Abstract
Purpose
Obesity and overweight are significant risk factors for many serious diseases. Several studies have investigated the relationship between emotional regulation and overweight or obesity in people with eating disorders. Although a few studies have explored alexithymia in individuals with severe obesity without eating disorders, no attention has been paid to individuals with overweight and preclinical form of obesity. This study aims to assess whether overweight and obesity are related to emotional dysregulation and alexithymia.
Methods
The study involved 111 undergraduate students who had not been diagnosed with an eating disorder. The sample was divided into two groups according to their body mass index (BMI): normal weight (N = 55) and overweight (N = 56). All of them completed the Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20), the Emotional Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ), and the Eating Disorder Inventory-2 (EDI-2).
Results
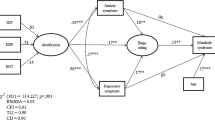
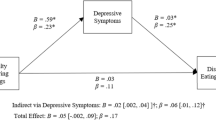
Results showed higher levels of alexithymia, and specifically higher difficulty in identifying feelings and an externally oriented thought, in participants with overweight. Multiple correlation analysis highlighted the positive relations between some EDI-2 subscales and both alexithymia and emotional regulation scores. Linear regressions revealed a significant relationship between body BMI and both alexithymia and emotional regulation strategies.
Conclusions
The condition of overweight/obesity seems to be associated with higher emotional dysregulation compared to normal weight condition. It is essential to study this relationship because it could represent a risk factor for the worsening of problems related to overeating and excessive body weight. These findings suggest that an integrated approach aimed at considering the promotion of emotional regulation could contribute to the effectiveness of a program designed to reduce overweight and obesity.
Level of evidence
Level III: case-control analytic study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO obesity and overweight (2016) http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/noncommunicable-diseases/obesity/data-and-statistics. Accessed 18 Nov 2018
Yumuk V, Tsigos C, Fried M, Schindler K, Busetto L, Micic D (2015) Obesity Management Task Force of the European Association for the study of obesity. European guidelines for obesity management in adults. Obes facts 8(6):402–424
Ricca V, Mannucci E, Moretti S, Di Bernardo M, Zucchi T, Cabras PL, Rotella CM (2000) Screening for binge eating disorder in obese outpatients. Compr Psychiatry 41(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-440X(00)90143-3
Rothman KJ (2008) BMI-related errors in the measurement of obesity. Int J Obes 32(S3):S56. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.87
Hill AJ (2007) Obesity and eating disorders. Obes rev 8:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00335.x
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Pub, Philadelphia
Ramacciotti CE, Coli E, Passaglia C, Lacorte M, Pea E, Dell’Osso L (2000) Binge eating disorder: prevalence and psychopathological features in a clinical sample of obese people in Italy. Psychiat Res 94(2):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03353413
Stice E, Bearman SK (2001) Body-image and eating disturbances prospectively predict increases in depressive symptoms in adolescent girls: a growth curve analysis. Dev Psychol 37(5):597. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.37.5.597
Svaldi J, Caffier D, Tuschen-Caffier B (2010) Emotion suppression but not reappraisal increases desire to binge in women with binge eating disorder. Psychother Psychosom 79(3):188–190. https://doi.org/10.1159/000296138
Gianini LM, White MA, Masheb RM (2013) Eating pathology, emotion regulation, and emotional overeating in obese adults with binge eating disorder. Eat Behav 14(3):309–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.05.008
Leehr EJ, Krohmer K, Schag K, Dresler T, Zipfel S, Giel KE (2015) Emotion regulation model in binge eating disorder and obesity—a systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 49:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.008
Zijlstra H, van Middendorp H, Devaere L, Larsen JK, van Ramshorst B, Geenen R (2012) Emotion processing and regulation in women with morbid obesity who apply for bariatric surgery. Psyc Health 27(12):1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2011.600761
