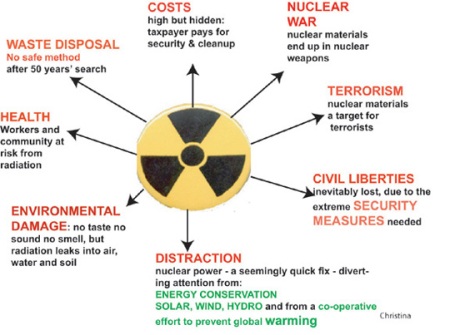
Informational items on various aspects of the nuclear industry
Nuclear issues
April 20, 2022Israel Didn’t Even Try to Defend the Legality of Its Occupation to World Court
March 9, 2024
Israel’s system is “an even more extreme form of the apartheid” than South Africa’s was, South African ambassador said.
By Marjorie Cohn , TRUTHOUT, March 6, 2024
or six days, more than 50 countries, the League of Arab States, the African Union and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation presented testimony to the International Court of Justice (ICJ, or World Court) about the legality of Israel’s occupation of Palestinian territory. The overwhelming majority of them, largely from the Global South, told the court that the occupation was illegal.
The historic hearing, which took place February 19-26, was held in response to the United Nations General Assembly’s December 30, 2022, request for an advisory opinion on the following questions:
(a) What are the legal consequences arising from the ongoing violation by Israel of the right of the Palestinian people to self-determination, from its prolonged occupation, settlement and annexation of the Palestinian territory occupied since 1967, including measures aimed at altering the demographic composition, character and status of the Holy City of Jerusalem, and from its adoption of related discriminatory legislation and measures?
(b) How do the policies and practices of Israel … affect the legal status of the occupation, and what are the legal consequences that arise for all States and the United Nations from this status?
The General Assembly asked the ICJ to discuss these issues with reference to international law, including the UN Charter; international humanitarian law; international human rights law; resolutions of the Security Council, General Assembly and Human Rights Council; and the 2004 advisory opinion of the ICJ finding that Israel’s wall on Palestinian land violated international law.
Israel regularly thumbs its nose at the World Court. It ignored the court’s ruling that the wall was illegal and refuses to implement the ICJ’s provisional order to refrain from committing genocidal acts and ensure humanitarian aid to Gaza.
Before the hearing, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu blasted the court: “Israel does not recognize the legitimacy of the proceedings of the international court in The Hague regarding ‘the legality of the occupation’ — which are an effort designed to infringe on Israel’s right to defend itself against existential threats,” he said. “The proceedings in The Hague are part of the Palestinian attempt to dictate the results of the diplomatic settlement without negotiations.”
Although Israel didn’t appear at the hearing, it submitted a five-page statement which called the General Assembly’s questions “a clear distortion of the history and present reality of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.” Israel didn’t even attempt to defend the legality of the occupation, focusing instead on why the ICJ should not issue an advisory opinion.
Israel complained that the ICJ “is asked simply to presume Israeli violations of international law — to accept, as given, plainly biased and flawed assertions directed against Israel alone.” Although consent of the parties is not required for the ICJ to render advisory opinions, Israel protested that it had “not given its consent to judicial settlement of its dispute with the Palestinian side.”
A handful of countries — including the U.S., Canada, U.K., Fiji, Hungary, Italy and Zambia — sided with Israel. Only Fiji argued that the occupation was lawful. The U.S. contended that an occupation can be neither lawful nor unlawful; it is rather governed exclusively by international humanitarian law, which only deals with acts by the occupying power, and doesn’t examine the legality of the occupation itself.
“The court should not find that Israel is legally obligated to immediately and unconditionally withdraw from occupied territory,” said Richard Visek from the U.S. State Department, urging the court to consider Israel’s “legitimate security needs.” Visek defended Israel in the ICJ the day after the U.S. vetoed a Security Council resolution demanding an immediate ceasefire in Gaza for the fourth time.
Israeli Genocide Is “Result of Decades of Impunity”
“The genocide underway in Gaza is the result of decades of impunity and inaction. Ending Israel’s impunity is a moral, political and legal imperative,” Palestine’s Foreign Minister Riyad al-Maliki told the court……………………………………………………………………………………………
Israel’s Occupation of Palestinian Territory Is Illegal
It is a peremptory norm of international law that territory cannot be acquired by force. In 1967, Israel launched a “preemptive” war against Egypt, Jordan and Syria, and seized the West Bank, Gaza, Jerusalem, the Golan Heights and the Sinai Peninsula. Israel has occupied those Palestinian territories ever since.
Visek from the U.S. State Department told the ICJ that Israel was defending itself in the 1967 war. But it was Israel that initiated the war. Rossa Fanning, Ireland’s attorney general, called it “the war [Israel] launched,” thus, an act of aggression. Wilde noted that Israel “claimed to be acting in self-defence, anticipating a non-immediately imminent attack,” but “even assuming, arguendo, its claim of a feared attack, States cannot lawfully use force in non-immediately imminent anticipatory self-defence.” Article 51 of the UN Charter forbids a state from using military force except in self-defense after an armed attack by another state.
…………………………………………………………….Israel asserts that it has not occupied the Gaza Strip since 2005, when it withdrew its military forces and settlements. But it continues to exercise military control over Gaza by continuous military operations in and against Gaza.
……………………….Gaza and its population remain under effective Israeli control and are, therefore, occupied. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Apartheid “Goes Hand-in-Hand” With Violation of Right to Self-Determination
Israel maintains a system of apartheid in the occupied Palestinian territory, as confirmed by Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and Israeli human rights group B’Tselem. Vusimuzi Madonsela, South Africa’s ambassador to the Netherlands, called Israel’s apartheid system “an even more extreme form of the apartheid that was institutionalized against Black people in my country.”
In the West Bank, Israel preserves its separation wall, segregated roads, checkpoints and restrictive permit requirements. While Israelis are subject to a civil legal system, Palestinians are controlled by a military system. They can be held indefinitely with no charges or due process in administrative detention and can be convicted based on secret evidence………………………………………………….
Israeli Settlements Constitute Illegal Annexation
More than 700,000 Israeli settlers — 10 percent of the nearly 7 million people in Israel — have been transferred into the occupied Palestinian territories, “continuously terrorizing and forcibly displacing Palestinians from even more of their territory and engaging in pogroms against them,” Shoman from Belize stated.
This constitutes a “disguised form of annexation,” Ireland’s Fanning said. “The prohibition on the acquisition of territory by force is firmly established in customary international law. Using force to occupy and maintain such occupation for the purposes of territorial acquisition or annexing an occupied territory by force in whole or in part, is each illegal.”
Israel’s policy of settling its civilians in occupied Palestinian territory and displacing the local population violates international humanitarian law, as the ICJ has ruled. Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention says: “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
Legal Consequences for All States and the UN
“Israel must dismantle the physical, legal and policy regime of discrimination and oppression … evacuate Israeli settlers from Palestinian territories, permit Palestinians to return to their country and property, and lift the siege and blockade of Gaza,” Webb from Belize told the ICJ. “These consequences, taken collectively, mean that Israel must immediately, unconditionally, and totally withdraw from the entire Palestinian territory.”
…………………………………………………………………………………… The ICJ will likely issue its advisory opinion in about six months. https://truthout.org/articles/israel-didnt-even-try-to-defend-the-legality-of-its-occupation-to-world-court/
The horrors of nuclear weapons testing
March 9, 2024
I think that enough time has gone by that the longer-term dangers of nuclear weapons, such as radioactive fallout, have largely disappeared from the public consciousness—much to the agony and despair of those afflicted to this day.
