Thursday 15 January 1942
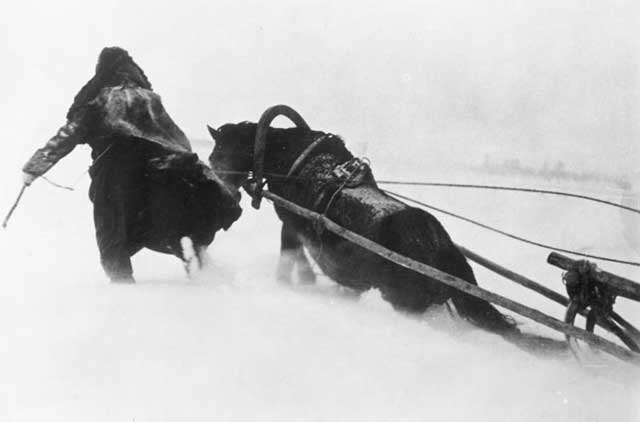 |
| A man and his horse pulling a Panje cart in Russia, 15 January 1942 (Lachman, Hans, Federal Archive Picture 183-B15084). |
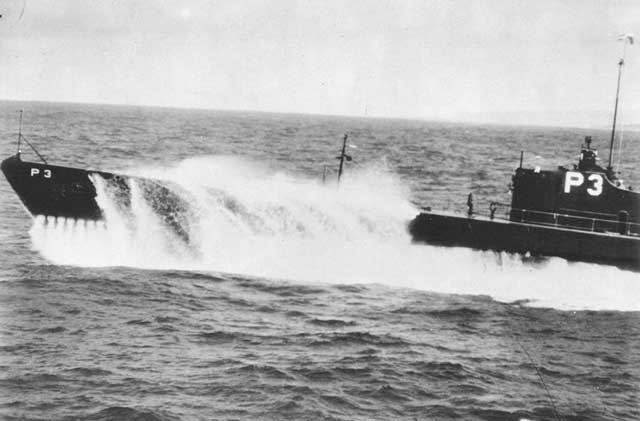
Battle of the Atlantic: Having already sunk two freighters on its Operation Drumbeat patrol to the east coast of the United States, U-123 (Kptlt Reinhard Hardegen) cruises on the surface to New York Harbor. The U-boat arrives in the early morning hours of
15 January 1942. The crew, having grown accustomed to the blacked out conditions in Europe, is dazzled by the bright lights of New York City. Hardegen records:
I cannot describe the feeling in words, but it was unbelievable and beautiful and great. . . We were the first to be here, and for the first time in this war, a German soldier looked out on the coast of the USA.
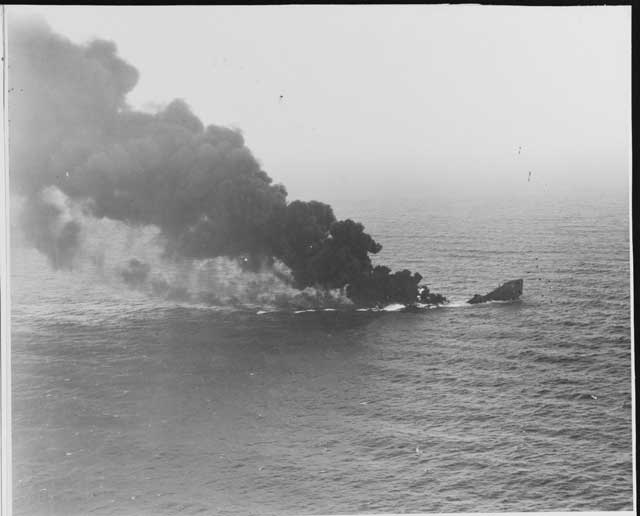
Hardegen is in position to lob a few shells from his deck at Coney Island (as Japanese submarines have been doing to Hawaii) just for the heck of it and to make a statement. However, he decides not to do that because it would give his position away for little profit. Instead, Hardegen uses the Americans' lack of preparedness to do a little real business. Before the night is out, he spots 6768-ton British tanker Coimbra. It is easy to spot, as the city lights behind the tanker are blotted out as it moves east to join the convoys heading for Great Britain. Hardegan torpedoes the tanker, which explodes in a massive fireball that rises 650 feet into the air. There are 36 deaths (ten perish in the lifeboats) and six survivors. People in the Hamptons, 27 miles directly to the north, see the explosion and report it. Hardegen is astounded that the US military does not respond at all to the sinking. He sails away on the surface looking for more prey, now with three solid victories during the patrol.
