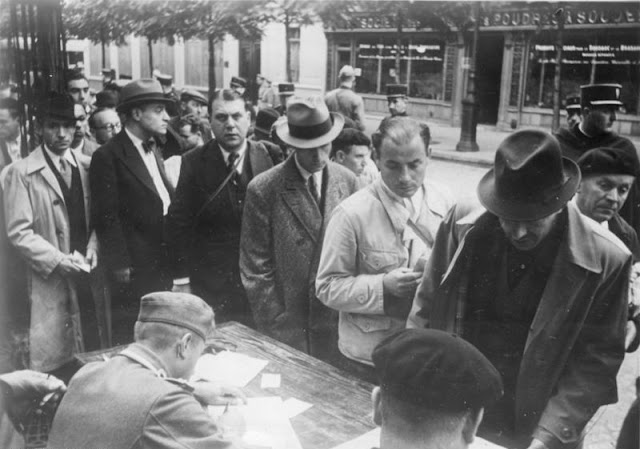
Sunday 24 August 1941
 |
| German transport destroyed by partisans on the railway line Sarajevo - Visegrad, Yugoslavia, 24 August 1941. |
My reply to [Guderian] is that I had no sympathy for such a 100% change of mind. His retort was: What he told us yesterday was framed with a view to furnishing OK with arguments against the ordered operation to the south. Now, having become convinced by his interview that the Fuehrer was firmly resolved to execute this drive to the south, it was his duty to make the impossible possible in order to put those ideas into effect.Halder concludes that "This conversation shows with devastating clearness with what complete irresponsibility official reports are twisted to fit any specific purposes."
In the Far North sector, the Soviet 115th and 123rd Rifle Divisions launch a counterattack against the Finnish bridgehead across the Vuoksi River. The Finnish Light Brigade T is partially surrounded and forced to fight for its life. Things look grim, but the Finns have reinforcements available while the Soviets do not, and the Soviet units are tired from long marches. The Finns quickly send units of IV Corps which are due to arrive on the 25th.
Finnish 8th Division (Col. Winell) crosses Viipuri Bay unopposed, isolating the Soviet forces in Viipuri by cutting their escape route along the coast. The Soviet troops are not going to retreat without orders anyway, as they know from experience that bad things happened to troops that retreated on their own initiative during the Winter War and the opening stages of Operation Barbarossa. Thus, the Soviets essentially allow the Finnish crossing because they are staying put anyway.
Finnish 36 Corps continues advancing in the area of Nurmi Lake and Nurmi Mountain. On their right flank, the Finns take the village of Vuoriyarvi, while in the left the Finnish 6th Division is racing to cut off Soviet troops that are trying to escape to the north along a logging road that they have found which is not on maps.
 |
| Fighting at Novogord, 24 August 1941 (Kempe, Federal Archive, Bild 183-L19934). |
In the Army Group Center sector, Soviet General Ivan Konev attacks toward Gomel, recently taken by the German 2nd Army. Second Army itself is planning an attack on the south in conjunction with General Guderian's Panzer Group 2, which is about 75 miles to the east at Starodub. General Hoth's Panzer Group 3 continues thrusting in the direction of Velikie Luki, advancing to within a mile of the city.
Field Marshal von Bock is bitter about the emphasis on Kyiv and Leningrad over Moscow, writing:
This is the seventh or eighth time in this campaign that the army group has succeeded in encircling the enemy. But I'm not really happy about it, because the objective to which I have devoted all my thought, the destruction of the enemy armies, has been dropped. Perhaps we will overrun the Russians in from of my northern wing and thus get things going to the point that at least pressure on my eastern front is relieved...If, after all the successes, the campaign in the east now trickles away in dismal defensive fighting for my army group, it is not my fault"
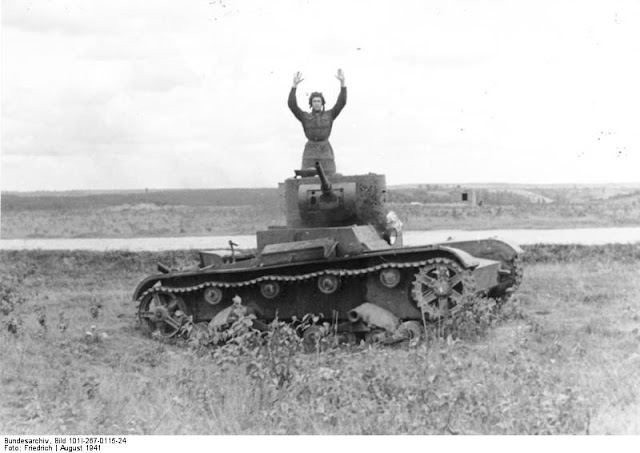 |
| A Soviet tanker surrenders his T-26B tank, August 1941 (Friedrich, Federal Archive, Bild 101I-267-0115-24). |
There is heavy fighting at Dnepropetrovsk and south of Kyiv. German 6th Army continues pulling the noose tight around Kyiv. German 11th Panzer Division reaches the Desna at Oster, but the retreating Soviets set it on fire.