Radioactive fallout and its long-term effects—things that the average person today does not really appreciate—would be the result from any future nuclear weapons explosion that touched the Earth’s surface. Fallout does not just affect the target, but also the surrounding areas—which could be as far as hundreds of miles away. And the effects could last for years, if not decades thereafter.
Bulletin By Walter Pincus, March 7, 2024
There has been talk in the national security community lately about the so-called “merits” of resuming underground or even atmospheric nuclear weapons tests. I think this would be a grave mistake for many reasons—chief among them is that it forgets the horrific health effects that resulted from some previous nuclear tests.
To be clear, since 1963, atmospheric tests of nuclear weapons have been banned, as have tests in outer space and under water. And underground explosive tests have been banned ever since the 1996 Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, or CTBT. (Technically speaking, while the United States and China have signed the CTBT, neither has ratified it. Russia did both sign and ratify the treaty but on November 2, 2023 Russia announced it had rescinded its ratification. All three countries, however, have so far abided by the CTBT treaty.)
Meanwhile, sub-critical nuclear tests—which use tiny amounts of plutonium but do not create self-sustaining, exponentially-growing, nuclear chain reactions—have continued to this day, in laboratories or in specially constructed underground tunnels. The US is building new tunnels for sub-critical tests at the Nevada Nuclear Test Site where they are expected to help in designing the new, US W93 nuclear warhead now under development.
Presumably, then, what we are referring to when we talk about the possible resumption of nuclear testing is not the latter sub-critical testing, but some version of atmospheric, outer space, underwater, or underground explosives testing.
And here things get tricky.
Because I think that enough time has gone by that the longer-term dangers of nuclear weapons, such as radioactive fallout, have largely disappeared from the public consciousness—much to the agony and despair of those afflicted to this day.
I believe that the more people understand and even can visualize the immediate and long-term dangers of nuclear weapons use, the less likely it is that they may be used. Several nuclear scientists have told me they have memories of specific past nuclear atmospheric tests, most memorably two who were involved in the Manhattan Project—Harold Agnew and Hans Bethe.
Agnew photographed the Hiroshima mushroom cloud from the US aircraft that followed the Enola Gay that dropped the atomic bomb. Agnew almost always brought up the effect that had on him when we met.
For his part, Bethe, at 88—on the 50th anniversary of the birth of the atomic bomb—wrote: “I feel the most intense relief that these weapons have not been used since World War II, mixed with horror that tens of thousands of such weapons have been built since that time—one hundred times more than any of us at Los Alamos could ever imagine.”
In an interview years earlier at Cornell University where he was teaching, Bethe had told me something similar—and at 91, I have never forgotten those words.
The closer you are to nuclear weapons, the more you are aware of the dangers if they were to be used again. However, I believe, most people today have forgotten, if they ever knew, what a single nuclear weapon could do.
Seeing is believing. But believing in this case should make you work to oppose their use, as can be seen in a very rough sort of timeline of my own life…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
It was in February 1966, well after the 1963 atmospheric test ban treaty, that I first wrote about the impact of nuclear weapons. It was a rather flip, three-paragraph note in The Reporter Magazine, which no longer exists. The story concerned a law that had passed Congress the previous month, a measure which required the US Government to pay $11,000 to each of the 82 men, women and children—or their survivors—who had been on Rongelap Atoll in the Marshall Islands in the central Pacific on March 1, 1954 when the United States detonated Test Bravo from a tower on an artificial island built within Bikini Atoll, more than 120 miles west of Rongelap.
Bravo was the first US test of a deliverable thermonuclear bomb and was expected to have a six-megaton yield, the equivalent of six million tons of TNT. In fact, the explosion was more than double that—15 megatons—and one thousand times more powerful than the atomic bomb that destroyed Hiroshima.
Thanks in good part to thousands of documents on nuclear weapons declassified and released during the Clinton Administration, I was able to describe details about the Bravo explosion two years ago in my book, Blown To Hell: America’s Deadly Betrayal of the Marshall Islanders, as follows:
In a few seconds the fireball, recorded at one hundred million degrees, had spread nearly three miles in diameter, then quickly spread to ten miles. The sandspit and nearby reef where Bravo had stood, along with coral island areas, were vaporized down almost two hundred feet into the sea, creating a crater about one mile in diameter.
It was estimated that three hundred million tons of vaporized sand, coral and water shot up into the air as the fireball rose, and one-hundred-mile-an-hour winds created by the blast pulled additional debris up into the fireball. Within one minute, the fireball had gone up forty-five thousand feet with a stem four miles wide filled with radioactive debris. It continued to zoom upward, shooting through the troposphere and into the stratosphere within five minutes.
Later data showed the cloud bottom was at fifty-five thousand feet, the secondary mushroom cloud bottom was at one-hundred-fourteen thousand feet, and the upper cloud hit one-hundred-thirty thousand feet.
Ten minutes after detonation the mushroom cloud had widened and measured seventy-five miles across just below the stratosphere.
Original projections had predicted Bravo radioactive fallout would emanate from a fifteen-mile-wide cylinder that could stretch into the stratosphere. Instead, it turned out to be a one-hundred-mile-wide cloud where “debris was carried up and dispersed over a much larger area than was thought possible,” wrote Dr. William Ogle, the test’s task force commander of the scientific group that dealt with radioactivity.
Radioactive fallout and its long-term effects—things that the average person today does not really appreciate—would be the result from any future nuclear weapons explosion that touched the Earth’s surface. Fallout does not just affect the target, but also the surrounding areas—which could be as far as hundreds of miles away. And the effects could last for years, if not decades thereafter. These effects are worth spelling out in detail, using what happened downwind of the test as an example.
That March 1, 1954 morning, the Japanese fishing boat Lucky Dragon, with a crew of 23 aboard, was trawling its nets 90 miles east-northeast of Bikini. A crewman at the stern rail saw a whitish flare in the west that briefly lit up the clouds and the water. It grew in size, turned to yellow-red, then orange. After a few minutes, the colors faded and shortly thereafter the ship was rocked by the blast of an explosion.
The Lucky Dragon’s captain and the fishing master, who had read ship warnings before they left port, realized they might have strayed into a nuclear test area. They quickly decided to haul in their fishing nets and head back to Japan, almost 2,500 miles away.
It was another two or three hours before a fine white dust began to come down on the boat. With a light rain, the radioactive dust continued to settle on crewmen and the fish on the deck as they worked for another two hours to bring in their lines.
On Rongelap about 30 miles further east, at about 11:30 a.m., a similar powdery, radioactive ash began falling in the area. It stuck to the Marshallese people’s skin, hair, and eyes; many walked barefoot and the powder stuck to their toes; it fell on fish drying on wooden racks that would be eaten that night. Rain briefly fell as the fallout continued into afternoon, dissolving the powdery ash on roofs and carrying it down drains into water barrels that provided drinking water to each household.
On parts of Rongelap Island, where most people lived, the almost five hours of fallout led to drifts of up to one-inch or more high on the ground, on roofs, and along the beach. People recalled that when the moon broke through the clouds that night, it looked like patches of snow on the ground.
It would be two days before the Marshallese were evacuated from Rongelap and taken to the Kwajalein Navy Base by a US Navy destroyer. By then, most of the Rongelapese people had suffered from acute radiation exposure and nausea; some had experienced skin lesions as well.
Since the Bravo test was highly classified, a decision was made in Washington to keep the fallout incident secret, although the Atomic Agency Commission (AEC) had released a statement on March 1, 1954 that a nuclear test had taken place in the Marshall Islands Pacific Proving Ground. That had generated a small front page story in the March 2, 1954, edition of The New York Times. It was not until March 11, 1954, that the AEC admitted people “unexpectedly exposed to some radioactivity” had been moved to Kwajalein “according to a plan as a precautionary measure.”