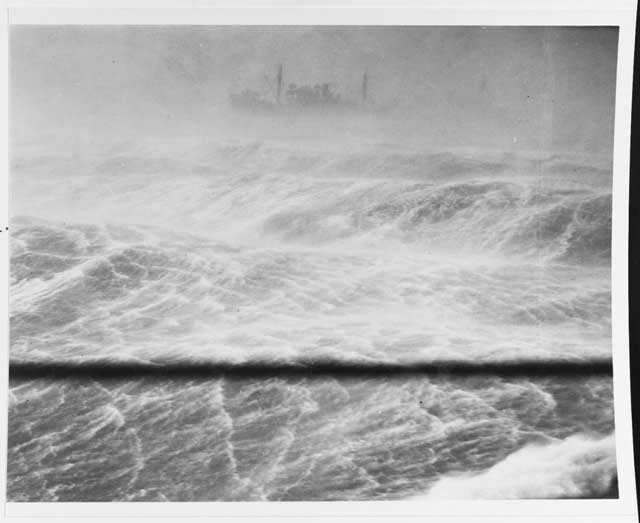 |
| A North Atlantic convoy seen as a storm lashes shipping off Hvalfjordur, Iceland, 15 January 1942. Seen from USS Albemarle (AV-5). |
Even aside from U-123, Admiral Doenitz's U-boat fleet has a mixed day in the Atlantic on a very stormy day in the northern latitudes. There are several other successes:
- U-552 sinks 4133-ton British freighter Dayrose just south of easternmost Newfoundland
- U-203 sinks 623-ton Portugues trawler Catalina southeast of Newfoundland
- U-553 torpedoes 8106-ton British tanker Diala, also southeast of Newfoundland. The tanker is badly damaged and ultimately sinks after a tug attempts to tow it. There are 57 deaths and 8 survivors.
However, on her seventh patrol from St. Nazaire, U-93 (Oblt.z.S. Horst Elfe) is sunk between Portugal and the Azores about 219 nautical miles (406 km) northeast of the Madeira Islands during a depth charge attack by HMS Hesperus (H-57). U-93 was a member of Wolfpack Seydlitz, which was tracking Convoy HG 78 out of Gibraltar. There are 6 deaths and 40 survivors. U-93 winds up its career with a total of eight ships sunk totaling 43,392 gross register tons. The war at sea already is heating up again after a brief quiet period during the winter. Another four U-boats are closing in on the east coast of the United States as part of Operation Drumbeat, so more successes are likely to occur soon.
