Thursday 3 April 1941
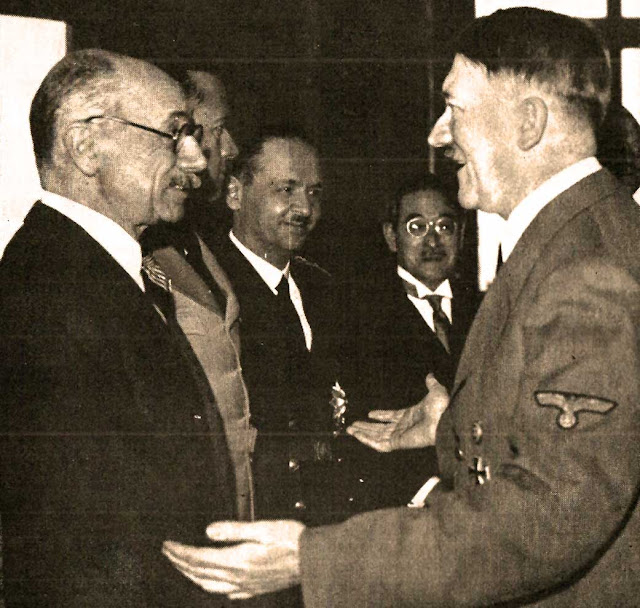 |
| Hitler and Count Teleki - both would commit suicide, Teleki today. |
German Foreign Minister Joachim Ribbentrop also is busy preparing for the post-invasion world in the Balkans. He sends Edmund Veesenmayer of the shadowy Dienststelle Ribbentrop - sort of a private Foreign Ministry which Ribbentrop used as a back-door channel during times of turmoil - to Zagreb. Veesenmayer is there to meet with General Slavko Kvaternik of the Ustaša to sort out who will be doing what after the pesky matter of the Yugoslavian military is brushed aside. The plan is to have Ante Pavelić and the Ustaša rule Croatia after things settle down. Veesenmayer himself is focused on the Balkans and becomes instrumental in persecuting Croatian and Serbian Jewry.
Throughout the Balkans, it is every man for himself. Nobody has a coherent plan, and the overwhelming sentiment is that the German wave is about to come crashing down on everyone. Croatian pilot Captain Vladimir Kren of the Royal Yugoslav Air Force defects to the Germans, telling all he knows so that the Luftwaffe will know how to best coordinate its opening strikes.
Operation Lustre, the British reinforcement of Greece, continues. Convoy ANF-24 from is in the Antikythera Straits when the Luftwaffe spots it. They bomb and sink 10,917-ton munitions ship HMS Northern Prince. Everyone survives, but the cargo is badly needed in Greece. Australian 19th Infantry Brigade arrives at Piraeus.
Yugoslavian General Jankovic meets with Greek General Papagos and British General Wilson in Athens to coordinate strategy.
East African Campaign: Italian Admiral Bonetti at Massawa plans to use his remaining destroyers to bombard Port Sudan in a virtual suicide mission. However, it does not go so well. En route, destroyer Cesare Battisti breaks down. The accompanying Italian destroyers scuttle it. As the Italian ships approach the port, the RAF sends up Swordfish of RAF No. 813 and 824 Squadrons from the aircraft carrier HMS Eagle, which happens to be in the harbor. The Swordfish sink destroyers Daniele Manin and Nazario Sauro, while destroyers Tigre and Pantera are disabled by the air attacks and later sunk by HMS Kingston. The incident is notable in another way because, during the night, sloop HMAS Parramatta passes the Italian destroyers (before they are sunk) at close range, but nobody on either side sees the other. That's the reality of war, weird things happen.
On land, the British tighten their grip on Asmara as advanced troops continue down the road toward Massawa.
Italian freighter Urania attempts to escape in the Red Sea from advancing British troops. However, RAF planes disable it, and the crew scuttles the ship off Dahlak Kebir, Eritrea to avoid capture. After the war, the ship is raised for scrap. The RAF also damages Italian patrol boat Acerbi in the Massawa harbor.
Italian authorities in Addis Ababa see the end approaching. The Duke of Aosta opens negotiations.
RAF Bomber Command, meanwhile, attacks Brest, where German cruisers Gneisenau and Scharnhorst are in dry dock. The bombers miss the two ships but hit the Continental Hotel - where many sailors are quartered. Many are killed by the "lucky hit." The RAF also does some minelaying in the Bay of Biscay during the night with 15 planes.
 |
| Swedish freighter Daphne was en route from Newport News to Petsamo carrying coal when U-76 torpedoed and sank it on 3 April 1941. |
U-73 (Kptlt. Helmut Rosenbaum) torpedoes and sinks three ships:
- 4313-ton British freighter Alderpool (after being damaged by U-46)
- 6875-ton British tanker British Viscount
- 5724-ton British freighter Westpool (35 dead and 8 survivors, sinks quickly because it is carrying scrap iron)
- 5409-ton Belgian tanker Indier (some claim U-74 sank this, 42 dead).