Gross JJ, Feldman Barrett L (2011) Emotion generation and emotion regulation: one or two depends on your point of view. Emot Rev 3(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073910380974
Thayer JF, Lane RD (2000) A model of neurovisceral integration in emotion regulation and dysregulation. J Affect Disord 61(3):201–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0327(00)00338-4
Gratz KL, Roemer L (2004) Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 26(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOBA.0000007455.08539.94
Gross JJ (1998) The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Rev Gen Psychol 2(3):271. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.25.3.394
Gross JJ (2002) Emotion regulation: affective, cognitive, and social consequences. Psychophysiology 39(3):281–291. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0048577201393198
Denollet J, Rombouts H, Gillebert TC, Brutsaert DL, Sys SU, Stroobant N (1996) Personality as independent predictor of long-term mortality in patients with coronary heart disease. Lancet 347(8999):417–421. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.25.3.394
Gross JJ, Levenson RW (1997) Hiding feelings: the acute effects of inhibiting positive and negative emotions. J Abnorm Psychol 106:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.106.1.95
Martin P (1998) The healing mind. Thomas Dunne Books, New York
Denollet J (2005) DS14: standard assessment of negative affectivity, social inhibition, and type D personality. Psychosom Med 67(1):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.psy.0000149256.81953.49
Hofmann SG, Sawyer AT, Fang A, Asnaani A (2012) Emotion dysregulation model of mood and anxiety disorders. Depression Anxiety 29(5):409–416. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.21888
Taylor GJ, Bagby RM, Parker JD (1991) The alexithymia construct: a potential paradigm for psychosomatic medicine. Psychosomatics 32(2):153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(91)72086-0
Bagby RM, Parker JD, Taylor GJ (1994) The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale—I. Item selection and cross-validation of the factor structure. J Psychosom Res 38(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(94)90005-1
Kauhanen J, Kaplan GA, Cohen RD, Julkunen J, Salonen JT (1996) Alexithymia and risk of death in middle-aged men. J Psychosom Res 41(6):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(96)00226-7
Kooiman CG, Bolk JH, Brand R, Trijsburg RW, Rooijmans HG (2000) Is alexithymia a risk factor for unexplained physical symptoms in general medical outpatients? Psychosom Med 62(6):768–778. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006842-200011000-00005
Honkalampi K, Koivumaa-Honkanen H, Lehto SM, Hintikka J, Haatainen K, Rissanen T, Viinamäki H (2010) Is alexithymia a risk factor for major depression, personality disorder, or alcohol use disorders? A prospective population-based study. J Psychosom Res 68(3):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2009.05.010
Kojima M (2012) Alexithymia as a prognostic risk factor for health problems: a brief review of epidemiological studies. BioPsychoSoc Med 6(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0759-6-21
Morie K, Ridout N (2018) Alexithymia and maladaptive regulatory behaviors in substance use disorders and eating disorders. In: Luminet O, Bagby R, Taylor G (eds) Alexithymia: advances in research, theory, and clinical practice. Cambridge University, Cambridge, pp 158–173. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108241595.012
Pinaquy S, Chabrol H, Simon C, Louvet JP, Barbe P (2003) Emotional eating, alexithymia, and binge-eating disorder in obese women. Obes Res 11(2):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2003.31
Ricca V, Castellini G, Sauro CL, Ravaldi C, Lapi F (2009) Correlations between binge eating and emotional eating in a sample of overweight subjects. Appetite 53(3):418–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.07.008
Nowakowski ME, McFarlane T, Cassin S (2013) Alexithymia and eating disorders: a critical review of the literature. J Eat Disord 1:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/2050-2974-1-21
Sasai K, Tanaka K, Hishimoto A (2010) Alexithymia and its relationships with eating behavior, self-esteem, and body esteem in college women. Kobe J Med Sci 56(6):E231–E238