Two weeks passed before the Lucky Dragon returned to its home port in Japan. It was only then that on March 16, 1954, the first story appeared in the Japanese Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper of what had happened to the boat’s crew and their fish—not what happened to the Marshallese. That story immediately triggered initial worldwide attention to the dangers of fallout from nuclear weapons.
However, it was not until President Eisenhower’s March 31, 1954 press conference that AEC Chairman Lewis Strauss, who had just returned from observing post-Bravo nuclear tests, admitted publicly that the Bravo test was “in the megaton range” and “the yield was about double that of the calculated estimate.” ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The early part of the 1955 report described the blast and heat effects of early atomic bombs detonated in the air, before discussing fallout from Bravo and other detonations. “In the air explosion, where the fireball does not touch the earth’s surface, the radioactivity produced in the bomb condenses only on solid particles from the bomb casing itself and the dust which happens to be in the air. In the absence of materials drawn up from the surface, these substances will condense with the vapors from the bomb and air dust to form only the smallest particles. These minute substances may settle to the surface over a very wide area—probably spreading around the world—over a period of days or even months. By the time they have reached the earth’s surface, the major part of their radioactivity has dissipated harmlessly in the atmosphere and the residual contamination is widely dispersed.”
The report then turned to what fallout would occur if the fireball hit the ground. “If however the weapon is detonated on the surface or close enough so that the fireball touches the surface, then large amounts of material will be drawn up into the bomb cloud. Many of the particles thus formed are heavy enough to descend rapidly while still intensely radioactive. The result is a comparatively localized area of extreme radioactive contamination, and a much larger area of some hazard. Instead of wafting down slowly over a vast area, the larger and heavier particles fall rapidly before there has been an opportunity for them to decay harmlessly in the atmosphere and before the winds have had an opportunity to scatter them.”
It described the Bravo fallout as looking like snow “because of calcium carbonate from coral,” and then noted its “adhesive” quality thanks to moisture picked up in the atmosphere as it descended. In the end it contaminated “a cigar-shaped area extending approximately 220 statute miles downwind, up to 40 miles wide,” from Bikini. It “seriously threatened the lives of nearly all persons in the area who did not take protective measures,” the report said.
The report then talked about radioactive strontium in fallout as having a long, average lifetime of nearly 30 years, noting it could enter the human body either by inhaling or swallowing. Deposited directly on edible plants, the strontium could be eaten by a human or animal. While rainfall or human washing of the plants would remove most of the radioactive material, radioactive strontium deposited directly on the soil or in the ocean, lakes, or rivers could be taken up by plants, animals, or fish. There it would lodge in their tissue where it could later be eaten by humans…………….
The other radioactive element in fallout described specifically as a threat in the report was radioactive iodine. Even though the average life of radioactive iodine was only 11.5 days, it was described as a serious hazard because, if inhaled, it concentrated in the thyroid gland where it could damage cells, depending on dosage………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Back on Rongelap, despite some cleanup, there are few in residence. A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in July 2019, done by researchers from Columbia University, found that levels of plutonium and cesium in the soil on Rongelap and other Marshall Island atolls were “significantly higher” than levels that resulted from fallout existing from the July 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power accident—which occurred 28 years after US nuclear tests had ended in the Marshalls.
The Rongelap Marshallese as well as the Japanese seamen who were exposed to fallout on March 1, 1954, can be seen as surrogates for anyone caught in a future nuclear war. Rongelap Atoll, as well as Bikini Atoll, for the most part still cannot be inhabited despite attempts to decontaminate them. Think of what today’s cities would be like if hit by a thermonuclear weapon whose fireball struck the ground and created radioactive fallout.
Within weeks it will be 70 years since the Bravo test. The more the US public and the world are reminded of that test and the resulting Rongelap story, the more they should work to deter any potential use of nuclear weapons. https://thebulletin.org/premium/2024-03/the-horrors-of-nuclear-weapons-testing/?utm_source=Newsletter&utm_medium=Email&utm_campaign=ThursdayNewsletter03072024&utm_content=NuclearRisk_NuclearTestingHorrors_03072024
Oppenheimer feared nuclear annihilation – and only a chance pause by a Soviet submariner kept it from happening in 1962
March 9, 2024on October 27, 1962, a nuclear war was averted not because President Kennedy and Premier Khrushchev were doing their best to avoid war (they were), but because Capt. Vasily Arkhipov had been randomly assigned to submarine B-59.”
This is but one of countless examples where global and military history has been dramatically altered by chance and luck. On Oct. 27, 1962, the world was extremely lucky. The question that Robert Oppenheimer would surely ask is, will we be so lucky the next time?
March 7, 2024, https://theconversation.com/oppenheimer-feared-nuclear-annihilation-and-only-a-chance-pause-by-a-soviet-submariner-kept-it-from-happening-in-1962-223148 Mark Robert Rank, Professor of Social Welfare, Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis
History has often been shaped by chance and luck.
One of the blockbuster films of the past year, “Oppenheimer,” tells the dramatic story of the development of the atomic bomb and the physicist who headed those efforts, J. Robert Oppenheimer. But despite the Manhattan Project’s success depicted in the film, in his latter years, Oppenheimer became increasingly worried about a nuclear holocaust resulting from the proliferation of these weapons.
Over the past 80 years, the threat of such nuclear annihilation was perhaps never greater than during the Cuban missile crisis of 1962.
President John F. Kennedy’s secretary of state, Dean Acheson, said that nuclear war was averted during that crisis by “just plain dumb luck.” As I detail in my forthcoming book, “The Random Factor,” nowhere was the influence of chance and luck more evident than on Oct. 27, 1962.
Russian missiles next door
To set the stage, a cold war of hostilities between the U.S. and the communist Soviet Union began almost immediately following World War II, resulting in a nuclear arms race between the two during the 1950s and continuing through the 1980s.
As a part of the Cold War, the U.S. was extremely concerned about countries falling under the Soviet communist influence and umbrella. That fear was magnified in the case of Cuba.
Tensions between the U.S. and Cuba had dramatically escalated following the failed 1961 U.S. attempt to overthrow revolutionary leader Fidel Castro and his communist ruling party. Known as the Bay of Pigs invasion, its failure proved to be a major embarrassment for the Kennedy administration and a warning to the Castro regime.
In May 1962, Castro and Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev agreed to secretly deploy strategic nuclear missiles in Cuba, with the intention of providing a strong deterrent to any potential U.S. invasion in the future. The Russian missiles and equipment would be disassembled and shipped aboard freighters bound for Havana, then be reassembled on-site.
On Oct. 14, a high-flying U.S. U-2 spy plane photographed the construction of a missile launch site in western Cuba. This marked the beginning of the 13 days in October known as the Cuban missile crisis.
After heated deliberations with his cabinet and advisers, Kennedy decided on a naval blockade surrounding Cuba to prevent further Soviet ships from passing through. In addition, Kennedy demanded removal of all missiles and equipment already in Cuba.
This began a standoff between the U.S. and Russia. Ultimately, the missiles were disassembled and removed from Cuba. In exchange, the U.S. removed its Jupiter ballistic missiles from bases in Turkey and Italy.
But one utterly random – and utterly crucial – aspect of this resolution was not known until years later through the memoirs of, and interviews with, Soviet sailors.
Read the rest of this entry »New Zealand is under siege by the Atlas Network
March 9, 2024
We have a handful of years to achieve a monumental shift from fossil fuel towards renewable energy: Atlas partners aim to ensure this does not take place.
March 3, 2024, by: Lucy Hamilton, https://theaimn.com/new-zealand-is-under-siege-by-the-atlas-network/—
Just as the Atlas Network-connected Advance body intervened in the Voice referendum in Australia and, in recent weeks, a by-election, similar organisations spawned from the American model are distorting New Zealand’s politics from within as well as from without.