 |
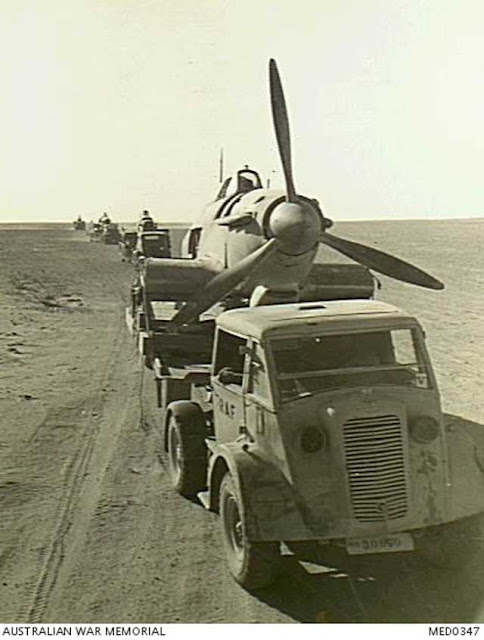
| "Benina, Cyrenaica, Libya. 15 January 1942. Obbedire...Combattere...Dux. 'Obey, fight, the Duce! says the large lettering on the hangar wall at Benina airfield. But the Axis mechanics, heedless of their instructions, fled incontinently leaving this German Junkers JU 87 dive bomber aircraft intact to fall into the hands of the advancing Allied forces." Australian War Memorial MED0289. In the Luftwaffe, it is considered a dishonor to allow your plane to fall intact to the enemy. There appears to be a Bf-109 virtually intact to the right, too. |
Battle of the Mediterranean: Royal Navy Swordfish from RAF No. 815 Squadron use depth charges to sink U-577 (K.Kapt. Herbert Schauenburg) northwest of Mersa Matruh, Egypt. Everyone aboard perishes. U-577 was an unlucky boat, sailing on three patrols with no victories. On Malta, RAF personnel are being trained in ground combat out of fear that the Axis is about to invade.
 |
| The Camden (New Jersey) News, 15 January 1942. "Americans Holding Out," screams the main headline, but the other headlines recite positive but largely fake news. |
Battle of the Pacific: Japanese submarine I-65 torpedoes and sinks 5102-ton Indian freighter Jalarajan northwest of Padang, West Sumatra in the Indian Ocean.
The Japanese increase their presence in Burma by sending the 55th Division across the border from Thailand north of Mergui (Myeik) in the middle of the southern sliver of the country. This protects the Japanese flank in the Malay Peninsula, though that is not under much of a threat. It also provides a potential launching pad for attacks to the north. The British have two divisions (one Burmese, one Indian) much further north to prevent a Japanese breakout into the heart of the country. However, already the Japanese have seized some very useful airfields in the south of the country, helping them to achieve local aerial supremacy.
 |
| "At this stage the guns of "C" Troop, 30th Battery, 2/15th Australian Field Regiment, here depicted, are ahead of the infantry, firing at 300 yards at Japanese advancing through the rubber plantation. A few men of the 2/30th Australian Infantry Battalion, which was deployed in the rear of the guns, can be seen in the foreground, Gemas, Malaya." This depicts the action of 15 January 1942 near Gemas. The guns are 25-pounders. Australian War Memorial ART24498. |
On the Malay Peninsula, the Japanese attack at a rubber plantation in the Gemas area in the morning. The Japanese troops, who suffered about 600 casualties at the Battle at Gemencheh Bridge on the 14th, are supported by dive-bombers and tanks. The artillery of 2/15th Australian Field Regiment and soldiers of Australian 2/30th Battalion, 27th Brigade, 8th Division, stop the attack and destroys six of eight tanks. The Australians, after holding for 24 hours, then withdraw after dark. The engagement is a costly Japanese victory, but at this stage of the war, they can afford such victories. On the west coast, the Japanese advance to the Muar River and establish a small bridgehead on the south bank between Muar and Batu Pahat. Indian 45th Brigade is defending this area, which is critical because an advance here would threaten British lines of communication to Singapore. In Singapore itself, the authorities impose martial law.