- 4274 ton Greek freighter Leonidas Z. Cambanis (sunk, 2 dead)
- 11,402 ton Royal Navy armed merchant cruiser HMS Worcestshire (damaged, 28 dead)
U-76 (Kptlt. Friedrich von Hippel), in the same vicinity, torpedoes and sinks 1939 ton Finnish collier Daphne, though it apparently is not part of Convoy SC-26 - it just crossed paths with the convoy at the wrong time. During the night, U-76 also sinks 5414-ton British freighter Harbledown (three dead) which most definitely is part of SC-26.
U-98 (Kptlt. Robert Gysae), on its first patrol, torpedoes and sinks:
- 2467-ton Norwegian freighter Helle (all survive)
- 5122-ton British freighter Wellcombe (15 dead)
Combined with other attacks in the surrounding days, such as by U-46 on the 2nd, Convoy SC-26 is devastated. The convoy scatters, then reforms later in the day. But the U-boats continue to prowl.
 |
| Belgian tanker Indier, sunk with other ships of Convoy SC-26 on 3 April 1941. |
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 250-ton British freighter Cairnie southwest of Tod Head. Everyone survives.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 6903-ton British freighter Geddington Court off St. Andrews.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks Royal Navy patrol boat HMS Fortuna in the Irish Sea.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 499-ton British freighter Assuan off Montrose, Scotland. The captain manages to beach the Assuan near Scurdy Ness. The ship later is refloated and taken to Montrose.
British 748-ton coaster Greenawn sinks from unknown causes in the North Sea off Montrose, Scotland. There are Luftwaffe attacks in the area during the day, but also many mines laid by both sides.
Royal Navy patrol boat HMS Bahram sinks when it hits a Luftwaffe IX Air Corps mine in the Humber Estuary. There are 8 deaths and only one survivor.
Royal Navy mine destructor vessel HMS Bushwood gets involved in a collision in the Bristol Channel. Taken to Cardiff, it is back in service by 7 May 1941.
Convoy OB 306 departs from Liverpool.
U-boats U-564 (Kptlt. Reinhard 'Teddy' Suhren) and U-652 (Oberleutnant zur See Georg-Werner Fraatz) are commissioned. U-564 will be the subject of a well-known film showing how U-boats can be resupplied with torpedoes while at sea - it isn't that easy.
Meanwhile, Lieutenant General Erwin Rommel in command of the Afrika Korps and flying about from point to point in his handy Fieseler Storch, can't believe his good fortune. The Luftwaffe, scouting ahead, reports that the Via Balbia is desolate for 60 km past Agedabia, with a few British tanks here and there in the desert after they broke down or ran out of fuel. With the British in astonishing flight to the north and northeast, Rommel orders an attack on the British southern flank. He orders the 5th Light Division to move out of Marada and join the advance, sending Italian forces to garrison it.
The Luftwaffe's Junkers Ju 87s mount a successful attack on a retreating British column around Antelat/Solluch, losing a Stuka and an escorting Bf 110. Rommel orders Lt. Colonel Gerhard von Schwerin, commanding Special Purposes Regiment No. 200, to lead a spearhead to Ben Gania, and he sets off in the evening. There is enthusiasm and dash in the Afrika Korps that for some reason is sadly lacking at this time on the other side.
Late in the day, Rommel drives to the front and orders reconnaissance troops to make a lightning occupation of Benghazi. Informal intelligence - an Italian priest - is that the British have fled Benghazi. Rommel has every vehicle that isn't actively fighting drive to a supply depot in the rear to get the necessary fuel.
Italian General Gariboldi, supposedly in charge of all Axis forces in North Africa, is nonplussed. He stumbles into the Afrika Korps headquarters at 21:00 demanding to be told what is going on. He remonstrates until midnight with Rommel, demanding to be allowed to give the orders to attack or not. Rommel counters that supplies are in good order and the situation is too fluid to go up the chain of command for every decision. OKW (the German military command) gets wind of the situation and quickly sends Rommel a message authorizing the offensive. While technically the OKW itself doesn't have the authority to do this, the message effectively takes the heavy burden of command off Gariboldi's shoulders. From this point forward, Rommel basically does what he wants and tells Gariboldi about it whenever he gets the chance. Since Gariboldi can now, unlike almost all of his peers, go to Mussolini with victories, it is a happy arrangement for everyone.