One of the key researchers into the Atlas Network, Lee Fang, observed that it has “reshaped political power in country after country.” In America, every Republican president since Ronald Reagan has begun office with a Roadmap provided by the Heritage Foundation, primary Atlas Network partner. The “Mandate” for 2025 puts America on a hard path to fascism should a Republican win in November. Britain’s economy and standing have been savaged by Atlas partners’ impacts on the Tories. In New Zealand, the recently-elected rightwing coalition government is aping the new “Atlas president” of Argentina, aiming to privatise national assets, but is increasingly also imitating Atlas strategies recently seen in Australia, inflaming racial tensions and harming the wellbeing of Māori people.
Dr Jeremy Walker called Australia’s attention to the local Atlas partner organisations’ impact on the Voice to Parliament referendum and is now helping draw together the focus on the New Zealand partners’ very similar distortion of their national debate. There is a deep racism at the heart of this ultra-free market ideology that has licensed the international right to exploit resources and people around the globe untrammelled, largely in American corporate interest, but more broadly for any corporation or allied sector big enough to be a contender. (They do not, by contrast, fight for the renewable energy sector’s interests, as a competitor to their dominant fossil fuel donors; this shapes their climate crisis denial and delay, and colours their loathing of First People’s capacity to interfere with their profits by environment-driven protest. A sense of Western Civilisation as the apex of human existence and deep disdain for non-Western cultures also pervade the network.)
The Atlas model is to connect and foster talent in the neoliberal sphere. Young men (mostly) are funded or trained to replicate the talking points that Ultra High Net Worth Individuals (UHNWI) and lobbyists have built into a global network of over 500 bodies in 100 nations. The fact that neoliberal orthodoxies are more religious ideology that fact-based theories explains why their impact has been so utterly disastrous everywhere they have reshaped societies. The goal is to spawn replicating bodies with benign-sounding names that promote the UHNWI and corporate talking points – but with a veil hiding the self-interest that is obvious when those groups speak for themselves. Some of the bodies feign being thinktanks, which George Monbiot recently renamed junktanks to clarify their disingenuousness. Others are “astroturf” organisations that pretend to be grass roots bodies representing popular opinion. Another model is the beach-head in universities, an independent organisation within those institutions intended to dignify the neoliberal religion and the chosen strategies, including climate denial. All these produce material to fill civic debate and train more acolytes to enter politics, strategy companies and junktanks. Mainstream media elevates their standing by hosting their operatives as experts without explaining that the benign-sounding organisation to which they belong is a foreign-influence operation’s local outlet.
These groups damage local conditions to favour international corporations. They lobby for the removal of the “regulations” that are actually protections for the public – as workers, as consumers, as residents. They push for the privatisation of national treasures so that (often foreign) corporations can exploit the profits at the expense of the public. The greater the damage to the local democracy, the easier it is for them to act unimpeded. The stronger their infiltration of the media, the harder it is for the local electorate to understand the stakes. The politicians and strategists that emerge from the sphere (or are its allies) know that none of this wins votes, so they fill the space with culture war division to distract the voter from paying attention. Race and sexuality are their most obvious targets, as reactionary nostalgia for a mythical past of white picket fences pervades their ideology: a valorisation of “Christianity” and “family” and the “sacredness of marriage” (preached by adulterous politicians) is equally apparent in their propaganda.
The coalition that took power in NZ late in 2023, after a campaign centred on attacking the country’s founding Waitangi Treaty, has considerable Atlas infiltration. There is concern about Atlas fossil fuel and associated tobacco interests perverting policy in parliament, as well as senior ministerial aides who might be compromised. The government has promised to repeal Jacinda Ardern’s ban on offshore gas and fuel exploration, plans to sell water to private interests, not to mention planning to enable the selling off of “sensitive” NZ land and assets to foreign corporations, just as Argentinian Milei is intending.’
One of the government members, the Act Party, began its existence as an Atlas partner thinktank and continues that close connection. It was founded by former parliamentarian Denis Quigley with two members of the Mont Pelerin Society (MPS), the Atlas Network’s inner sanctum. One, Roger Douglas, was responsible for Rogernomics in NZ which has been described as a “right wing coup” that worked to “dismantle the welfare state.” The other, Alan Gibbs, who has been characterised as the godfather of the party, and a major funder, argued Act ought to campaign for government to privatise “all the schools, all the hospitals and all the roads.” This may not be surprising since he made much of his fortune out of the privatisation of NZ’s telecommunications.
The Act Party is currently led by David Seymour who functions as a co-deputy prime minister in the government. He has worked almost his entire adult life within Atlas partner bodies in Canada and boasts a (micro) MBA dispensed by the Network.
Read the rest of this entry »US Refuses to Assure UK Judges That Assange Won’t Be Executed If He’s Extradited
March 9, 2024
UK law prohibits extradition to a country that may impose capital punishment.
By Marjorie Cohn , TRUTHOUT, February 27, 2024
n February 20 and 21, as nearly 1,000 supporters of Julian Assange gathered outside the London courthouse, a two-judge panel of the High Court of Justice presided over a “permission hearing.” Assange’s lawyers asked the judges to allow them to appeal the home secretary’s extradition order and raise issues that the district court judge had rejected without full consideration.
The High Court panel, Dame Victoria Sharp and Justice Jeremy Johnson, were concerned that the U.S. government could execute Assange if he is extradited to the United States, a penalty outlawed in the U.K. Although Assange faces 175 years in prison for the charges alleged in the indictment, there is nothing to prevent the U.S. from adding additional offenses which would carry the death penalty.
The Trump Administration Indicted Assange for Exposing U.S. War Crimes
Assange is charged with 17 counts of alleged violations of the Espionage Act, based on obtaining, receiving, possessing and publishing national defense information. He is accused of “recruit[ing] sources” and “soliciting” confidential documents just by maintaining the WikiLeaks website that stated it accepted such materials. Assange is also charged with one count of “conspiracy to commit computer intrusion” with intent to “facilitate [whistleblower Chelsea] Manning’s acquisition and transmission of classified information related to the national defence of the United States.”
The basis for the indictment, Assange’s lawyers told the panel, is WikiLeaks’s “exposure of criminality on the part of the U.S. government on an unprecedented scale.” Assange is charged for revealing war crimes committed by the United States in Iraq, Afghanistan and Guantánamo Bay. The indictment has nothing to do with Hillary Clinton and the 2016 election or Swedish allegations of sexual misconduct, which have been dropped.
WikiLeaks revealed the “Iraq War Logs” — 400,000 field reports including 15,000 unreported deaths of Iraqi civilians, as well the as systematic rape, torture and murder after U.S. forces handed over detainees to a notorious Iraqi torture squad. The revelations also included the “Afghan War Diary” — 90,000 reports of more civilian casualties by coalition forces than the U.S. military had reported.
In addition, WikiLeaks revealed the “Guantánamo Files,” 779 secret reports with evidence that 150 innocent people had been held at Guantánamo Bay for years, and 800 men and boys had been tortured and abused, in violation of the Geneva Conventions and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.
WikiLeaks also revealed the notorious 2007 “Collateral Murder Video,” in which a U.S. Army Apache attack helicopter targeted and killed 11 unarmed civilians in Baghdad, including two Reuters journalists and a man who came to rescue the wounded. Two children were injured. The video contains evidence of war crimes prohibited by the Geneva Conventions.
And WikiLeaks exposed “Cablegate” — 251,000 confidential U.S. State Department cables that “disclosed corruption, diplomatic scandals and spy affairs on an international scale.” According to The New York Times, they told “the unvarnished story of how the government makes its biggest decisions, the decisions that cost the country most heavily in lives and money.”
