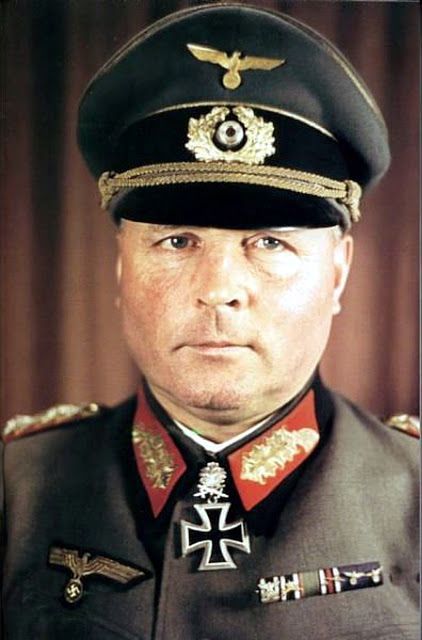
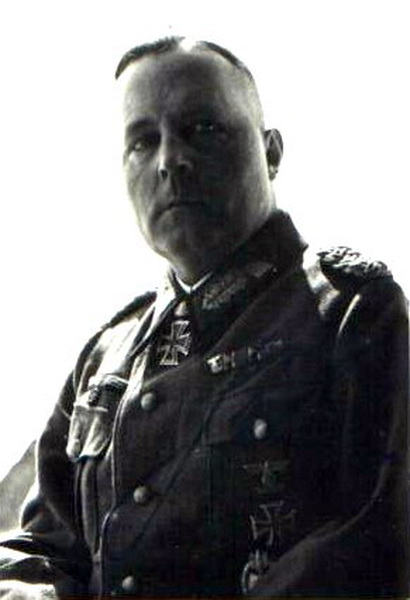
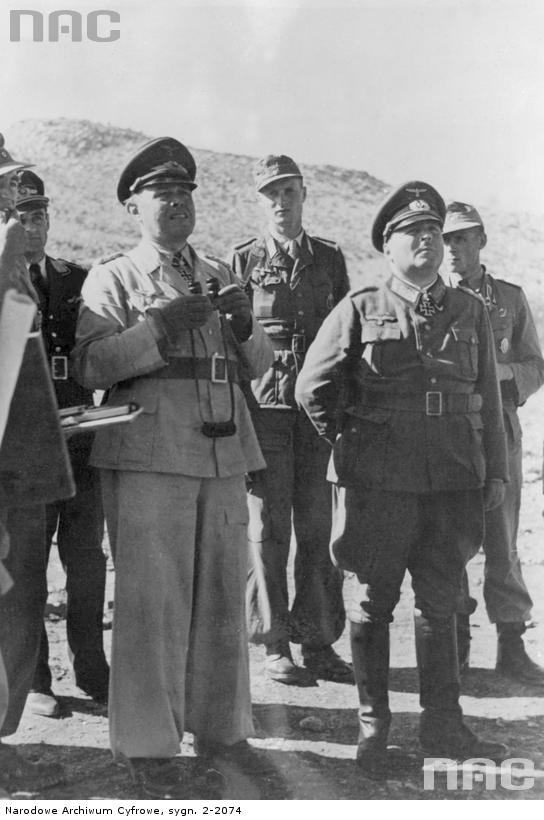
A True Panzer General in American Uniform
 |
| "Document everything, leave nothing to chance... because one day, some cockroach will crawl up out of the latrine and deny all this ever happened, God Damn Them." - Gen. George Patton, spoken during visit to Buchenwald. |
George Smith Patton, Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was one of the top Allied Generals of World War II, perhaps the very best. An uncompromising taskmaster, he Got Things Done one way or the other. In many respects, he was as close in tactics and strategy to a true Panzer General as any German, and perhaps in some ways their superior. Like a Roman Gladiator of old, he was at his best in the ring, fighting his enemies with everything he had, uncompromising and pitiless, and at a loss when he no longer had a worthy opponent.
Patton is sometimes referred to as a "California patrician." He was born into a weathy Scotch-Irish-English family on a San Marino 2000-acre ranch, and the family lineage was full of military valor. One grandfather commanded an Infantry Division (22nd Virginian) during the Civil War, a great uncle died during Pickett's Charge at Gettysburg. The military associations extended further back than that, and his family also had major political sway in California.
Patton was a clever boy, but had some difficult learning to read - something he not only overcame, but turned into an advantage due to his reading extensively about historical military figures. He wrote to one of California's Senators, Thomas R. Bard, for admission to West Point, but wound up at the Virginia Military Institute from 1903-04. Finally, he secured admission to West Point in 1904 with the Senator's help.
 |
| Patton 1904 |
Patton graduated in the middle of his class and was commissioned a second lieutenant in the cavalry in 1909. During a family trip to Catalina Island in 1902 (a trip only the well-to-do could contemplate), he met
Beatrice Banning Ayer, daughter of a wealthy Boston merchant. They wed in 1910. They had three children.
 |
| Wedding photo of General George Patton and Beatrice Ayer, May 26, 1910. Throughout his military career, George wrote the most beautiful love letters to Beatrice - "I love you so, Bea ... I am not so hellish young and it is not spring, yet still I love you just as much as if we were 22 again on the baseball grandstand at West Point the night I graduated." |
Patton was a superb athlete. During his first posting at Fort Sheridan, Illinois, he was chosen to represent the Army at the 1912 Olympic Games in Stockholm, Sweden. He was the top non-Swedish finisher, coming in fifth, at a time when the home-field advantage was huge. He had a legitimate complaint about the scoring at one point, but sucked it up like a soldier and moved on without complaint. Patton also was a top swordsman, and he re-wrote the U.S. Army's manuals on swordsmanship removing the 'parry.' He did not believe, even then, in defensive maneuvers, only aggressive attacks (see his June 5, 1944 speech below).
 |
| Patton as an athlete in 1908 |
The US was on the sidelines for the first few years of World War I, but the Army was quite busy anyway. Mexican outlaw Pancho Villa was staging raids into US territory, and something had to be done about it. Lieutenant Patton, seeking action, applied for and received an appointment as an aide to General John J. Pershing so he could get in on the action down south. Obviously, Patton's contacts came in handy in securing this position. Patton was assigned to the border patrol in Sierra Blanca. It was at this time, in this rough environment, that he took to wearing an ivory-handled Colt pistol.
