Sunday 15 March 1942
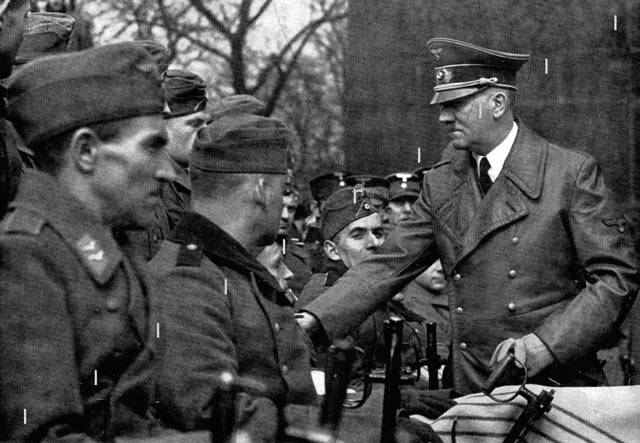 |
| Adolf Hitler greets disabled veterans as part of the Heroes Day celebrations, 15 March 1942 (Polish National Digital Archives). |
The two German attacks advance slowly, with the northern group advancing about 3500 yards (3200 meters) and the southern group only about 880 yards (800 meters). The Germans find that the snow greatly lessens the effectiveness of the Stukas, because when the planes drop their bombs far ahead of the advancing troops, the Soviets have time to recover. When the Stukas drop their bombs closer to the advancing troops, they often hit their fellow German soldiers. Operation Raubtier continues despite the slow progress, however, and eventually does cut off the Soviet salient and create a Soviet pocket on the west side of the Volkhov River.
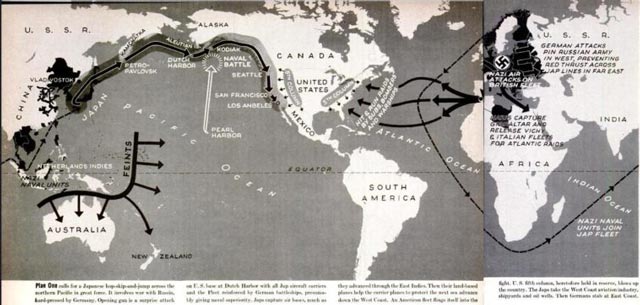 |
| This March, 1942, infographic from Life magazine showed the lines of Axis attack against the United States and its Allies. |
The Germans have destroyed 157 Soviet tanks in three days, including 88 tanks of the 56th Tank Brigade. Among the heroes of the defensive victory for the Germans is Fritz Schrödel, whose StuG III destroyed eight Soviet tanks, of which two were KV-1s, and Lieutenant Johann Spielmann, whose StuG III destroyed 14 T-34s in one day. This is the heyday of the German tank destroyers, which are almost as effective as tanks but vastly cheaper to produce because they lack expensive turrets.
The Japanese High Command is beginning to plan Operation C, a full carrier strike in the Indian Ocean against the British Eastern Fleet stationed in Colombo, Ceylon (Sri Lanka). They order reconnaissance of the western coast of India and Ceylon. Meanwhile, on the British side, Vice-Admiral Sir Geoffrey Layton is announced as the new commander-in-chief of Ceylon.
The front on the Bataan Peninsula in the Philippines remains deceptively quiet, but the Japanese are working furiously to build up their forces. Heavy artillery along the southern shore of Manila Bay southwest of Ternate renews intensive bombardment of the fortified Allied islands in the bay such as Forts Frank and Drum. The US Army attempts counterfire, but it is insufficient to make a difference. The Japanese bombardment damages four guns at Battery Ermita (Battery E, 91st Coast Artillery) in Fort Frank, two beyond repair.
 |
| British tanker British Resources, sunk on 15 March 1942. |
Pursuant to President Roosevelt's telegram to Winston Churchill of 14 March 1942, the US Army informs Lieutenant General Joseph Stilwell, Commanding General American Army Forces, China, Burma, and India, that Chiang Kai-Shek's request that he be placed in charge of Allied operations in Burma is being denied. This is a delicate diplomatic situation because Chiang is still bitter about the British attempt to commandeer lend-lease supplies allocated to him in December 1941. Chiang has gotten along well with Stilwell and apparently wants to show his preference for the Americans. British General Archibald Wavell, Commander in Chief India, will remain responsible for operations In Burma even though he is no favorite of Churchill's. The British power base in India makes this a pragmatic if not altogether ideal solution.
 |
| An Oberleutnant (first lieutenant) of a Luftwaffe Field Division (the Meindl division) in Russia, March 1942. He has the Iron Cross First Class and a pilot's badge (House Block, Federal Archive Figure 101I-395-1513-30). |
The Luftwaffe conducts a coastal sweep and sinks 91-ton Belgian fishing boat Gratie Gods in Oxwich Bay on the south of the Gower Peninsula, Wales.
 |
| HMS Vortigern (D 37), sunk on 15 March 1942. |
The crew of another Royal Navy destroyer nearby witnesses the Vortigern sinking but they do not stop to render aid, as Captain S. Lonbard-Hobson feels that it makes more sense to remain with the fleeing convoy to protect it. This action leads to a Court of Inquiry that is inconclusive. The loss of life is the worst for any single sinking along the English east coast during World War II.