“These were the most important revelations of criminal U.S. state behavior in history,” Assange attorney Mark Summers argued to the High Court panel.
Assange’s Appellate Issues
Assange is asking the U.K. High Court to review issues of treaty obligations, human rights violations and political persecution.
The U.S.-U.K. Extradition Treaty would allow the U.S. to amend or add charges which could expose Assange to the death penalty, a punishment prohibited in the U.K. In response to questioning by one of the judges, the prosecutor admitted that the U.S. had not provided assurances that Assange would not be subject to the death penalty if extradited.
Article 4(1) of the extradition treaty does not allow extradition for political offenses. Espionage is the “quintessential” political offense, Assange attorney Edward Fitzgerald told the panel. “The gravamen (and defining legal characteristic) of each of the charges is thus an alleged intention to obtain or disclose US state secrets in a manner that was damaging to the security of the US state,” which makes them political offenses, Assange’s lawyers wrote. The defense claimed it was an abuse of process for the United States to pursue extradition of Assange for a political offense……………………………………………………………………………….
“The Most Important Revelation Since Abu Ghraib”
The Collateral Murder video is “the most important revelation since Abu Ghraib,” Summers told the panel. “The cables Assange published disclosed extrajudicial assassinations, rendition, torture, dark prisons and drone killings.” Summers said the Guantánamo Files revealed a “colossal criminal act.” The defense pointed out that WikiLeaks’s revelations actually saved lives. After WikiLeaks published evidence of Iraqi torture centers established by the U.S., the Iraqi government refused President Barack Obama’s request to grant immunity to U.S. troops who committed criminal and civil offenses there. As a result, Obama had to withdraw U.S. forces from Iraq.
The Obama administration, which prosecuted more whistleblowers under the Espionage Act than all prior U.S. administrations combined, considered prosecuting Assange, but feared it would violate the First Amendment. The administration was unable to distinguish what WikiLeaks did from what The New York Times and The Guardian did since they also published documents that Chelsea Manning had leaked.
But the Trump administration did indict Julian Assange. The U.K. arrested Assange and has held him in Belmarsh Prison for nearly five years pending a decision on whether he should be extradited to the U.S. to stand trial.
In January 2021, following a three-week hearing, Baraitser denied extradition after finding that Assange’s mental health was so frail there was a “substantial risk” of suicide if he was extradited to the U.S. because of the harsh conditions of confinement in which he would be held. But she rejected all other legal objections to extradition that Assange had raised.
U.S. “Assurances” That Assange Will Be Treated Humanely
After Baraitser had already ruled, the U.S. came forward with diplomatic “assurances” that Assange would be treated humanely if extradited to the United States. The Biden administration assured the court that Assange: (1) would not be subject to onerous Special Administrative Measures (SAMs) that would keep him in extreme isolation and monitor his confidential communications with his attorneys; (2) would not be housed at the notorious ADX Florence maximum security prison in Colorado; (3) would receive psychological and clinical treatment in custody; and (4) could serve any custodial sentence in Australia.
But the U.S. said the assurances wouldn’t apply if Assange committed a “future act” that “met the test” for the SAMs. That unspecified contingency would be based on a subjective determination of prison authorities with no judicial review.
Although the United States has reneged on nearly identical assurances in the past, the High Court accepted them at face value, saying it was satisfied that the U.S. was acting in good faith, and in December 2021, the High Court reversed Baraitser’s denial of extradition.
However, in a 2023 decision, the U.K. Supreme Court unanimously held that the court has an independent duty to determine the validity of assurances,
writing, “The government’s assessment of whether there is such a risk is an important element of that evidence, but the court is bound to consider the question in the light of the evidence as a whole and to reach its own conclusion.”
In June 2023, a single High Court judge, Jonathan Swift, refused Assange permission to appeal in a cursory three-page ruling. The hearing on February 20 and 21 was an effort by Assange’s legal team to reverse that decision so that the High Court will entertain his appeal.
Assange Redacted Names of Informants to Protect Them
…………………… Several witnesses testified at the 2020 extradition hearing that Assange took great care to ensure that the names were redacted. Other outlets published the unredacted cables before WikiLeaks with no adverse consequences.
………………….Moreover, Brig. Gen. Robert Carr testified at Manning’s court martial that no one was harmed by the WikiLeaks releases. Summers told the panel that Baraitser never balanced the public interest in the disclosures against the fact that no harm came from them.
Conviction of Assange Would Chill Investigate Journalists From Exposing Government Secrets
In November 2022, The New York Times, The Guardian, Le Monde, DER SPIEGEL and El País signed a joint open letter calling on the Biden administration to drop the Espionage Act charges against Assange. They wrote, “Publishing is not a crime,” noting that Assange is the first publisher to be charged under the Espionage Act for revealing government secrets.
The indictment would punish conduct that national security journalists routinely engage in, including cultivating and communicating confidentially with sources and soliciting information from them, shielding their identities from disclosure, and publishing classified information. If Assange is prosecuted and convicted, it will discourage journalists both in the U.S. and abroad from publishing evidence of government wrongdoing.
No publisher has ever been prosecuted under the Espionage Act for disclosing government secrets. The U.S. government has never prosecuted a publisher for publishing classified information, which constitutes an essential tool of investigative journalism.
But rather than dropping Trump’s prosecution of Assange consistent with the position of the Obama-Biden administration, Joe Biden has zealously pursued extradition and prosecution.
Pending House Resolution Would Call for Dismissal of All Charges Against Assange.
On December 13, 2023, House Resolution 934 was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives by Rep. Paul A. Gosar (R-Arizona), with cosponsors from both political parties. It would express “the sense of the House of Representatives that regular journalistic activities are protected under the First Amendment, and that the United States ought to drop all charges against and attempts to extradite Julian Assange.” The resolution states that the WikiLeaks disclosures “promoted public transparency through the exposure of the hiring of child prostitutes by Defence Department contractors, friendly fire incidents, human rights abuses, civilian killings, and United States use of psychological warfare.”
…………… The conviction of Assange under the Espionage Act, the resolution continues, “would set a precedent allowing the United States to prosecute and imprison journalists for First Amendment protected activities, including the obtainment and publication of information, something that occurs on a regular basis.”
…………..
At the conclusion of the two-day hearing, the High Court panel set a due date of March 4 for further written submissions from the parties. If the court agrees to review at least one of Assange’s appellate issues, there will be a full hearing. Meanwhile, Assange, who is in poor physical and emotional health, remains in prison.
If the High Court denies his right to appeal, Assange can ask the European Court of Human Rights to hear his case. If that court finds “exceptional circumstances” and an “imminent risk of irreparable harm,” it can order provisional measures, including a stay of execution while the case is pending in the European court. But there is a danger that the U.K. could immediately extradite Assange to the United States before the European Court of Human Rights has a chance to consider Assange’s petition.
Fatal Flaws Undermine America’s Defense Industrial Base
March 9, 2024
“military industrial complex” has grown to such proportions that it is no longer subordinated to the government and national interests, but rather the government and national interests are subordinated to it.
the collective West has organized itself as a profit-driven rather than purpose-driven society………………………………across the collective West, the defense industry, like all other industries in the West, exists solely to maximize profits.
By Brian Berletic, Orinoco Tribune. February 24, 2024 https://popularresistance.org/fatal-flaws-undermine-americas-defense-industrial-base/
The first-ever US Department of Defense National Defense Industrial Strategy (NDIS) confirms what many analysts have concluded in regard to the unsustainable nature of Washington’s global-spanning foreign policy objectives and its defense industrial base’s (DIB) inability to achieve them.
The report lays out a multitude of problems plaguing the US DIB including a lack of surge capacity, inadequate workforce, off-shore downstream suppliers, as well as insufficient “demand signals” to motivate private industry partners to produce what’s needed, in the quantities needed, when it is needed.