Luftwaffe Oblt. Hans Philipp of II./JG 54 receives the Eichenlaub, becoming the 33rd soldier to receive it. Philipp has 62 kills, over 40 in the USSR.
RAF Bomber Command mounts a large raid over Düsseldorf with 25 Whitleys, 12 Hampdens, and 7 Halifax bombers (44 total). It is cloudy and accuracy is very poor. The RAF loses 2 Whitleys and one Halifax.
The RAF mounts a special operation targeting searchlights in the Wesel area. Six Hampden bombers mount a sustained attack against searchlights that are illuminating another bomber and find that directly attacking them causes them to either go out (either from being destroyed or voluntarily) or lose their tracks on other bombers.
The Luftwaffe takes advantage of low cloud cover over England to send six planes against targets from Blyth to Teesside. The RAF responds, and a tragedy results. There is a friendly fire incident when RCAF Hurricane Mk. I Hurricanes of No. 1 Squadron based at Northolt, Middlesex mistake two Blenheim bombers for Junkers Ju-88s and shoot them down.
Battle of the Baltic: The Germans are closing in on Tallinn (Reval), Estonia, so the Soviets send a convoy carrying departing troops and refugees. The convoy sails into a German minefield off Cape Juminda (near Keri Island), with disastrous results. The following ships hit mines and sink:
- Destroyer Engels (formerly the Desna)
- Minesweeper T-209/Knecht
- Minesweeper T-213/Krambol
- Minesweeper T-212/Shtag
- 3618-ton freighter Lunacharski
- 1430-ton freighter Daugava
- 2029-ton freighter Zheleznodorozhnik
.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages Soviet freighter VT-532 in the Baltic. The master manages to beach the freighter near Prangli Island. There are 44 deaths.
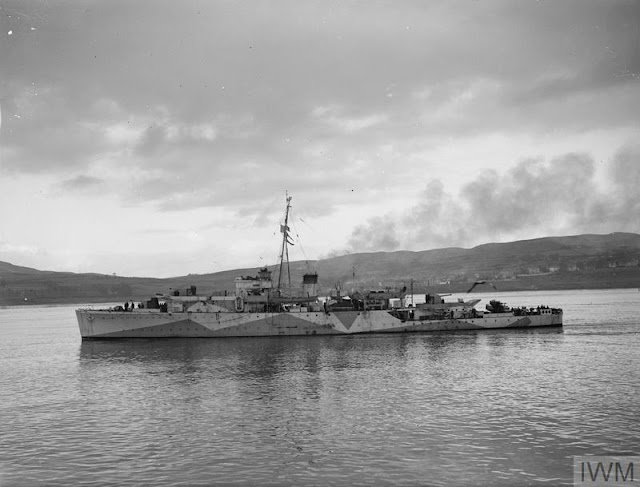 |
| HMS Black Swan, damaged on 24 August 1941, in Londonderry on 26 February 1942 (© IWM (A 7309)). |
Royal Navy anti-submarine whaler Kos XVI collides at 23:30 with destroyer Wolsey in the Irish Sea and sinks just after midnight in the early hours of the 25th. Wolsey remains in service.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages Royal Navy sloop Black Swan while Black Swan is escorting a convoy in the Irish Sea. Black Swan makes it to Milford Haven for repairs that take three weeks.
An RAF Catalina sights an attack a U-boat about 30 miles southwest of the River Tagus near Lisbon but apparently misses.
In Operation Cutting, Royal Navy sloop Milford departs from Freetown escorting 1984-ton British freighter Lady Denison-Pender. The latter ship is to cut and remove the Dakar-Pernambuco cable.
The Newfoundland Escort Force (NEF), established at St. John's on 23 May, continues adding ships and expanding its operations. Today, Canadian corvettes Agassiz, Alberni, Chambly, Cobalt, Collingwood, Orillia, and Wetaskiwin depart from Halifax for St. John's, while corvette Kenogami arrives there.
Royal Navy Force A, beginning operations in the Arctic, arrives at a point 60 miles west of Isfjord, Spitsbergen. It prepares to conduct Operation Gauntlet, a Royal Navy raid on Spitzbergen scheduled to begin in the early hours of 25 August.
First Lord of the Admiralty A.V. Alexander visits Scapa Flow for an inspection tour of battleship HMS Prince of Wales.
Royal Navy minesweeper Fort York is launched.