 |
| Lieutenant Patton standing behind General Pershing during the Pancho Villa (center) expedition in Mexico. Photo taken at Fort Bliss. General Alvaro Obregón, later leader of Mexico, is on the left. |
Patton first came to the public's attention when, as a member of the 6th Infantry stationed on the border, Patton's unit heard of a nearby sighting of Julio Cárdenas, a close comrade of Pancho Villa. Lieutenant Patton took ten soldiers and two civilian guides in three Dodge Model 30 touring cars across the border to San Miguelito, Sonora. Patton's men ambushed Cárdenas in a ranch house, killing him and two associates. Patton brought the three back to Pershing's headquarters at Colonia Dublán, Chihuahua tied to the hoods of the three cars, where Patton briefed the media. Patton told them that he had walked toward the ranch house alone, armed only with his ivory handled Colt SAA in .45 Colt. As Patton approached the farmhouse, the three besieged banditos burst out at him on horseback. Patton hit the lead rider in the arm, then shot his horse. The other two riders rode past while Patton emptied his gun at them and then reloaded. Patton then shot the horse out from beneath one of the bandits, then calmly waited until the man was back on his feet and reaching for his gun before killing him. The third man rode away, but was shot dead by Patton's troops.
 |
| Patton wearing his ivory-handled pistol in Tunisia in 1942. He got quite upset if anyone referred to it as pearl-handled - "Only a pimp in a New Orleans whorehouse or a tin-horn gambler would carry a pearl-handled pistol." He would then add that his revolver was indeed "IVORY-GOD-****ING-DAMN-HANDLED." |
During their time together, Patton adopted some of "Black Jack" Pershing's decisive leadership style, which included leading from the front, which was not always expected of a General.
 |
| General Pershing |
Patton impressed Pershing, and when Patton asked to see some action, Pershing attached him to Troop C of the U.S. 13th Cavalry Regiment. In the first motorized attack in US history on May 14, 1916 (n touring cars), Patton and his men ambushed three of Villa's men and killed them. Patton shot all three, though it's unclear if he actually was the one who killed them. The ivory-handled pistol came in handy. This led to promotion, but President Wilson halted the expedition, not wanting war with Mexico while the European conflict loomed.
 |
| Pancho Villa and some of his men |
The United States finally entered World War I in spring 1917. Pershing was named its commander, and Patton asked to join the General's staff. They departed on May 28, 1917 and arrived in Liverpool on June 8. While overseeing training and carrying out administrative duties, Patton became interested in tanks. He convinced Pershing to assign him to establish the Army's Light Tank School in France.
 |
| Patton next to a M2 tank, Tunisia, Nov-Dec 1942; he developed his interest in tanks during World War I. Source: United States National Archives |
Patton was the only American who even knew how to drive a tank, so he personally drove the first seven US tanks off the train. In August 1918, he assumed command of the U.S. 1st Provisional Tank Brigade within the First U.S. Army. Patton closely supervised their first use at the Battle of Saint-Mihiel, leading from the front.
 |
| Patton with the first US tanks in 1918 |
Patton literally rode the first tanks into battle and even walked in front of them to guide them, as if a teacher coaching along his pupils - but the Germans were ready to shoot him down on sight! He was like a ringmaster leading trained lions.
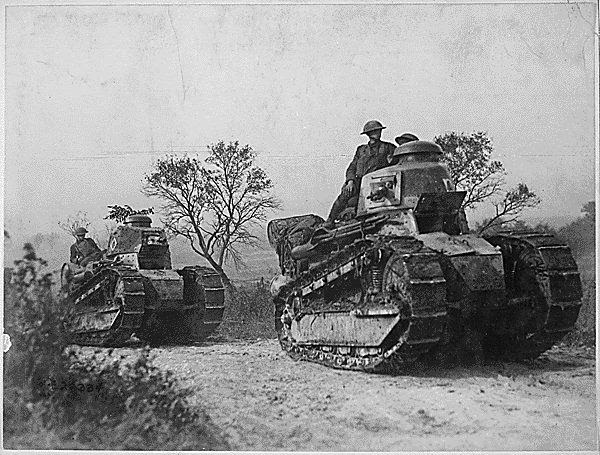 |
| American troops with FT-17 light tanks moving toward the Argonne Forest, France, 26 Sep 1918 - the very day that Patton was wounded. One of these easily could be the very same tank as the one shown with Patton, above; there weren't that many. |
Wounded during the Meuse-Argonne Offensive on September 26, 1918 (no wonder, given his bravery!) by German machine guns, he returned to headquarters and submitted his report before going to the hospital.
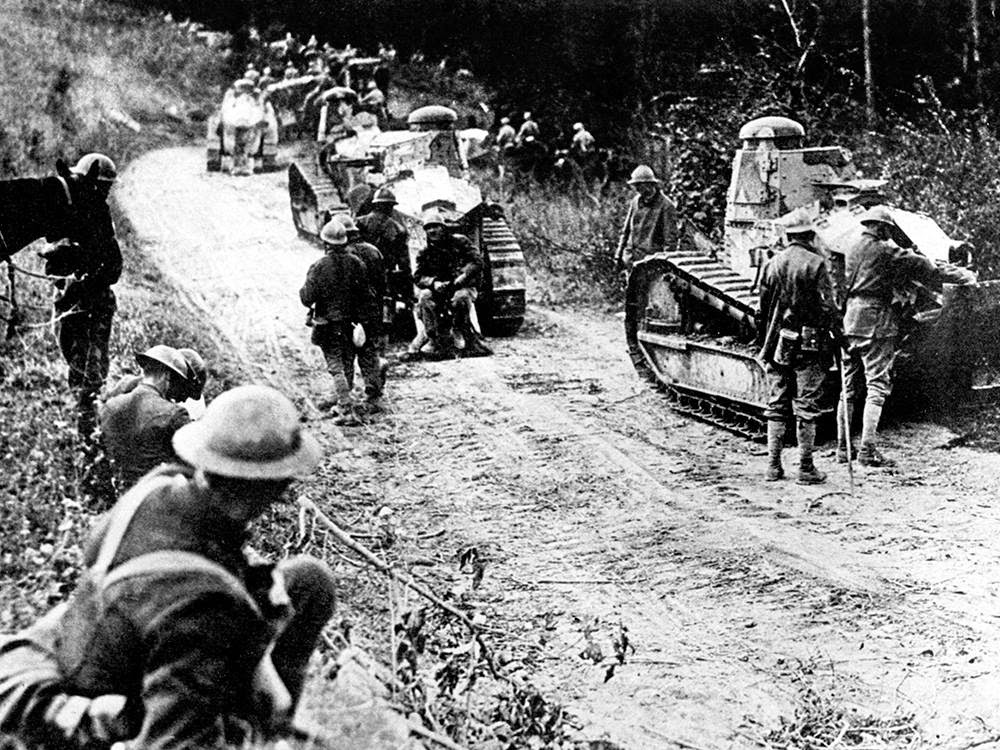 |
| Another picture of the US tanks in the Argonne, with French infantry. Do not know the exact date, but it easily could be the same date as the other picture above - the day Patton was wounded. One assumes the war correspondent who took the pictures probably did not tarry long in the battle zone. |
He received promotion to Colonel and the Distinguished Service Cross and Distinguished Service Medal, along with the Purple Heart (after its creation in 1932).
