Abstract
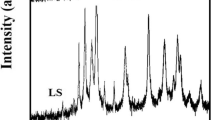
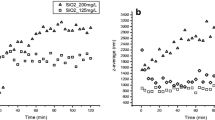
Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles (ZIF-8 NPs) are metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) that have gained significant attention in various fields due to their unique properties. They have potential applications in drug delivery, gas storage, and catalysis. However, their increasing use raises concerns about their potential environmental impact. Our study evaluates the effects of ≈90 nm ZIF-8 NPs in two planktonic species, the green microalga Nannochloropsis oculata and the brine shrimp Artemia salina. After synthesis and characterization (SEM, EDS, BET, and DLS) of nanoporous ZIF-8 NPs, a growth inhibition test on microalgae (72 h) and acute immobilization test on instar I and II of Artemia nauplii (48 h) were conducted following, OECD 201 and ISO/TS 20787, respectively. The toxicity of ZIF-8 NPs to both species was time- and concentration-dependent. The 72-h median inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ZIF-8 NPs for N. oculata based on average specific growth rate and yield were calculated as 79.71 ± 8.55 mg L−1 and 51.73 ± 5.16 mg L−1, respectively. Also, the 48-h median effective concentration (EC50) of ZIF-8 NPs on immobilization rate of instar I and II were calculated as 175.09 ± 4.14 mg L−1 and 4.69 ± 0.34 mg L−1, respectively. Moreover, the swimming type of non-immobilized animals was affected by ZIF-8 NPs. These findings provide a good insight into the toxicity of nanoparticulate ZIF-8 to saltwater planktons and also confirm that instar II Artemia is more sensitive than instar I. This study demonstrated that ZIF-8 NPs, despite all their advantages, could have toxic effects on aquatic organisms. More studies are required to assess their potential environmental impact and develop strategies to mitigate their toxicity.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data and materials are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd El-Aziz FEZA, Ebrahem NE, Abdelhamid HN (2022) A comparative study of the toxic effect of ZIF-8 and ZIF-L on the colonization and decomposition of shaded outdoor mice carrions by arthropods. Sci Rep 12:14240. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18322-5
Abdelhamid HN (2021) Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8) for biomedical applications: a review. Curr Med Chem 28:7023–7075. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867328666210608143703
Arun U, Sreeja R, Abraham A (2019) Evaluation of apoptotic potential of ZIF-8 nanoparticles. The 3rd International Conference on Optoelectronic and Nano Materials for Advanced Technology (icONMAT 2019). AIP Conference Proceedings 2082, 080001–1–080001–4. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5093884
Asadidokhtlish R, Johari SA, Sarkheil M, Yu IJ (2019) On how environmental and experimental conditions affect the results of aquatic nanotoxicology on brine shrimp (Artemia salina): a case of silver nanoparticles toxicity. Environ Pollut 255:113358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113358
Ates M, Arslan Z, Demir V, Daniels J, Farah IO (2015) Accumulation and toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environ Toxicol 30:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22002
Bhattacharya P, Lin S, Turner JP, Ke PC (2010) Physical adsorption of charged plastic nanoparticles affects algal photosynthesis. J Phys Chem C 114:16556–16561. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1054759
Carne A, Carbonell C, Imaz I, Maspoch D (2011) Nanoscale metal–organic materials. Chem Soc Rev 40:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00042F
Chandra R, Mukhopadhyay S, Nath M (2016) TiO2@ZIF-8: a novel approach of modifying micro environment for enhanced photo-catalytic dye degradation and high usability of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 164:571–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.11.018
Chen B, Wang L, Zapata F, Qian G, Lobkovsky EB (2008) A luminescent microporous metal−organic framework for the recognition and sensing of anions. J Am Chem Soc 130:6718–6719. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja802035e
de Paiva Pinheiro SK, Lima AKM, Miguel TBAR, Pireda S, Fechine PBA, Souza Filho AG, de Castro Miguel E (2023) Acute toxicity of titanium dioxide microparticles in Artemia sp. nauplii instar I and II. Microsc Res Tech 86:636. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.24312
Du J, Qv M, Qv W, Liu L, Zhang Y, Cui M, Zhang H (2021) Potential threats of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles to aquatic fungi associated with leaf decomposition. J Hazard Mater 401:123273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123273
Duan LN, Dang QQ, Han CY, Zhang XM (2015) An interpenetrated bioactive nonlinear optical MOF containing coordinated quinolone-like drug and Zn(II) for pH-responsive release. Dalton Trans 44:1800–1804. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT02672A
EC (1999) Annex VI of Directive 1999/45/EC to consolidated version of directive 67/548/EEC. General classification and labeling requirements for dangerous substances and preparations