Norwegian Navy submarine HNoMS Uredd, formerly HMS P-41, is launched (the formal transfer to the Norwegians is on 7 December 1941).
Convoy SC-41 departs from Sydney, Cape Breton bound for Liverpool, Convoy SL-85 departs from Freetown bound for Liverpool.
 |
| HMS Manxman, a key part of Operation Mincemeat. |
The Italian fleet, led by battleships, continues patrolling off the western Italian coast but does not locate the British ships. The Royal Navy, however, does spot the Italian fleet. After aerial reconnaissance reveals the presence of battleships, the British head back to Gibraltar. In any event, the British have accomplished their main objective, the minelaying of Manxman.
The Italian Navy sets up a patrol line of five submarines and 13 motor torpedo (MAS) boats across the Sicilian Strait in order to waylay an expected Royal Navy move through the Mediterranean. Other submarines take up position southwest of Sardinia. The Italian fleet sets up station at the entrance to the Sicilian Strait, waiting for the British - while ships of the Royal Navy now are heading in the other direction. Royal Navy submarine Upholder spots the fleet and attacks light cruiser Luigi Di Savoia, but misses.
The Royal Navy officially writes off submarine P-33 (Lieutenant R.D. Whiteway-Wilkinson). It is the second U-Class submarine lost in two days, the other being P-32.
Operation Treacle, the replacement of Australian soldiers at Tobruk with Polish troops of the Carpathian Brigade, continues. The Polish troops depart from Alexandria aboard minelaying cruiser Latona and destroyers Griffin, Kingston, and Kipling. The mission proceeds without incident.
British patrol planes from Malta spot Italian patrol boat Grazioli Lante between Tripoli and Benghazi and sink it. Nine Wellingtons attack Tripoli and damage the docks and the city.
Battle of the Black Sea: Soviet submarine L-4 (Lt Cdr Polyakov) lays 20 mines off Cape Olinka, Romania. The Soviets have four other submarines patrolling off the Romanian coast while two others patrol off the Bulgarian coast.
Battle of the Indian Ocean: Royal Navy light cruiser HMS Ceres collides with 6129-ton Norwegian tanker Gylfe off Bombay. Ceres sustains major damage to its stem, fracturing it, but proceeds with its mission anyway, escorting Convoy BM-8 to Port Swettenham, Trincomalee.
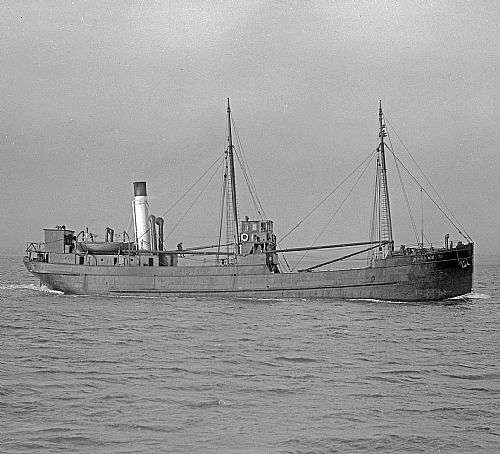 |
| Australian coaster Dellie, sunk on 24 August 1941. |
Japanese Military: The Imperial Japanese Navy begins reconstructing patrol boat PB-2, adding 4.47-inch/45 cal main guns. It also is modified to be able to carry and launch two 46-foot Daihatsu landing craft.
British Government: Prime Minister Winston Churchill addresses the House of Commons:
Napoleon in his glory and genius spread his Empire far and wide. ... Napoleon's armies had a theme. They carried with them the surges of the French Revolution - Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity. ... There was a sweeping away of outworn, medieval systems and aristocratic privilege. There was the land for the people, a new code of law. Nevertheless, Napoleon's empire vanished like a dream.Both sides use historical precedent throughout the war, with the British awkwardly using the example of Napoleon (and subtly appealing to Gallic pride) and the Germans just as awkwardly using the example of the Teutonic Knights battling Russia - both of whose forces lost.
China: Japanese planes sink Chinese gunboats Chiang Hsi and Chiang Kum at Patung, Szechuan, China.
Holocaust: During his radio address to the nation today, Winston Churchill refers to the "scores of thousands" of executions of civilians by the Germans. He does not, however, mention that the primary victims are Jews.
The Germans in Vilna, Lithuania arrest local leader Dr. Jacob Wigodsky, 86 years old. They schedule his execution to take place in a week.