 |
| General Patton wearing his medals |
The war ended soon after Patton's injury, and he returned home on March 2, 1919. He served in the Washington, D.C. area, where he soon met rising star Dwight D. Eisenhower. Patton served at a variety of postings, and he continued his officer education during the inter-war years. He saved some children from drowning in August 1923 when they fell off a yacht. During a posting to Hawaii in 1925, he helped develop the first defense plans for the island against air attack. Back in Washington, he dispersed the "Bonus Army" with General Douglas MacArthur in 1932. A hard man, he rejected a man among his opponents the marchers, Joe Angelo, who had saved his life during his injury in World War I, telling his men to escort the man away with "I do not know this man." He knew him.
 |
| The 1932 Bonus Army |
The late 1930s were a depressing time for Patton. Promotions were slow, and he was a warrior who missed having a war to fight. Patton took to drinking heavily and cheated on his wife with her young niece (some claim they were just "friends," but that's not what Patton said). The German invasion of Poland in 1939 finally began the long, slow process of US mobilization. He was part of the decision to form an armored force, and became the commander of the 2nd Armored Brigade. At this time he finally received promotion to Brigadier General, and then to Major General on April 4, 1941, when he became Division Commander of the 2nd Armored Division. He even earned a pilot's license so he could observe tank maneuvers, a fact which altered his image.
 |
| Lt. General George Patton Jr. wearing Type B-3 Flying Jacket. Part of his iconic image derives from his adoption of flying jackets, which stemmed from his qualification as a pilot so he could observe tank maneuvers. |
The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December, 1941 brought the US into the war. After coordination with the British, it was agreed to invade North Africa on November 8, 1942 (Operation Torch). Patton commanded the western task force, centered upon Casablanca, Morocco. Patton arranged an armistice with Vichy French General Charles Noguès. It was at Patton's headquarters in Casablanca that the fateful conference of Roosevelt and Churchill took place the following January which issued the demand of unconditional surrender to the Axis.
 |
| Casablanca conference January 1943: Giraud, Roosevelt, de Gaulle, Churchill |
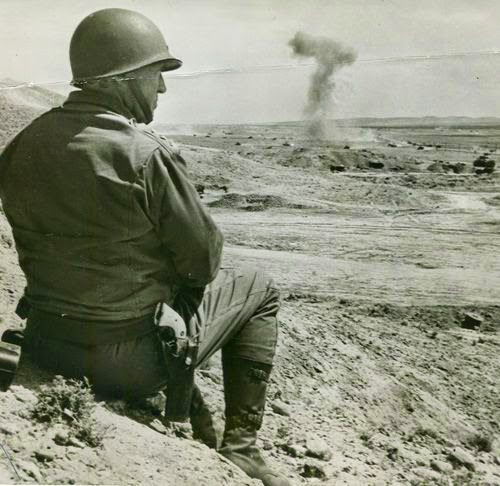
Meanwhile, German Field Marshall Erwin Rommel was leading his Afrika Korps in retreat from Egypt back in Patton's direction, toward Tunisia. Despite the surrender of some Vichy French Generals and widespread disaffection due to Germany's invasion of Vichy Franch after Torch, Vichy France was still supporting Germany. The French opened the Tunisian ports to the Germans, who then used Italian transport to flood troops into North Africa. Advancing American forces were solidly rebuffed by Rommel at the battle of Kasserine Pass in February 1943. It was the worst land defeat of the war by the Americans aside from the initial Japanese attacks in the Pacific. Washington called on the old tank expert, Patton, to figure things out. He replaced Major General Lloyd Fredendall as commander of II Corps, and also receiving promotion to Lieutenant General. General Omar Bradley became Patton's deputy commander.
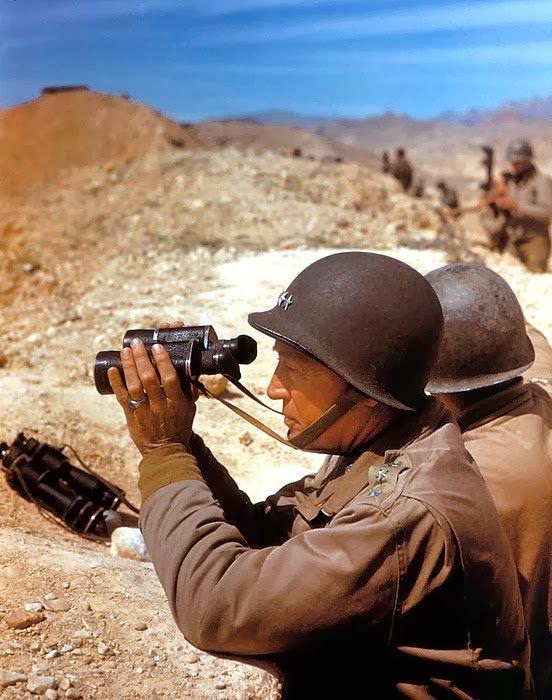 |
| Patton 1943 |
It was a time of crisis. The British, hardened by four years of warfare, patronized the untested American soldiers, and the Germans outright laughed at them. Patton stepped in and introduced sweeping changes, demanding strict discipline and pushing the men to sprint up the battle learning curve. Before an attack at Gafsa, he issued the following order:
"I expect to see such casualties among officers, particularly staff officers, as will convince me that a serious effort has been made to capture this objective."
This quote is highly reminiscent of things some of the most ruthless German Generals such as Ferdinand Schörner were saying. Naturally, not everyone was thrilled by this no-nonsense attitude, and no doubt many hated him for it, but it worked. He dismissed a General whose attack failed and quarrelled with his British allies. In imperious manner, the British sent over a delegation to set Patton straight about the quality of British air coverage, but during the meeting the Luftwaffe strafed and bombed Patton's headquarters, completely ruining their case and proving Patton's point. Patton later said about those Luftwaffe pilots, "if I could find the SOBs who flew those planes, I'd mail each of them a medal."