 |
| British 181-ton fishing trawler Nordale is among the ships wrecked during the storms sweeping the North Atlantic, though the weather apparently is not the cause. Around dusk on the 14th, the Nordale hits the Carskey Rocks off the tip of Kintyre two miles southwest of Borgadelmore Point. The crew, unable to take to the boats, spends a perilous night aboard. At daylight on 15 January 1942, one crewman gets ashore to alert local authorities and they are rescued using a Breeches Buoy. Despite all of the 14 crew surviving the night, five men perish during the 15th due to exposure, drowning, or fatigue. A court of inquiry later finds the mate responsible. |
In the Philippines, the Japanese attack II Corps, which holds the eastern half of the line across the Bataan Peninsula. Despite fierce resistance by Filipino 41st and 51st Divisions, the Japanese secure a small foothold across the Balantay River. This is a very dangerous incursion into the Allies' main line of defense, and General MacArthur transfers several units east from I Corps to contain the Japanese and attempt to throw them back across the river. In the I Corps sector on the western half of the Peninsula, the Japanese advance closer to Moron along the coast. They are supported by powerful naval units just offshore.
 |
| "A female war worker fixes her hair and checks her appearance in the mirror in the bedroom she shares with another war worker at the hostel attached to ROF Bridgend. Her friend is looking for something in the wardrobe. Family photos and a vase of flowers help to brighten up the dressing table. According to the original caption, this was a "central-heated bedroom, fitted with wash-basin, wardrobe, and chest of drawers." January 1942. © IWM (D 6332). |
The Netherlands East Indies are not yet a battlefield, but everyone knows it is only a matter of time before the Japanese attack. Pursuant to the recently concluded Arcadia Conference in Washington, D.C., British General Sir Archibald Wavell establishes his ABDA command assumes supreme oversight of all forces in the area. Wavell's deputy is Lieutenant General George H. Brett, USAAF, while Admiral Thomas C. Hart, USN, is to command naval forces. The Dutch have a very powerful naval squadron on hand under Rear Admiral Karel Doorman, who has his flag aboard light cruiser De Ruyter based at Surabaya. Doorman's orders are to use the ABDA Combined Striking Force to intercept and defeat invasion attempts.
 |
| British 227-ton trawler Ocean Tide gets caught in the storms sweeping the North Atlantic on 15 January 1942 and runs aground at Mammal, Tiree, Inner Hebrides. The trawler, based at Ayr, is wrecked. |
Eastern Front: The Soviet General Offensive continues unabated on 15 January 1942. Third Shock Army crosses the vital Kholm-Demyansk Road, threatening both cities with encirclement. With his entire position south of Lake Ilmen at risk, Field Marshal Ritter von Leeb of Army Group North issues Adolf Hitler with an ultimatum. Either give me the necessary freedom of action, Leeb demands, or relieve me. Hitler does not have to think about this very long and has OKH chief of staff General Franz Halder call Leeb's chief of staff - not Leeb - General Brennecke with a message:
[P]ut all of the powers of the General Staff in motion... and extirpate this mania for operating. The army group has a clear order to hold.
In the Wehrmacht at this point, "operating" is a synonym for "retreating," which pretty much encapsulates the entire situation on the Eastern Front. Leeb technically remains in command for the time being, but it is common practice within the Wehrmacht at this point to simply bypass a general who is soon to be relieved.