In fact, the majority of the problems identified by the report involved private industry and its unwillingness to meet national security requirements because they were not profitable.
For example, the report attempts to explain why many companies across the US DIB lack advanced manufacturing capabilities, claiming:
Prior to the invasion, weapon procurements for some of the in-demand systems were driven by annual training requirements and ongoing combat operations. This modest demand, along with recent market dynamics, drove companies to divest excess capacity due to cost. This meant that any increased production requirements would require an increase in workforce hours in existing facilities—commonly referred to as “surge” capacity. These, in turn, were limited further by similar down-stream considerations of workforce, facility, and supply chain limitations.
Costs are most certainly a consideration across any defense industry, but costs cannot be the primary consideration.
A central element of Russia’s defense industry is Rostec, a massive state-owned enterprise under which hundreds of companies related to national industrial needs including defense are organized. Rostec is profitable. However, the industrial concerns organized under Rostec serve purposes related to Russia’s national interests first and foremost, be it national health, infrastructure or security.
Because Russia’s defense industry is purpose-driven, it produced military equipment because it was necessary, not because it was profitable. As a result, Russia possessed huge stockpiles of ammunition and equipment ahead of the Special Military Operation (SMO) in February 2022. In addition to this, Russia maintained large amounts of surge capacity enabling production rates of everything from artillery shells to armored vehicles to expand quickly over the past 2 years.
Only relatively recently have Western analysts acknowledged this.
Read the rest of this entry »
Many elements of the traditional DIB have yet to adopt advanced manufacturing technologies, as they struggle to develop business cases for needed capital investment.
In other words, while adopting advanced manufacturing technologies would fulfill the purpose of the US Department of Defense, it is not profitable for private industry to do so.
Despite virtually all the problems the report identifies stemming from private industry’s disproportionate influence over the US DIB, the report never identifies private industry itself as a problem.
If private industry and its prioritization of profits is the central problem inhibiting the DIB from fulfilling its purpose, the obvious solution is nationalizing the DIB by replacing private industry with state-owned enterprises. This allows the government to prioritize purpose over profits. Yet in the United States and across Europe, the so-called “military industrial complex” has grown to such proportions that it is no longer subordinated to the government and national interests, but rather the government and national interests are subordinated to it.
US defense industrial strategy built on a flawed premise
Beyond private industry’s hold on the US DIB, the very premise the NDIS is built on is fundamentally flawed, deeply rooted in private industry’s profit-driven prioritization.
The report claims:
The purpose of this National Defense Industrial Strategy is to drive development of an industrial ecosystem that provides a sustained competitive advantage to the United States over its adversaries.
The notion of the United States perpetually expanding its wealth and power across the globe, unrivaled by its so-called “adversaries” is unrealistic.
China alone has a population 4-5 times greater than the US. China’s population is, in fact, larger than that of the G7 combined. China has a larger industrial base, economy, and education system than the US. China’s education system not only produces millions more graduates each year in essential fields like science, technology, and engineering than the US, the proportion of such graduates is higher in China than in the US.
China alone possesses the means to maintain a competitive advantage over the United States now and well into the foreseeable future. The US, attempting to draw up a strategy to maintain an advantage over China (not to mention over the rest of the world) regardless of these realities, borders on delusion.
Yet for 60 pages, US policymakers attempt to lay out a strategy to do just that.
Not just China, but also Russia
While China is repeatedly mentioned as America’s “pacing challenge,” the ongoing conflict in Ukraine is perhaps the most acute example of a shifting balance of global power.
Despite a combined population, GDP, and military budget many times greater than Russia’s, the collective West is incapable of matching Russian production of even relatively simple munitions like artillery shells, let alone more complex systems like tanks, aircraft, and precision-guided missiles.
While the US and its allies appear to have every conceivable advantage over Russia on paper, the collective West has organized itself as a profit-driven rather than purpose-driven society.
In Russia, the defense industry exists to serve national security. While one might believe this goes without saying, across the collective West, the defense industry, like all other industries in the West, exists solely to maximize profits.
To best serve national security, the defense industry is required to maintain substantial surge capacity – meaning additional, unused factory space, machines, and labor on standby if and when large surges in production are required in relatively short periods of time. Across the West, in order to maximize profits, surge capacity has been ruthlessly slashed, deemed economically inefficient. Only rare exceptions exist, such as US 155 mm artillery shell production.
While the West’s defense industry remains the most profitable on Earth, its ability to actually churn out arms and ammunition in the quantities and quality required for large-scale conflict is clearly compromised by its maximization of profits.
The result is evident today as the West struggles to expand production of arms and ammunition for its Ukrainian proxies.
The NDIS report would note:
Prior to the invasion, weapon procurements for some of the in-demand systems were driven by annual training requirements and ongoing combat operations. This modest demand, along with recent market dynamics, drove companies to divest excess capacity due to cost. This meant that any increased production requirements would require an increase in workforce hours in existing facilities—commonly referred to as “surge” capacity. These, in turn, were limited further by similar down-stream considerations of workforce, facility, and supply chain limitations.
Costs are most certainly a consideration across any defense industry, but costs cannot be the primary consideration.
A central element of Russia’s defense industry is Rostec, a massive state-owned enterprise under which hundreds of companies related to national industrial needs including defense are organized. Rostec is profitable. However, the industrial concerns organized under Rostec serve purposes related to Russia’s national interests first and foremost, be it national health, infrastructure or security.
Because Russia’s defense industry is purpose-driven, it produced military equipment because it was necessary, not because it was profitable. As a result, Russia possessed huge stockpiles of ammunition and equipment ahead of the Special Military Operation (SMO) in February 2022. In addition to this, Russia maintained large amounts of surge capacity enabling production rates of everything from artillery shells to armored vehicles to expand quickly over the past 2 years.
Only relatively recently have Western analysts acknowledged this.
Read the rest of this entry »
February 2024: 10th anniversary of the conflict in Ukraine
March 9, 2024
Russia preferred to maintain the Ukrainian state and did not recognize the breakaway republics of Donetsk and Lugansk. It strove to find a solution that would protect the rights of Russian speakers (language, administrative autonomy) without removing them from Ukraine. The Minsk I (September 2014) and Minsk II (February 2015) agreements were neutralized by the Western signatories who later admitted having signed them only to give themselves time to arm and train the Ukrainian forces.
Russia’s categorical refusal to the inclusion of Ukraine into NATO since this would be followed by the installation of American missiles on its southern flank.
February 24, 2022, was not the beginning of a war with Ukraine but the last stage of the war that had begun in 2014.
Used as a disposable tool by the United States and NATO against Russia, Ukraine is in ruins and its future is in jeopardy.
22.02.24 – Europe – Samir Saul – Michel Seymour https://www.pressenza.com/2024/02/february-2024-10th-anniversary-of-the-conflict-in-ukraine/
In the coming days, we will surely hear about the so-called second anniversary of the war in Ukraine. Western governments, corporate media broadcasting the official pro-US line all day long, and “experts”-propagandists of this line will deliver their pseudo-analyses. All will be based on the double premise that the conflict in Ukraine began on February 24, 2022, and that it consists of a Russo-Ukrainian war unilaterally provoked by Russia to satisfy the expansionist ambitions of “dictator” Putin.
According to the US/NATO/Kiev “narrative”, everything was peaceful and normal before February 24. On that day, without the slightest justification and warning, like lightning in a blue sky, a Russian invasion descended on innocent Ukraine. As good Samaritans, the USA and its camp rushed to the aid of the victim by becoming its source of dollars and weapons, not to mention mercenaries and NATO “advisers” to operate these weapons systems. The conflict was supposed to last at most a few weeks, which was all the time that was needed to bleed Russia, while economic “sanctions” would bludgeon it and open the way to a “popular uprising” on the model of the “colored revolutions” (i.e. a putsch sponsored by the Western camp to carry out regime change and install a new leadership which would place Russia under the control of US imperialism).