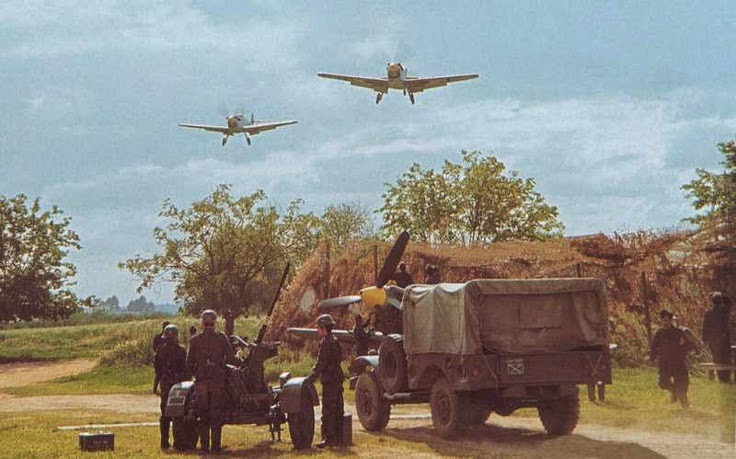 |
| Luftwaffe Stukas in North Africa |
After that, the German defenses in Tunisia collapsed. Patton handed off command of the Corps to Bradley and returned to Casablanca to plan
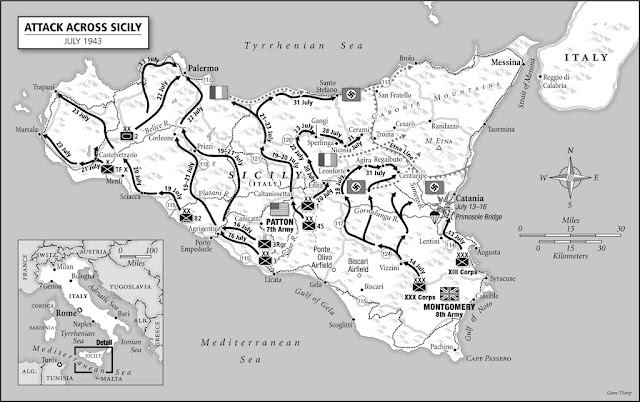
Operation Husky, the invasion of Sicily. Patton was assigned command of the US Seventh Army for the invasion, which took place on July 10, 1943. His troops disembarked on the west coast, at Gela, Licata and Scoglitti, and while initial resistance was light, the Germans immediately counterattacked with the crack Hermann Goering Panzer Division under General Paul Conrath at Gela. Blunted by Allied naval artillery, the German riposte failed, but it was a close-run thing, much, much dicier than D-Day.
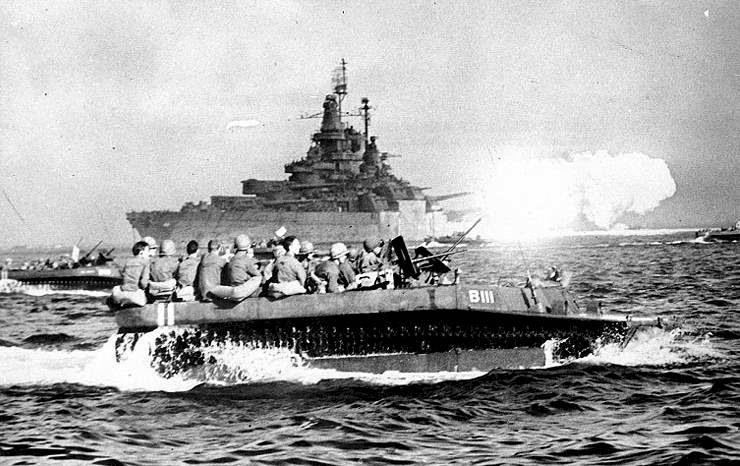 |
| The Gela, Sicily landings on July 10, 1943. Naval bombardment was the key to the success of the landings when they dispersed a fierce counterattack. |
The British had landed on the east coast of Sicily without too much trouble. However, the Germans knew that the British were on the short road to Messina, the city through which a German evacuation would have to be organized. German General Hans Hube, a veteran of Stalingrad and one of the best battlefield Generals of the war (in fact, he had many similarities to Patton), was in actual command under the nominal command of Italian General Guzzoni, who basically was a cipher.
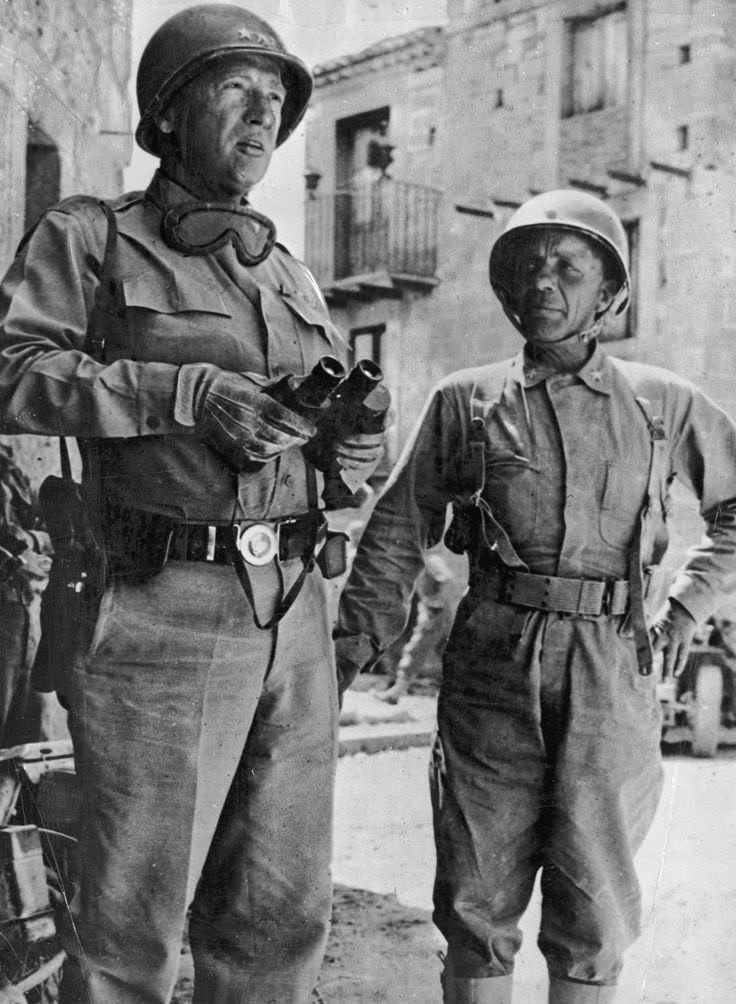 |
| Patton with General Teddy Roosevelt, probably in Sicily |
The island effectively was divided into the east coast plain and the west/north approach to Messina because of Mount Etna in the center of the island. Hube placed his best troops to block the British and basically handed the western portion of the island to the Americans in a sort of triage plan.