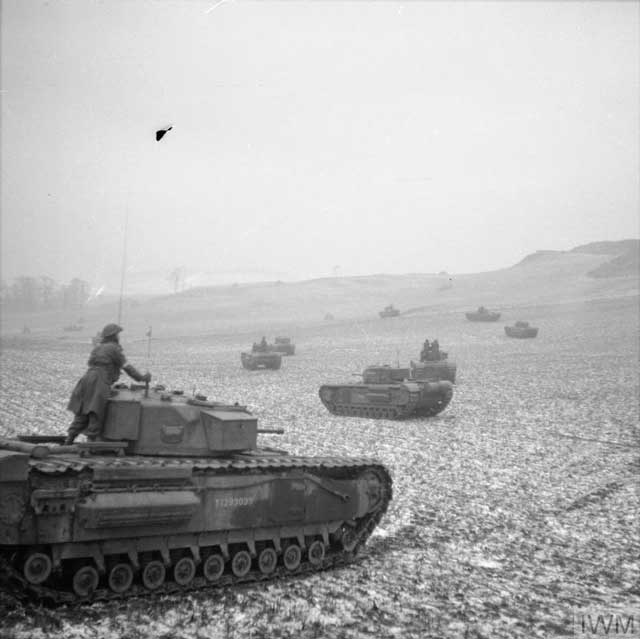 |
| "Churchill Mark IV infantry tanks of the 16th Tank Brigade (1st Polish Corps) go into action during the 'Jay' Exercise. Fife, Scotland, 15 January 1942." © IWM (H 16628). |
On the Crimea, both sides are gearing up for their own offensives to break the stalemate at the Parpach Narrows. Neither side believes the other is strong enough to launch its own attack, so neither adopts a defensive posture. Both sides make their own moves today. The Soviets land 226 soldiers from destroyer Sposobnyi about 40 km southwest of Feodosia. This is intended as a diversion, but the Germans are not fooled and only divert one company of Panzerjäger to contain this small force. Red Army General Dmitry Kozlov, hearing reports of this incident and the seemingly desultory Wehrmacht response, wrongly concludes that the Germans have few troops nearby. In fact, the Germans have been transferring forces east from the perimeter at Sevastopol and have four full divisions at hand ready to launch their own offensive.
The Germans, however, have plans of their own and are not allowing themselves to be distracted. At daybreak on 15 January, the Luftwaffe begins attacking the Red Army line along the Parpach Narrows with Stukas and Heinkel He 111 bombers. The bombers hit the headquarters of the Soviet 44th Army, wounding its commander and leaving it leaderless. The German 213 Infantry Regiment jumps off following the Luftwaffe preparation and makes good progress. By mid-afternoon, the Germans are in possession of the ridgeline to the west of Feodosia and in a good position to launch an attack on the port within a couple of days. The German 30 Corps of General Fretter-Pico takes 500 casualties during the day but re-establish German dominance in the field of battle.
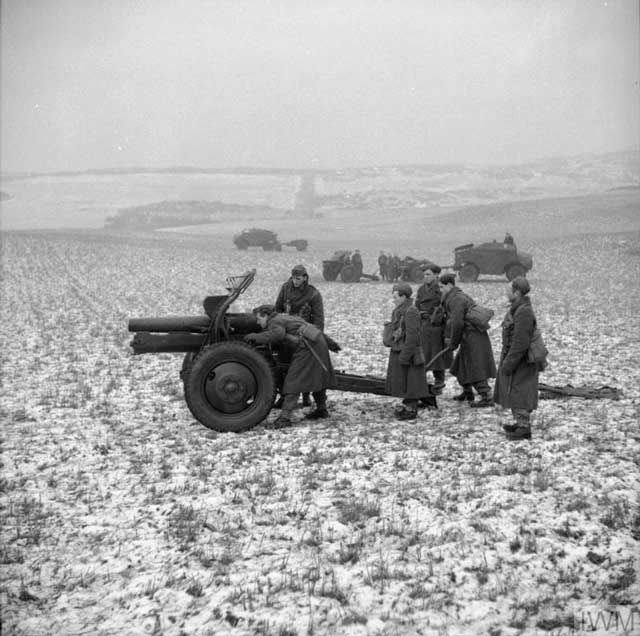 |
| "Gunners of the 1st Polish Corps preparing to repel a 'tank attack' with 4.5-inch howitzers during the 'Jay' Exercise. Fifeshire, Scotland, 15 January 1942." © IWM (H 16623). |
Partisans: The Germans launch the first of many large-scale counter-insurgency operations, Operation Southeast Croatia (Unternehmen Südost Kroatien). It targets Yugoslav Partisans in eastern Bosnia, who call it the "Second Enemy Offensive." The German 342nd Infantry Division pushes into the Drina Valley from the east while the 718th Infantry Division advances from the west near Sarajevo and Tuzla.