de Zwaan M, Bach M, Mitchell JE, Ackard D, Specker SM, Pyle RL, Pakesch G (1995) Alexithymia, obesity, and binge eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord 17(2):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X(199503)17:2%3c135:AID-EAT2260170205%3e3.0.CO;2-7
Udo T, McKee SA, White MA, Masheb RM, Barnes RD, Grilo CM (2013) Sex differences in biopsychosocial correlates of binge eating disorder: a study of treatment-seeking obese adults in primary care setting. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 35(6):587–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2013.07.010
Carriere C, Michel G, Féart C, Pellay H, Onorato O, Barat P, Thibault H (2019) Relationships between emotional disorders, personality dimensions, and binge eating disorder in French obese adolescents. Arch Pediatr 26(3):138–144
Conti C, Di Francesco G, Lanzara R, Severo M, Fumagalli L, Guagnano MT, Porcelli P (2019) Alexithymia and binge eating in obese outpatients who are starting a weight-loss program: a structural equation analysis. Eur Eat Disord Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2696
Jansen A, Vanreyten A, van Balveren T, Roefs A, Nederkoorn C, Havermans R (2008) Negative affect and cue-induced overeating in non-eating disordered obesity. Appetite 51(3):556–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2008.04.009
Fereidouni F, Atef-Vahid MK, Lavasani FF, Orak RJ, Klonsky ED, Pazooki A (2015) Are Iranian obese women candidate for bariatric surgery different cognitively, emotionally and behaviorally from their normal weight counterparts? Eat Weight Disord 20(3):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-014-0168-6
Pink AE, Lee M, Price M, Williams C (2019) A serial mediation model of the relationship between alexithymia and BMI: the role of negative affect, negative urgency and emotional eating. Appetite 133:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.11.014
Elfhag K, Lundh LG (2007) TAS-20 alexithymia in obesity, and its links to personality. Scand J Psychol 48(5):391–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.2007.00583.x
Behar R, Arancibia M (2014) Alexithymia in eating disorders. Advances in psychology research. Nova Science Publishers, New York, pp 81–108
Racine SE, Horvath SA (2018) Emotion dysregulation across the spectrum of pathological eating: comparisons among women with binge eating, overeating, and loss of control eating. Eat Disord 26(1):13–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10640266.2018.1418381
Baldaro B, Rossi N, Caterina R, Codispoti M, Balsamo A, Trombini G (2003) Deficit in the discrimination of nonverbal emotions in children with obesity and their mothers. Int J Obes 27(2):191. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.802228
Da Ros A, Vinai P, Gentile N, Forza G, Cardetti S (2011) Evaluation of alexithymia and depression in severe obese patients not affected by eating disorders. Eat Weight Disord 16(1):24–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03327517
Fukunishi I, Kaji N (1997) Externally oriented thinking of obese men and women. Psychol Rep 80(1):219–224. https://doi.org/10.2466/PR0.80.1.219-224
Paone E, Pierro L, Damico A, Aceto P, Campanle FC, Silecchia G, Lai C (2019) Alexithymia and weight loss in obese patients underwent laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Eat Weight Disord 24(1):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-017-0381-1
Perdue TO, Schreier A, Swanson M, Neil J, Carels R (2018) Majority of female bariatric patients retain an obese identity 18–30 months after surgery. Eat Weight Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0601-3
Źak-Gołąb A, Tomalski R, Bąk-Sosnowska M, Holecki M, Kocełak P, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Zahorska-Markiewicz B (2013) Alexithymia, depression, anxiety and binge eating in obese women. Eur Psychiatry 27(3):149–159. https://doi.org/10.4321/S0213-61632013000300001
Legorreta G, Bull RH, Kiely MC (1988) Alexithymia and symbolic function in the obese. Psychother Psychosom 50(2):88–94. https://doi.org/10.1159/000288105
Clerici M, Albonetti S, Papa R, Penati G, Invernizzi G (1992) Alexithymia and obesity. Psychother Psychosom 57(3):88–93. https://doi.org/10.1159/000288580
Noli G, Cornicelli M, Marinari GM, Carlini F, Scopinaro N, Adami GF (2010) Alexithymia and eating behaviour in severely obese patients. J Hum Nutr Diet 23(6):616–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2010.01079.x
Speranza M, Loas G, Wallier J, Corcos M (2007) Predictive value of alexithymia in patients with eating disorders: a 3-year prospective study. J Psychosom Res 63(4):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.03.008