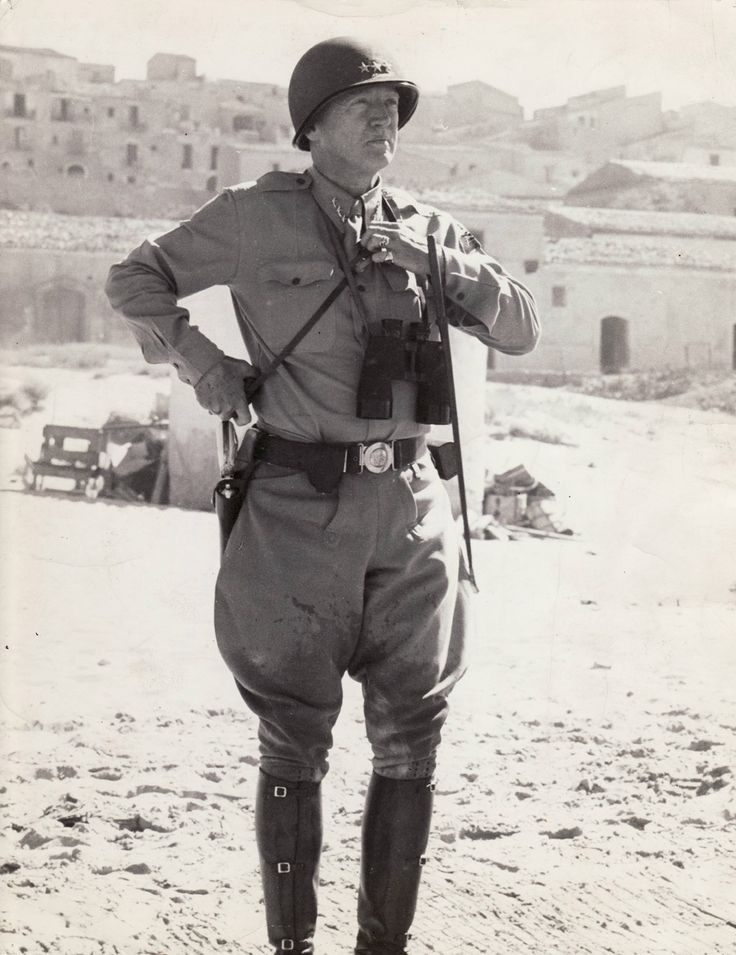 |
| General Patton on the beach at Gela, an area in the province of Caltanissetta in the south of Sicily, Italy. The Germans and Italians mounted a violent counter-attack here against the US landing which came very close to succeeding. Only naval guns and US planes held off the attacking panzers. |
Patton took advantage of this quickly, seizing Palermo on the west coast and swinging north around the volcano in a hook toward Messina. There was intense fighting, as the German troops were veterans of North Africa and knew what they were about. However, the Allied numerical superiority told in the end. Patton exulted in his ability to get into Messina a day ahead of the British, on August 20, 1943. The Germans, though, escaped completely in a brilliant evacuation.
 |
| In Sicily, it was all about Messina. This posed photo with the signpost for Messina carefully centered in the background illustrated Patton's priority to get there first. |
Patton obviously still nursed a grudge against the British and would let absolutely nothing get in the way. Technically under the command of British General Alexander, Patton ignored an order from Alexander to slow down his advance on Messina. Patton also personally attacked a Sicilian civilian whose animals Patton felt had been blocking the US advance. He wrote in his diary about proposing a plan to cover up a massacre of Italian prisoners at Biscani. Most damaging, though, was the infamous "slapping incident." On August 3, 1943, Patton slapped and verbally slurred a US Private at a hospital in Nicosia for being a shirker. The Private allegedly was suffering from battle fatigue. Patton did the same to another Private on August 10. Patton peremptorily ordered the men back to duty. This caused all sorts of trouble in the media when it was revealed months later despite attempt by Eisenhower to cover it up. However, Patton was understood to be so valuable that he was retained in command. It was a close-run thing, however.
 |
| General Patton was a hard man who slapped men he thought were malingerers. "No [SOB] ever won a war by dying for his country. He won it by making the other poor dumb [SOB] die for his country." |
The incident did, however, have very real effects on Patton's career. He did not command again for months, and he was passed over for command of the First United States Army in England in favor of his junior, Bradley (though the official version is that Bradley would have been chosen anyway). Patton instead was given command in England of the Third United States Army on January 26, 1944, a new formation that he had to whip into shape before it could enter operations. The Allies knew the Germans feared Patton more than anyone, though, so they engaged in an elaborate deception campaign designed to indicate that Patton was in command of the invasion forces (the fictional First US Army Group, or FUSAG) and that it would take place at the Pas de Calais. So, while effectively demoted in reality, Patton was lauded in the press as the dominant commander of Allied forces.
 |
| A fake FUSAG tank, put in place for Luftwaffe reconnaissance to spot |
The Germans largely were deceived, but the deception didn't have much effect on the D-Day invasion, which was a complete success. Patton shipped his now-trained Third Army to Normandy throughout July. The British were blocked at Caen by the bulk of German forces, and in late July they drew defending German forces in from other sectors during Operation Goodwood. This reduced German defenses at the base of the peninsula, and that is where Patton struck. He funnelled the Third Army through a single road at Avranches during the last days of July, and they broke out into France. Hitler saw the danger and launched a major attempt to cut Third Army off at Avranches, sending in ten panzer divisions, but Patton's men stopped them cold. This resulted in the virtual encirclement of the Germans at Mortain and the German loss of all of France. Patton was a hero again.