Allied Relations: In Brazil, representatives from 21 American republics meet in Rio de Janeiro for an Inter-American Conference. They unanimously agree to sever diplomatic relations with the Axis powers, but Argentina and Chile actually do not do this. The United States government already has prevailed upon high-profile ambassadors, including Walt Disney and Orson Welles, to drop all of their other projects and head south to Latin America. This is a public relations move to show unity with the country's southern neighbors. Disney and Welles gladly volunteer to help the war effort. While Welles' career suffers due to his absence from Hollywood, some believe that Walt Disney saves his studio by helping the war effort in this way following some disastrous losses from unsuccessful (financially) films such as "Pinocchio." This is because Walt Disney Studios earns substantial sums of money by making films for the government related to this endeavor such as "
Saludos Amigos" (1942) and "
Los Tres Caballeros" (1944).
 |
| Original caption: "A runaway freighter at Hvaljardur, Iceland, during the "big blow." This shows USS Wichita (CA-45), a heavy cruiser, colliding with freighter SS West Nohno in Hvalfjörður, Iceland, on 15 January 1942. The freighter (apparently, judging by the caption) broke loose from its moorings during a strong winter storm. Wichita not only hit freighter West Nohno but it also hit British trawler Ebor Wyke. The cruiser then ran aground off Hrafneyri Light but was quickly got off. The Wichita then turned around and made it to New York City for repairs, where Captain Alexander of the Wichita was relieved of his command. The Wichita, which had been at Iceland on a journey to join the British Home Fleet, ultimately made it to its destination, Scapa Flow, on 5 April 1942 (US Navy via the "USS Wichita (CA-45) 1939-1945 cruise book" at Navysite.de). |
US Military: The US Army Air Force activates the Alaskan Air Force at Elmendorf Field, Anchorage, Alaska. Lieutenant Colonel Everett S Davis is in command of the base, which is named in honor of Captain Hugh M. Elmendorf, killed on 13 January 1933, while flight testing the experimental Consolidated Y1P-25, fighter, 32-321, near Wright Field, Ohio. The base has been under construction since 8 June 1940 and is intended as a major and permanent military airfield. While the base is active, it does not yet have any USAAF units assigned to it. Elmendorf is perfectly situated to conduct operations over the Aleutian Islands, which both sides already are eyeing as strategically important locations due to their proximity to Japan. The 23rd Air Base Group, 18th Pursuit Squadron, and Eleventh Air Force all will be at Elmendorf soon.
US Secretary of War Henry Stimson projects that almost 2 million men will be inducted into the US military during 1942. The draft is in full swing, but many men are volunteering, too.
 |
| Maclean's, 15 January 1942. |
Indian Government: Jawaharlal Nehru, recently released from prison by the British, succeeds his fellow nationalist, Mohandas K. Gandhi, as head of India's National Congress Party.
China: The Third Battle of Changsha, which began on 24 December 1941, concludes after a successful Chinese counterattack. Three Japanese divisions that have crossed the Liuyang River flee back across it and are devastated by Chinese troops waiting there for them. Overall, the Japanese lose 1591 killed and 4412 wounded (according to the Japanese), while the Chinese suffer 29,217 total casualties. While the Chinese suffer more losses, they occupy the battleground, and this is the first land victory over the Japanese since Pearl Harbor. While the Japanese are hardly defeated in China and the battle is only a Chinese victory in the sense that they stopped a Japanse attack, the Battle of Changsha greatly enhances China's standing in the Allied community and earns Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek greatly enhanced prestige both abroad and at home.