Wagner A, Aizenstein H, Mazurkewicz L, Fudge J, Frank GK, Putnam K (2008) Altered insula response to taste stimuli in individuals recovered from restricting-type anorexia nervosa. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(3):513. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301443
Harrison A, Sullivan S, Tchanturia K, Treasure J (2010) Emotional functioning in eating disorders: attentional bias, emotion recognition and emotion regulation. Psychol Med 40(11):1887–1897. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291710000036
Fernandes J, Ferreira-Santos F, Miller K, Torres S (2018) Emotional processing in obesity: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. Obes Rev 19(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12607
World Health Organization. Body mass index—BMI. http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi. Accessed May 2019
Bressi C, Taylor G, Parker J, Bressi S, Brambilla V, Aguglia E (1996) Cross validation of the factor structure of the 20-item Toronto Alexithymia Scale: an Italian multicenter study. J Psychosom Res 41(6):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(96)00228-0
Gross JJ, John OP (2003) Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. J Pers Soc Psychol 85(2):348. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.2.348
Balzarotti S, John OP, Gross JJ (2010) An Italian adaptation of the emotion regulation questionnaire. Eur J Psychol Assess 26(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1027/1015-5759/a000009
Garner DM (1991) Eating disorder inventory-2. Professional manual. Psychological Assessment Research, Inc, Odessa
Rizzardi M, Trombini E, Trombini G (1995) EDI-2 eating disorder inventory-2: manuale. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Erdfelder E, Faul F, Buchner A (1996) GPOWER: a general power analysis program. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 28:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03203630
Field A (2005) Discovering statistics using SPSS. Sage Publications, Thousand Oak
Korhonen PE, Seppälä T, Järvenpää S, Kautiainen H (2014) Body mass index and health-related quality of life in apparently healthy individuals. Qual Life Res 23(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-013-0433-6
Carano A, De Berardis D, Gambi F, Di Paolo C, Campanella D, Pelusi L et al (2006) Alexithymia and body image in adult outpatients with binge eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord 39(4):332–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20238
Carano A, Totaro E, De Berardis D, Mancini L, Faiella F, Pontalti I et al (2011) Correlazioni tra insoddisfazione corporea, alessitimia e dissociazione nei disturbi del comportamento alimentare. Giornale Italiano di Psicopatologia 17:174–182
Berger SS, Elliott C, Ranzenhofer LM, Shomaker LB, Hannallah L et al (2014) Interpersonal problem areas and alexithymia in adolescent girls with loss of control eating. Compr Psychiatry 55(1):170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.08.005
Eichen DM, Chen E, Boutelle KN, McCloskey MS (2017) Behavioral evidence of emotion dysregulation in binge eaters. Appetite 111:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.12.021
Jimerson DC, Wolfe BE, Franko DL, Covino NA, Sifneos PE (1994) Alexithymia ratings in bulimia nervosa: clinical correlates. Psychosom Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006842-199403000-00002
Beales DL, Dolton R (2000) Eating disordered patients: personality, alexithymia, and implications for primary care. Br J Gen Pract 50(450):21–26
Zonnevijlle-Bendek MJS, Van Goozen SHN, Cohen-Ketteni PT, Van Elburg A, Van Engeland H (2002) Do adolescent anorexia nervosa patients have deficits in emotional functioning? Eur Child Adoles Psy 11(1):38–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007870200006
Eizaguirre AE, de Cabezon AOS, de Alda IO, Olariaga LJ, Juaniz M (2004) Alexithymia and its relationships with anxiety and depression in eating disorders. Pers Indiv Differ 36(2):321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00099-0
Bourke MP, Taylor GJ, Parker JD, Bagby RM (1992) Alexithymia in women with anorexia nervosa: a preliminary investigation. Br J Psychiatry 161(2):240–243. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.161.2.240
