. Djordjević, MI = M. Ilić Milošević, MJ = M. Janković, NK = N. Kavalliearatos, PS = P. Starý, SS = S. Stanković, VŽ = V. Žikić, ZK = Z. Kojičić, ŽT = Ž. Tomanović (XLSX 16 kb)
Supplement 2
DNA extraction, amplification, sequencing and phylogenetic reconstruction. (DOCX 13 kb)
Suppl. Fig. 1
Phylogenetic relationships of Aphidiinae obtained from sequences of cytochrome c oxidase I using Maximum likelihood method. Bootstrap values are indicated above/below branches. Scale bar indicates the number of substituted bases per site. Information is presented with parasitoid species name following with specimen GenBank accession number or voucher code (Apendix 1). A phylogenetic three supports the traditional phylogenetic relations of Aphidiinae species based on morphological traits (Mackauer 1961; Gärdenfors 1986) and molecular data (Belshaw and Quicke 1997; Sanchis et al. 2000). Also in accordance with literature, Pseudephedrus stands out as a completely separate clade at the very base of the phylogenetic tree like it is earlier shown based on other genes (Belshaw et al. 2000). The position of Lipolexis gracilis out of the clade that comprise Trioxys and Monoctonus (subtribe Trioxina) is unexpected as estimations of phylogenetic relationships based on ribosomal DNA indicated that Lipolexis was coherent within the subtribe Trioxina (Sanchis et al. 2000). (GIF 94 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Žikić, V., Stanković, S.S., Petrović, A. et al. Evolutionary relationships of wing venation and wing size and shape in Aphidiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Org Divers Evol 17, 607–617 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-017-0338-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-017-0338-2