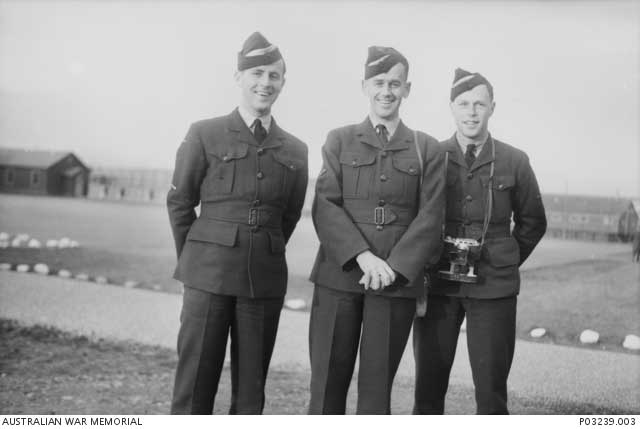 |
| "Edmonton, Alberta. 15 January 1942. Leading Aircraftman (LAC) H. J. Barker (front left), 405381 LAC Thomas Hector McNeill of No. 460 Squadron (middle), LAC E. R. (Blue) Freeman (right) at the passing out dinner. LAC Barker finished the war as a Squadron Leader and was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC) for night photographs of Essen Dortmund and Dusseldorf and the Bar to DFC for continued enthusiasm and skill on sorties to Berlin after ninety operations over Europe, sixty with the Pathfinder Force. LAC McNeill was killed in action over Holland, in a flying battle. LAC Freeman survived fifty operations and was then awarded DFC for skill and fortitude in operations against the enemy." Australian War Memorial P03239.003. |
American Homeland: President Franklin D. Roosevelt sends a "green light" letter to longtime Commissioner of Baseball Kenesaw Mountain Landis allowing Major League Baseball to play the 1942 season. He writes, "I honestly think it would be best for the country to keep baseball going." This comports with general US policy to keep important entertainment producers such as the film industry functioning during the war. While FDR also encourages more night baseball so as to allow war workers to attend the games or listen to them on radio, the Chicago Cubs already have dropped plans to install lights at Wrigley Field.
 |
| Franklin Roosevelt's "Greenlight" letter to Judge Landis, 15 January 1942 (National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum). |
General Motors produces its first "blackout" Cadillacs. These 1942 models lack items that contain materials banned by the government, such as spare tires (rubber), trim (chrome), and other normal accessories. Auto production at the major car factories now is taking place side-by-side with military production.
 |
| The Shadow, "The Book of Death," 15 January 1942. This is considered one of the classic covers of The Shadow. |
1942January 1942January 1, 1942: Declaration By United NationsJanuary 2, 1941: Manila Falls to JapanJanuary 3, 1942: ABDA Command AnnouncedJanuary 4, 1942: MacArthur on His Own in the PhilippinesJanuary 5, 1942: Soviets Plan General OffensiveJanuary 6, 1942: US Army in EuropeJanuary 7, 1942: Soviet General Offensive OpensJanuary 8, 1942: Hitler Sacks HoepnerJanuary 9, 1942: Battle of DražgošeJanuary 10, 1942: Building the JeepJanuary 11, 1942: Japan Takes Kuala LumpurJanuary 12, 1941: Rommel Plans CounterattackJanuary 13, 1942: First Ejection Seat UseJanuary 14, 1942: Operation Drumbeat First SinkingJanuary 15, 1942: U-Boat Off NYCJanuary 16, 1942: Carole Lombard CrashJanuary 17, 1942: British Take Halfaya PassJanuary 18, 1942: Soviet Paratroopers in ActionJanuary 19, 1942: FDR Approves Atomic BombJanuary 20, 1942: The Wannsee ConferenceJanuary 21, 1942: Parit Sulong Bridge BattleJanuary 22, 1942: Parit Sulong MassacreJanuary 23, 1942: Japan Takes RabaulJanuary 24, 1942: Battle of Makassar StraitJanuary 25, 1942: Kholm SurroundedJanuary 26, 1942: GIs Land in EuropeJanuary 27, 1942: Battle of EndauJanuary 28, 1942: Rommel Takes BenghaziJanuary 29, 1942: First US Coast Guard Ship SunkJanuary 30, 1942: Singapore IsolatedJanuary 31, 1942: Army Group South Averts Disaster2020