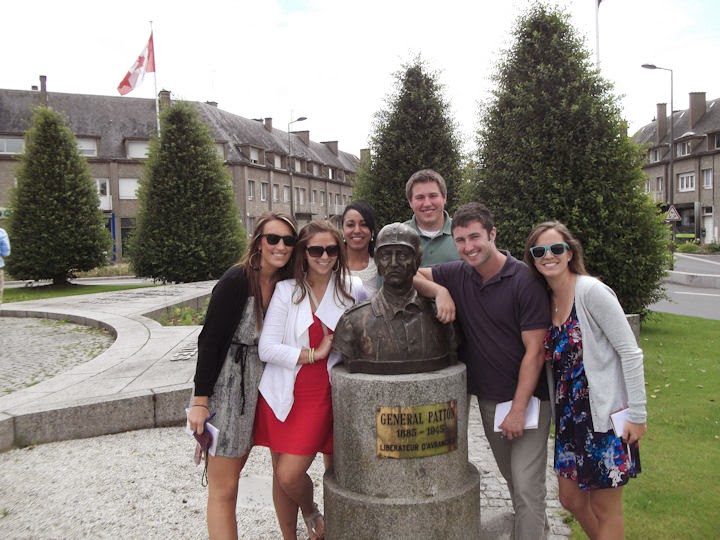 |
| Students at the statue of General Patton at Avranches, where he broke the Normandy stalemate once and for all |
After the stunning victory at Avranches that ended the Normandy stalemate and freed France, Patton was in everyone's good graces again. There simply was no better Allied tank commander, perhaps no better tank commander in the entire world (Heinz Guderian might have disagreed). Third US Army headed east, meeting resistance only at the German West Wall near the Moselle River in Lorraine. Patton's forces were hampered by supply troubles, as the British demanded and received priority of supplies for their failed adventure at Arnhem and further operations. Rumors flew that Patton's men resorted to taking Allied supplies that were destined for others by shooting up trains and at gunpoint - from other Americans! Regardless, the entire front stabilized throughout the fall as the Germans fell back on their supply depots. Patton correctly questioned the British attempt to force their way through the Germans in the north when he was practically in Germany already in the south, but that was a political matter.
 |
| Patton's troops had a fierce battle for Metz, which did not fall until November 1944. Troops entering Metz, November 18, 1944. The German Generals later said that Patton either should have just bypassed the city or attacked it full-force, but not gotten bogged down fighting over it. They would have known about errors like that. |
Patton remained low on supplies in a low-priority sector. British General Montgomery and Eisenhower were determined to break through in the north, mounting a major attack on the heavily defended German frontier city of Aachen. Third Army was at a standstill, and it looked as if that would remain the case throughout the winter. However, Hitler also had noticed the Allied preoccupation with the northern sector of the front, and he decided to mount a major counterattack to cut them off. His Generals suggested just cutting off the exposed Allied forces at Aachen, but Hitler went for the "Big Solution," a drive all the way to Rotterdam. It was an overly ambitious plan, but he launched the attack on December 16, 1944. The Germans made quick advances, but some Americans held out at the key crossroads of Bastogne. Patton volunteered to strike due north immediately and free the encircled Americans. Eisenhower said that was impossible, but Patton claimed that he already had his staff preparing the orders. Eisenhower reluctantly approved, so Patton walked out of the conference and telephoned his staff with the code words "play ball." The attack was a brilliant success. Patton freed the trapped men and broke the entire German offensive. It was a huge triumph owing to Patton and his men, another victory over the doubters.
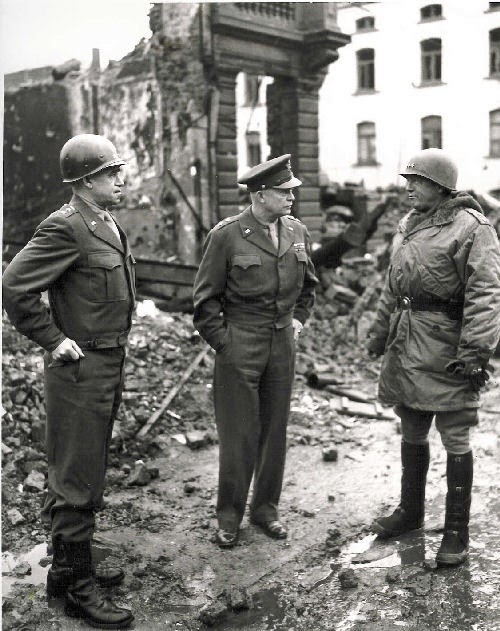 |
| Bradley, Ike, & Patton in a secured Bastogne, January 1945. This is an iconic, though little-known photo. Each General illustrates their image here. Eisenhower is in the center, in office garb, apparently wearing dress shoes in the mud, standing in the middle of the dirt and devastation without a care like it was his conference room. Bradley on the left is standing ramrod straight, his lips characteristically pursed, wearing his perpetual constipated look. Patton on the right obviously is the field General, dressed in outdoor gear and Hunter rain boots. One thing about World War II Generals, they were careful about their appearance, and it could be telling. |
After Patton helped stop the German Ardennes Offensive, the Germans were in full retreat and basically finished. Patton's forces still, however, were given low priority for supplies. His men secured them anyway by any hook or crook, including in one documented instance securing gasoline supplies by pretending to be from the favored First US Army. This enabled Third Army to invade Germany in tandem with the northern Allied forces. Third Army crossed the Rhine on March 22, quickly gaining a beachhead. Patton, however, got a little cocksure. He made an unwise attempt to liberate a POW camp behind the German lines that failed, and Eisenhower was furious. Everybody forgot about it, though, as Patton rushed into Germany. Third Army secured Bavaria and the supposed "Final Redoubt" to be manned by the German last-ditch WERWOLVES, who turned out to be fictional.