U-503 (Kptlt. Otto Gericke), on its maiden patrol out of Bergen, has been at sea for only 16 days when it is spotted by a patrolling US PBO-1 Hudson aircraft (VP-82 USN) about 250 miles southeast of St. John's, Newfoundland. The Hudson quickly attacks and sinks U-503. All 51 men on board perish. U-503 has sunk no ships during its brief career.
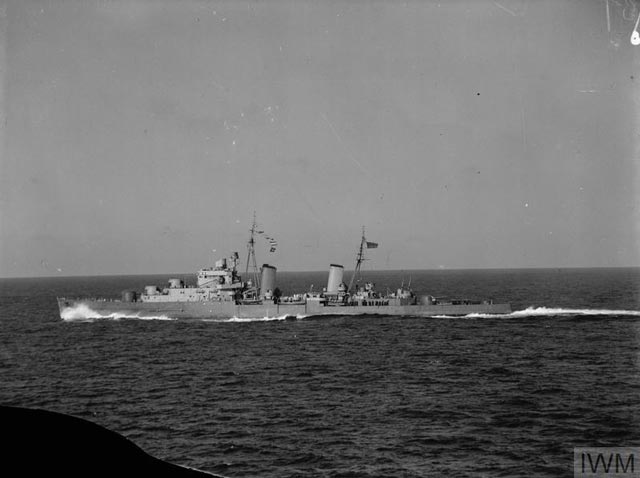 |
| HMS Dido as seen from HMS Euryalus in the Meditteranean, 14 or 15 March 1942. They are en route to bombard the Italian base at Rhodes (© IWM (A 8578)). |
U-158 is not done for the day. At 07:22, Rostin spots a second tanker, 6952-ton Ario about four miles from Olean. He pumps one torpedo into Ario, then surfaces and opens fire with his deck gun. The tanker's crew abandons ship but reboards it after U-158 (which is close by and almost collides with a lifeboat) departs the scene. Unlike Olean, though, this tanker really is sinking, though it takes its time and drifts to within 10 miles east of Cape Lookout before finally going under. There are 26 survivors and 8 dead, most of whom perish as their lifeboat is struck by a shell as it is being lowered to the water.
U-161 (Kptlt. Albrecht Achilles), on its second patrol out of Lorient, concludes a successful patrol by using its deck gun to sink 1130-ton USCG Acacia, a Coast Guard lighthouse west of St. John's and north of Haiti (about 80 miles southwest of Saint Kitts and Nevis). This is the only US Lighthouse Service vessel lost during World War II. All 35 men aboard the lighthouse are rescued and taken to San Juan.
 |
| Canadian freighter Sarniadoc, sunk on 15 March 1942. |
U-124 (KrvKpt. Johann Mohr), on its eighth patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes 7209-ton British tanker British Resource about 230 miles north of Bermuda late on 14 March. After the first two torpedoes do not sink her, Mohr fires another which turns the tanker into a blazing wreck. It sinks during 15 March, with 46 deaths and only seven survivors, including the master, third radio operator, and three gunners.
Italian submarine Enrico Tazzoli sinks 8780-ton British tanker Athelqueen near the Bahamas using torpedoes and gunfire. There are three deaths.
British 971-ton freighter Presto sinks during a convoy from Blyth to Dover due to a collision with fellow freighter Llandover. There is no record of casualties.
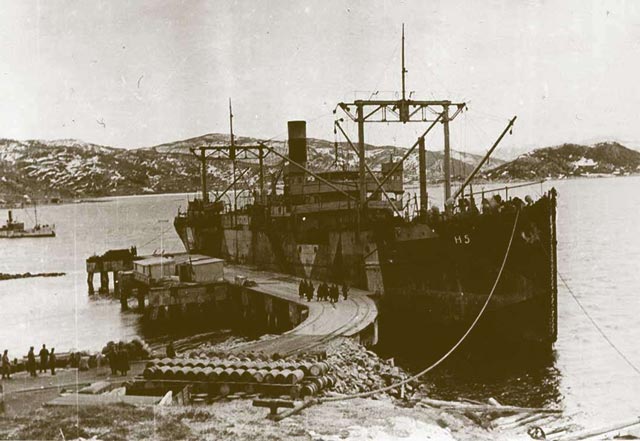 |
| German freighter H-5, sunk on 15 March 1942. |
German FW 200 Condor aircraft bomb and sink 1757-ton British freighter Dago near Cape Carvoeiro during a passage from Lisbon to Oporto. There is no record of casualties. The location of this wreck was finally pinpointed in 2014 by a volunteer team of divers (International Journal of Nautical Archaeology).