EC (2008) Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labeling and packaging of substances and mixtures. Official J Eur Union
Fairen-Jimenez D, Moggach SA, Wharmby MT, Wright PA, Parsons S, Uren TD (2011) Opening the gate: framework flexibility in ZIF-8 explored by experiments and simulations. J Am Chem Soc 133:8900–8902. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja202154j
Falkowski JM, Sawano T, Zhang T, Tsun G, Chen Y, Lockard JV, Lin W (2014) Privileged phosphine-based metal-organic frameworks for broad-scope asymmetric catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 136:5213–5216. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja500090y
Fan G, Hong L, Zheng X, Zhou J, Zhan J, Chena Z, Liua S (2018) Growth inhibition of Microcystic aeruginosa by metal–organic frameworks: effect of variety, metal ion and organic ligand. RSC Adv 8:35314. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05608k
Férey G (2008) Hybrid porous solids: past, present, future. Chem Soc Rev 37:191–214. https://doi.org/10.1039/B618320B
Fischer BF, Pomati F, Eggen RIL (2013) The toxicity of chemical pollutants in dynamic natural systems: the challenge of integrating environmental factors and biological complexity. Sci Total Environ 449:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.066
GHS (2011) UN (United Nations) Globally harmonized system of classification and labelling of chemicals). Fourth revised edition. New York and Geneva
Gross AF, Sherman E, Vajo JJ (2012) Aqueous room temperature synthesis of cobalt and zinc sodalite zeolitic imidizolate frameworks. Dalton Trans 41(18):5458–5460. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt30174a
Hayashi H, Cote AP, Furukawa H, O’Keeffe MO, Yaghi OM (2007) Zeolite A imidazolate frameworks. Nat Mater 6:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1927
Hoop M, Walde CF, Riccò R, Mushtaq F, Terzopoulou A, Chen XZ, de Mello A, Doonan CJ, Falcaro P, Nelson BJ, Puigmartí-Luis J, Pané S (2018) Biocompatibility characteristics of the metal organic framework ZIF-8 for therapeutical applications. Appl Mater Today 11:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2017.12.014
Hou J, Wu Y, Li X, Wei B, Li S, Wang X (2018) Toxic effects of different types of zinc oxide nanoparticles on algae, plants, invertebrates, vertebrates and microorganisms. Chemosphere 193:852–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.077
Hund-rinke K, Simon M (2006) Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.06.311
ISO TS 20787, International Organization for Standardization (2017) Nanotechnologies - aquatic toxicity assessment of manufactured nanomaterials in saltwater lakes using Artemia sp. nauplii. Also is accessible at: https://www.iso.org/standard/69087.html. Accessed 20 April 2023
Ji J, Long Z, Lin D (2011) Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chem Eng J 170:525–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.026
Jin L, Wang S, Chen C, Qiu X, Wang C-C (2023) ZIF-8 nanoparticles induce behavior abnormality and brain oxidative stress in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Antioxidants 12:1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071345
Jing HP, Wang CC, Zhang YW, Wang P, Lia R (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in ZIF-8. RSC Adv 4:54454–54462. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA08820D
Johari SA, Rasmussen K, Gulumian M, Ghazi-Khansari M, Tetarazako N, Kashiwada S, Asghari S, Park JW, Yu IJ (2019) Introducing a new standardized nanomaterial environmental toxicity screening testing procedure, ISO/TS 20787: aquatic toxicity assessment of manufactured nanomaterials in saltwater Lakes using Artemia sp. nauplii. Toxicol Mech Methods 29:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2018.1512695
Johari SA, Sarkheil M, Veisi S (2021) Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) and colon cancer (SW480) cell lines exposed to nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 (ZIF-8). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:56772–56781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14636-5
Keskin S, Kizilel S (2011) Biomedical applications of metal organic frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:1799–1812. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101312k
Kitagawa S, Kitaura R, Noro SI (2004) Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:2334–2375. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200300610
Li F, Liang Z, Zheng X, Zhao W, Wu M, Wang Z (2015) Toxicity of nano-TiO2 on algae and the site of reactive oxygen species production. Aquat Toxicol 158:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.10.014
Lin D, Xing B (2008) Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 42:5580–5585. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800422x
Liu Y, Zhan JJ, Hong Y (2017) Effects of metal ions on the cultivation of an oleaginous microalga Chlorella sp. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:26594–26604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0258-x