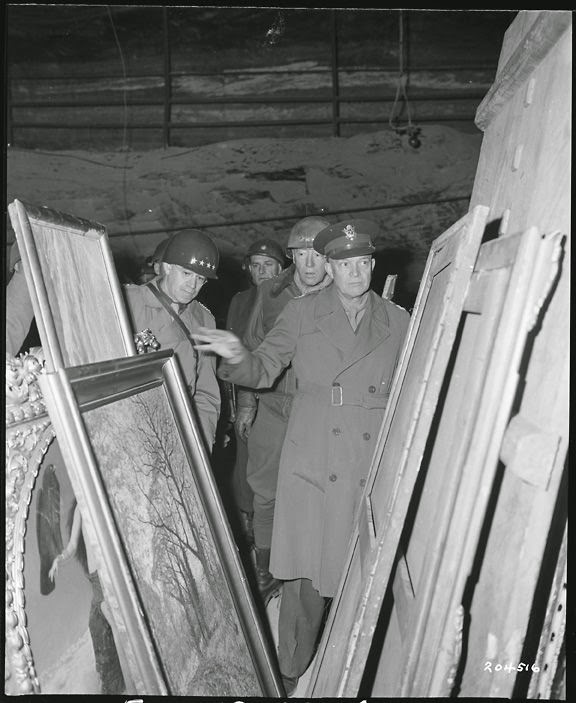 |
| Patton with Bradley and Eisenhower in German salt mines where Germans hid some of their stolen art treasures. They were in Patton's zone of operations. It is impossible to see all the pictures of Eisenhower, Patton and Bradley together without thinking that these guys were all buddies who worked as a team throughout all the vicissitudes in the war and their personal difficulties, each with their own irreplaceable talent. |
The European war ended in May, and Patton was a major hero. He wasn't through with war, however. He requested a command in the Pacific theater, but that proved unfeasible. Patton then went on extended leave, but he couldn't help himself from causing even more controversy back in the States when he implied that men who died in battle were "fools," with the true heroes the wounded. He returned to Germany as military governor of Bavaria. He wanted to fight, but Japan surrendered and the war was over. His behavior became erratic, and there may have been medical reasons. He resumed relations with the niece with whom he had had the affair in the 1930s, falling back into his malaise from that time. His handling of cleansing efforts was shaky and he made some typical Patton-style comments about Germans being comparable to a certain US political party. Ultimately, Eisenhower relieved Patton of his governorship. He was demoted to command of Fifteenth Army in Bad Nauheim. Patton soon after passed away on December 21, 1945 due to injuries related to a low-speed car accident.
 |
| Patton relaxing a bit, at last. |
General George S. Patton was gruff, coarse, completely politically incorrect, and the best American combat General of World War II. He worked in tandem with the best political and strategic General of the war, Dwight D. Eisenhower, to achieve Allied victory. His colorful personality and battlefield prowess have served as a beacon for all military commanders that follow him. He was a true modern Gladiator.
 |
| The General's dog, the day of his passing. |
General Patton's Christmas Greeting and Prayer
On December 14, 1944, two days before the Germans launched the Battle of the Bulge, General Patton asked Chaplain O'Neill to write a prayer to the Lord for good weather to help his troops kill Germans. When the Chaplain demurred because he could not pray for people to be killed, the General responded:
"Chaplain, are you teaching me theology or are you the Chaplain of the Third Army? I want a prayer."
The chaplain then prepared something, which was placed on approximately 250,000 cards and issued to every man in the army. Before he had it sent to the printers, though, Patton, at the urging of his men, added a short personal message:
To each officer and soldier in the Third United States Army, I wish a Merry Christmas. I have full confidence in your courage, devotion to duty, and skill in battle. May God's blessing rest upon each of you on this Christmas Day.
G. S. Patton, Jr.
Lieutenant General
Commanding, Third United States Army
The prayer read as follows:
Almighty and most merciful Father, we humbly beseech Thee, of Thy great goodness, to restrain these immoderate rains with which we have had to contend. Grant us fair weather for Battle. Graciously hearken to us as soldiers who call upon Thee that, armed with Thy power, we may advance from victory to victory, and crush the oppression and wickedness of our enemies and establish Thy justice among men and nations.
The weather cleared the day after the cards were issued. Chaplain O'Neill received the Bronze Star at General Patton's hand.
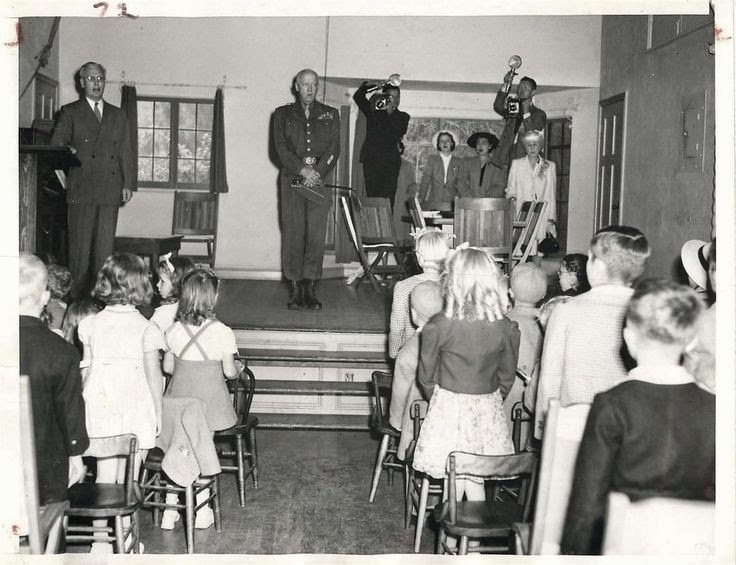 |
| 1945- General George Patton addresses Sunday School children at the Church of Our Savior in San Gabriel. Note: Patton was baptised at this church. It is also where his parents and grandparents are buried. |
General Patton's address to Third Army, June 5, 1944
The day before D-Day, on June 5, 1944, General Patton gave an address to his command Third Army. He had done this before on multiple occasions, and would again, but this speech - the day before D-Day - was special.
In one of those previous speeches, a week before, General Patton had uttered the immortal phrase:
No [SOB] ever won a war by dying for his country. You won it by making the other poor dumb [SOB] die for his country.
While that was a brilliant speech, the address of June 5th, 1944 was the one that entered the history books. It is one of the most authentic, genuine and effective military speeches ever given, any time, anywhere, and shows that profanity was used exactly in the same way then as it is now. It is worth reading for anyone who wants to understand the meaning of "total commitment."
After making his usual dramatic entrance in full uniform, holding a riding crop and wearing riding breeches and boots, the General began:
Be seated.
Men, all this stuff you hear about America not wanting to fight, wanting to stay out of the war, is a lot of BS. Americans love to fight. All real Americans love the sting and clash of battle. When you were kids, you all admired the champion marble shooter, the fastest runner, the big-league ball players and the toughest boxers. Americans love a winner and will not tolerate a loser. Americans play to win all the time. That's why Americans have never lost and will never lose a war. The very thought of losing is hateful to Americans. Battle is the most significant competition in which a man can indulge. It brings out all that is best and it removes all that is base.