Taylor GJ, Parker JD, Bagby RM, Bourke MP (1996) Relationships between alexithymia and psychological characteristics associated with eating disorders. J Psychosom Res 41(6):561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(96)00224-3
Harrison A, Sullivan S, Tchanturia K, Treasure J (2009) Emotion recognition and regulation in anorexia nervosa. Clin Psychol Psychother 16(4):348–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.628
Perry RM, Hayaki J (2014) Gender differences in the role of alexithymia and emotional expressivity in disordered eating. Pers Indiv Differ 71:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.07.029
Grilo CM, Masheb RM, Wilson GT (2001) A comparison of different methods for assessing the features of eating disorders in patients with binge eating disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 69(2):317. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.69.2.317
Svaldi J, Griepenstroh J, Tuschen-Caffier B, Ehring T (2012) Emotion regulation deficits in eating disorders: a marker of eating pathology or general psychopathology? Psychiatry Res 197(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2011.11.009
Frayn M, Sears CR, von Ranson KM (2016) A sad mood increases attention to unhealthy food images in women with food addiction. Appetite 100:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.02.008
De Panfilis C, Rabbaglio P, Rossi C, Zita G, Maggini C (2003) Body image disturbance, parental bonding and alexithymia in patients with eating disorders. Psychopathology 36(5):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1159/000073449
Montebarocci O, Codispoti M, Surcinelli P, Franzoni E, Baldaro B, Rossi N (2006) Alexithymia in female patients with eating disorders. Eat Weight Disord St 11(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03327739
Salminen JK, Saarijärvi S, Äärelä E, Toikka T, Kauhanen J (1999) Prevalence of alexithymia and its association with sociodemographic variables in the general population of Finland. J Psychosom Res 46(1):75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(98)00053-1
Laloyaux J, Fantini C, Lemaire M, Luminet O, Larøi F (2015) Evidence of contrasting patterns for suppression and reappraisal emotion regulation strategies in alexithymia. J Nerv Ment Dis 203(9):709–717. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005751
Swart M, Kortekaas R, Aleman A (2009) Dealing with feelings: characterization of trait alexithymia on emotion regulation strategies and cognitive-emotional processing. PLoS One 4(6):e5751. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005751
McLean CP, Miller NA, Hope DA (2007) Mediating social anxiety and disordered eating: the role of expressive suppression. Eat Disord 15(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/10640260601044485
Quinton S, Wagner HL (2005) Alexithymia, ambivalence over emotional expression, and eating attitudes. Pers Indiv Differ 38(5):1163–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2004.07.013
Mingarelli A, Casagrande M, Benevento M, Stella E, Germanò G, Solano L, Bertini M (2006) Promuovere la capacità di regolazione emozionale negli ipertesi: un’esperienza di psicosalutogenesi (Promoting the ability of emotion regulation in hypertensive patients: an experience of psychological health promotion). Psicologia della Salute 1:137–153
Moreno LA, Gonzalez-Gross M, Kersting M, Molnar D, De Henauw S et al (2008) Assessing, understanding and modifying nutritional status, eating habits and physical activity in European adolescents: the HELENA (Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence) Study. Public health Nutr 11(3):288–299. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980007000535
O’Reilly GA, Cook L, Spruijt-Metz D, Black DS (2014) Mindfulness-based interventions for obesity-related eating behaviours: a literature review. Obes Rev 15(6):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12156
Funding
This work has not supported by any grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Department of Dynamic and Clinical Psychology of the University of Rome “Sapienza” (approval number: 0000197) and with the Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of topical collection on Personality and eating and weight disorders.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casagrande, M., Boncompagni, I., Forte, G. et al. Emotion and overeating behavior: effects of alexithymia and emotional regulation on overweight and obesity. Eat Weight Disord 25, 1333–1345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00767-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00767-9