Malta is relieved when a dozen Hurricanes are successfully flown off of aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal and Argus and make it to the island as part of Operation Winch. However, one Hurricane crashes on landing and is lightly damaged. Off Malta, the Luftwaffe catches Royal Navy minesweeper/high-speed launch HMS Abingdon, which has been sent to loiter 40 miles off the coast in case planes have to ditch (as happened on some previous convoys). They hit the Abingdon, but the ship makes it back to port, along with its fellow minesweeper Jade.
Convoy HG 58 departs from Gibraltar, bound for Freetown.
 |
| Count Teleki's suicide note. |
We broke our word, – out of cowardice [...] The nation feels it, and we have thrown away its honor. We have allied ourselves to scoundrels [...] We will become body-snatchers! A nation of trash. I did not hold you back. I am guilty.The breaking point for Count Teleki apparently was learning that others in the government had secretly permitted German troops to enter the country. There was little that Count Teleki could do, unlike Yugoslavia, the government and military in Hungary are solidly pro-German. Bárdossy, meanwhile, now combines his job of the foreign minister with that of prime minister.
There is wild speculation in the British media that Teleki was murdered for opposing Hitler. There is no evidence of that, and the suicide note would seem to contradict that conspiracy theory.
Meanwhile, Wehrmacht troops are pouring across the Hungarian border to take up positions for a move south.
German/Yugoslav Relations: Despite definite indications from the new Yugoslavian government that it is willing to deal with Hitler, the German legation, for the most part, leaves Belgrade under orders from Foreign Minister Ribbentrop.
Anglo/Soviet Relations: Sir Stafford Cripps, an avowed Socialist who is viewed as a specialist in dealings with the USSR, warns Joseph Stalin (at the behest of Churchill) about Wehrmacht troop movements in Poland that appear oriented toward the Soviet Union.
In Washington, Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Harold Stark pens and sends out a memorandum to his three fleets (Pacific, Asiatic and Atlantic) expressing confidence in keeping the US fleet at Pearl Harbor. He feels its presence there has a calming effect on Asia.
Iraq: Rashid Ali continues tightening his hold on the government. He has assurances from pro-German Vichy French officials in Syria that they will permit passage of Luftwaffe aircraft to Iraq to support him. These aircraft also could bomb British positions in Iran. However, there remains a large British garrison and RAF contingent at Habbaniyah Field just outside Baghdad that remains to be subdued.
Future History: Hans-Jörg Gudegast is born in Bredenbek, Germany. He emigrates to the USA "with only the money in my pocket" and attends the University of Montana at Missoula. Under the stage name of Eric Braeden, Gudegast enters the acting field and plays a variety of roles, usually as a Wehrmacht soldier (as in television series "Combat!") or ominous secret agent (as in "The Man From U.N.C.L.E."). However, Braeden is perhaps best remembered for playing the fictional German Hauptmann (Captain) Hans Dietrich on the TV series "The Rat Patrol" (1966–1968) - a character that would have been active in the desert on the day that he was born. Eric Braeden appears to be semi-retired from acting as of this writing, but he remains active; Braeden published his autobiography, "I'll Be Damned," with Harper Collins in 2017.
El Rancho Vegas, the first resort hotel (complete with gambling) on what will become the Las Vegas Strip, opens today. After it burns down in 1960, Howard Hughes will buy the property but do nothing with it. While it is the site of the first hotel on the Strip, and you would think somewhat important and remarkable in Las Vegas history, it now somewhat incongruously stands almost completely vacant, as if nothing at all important ever sat there at all.
April 1941
April 1, 1941: Rommel Takes Brega
April 2, 1941:Rommel Takes Agedabia
April 3, 1941: Convoy SC-26 Destruction
April 4, 1941: Rommel Takes Benghazi
April 5, 1941: Rommel Rolling
April 6, 1941: Operation Marita
April 7, 1941: Rommel Takes Derna
April 8, 1941: Yugoslavia Crumbling
April 9, 1941: Thessaloniki Falls
April 10, 1941: USS Niblack Attacks
April 11, 1941: Good Friday Raid
April 12, 1941: Belgrade and Bardia Fall
April 13, 1941: Soviet-Japanese Pact
April 14, 1941: King Peter Leaves
April 15, 1941: Flying Tigers
April 16, 1941: Battle of Platamon
April 17, 1941: Yugoslavia Gone
April 18, 1941: Me 262 First Flight
April 19, 1941: London Smashed
April 20, 1941: Hitler's Best Birthday
April 21, 1941: Greek Army Surrenders
April 22, 1941: Pancevo Massacre
April 23, 1941: CAM Ships
April 24, 1941: Battle of Thermopylae
April 25, 1941: Operation Demon
April 26, 1941: Operation Hannibal
April 27, 1941: Athens Falls
April 28, 1941: Hitler Firm about Barbarossa
April 29, 1941: Mainland Greece Falls
April 30, 1941: Rommel Attacks
2020