That is the official “story”, rehashed ad nauseam, by “major” media, with all analysis of what is happening shut out. Only pro-US/NATO/Kiev propaganda is permitted because it would not survive if serious analyses were also allowed. It turns out that censorship, presented as the practice solely of “authoritarian regimes” against which Western “democracies” are leading a worldwide struggle in the name of “values”, is very much at home in the West. It is endorsed, sometimes hypocritically, sometimes proudly.
In propaganda and the now culture, there is no history. Events occur as sudden appearances or random occurrences based on spontaneous impulses. The “good guys” (the US and those who are aligned with them) and the “bad guys” (those who stand up to them) are known in advance, nothing else. With this simplistic and distorting grid, a conflict only begins when the “bad guys” retaliate, and never before, when the “good guys” have taken the initiative to threaten or attack them, leading to the retaliation. These initial actions are simply erased from memory.
Choosing February 24, 2022 as the starting date of the conflict in Ukraine shows bias, myopia and ignorance. It is equivalent to becoming a sounding board for the official “narrative”, the primary aim of which is to conceal the central role of Western governments as initiators of the conflict in Ukraine. Their aim is less Ukraine itself than the utilization of Ukraine, first against the Soviet Union, then against Russia.
A conflict that dates back to 1945
The Ukrainian question went through four phases: from 1945 to 1956, it was a war of sabotage and terrorism; from 1956 to 1990, there was a lull; from 1990 to 2014, a new conflict was brewing; in 2014, the war began.
As early as 1945, well before February 24, 2022, the ancestor of the CIA recruited German Nazis and their Ukrainian collaborators. Surrendering to the Americans, Reinhard Gehlen put his network of agents in Eastern Europe at the service of the US. Ukrainian ultranationalist collaborator Stepan Bandera joined Gehlen in Germany and, with his organization, waged a bloody war against the USSR in Ukraine, a Soviet territory. The USSR won and the KGB assassinated Bandera in 1959. It was in 1954 that Khrushchev transferred the Crimean peninsula to the Republic of Ukraine, then part of the USSR.
Latent tension since 1991
Read the rest of this entry »DAY ONE: Assange Timeline Exposes US Motives
March 9, 2024
February 20, 2024
Julian Assange’s lawyers on Tuesday argued before the High Court about why the imprisoned publisher must be allowed to appeal against his extradition order, reports Joe Lauria.
By Joe Lauria, in London, Consortium News
On Day One of Julian Assange’s attempt to appeal Britain’s order to extradite him to the United States, his lawyers laid out a timeline that exposed U.S. motives to destroy the journalist who revealed their high-level state crimes.
Before two High Court judges in the cramped, wood-paneled Courtroom 5 at the Royal Courts of Justice, Assange’s lawyers argued on Tuesday that two judges had seriously erred in the case on a number of grounds necessitating an appeal of the home secretary’s decision to extradite Assange to the United States.
High to the left of the court, next to oak shelves with neat rows of law books, was an empty iron cage. The court said it had invited Assange to either attend in person or via video link from Belmarsh Prison, where he has been locked up on remand for nearly five years. But Assange said he was too ill take part in any capacity, his lawyers confirmed.
Vanessa Baraitser, the district judge who presided over Assange’s 2020 extradition hearing, and Jonathan Swift, a High Court judge, came in for heavy criticism from Assange’s lawyers. Baraitser in January 2021 ordered Assange released on health grounds.
But she refused him bail while the U.S. appealed. On the basis of assurances that it would not mistreat Assange in the United States, the High Court reversed Baraitser’s decision. The U.K. Supreme Court then refused to take Assange’s challenge of the legality of these assurance and the home secretary signed the extradition order.
Assange’s last avenue of appeal is of the home secretary’s order as well as Baraitser’s 2021 decision, in which, on every point of law and many of fact, she sided with the United States. The application to pursue this appeal was rejected by a single High Court judge, Swift, last June.
He permitted his rejection of the application to itself be appealed. That two-day hearing began Tuesday before Justice Jeremy Johnson and Dame Victoria Sharp.
The Timeline
Assange lawyer Mark Summers made a forceful argument that the United States in essence is treating Assange no differently than any authoritarian regime would deal with a dissident journalist who revealed its secret crimes.
“There was evidence before the district judge that this prosecution was motivated to punish and inhibit the exposure of American state-level crimes,” Summers told the court. “There was unchallenged evidence” during Baraitser’s 2020 extradition hearing “of crimes that sit at the apex of criminality,” he said.
He said there was a direct nexus between Assange’s work to expose U.S. crimes and the U.S. pursuing him. “This is a prosecution for those disclosures,” he said. “There is a straight-line correlation between those disclosures and the prosecution, but the district judge (Baraitser) addressed none of this and neither did Swift.”
Summers then sketched out a timeline of events showing successive stages of motivation for the United States to go after Assange. “There was compelling circumstantial evidence why the U.S. brought this case,” he said.
First, he said, there was no prosecution of Assange (despite the Obama administration empaneling a grand jury) until 2016, when the International Criminal Court announced it would look into possible U.S. crimes in Afghanistan, following Assange’s disclosures. The U.S. then denounced him as a political actor.
Summers said “that morphed into plans to kill or rendition Assange” from the Ecuadorian embassy, where he had asylum, following the Vault 7 release of C.I.A. spying tools in 2017.
The then new C.I.A. Director Mike Pompeo, in his first public appearance in that position, denounced WikiLeaks as a hostile, non-state intelligence service, a carefully chosen legal term, Summers said, that permitted taking covert action against a target without Congressional knowledge.
Because these plans to kill or rendition Assange, asked for by President Donald Trump, raised alarms with White House lawyers, a legal prosecution was pursued as a way to determine where to put Assange if he were renditioned to the U.S., Summers said.
“This prosecution only emerged because of that rendition plan,” he said. “And the prosecution that emerged is selective and it is persecution.” It was selective because even though other outlets, such as Freitag and cryptome.org,, had published the unredacted diplomatic cables first, Assange was the only one charged.
“This is not a government acting on good faith pursuing a legal” path, he said……………………………………
Assange lawyer Edward Fitzgerald called espionage, with which Assange is charged, a “pure political offense.” The issue is crucial to Assange’s defense because the U.S.-U.K. Extradition Treaty bars extraditions for political offenses.
However, the Extradition Act, Parliament’s implementing legislation of the Treaty, does not mention political offenses. Baraitser ruled that the Act and not the Treaty should take precedence.
Assange’s team has been arguing that he is wanted for a political crime and therefore the extradition should not proceed. They argued that the Act bars extradition for “political opinion,” which they equate with “political offense.
A considerable amount of time in the five-hour hearing was thus spent by Assange’s lawyers making the point that Assange’s charges are political. Fitzgerald argued that Britain has extradition treaties with 158 nations and in all but two (Kuwait and the UAE), political offenses are barred.
Assange’s work was to influence and change U.S. policy, Fitzgerald said, therefore his work was political and he could not be extradited for his political views or opinions.
Informants!
Justices Johnson and Sharp appeared to be not extremely well-versed in the Assange case and seemed at times surprised by what they were hearing from Assange’s lawyers. But they had been prepared on the U.S. view of Assange allegedly harming U.S. informants.
What they didn’t know is that Assange had actually spent time redacting the names of U.S. informants from the Diplomatic Cables, while WikiLeaks‘ mainstream partners in 2010 did not.