You are not all going to die. Only two percent of you right here today would be killed in a major battle. Every man is scared in his first action. If he says he's not, he's a liar. But the real hero is the man who fights even though he's scared. Some men will get over their fright in a minute under fire, some take an hour, and for some it takes days. But the real man never lets his fear of death overpower his honor, his sense of duty to his country, and his innate manhood.
All through your army career you men have bitched about what you call 'this chicken-S(*! drilling.' That is all for a purpose—to ensure instant obedience to orders and to create constant alertness. This must be bred into every soldier. I don't give a F&(*( for a man who is not always on his toes. But the drilling has made veterans of all you men. You are ready! A man has to be alert all the time if he expects to keep on breathing. If not, some German SOB will sneak up behind him and beat him to death with a sock full of S@!&. There are four hundred neatly marked graves in Sicily, all because one man went to sleep on the job—but they are German graves, because we caught the [SOB] asleep before his officer did.
An army is a team. It lives, eats, sleeps, and fights as a team. This individual hero stuff is BS. The bilious [SOB]s who write that stuff for the Saturday Evening Post don't know any more about real battle than they do about F&(*ing. And we have the best team—we have the finest food and equipment, the best spirit and the best men in the world. Why, by God, I actually pity these poor [SOB]s we're going up against.
All the real heroes are not storybook combat fighters. Every single man in the army plays a vital role. So don't ever let up. Don't ever think that your job is unimportant. What if every truck driver decided that he didn't like the whine of the shells and turned yellow and jumped headlong into a ditch? That cowardly SOB could say to himself, 'Hell, they won't miss me, just one man in thousands.' What if every man said that? Where in the hell would we be then? No, thank God, Americans don't say that. Every man does his job.
Every man is important. The ordnance men are needed to supply the guns, the quartermaster is needed to bring up the food and clothes for us because where we are going there isn't a hell of a lot to steal. Every last damn man in the mess hall, even the one who boils the water to keep us from getting the GI S)&@s, has a job to do.
Each man must think not only of himself, but think of his buddy fighting alongside him. We don't want yellow cowards in the army. They should be killed off like flies. If not, they will go back home after the war, cowards, and breed more cowards. The brave men will breed more brave men. Kill off the cowards and we'll have a nation of brave men.
One of the bravest men I saw in the African campaign was on a telegraph pole in the midst of furious fire while we were moving toward Tunis. I stopped and asked him what the hell he was doing up there. He answered, 'Fixing the wire, sir.' 'Isn't it a little unhealthy up there right now?' I asked. 'Yes sir, but this wire has got to be fixed.' I asked, 'Don't those planes strafing the road bother you?' And he answered, 'No sir, but you sure as hell do.' Now, there was a real soldier. A real man. A man who devoted all he had to his duty, no matter how great the odds, no matter how seemingly insignificant his duty appeared at the time.
And you should have seen the trucks on the road to Gabès. Those drivers were magnificent. All day and all night they crawled along those SOB roads, never stopping, never deviating from their course with shells bursting all around them. Many of the men drove over 40 consecutive hours. We got through on good old American guts. These were not combat men. But they were soldiers with a job to do. They were part of a team. Without them the fight would have been lost.
Sure, we all want to go home. We want to get this war over with. But you can't win a war lying down. The quickest way to get it over with is to get the [SOB]s who started it. We want to get the hell over there and clean the thing up, and then get at those purple-going Japs. The quicker they are whipped, the quicker we go home. The shortest way home is through Berlin and Tokyo. So keep moving. And when we get to Berlin, I am personally going to shoot that paper-hanging SOB Hitler.
When a man is lying in a shell hole, if he just stays there all day, a Boche will get him eventually. The hell with that. My men don't dig foxholes. Foxholes only slow up an offensive. Keep moving. We'll win this war, but we'll win it only by fighting and showing the Germans that we've got more guts than they have or ever will have. We're not just going to shoot the [SOB]s, we're going to rip out their living guts and use them to grease the treads of our tanks. We're going to murder those lousy Hun cocksuckers by the bushel-F(*&ing-basket.
Some of you men are wondering whether or not you'll chicken out under fire. Don't worry about it. I can assure you that you'll all do your duty. War is a bloody business, a killing business. The Germans are the enemy. Wade into them, spill their blood or they will spill yours. Shoot them in the guts. Rip open their belly. When shells are hitting all around you and you wipe the dirt from your face and you realize that it's not dirt, it's the blood and gut of what was once your best friend, you'll know what to do.
I don't want any messages saying 'I'm holding my position.' We're not holding a thing. We're advancing constantly and we're not interested in holding anything except the enemy's balls. We're going to hold him by his balls and we're going to kick him in the ass; twist his balls and kick the living S(*^ out of him all the time. Our plan of operation is to advance and keep on advancing. We're going to go through the enemy like S%(* through a tinhorn.
There will be some complaints that we're pushing our people too hard. I don't give a damn about such complaints. I believe that an ounce of sweat will save a gallon of blood. The harder we push, the more Germans we kill. The more Germans we kill, the fewer of our men will be killed. Pushing harder means fewer casualties. I want you all to remember that. My men don't surrender. I don't want to hear of any soldier under my command being captured unless he is hit. Even if you are hit, you can still fight. That's not just BS either. I want men like the lieutenant in Libya who, with a Luger against his chest, swept aside the gun with his hand, jerked his helmet off with the other and busted the hell out of the Boche with the helmet. Then he picked up the gun and he killed another German. All this time the man had a bullet through his lung. That's a man for you!
Don't forget, you don't know I'm here at all. No word of that fact is to be mentioned in any letters. The world is not supposed to know what the hell they did with me. I'm not supposed to be commanding this army. I'm not even supposed to be in England. Let the first [SOB]s to find out be the Germans. Some day, I want them to rise up on their urine-soaked hind legs and howl 'Ach! It's the Third Army and that SOB Patton again!'
Then there's one thing you men will be able to say when this war is over and you get back home. Thirty years from now when you're sitting by your fireside with your grandson on your knee and he asks, 'What did you do in the great World War Two?' You won't have to cough and say, 'Well, your granddaddy shoveled S(^# in Louisiana.' No sir, you can look him straight in the eye and say 'Son, your granddaddy rode with the great Third Army and a SOB named George Patton!'
All right, you SOBs. You know how I feel. I'll be proud to lead you wonderful guys in battle anytime, anywhere. That's all.
 |
| "May God have mercy on my enemy, because I won't." |
2014