Liu B, Yang Y, Wu H, Wang S, Tian J, Dai C, Liu T (2023) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 triggers the inhibition of arginine biosynthesis to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Small 19:2205682. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202205682
Luanwuthi S, Krittayavathananon A, Srimuk P, Sawangphruk M (2015) In situ synthesis of permselective zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/graphene oxide composites: rotating disk electrode and Langmuir adsorption isotherm. RSC Adv 5:46617–46623. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra05950j
McKinlay AC, Morris RE, Horcajada P, Ferey G, Gref R, Couvreur P (2010) BioMOFs: metal-organic frameworks for biological and medical applications. Angew Angewandte Chemie Int Ed 49:6260–6266. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000048
Miao AJ, Schwehr KA, Xu CX, Zhang SJ, Luo Z, Quigg A, Santschi PH (2009) The algal toxicity of silver engineered nanoparticles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances. Environ Pollut 157:3034–3041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.047
Moggach SA, Bennett TD, Cheetham AK (2009) The effect of pressure on ZIF-8: increasing pore size with pressure and the formation of a high-pressure phase at 1.47 GPa. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:7087–7089. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200902643
Moore MN (2002) Biocomplexity: the post-genome challenge in ecotoxicology. Aquat Toxicol 59:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-445x(01)00225-9
Nabipour N, Hossainisadr M, RezanejadeBardajee G (2017) Synthesis and characterization of nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with ciprofloxacin and their applications as antimicrobial agents. New J Chem 41(7364):7370. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ00606C
Nordin NAHM, Ismail AF, Mustafa A, Murali RS, Matsuura T (2014) The impactof ZIF-8 particle size and heat treatment on CO2/CH4 separation using a symmetric mixed matrix membrane. RSC Adv 4:52530–52541. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA08460H
Noro SI, Kitagawa S, Kondo M, Seki K (2000) A new, methane adsorbent, porous coordination polymer [{CuSiF6(4,4′-bipyridine)2}n]. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:2082–2084. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20000616)39:12%3c2081::AID-ANIE2081%3e3.0.CO;2-A
OECD 202, Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. (2004). OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Test no. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069947-en
OECD 201, Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (2011) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Test no. 201: freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en
Oh M, Mirkin CA (2006) Ion exchange as a way of controlling the chemical compositions of nano- and microparticles made from infinite coordination polymers. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:5492–5494. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200601918
Pan Y, Liu Y, Zeng G, Zhao L, Lai Z (2011) Rapid synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals in an aqueous system. Chem Commun 47:2071–2073. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC05002D
Prince JA, Bhuvana S, Anbharasi V, Ayyanar N, Boodhoo KV, Singh G (2014) Selfcleaning metal organic framework (MOF) based ultrafiltration membranes–a solution to bio-fouling in membrane separation processes. Sci Rep 4:6555. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06555
Qiu X, Liu L, Xu W, Chen C, Li M, Shi Y, Wu X, Chen K, Wang C (2022) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles exhibit more severe toxicity to the embryo/larvae of zebrafish (Danio rerio) when co-exposed with cetylpyridinium chloride. Antioxidants 11:945. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050945
Quirós J, Boltes K, Aguado S, de Villoria RG, Vilatela JJ, Rosal R (2015) Antimicrobial metal–organic frameworks incorporated into electrospun fibers. Chem Eng J 262:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.104
Raju P, Natarajan S (2023) Anticancer, anti-biofilm and antimicrobial activity of fucoidan-loaded zeolitic imidazole framework fabricated by one-pot synthesis method. Appl Nanosci 13:1919–1937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01881-w
Raju P, Arivalagan P, Natarajan S (2020) One-pot fabrication of multifunctional catechin@ZIF-L nanocomposite: assessment of antibiofilm, larvicidal and photocatalytic activities. J Photochem Photobiol, B 203:111774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111774
Raju P, Muthushanmugam M, Lakshminarayanan RR, Natarajan S (2023) One-pot synthesis of zeolitic imidazole nanoframeworks with encapsulated Leucas aspera leaf extract: assessment of anticancer and antimicrobial activities. J Cluster Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-023-02434-7
Ruyra N, Yazdi AA, Epsin J, Carn-Snchez A, Roher N, Lorenzo J, Imaz I, Maspoch D (2014) Synthesis, culture medium stability, and in vitro and in vivo zebrafish embryo toxicity of metal-organic framework nanoparticles. Chem A Eur J 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201405380