Justice Johnson asked before lunch whether there were cases where someone had published the names of informants and were not prosecuted. After the break, Summers offered the example of Philip Agee, the ex-C.I.A. agent who revealed undercover agents’ names, some of whom were harmed, but he was never indicted for it.
Summers also mentioned The New York Times publishing names of informants in the Pentagon Papers. “The New York Times was never prosecuted,” Summers said. However, Richard Nixon indeed empaneled a grand jury in Boston to indict Times reporters but after it was revealed the government tapped whistleblower Daniel Ellsberg’s phone — and thus also the reporters’ — the case was dropped.
Despite their apparent unfamiliarity with the Assange case both judges seemed intrigued by its serious political, legal and press freedom issues. They are senior judges who might be less susceptible to political pressure.
The Death Penalty
The judges may also have been surprised to learn that under U.S. law and practice, (in this case with agreement from the British government), new charges could be added to Assange’s indictment after he would arrive in America. The Espionage Act, for instance, carries a provision for the death penalty if committed during wartime.
Britain does not have the death penalty and cannot extradite someone who could face capital punishment. Though the U.S. could offer Britain diplomatic assurances that it would not seek the death penalty against Assange, so far it has refused.
Fitzgerald also seemed to shock the courtroom by speaking of instances in U.S. courts where someone convicted for one crime could at sentencing receive time for another offense he or she was never tried for.
He expressed concern that though Assange was never charged with the Vault 7 C.I.A. leak, he might still be sentenced for it. He also said that at sentencing the rules of admissibility could be discarded, for example to consider evidence that was obtained through surveillance.
First Amendment
The judges may have been surprised to hear that the U.S. prosecutor in Virginia has said he may deny Assange his First Amendment rights during trial on U.S. soil because he is not a U.S. citizen. Pompeo stated more categorically that Assange would be without First Amendment protection.
Stripping the right of free speech is a violation of Article 10 of the European Court of Human Rights, Assange’s lawyers argued.
What Strasbourg Would Do
Summers brought the court through a scenario in which the European Court of Human Rights had tried Chelsea Manning, instead of a U.S. military court. He said whistleblower protection laws in Europe had advanced to the point where he believed the court would have weighed the harm done by breaking a confidentiality agreement and the harm prevented by blowing the whistle…….
The overall strategy of Assange’s lawyers appeared to be to make it obvious to these judges that there are vast grounds for appeal as well as arguments to toss the case (such as evidence of C.I.A. spying on Assange’s privileged conversations with his lawyers)
Forseeable
Assange’s lawyers also argued that Article 7 of the European Convention on Human Rights says someone must foresee that their behavior is a crime before he or she could be charged with it.
They said Assange could not have known that publishing his classified disclosures could have led to prosecution under the Espionage Act because no journalist or publisher had ever been charged under it for possession and publication of classified material. Therefore a violation of Article 7 should bar extradition, they say……………………
The hearing continues on Wednesday with lawyers representing the United States presenting their arguments about why Assange should not be allowed to appeal. https://consortiumnews.com/2024/02/20/day-one-assange-timeline-exposes-us-motives/
—
Germany and nuclear weapons: A difficult history
March 9, 2024
Volker Witting | Rina Goldenberg, 02/17/2024February 17, 2024
Donald Trump’s suggestion the US will no longer apply NATO’s principle of collective defense should he become president again has sent shockwaves through Europe.
German Defense Minister Boris Pistorius is annoyed by the current debate about European nuclear weapons.“There is no reason to discuss the nuclear umbrella now,” he told public broadcaster ARD.
Ever since Donald Trump suggested that, as US president, he would not provide military assistance to NATO countries if they invested less than 2% of their GDP in their defense, German politicians have been discussing whether French and British nuclear weapons would suffice as a protective shield or whether Europe needs new nuclear weapons.
“The debate about European nuclear weapons is a very German debate that we don’t see in any other country,” political scientist Karl-Heinz Kamp from the German Council on Foreign Relations (DGAP) told DW — especially not in Eastern Europe, where there is a constant perceived threat from Russian President Vladimir Putin’s Russia.
Germany has a special history: Germany was “seen as an intrinsically aggressive country, that had started two world wars and could not be trusted with nuclear weapons,” said Kamp.
Germany-based nukes during the Cold War
In 1954, not long after the end of World War II, the first chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, Konrad Adenauer, signed an agreement renouncing the production of its own nuclear, biological or chemical weapons on its territory. In return, the US included West Germany in its nuclear deterrence policy against the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact.
In 1958, the German parliament, the Bundestag, approved the deployment of US nuclear weapons, despite some pacifist protests among the population. In 1960, 1,500 US nuclear warheads were stored in West Germany and a further 1,500 in the rest of Western Europe.
The nuclear weapons were also available to the Bundeswehr for training and use in the “case of defense.” “There was never any discussion about Germany acquiring its own nuclear weapons,” said Kamp.
The West German and European peace movements grew. The protest against the “NATO Dual-Track Decision” in 1982 saw over a million people in West Germany take to the streets in protest against the planned stationing of new US medium-range missiles in the country.
Nevertheless, on November 22, 1983, a center-right majority in the Bundestag approved the stationing of the missiles in US bases shortly thereafter. At the time, the Greens were newly represented in the Bundestag and appealed to the Federal Constitutional Court against the storing and deployment of nuclear missiles on West German territory. This bid was rejected as unfounded in December 1984.
During the Cold War, East Germany, the communist German Democratic Republic (GDR), was part of the Warsaw Pact military alliance, and from 1958, nuclear missiles and warheads were stationed in Soviet military bases on GDR territory. Some were withdrawn in 1988 as part of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty between the US and the Soviet Union.
After German reunification and the withdrawal of the Soviet military, the territory of the former GDR officially became free of nuclear weapons in 1991.
Post-Cold War Germany
After the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, the collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the division between East and West Germany, the German position was once again cemented in the so-called “Two-Plus-Four Treaty”: No nuclear weapons! On September 12, 1990, the four victorious powers of World War II (the US, the Soviet Union, France and UK) stipulated that Germany East and West should be reunified and renounce nuclear weapons.
Kamp says this was hardly surprising, because “a German nuclear power would be something that would cause horror. For historical reasons alone.”
The US government withdrew many of these nuclear warheads after the collapse of the Soviet Union, though an estimated 180 US nuclear weapons are still stored in Europe, in Italy, Turkey, Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany.
Experts believe that 20 US nuclear warheads are currently stored in the town of Büchel in Rhineland-Palatinate, western Germany. “But the decision-making authority over these weapons lies solely with the American president,” explained Kamp.
Any debate about Germany acquiring its own nuclear weapons is completely unrealistic, says political scientist Peter Rudolf from the German Institute for International and Security Affairs. Nuclear bombs need to be stored so that they are not easy targets, he told the Frankfurter Allgemeine daily.
“Survivable nuclear weapons would have to be on nuclear-powered submarines that can remain underwater for a very long time, he said, pointing to equipment the Bundeswehr does not have. “So there are so many problems standing in the way of a German nuclear bomb that it has no relevance to current crises,” Rudolf concluded.
“Those who are now talking about a European defense dimension are not talking about German nuclear weapons, because Germany is a member of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty and has made several binding commitments under international law to renounce the possession of weapons of mass destruction — including nuclear weapons,” agreed Kamp.
Defense Minister Pistorius, meanwhile, who made headlines not so long ago saying Germany should get “war-ready”, is now keen to brush the whole debate aside: He told ARD that “the majority of those in charge in the United States of America know exactly what they have in their transatlantic partners in Europe, what they have in NATO.”
And Kamp agrees: “Trump may be able to damage NATO considerably, but he cannot destroy it. You can’t destroy decades of transatlantic relations in one term of office.”
Edited by Ben Knight and Peter Hille