Abstract
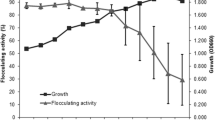
Bacillus subtilis was cultivated to high cell density for nattokinase production by pH-stat fed-batch culture. A concentrated mixture solution of glucose and peptone was automatically added by acid-supplying pump when culture pH rose above high limit. Effect of the ratio of glucose to peptone in feeding solution was investigated on cell growth and nattokinase production by changing the ratio from 0.2 to 5 g glucose/g peptone. The highest cell concentration was 77 g/L when the ratio was 0.2 g glucose/g peptone. Cell concentration decreased with increasing the ratio of glucose to peptone in feeding solution, while the optimum condition existed for nattokinase production. The highest nattokinase activity was 14,500 unit/mL at a ratio of 0.33 g glucose/g peptone, which was 4.3 times higher than that in batch culture.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sumi H, Hamada H, Tsushima H, Mihara H, Muraki H (1987) A novel fibrinolytic enzyme (nattokinase) in the vegetable cheese Natto; a typical and popular soybean food in the Japanese diet. Experientia 43:1110–1111
Kim W, Choi K, Kim Y, Park H, Choi J, Lee Y, Oh H, Kwon I, Lee S (1996) Purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme produced from Bacillus sp. strain CK 11-4 screened from Chungkook-Jang. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2482–2488
Kim SH, Choi NS (2000) Purification and characterization of subtilisin DJ-4 secreted by Bacillus sp. Strain DJ-4 screened from Doen-Jang. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1722–1725
Peng Y, Yang X, Zhang Y (2005) Microbial fibrinolytic enzymes: an overview of source, production, properties, and thrombolytic activity in vivo. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:126–132
Deepak V, Kalishwaralal K, Ramkumarpandian S, Venkatesh Babu S, Senthilkumar SR, Sangiliyandi G (2008) Optimization of media composition for Nattokinase production by Bacillus subtilis using response surface methodology. Biores Technol 99:8170–8174
Kim BS (2007) High cell density culture techniques for production of industrial products. In: Shaw J-F, Hou CT (eds) Biocatalysis and biotechnology for functional foods and industrial products. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 505–520
Shiloach J, Fass R (2005) Growing E. coli to high cell density-a historical perspective on method development. Biotechnol Adv 23:345–357
Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Esherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci 61:876–885
Suzuki T, Yamane T, Shimizu S (1990) Phenomenological background and some preliminary trials of automated substrate supply in pH-stat modal fed-batch culture using a setpoint high limit. J Ferment Bioeng 69:292–297
Kim BS (2002) Production of medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates by fed-batch culture of Pseudomonas oleovorans. Biotechnol Lett 24:125–130
Kim JS, Lee BH, Kim BS (2005) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) by Ralstonia eutropha. Biochem Eng J 23:169–174
Kim BS, Lee SC, Lee SY, Chang YK, Chang HN (2004) High cell density fed-batch cultivation of Esherichia coli using exponential feeding combined with pH-stat. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26:147–150
Kim BS, Hou CT (2006) Production of lipase by high cell density fed-batch culture of Candida cylindracea. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29:59–64
Kim BS, Lee SC, Lee SY, Chang HN, Chang YK, Woo SI (1994) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) by fed-batch culture of Alcaligenes eutrophus with glucose concentration control. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:892–898
Liu J, Xing J, Chang T, Ma Z, Liu H (2005) Optimization of nutritional conditions for nattokinase production by Bacillus natto NLSSE using statistical experimental methods. Proc Biochem 40:2757–2762
Po TC, Chiang C-J, Chao Y-P (2007) Strategy to approach stable production of recombinant nattokinase in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Prog 23:808–813
Cho YH, Song JY, Kim KM, Kim MK, Lee IY, Kim SB, Kim HS, Han NS, Lee BH, Kim BS (2010) Production of nattokinase by batch and fed-batch culture of Bacillus subtilis. New Biotechnol 27:341–346
Wang D-S, Torng C-C, Lin I-P, Cheng B-W, Liu H-R, Chou C-Y (2006) Optimization of nattokinase production conduction using response surface methodology. J Food Process Eng 29:22–35
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) and Korea Institute for Advancement in Technology (KIAT) through the Workforce Development Program in Strategic Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, EY., Kim, K.M., Kim, M.K. et al. Production of nattokinase by high cell density fed-batch culture of Bacillus subtilis . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34, 789–793 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0527-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0527-x