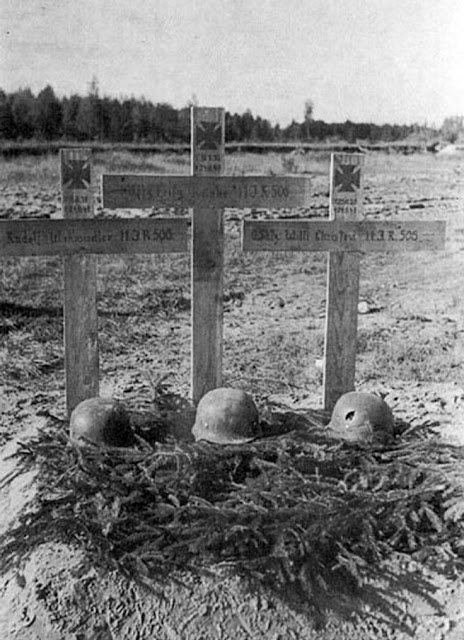 |
| German graves of 11/506 in Estonia, all three KIA 24 August 1941. |
It is a rare instance of popular pressure within the Reich forcing Hitler's hand. Hitler, however, knows that the Catholic Church is one of the only institutions that have a large following other than him - and privately he vows retribution after "final victory." This also is a rare case of the Church opposing Hitler, something for which it gets scant credit in postwar histories. The killings, however, continue within concentration camps after this date. It is estimated that about 70,000 people perish before this date and about 20,000 people after under the T-4 program, including one of Hitler's own relatives.
The now-unemployed T-4 personnel are not out of work for long. They soon are shipped to the Eastern Front, where they turn their extermination expertise against Jews.
 |
| King Haakon taking the salute at the March Past. Left to right: Commodore F A Buckley, CB; His Majesty King Haakon of Norway; Commander Collett-Muller, RNN; Crown Prince Olaf of Norway; Commander W W Sitwell, RN." 24 August 1941 (© IWM (A 5256)) |
This was a meeting which marks forever in the pages of history the taking up by the English-speaking nations, amid all this peril, tumult and confusion, of the guidance of the fortunes of the broad toiling masses in all the continents, and our loyal effort, without any clog of selfish interest, to lead them forward out of the miseries into which they have been plunged, back to broad high road of freedom and justice.He warns Japan that Great Britain will aid the Americans in the Pacific if war breaks out.
American Homefront: Tom Dewey, District Attorney of New York County, gives a speech to the Williamstown Institute of Human Relations. He concludes that "Only by a respect for the rights of every other individual can we protect our own rights."
Today is the first performance of the Dodger "SymPhony" (a named coined by announcer Red Barber), a five-man pop band that becomes an institution at Brooklyn Dodgers home games at Ebbets Field, Brooklyn.
Future History: Paola Pitagora is born in Parma, Italy. Paola becomes an Italian television hostess in 1960, then makes her theatrical debut in debut in "Gog e Magog." Pitagora goes on to become a major Italian film and television star, debuting in motion pictures with "Shot in Three-Quarter Time" (1965) and continuing through "Help Me Dream" 1981). Paola Pitagora also has written some popular songs for children. She continues to work as of this writing in 2018.
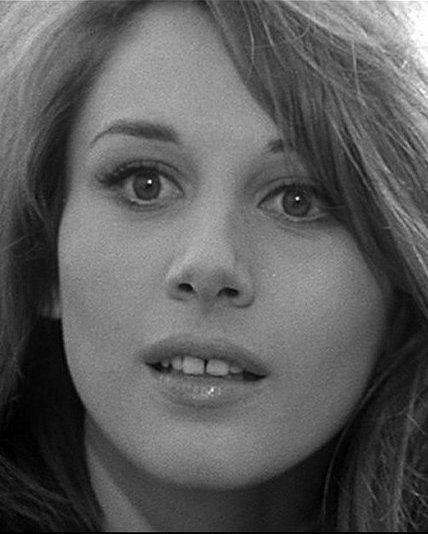 |
| Paola Pitagora, born on 24 August 1941. |
August 1941
August 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement Closes
August 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces Euthanasia
August 4, 1941: Hitler at the Front
August 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk
August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the Arctic
August 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb Berlin
August 8, 1941: Uman Pocket Captured
August 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia Bay
August 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over Berlin
August 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in Life
August 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter Announced
August 13, 1941: The Soybean Car
August 14, 1941: The Anders Army Formed
August 15, 1941: Himmler at Minsk
August 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270
August 17, 1941: Germans in Novgorod
August 18, 1941: Lili Marleen
August 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 Destruction
August 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad Begins
August 21, 1941: Stalin Enraged
August 22, 1941: Germans Take Cherkassy
August 23, 1941: Go to Kiev
August 24, 1941: Finns Surround Viipuri
August 25, 1941: Iran Invaded
August 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the Desna
August 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate Tallinn
August 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets Savaged
August 29, 1941: Finns take Viipuri
August 30, 1941: Operation Acid
August 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No
2020