Sadiq IM, Pakrashi S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2011) Studies on toxicity of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles to microalgae species: Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. J Nanopart Res 13:3287–3299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0243-0
SalariJoo H, BehzadiTayemeh M, Abaei H, Johari SA (2023) On how zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 reduces silver ion release and affects cytotoxicity and antimicrobial properties of AgNPs@ZIF8 nanocomposite. Colloids Surf, A 668:131411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.131411
Sarkheil M, Johari SA, An HJ, Asghari S, Park HS, Sohn EK, Yu IJ (2018) Acute toxicity, uptake, and elimination of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using saltwater microcrustacean, Artemia franciscana. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 57:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.12.018
Shi YH, Rong XS, Chen C, Wu M, Takai Y, Qiu XC, Wang CC, Shimasaki Y, Oshima Y (2021) Effects of ZIF-8 nanoparticles on the survival, development, and locomotor activity of early-life-stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Faculty Agric, Kyushu University 66:211–216. https://doi.org/10.15017/4486553
Singco B, Liu LH, Chen YT, Shih YH, Huang HY, Lin CH (2016) Approaches to drug delivery: confinement of aspirin in MIL-100(Fe) and aspirin in the de novo synthesis of metal-organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 223:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.08.017
Slater AG, Cooper AI (2015) Function-led design of new porous materials. Science 348(6268):aaa8075. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa8075
Tayemeh MB, Esmailbeigi M, Shirdel I, Joo HS, Johari SA, Banan A, Nourani H, Mashhadi H, Jami MJ, Tabarrok M (2020) Perturbation of fatty acid composition, pigments, and growth indices of Chlorella vulgaris in response to silver ions and nanoparticles: a new holistic understanding of hidden ecotoxicological aspect of pollutants. Chemosphere 238:124576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124576
Vasconcelos IB, Teresinha GDS, Gardenia CGM, Thereza AS, Nailton MR, Marcelo OR, Nivan BDC, Ricardo OF, Severino AJ (2012) Cytotoxicity and slow release of the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin from ZIF-8. RSC Adv 2:9437–9442. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21087h
Wong SWY, Leung PTY, Djurisic AB, Leung KMY (2010) Toxicities of nano zinc oxide to five marine organisms: influences of aggregate size and ion solubility. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3249-z
Wyszogrodzka G, Marszalek B, Gil B, Dorozynski P (2016) Metal-organic frameworks: mechanisms of antibacterial action and potential applications. Drug Discovery Today 21:1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.04.009
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR, Nel AE (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 6:1794. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl061025k
Zhang X, Hu X, Wu H, Mu L (2021) Persistence and recovery of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 phytotoxicity. Environ Sci Technol 55:15301–15312. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c05838
Zheng M, Liu S, Guan X, Xie Z (2015) One-step synthesis of nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with high curcumin loading for treatment of cervical cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:22181–22187. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04315
Zhu S, Xue MY, Luo F, Chen WC, Zhu B, Wang GX (2017) Developmental toxicity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on cysts and three larval stages of Artemia salina. Environ Pollut 230:683–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.065
Funding
This study was financially supported by the University of Kurdistan (UOK, Iran) under research grant no. 00115321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAJ: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, methodology, resources, project administration, validation, writing — original draft, and writing — review and editing; MBT: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and formal analysis; ShV: investigation; MS: conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing — original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• ZIF-8 NPs were synthesized and well-characterized.
• Salina nauplii were immobilized following exposure to ZIF-8 NPs.
• Swimming type of non-immobilized nauplii was affected by ZIF-8 NPs.
• Instar II was more sensitive than instar I to ZIF-8 NPs.
• The growth of N. oculata was inhibited following exposure to ZIF-8 NPs.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Johari, S.A., Tayemeh, M.B., Veisi, S. et al. Acute toxicity of nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 (ZIF-8) to saltwater planktonic species Artemia salina and Nannochloropsis oculata. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 4025–4035 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31436-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31436-1