British 127-ton utility barge Sparsholt hits a mine and sinks in the Thames Estuary. There are seven deaths.
British 231-ton fishing vessel Danearn runs aground at Scotstoun, North of Peterhead, and is written off. There is no record of casualties.
 |
| "Two Wrens having a banquet of oranges, a rare treat for them." The ladies have just arrived in the Middle East, probably Cairo, on 14 or 15 March 1942 (© IWM (A 8440)). |
With the British occupied in Malta, the Italian Navy mounts Operation Sirio, a supply convoy of two transport ships from Naples to North Africa via Messina. The British also send supply ships of their own in Operation MF-8 to transfer supplies to Malta and return empty freighters to Alexandria.
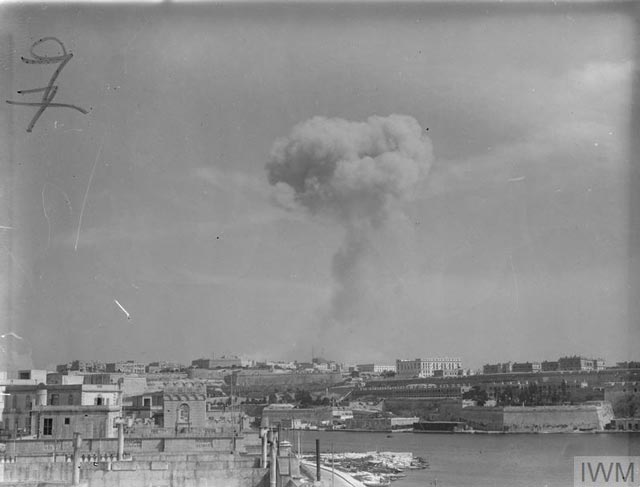 |
| "A large cloud of smoke rising from the center of Valletta as a bomb bursts on St Ursula's Church." Malta, 15 March 1942. © IWM (A 9624). |
US Military: The US Army Air Force activates the XI Interceptor Command (11th and 18th Pursuit Squadrons) at Elmendorf Field, Anchorage.
The USAAF 67th Pursuit Squadron arrives in New Caledonia. This is the first USAAF tactical unit in the theater. It brings with it 45 crated P-40 fighters.
 |
| A three-volume collection of Adolf Hitler's speeches issued by the Central Publishing House of the NSDAP concludes with his address at the Sportspalast on 15 March 1942. |
Therefore, there can be only one solution, which is, to continue this fight until a permanent peace has been guaranteed, i.e., until the destruction of the enemies of such a peace has been accomplished.The 15 March 1942 speech is notable for a somewhat pessimistic tone. Rather than bragging about Wehrmacht successes as in past speeches, Hitler makes a curiously truthful reference to the role played by the Russian winter on the course of the conflict:
Sooner than any experience or scientific knowledge had anticipated, a winter broke upon our army which now gave the adversary four months' time, to bring about on his part the turning point in this fateful struggle. It was the sole hope for the potentates of the Kremlin, in this behavior of the elements of nature which even they had never experienced, to inflict the Napoleonic fate of 1812 on the German Wehrmacht. In the superhuman struggle, under the exertion of the last forces of body and soul, the German and allied soldiers have withstood these trials and thus have conquered the hordes.Of course, the Wehrmacht still faces the "hordes" and they are far from conquered, a fact his audience well knows.
 |
| Uncanny Tales, March 1942. Melvin R. Colby, No. 15 Volume 2, Canadian pulp magazine. |
The Dünamünde Action is notable because it marks the beginning of efforts to make these kinds of mass killings more "efficient." General Jeckeln has become disturbed by the haphazard manner in which his troops have been conducting executions, which he considers wasteful. In the Dünamünde Actions, Jeckeln invents Sardinenpackung (sardine packing). This involves forcing the victims to climb down into the pit and lie down in a pattern that occupies the least amount of space, usually above the corpses of previous victims in a head-to-foot arrangement, before they are shot. This greatly reduces the number of pits that must be dug.
At Auschwitz, the SS men running the camp get drunk and decide to have some fun. They force prisoners to exercise, which directly leads to 278 prisoner deaths and 28 others who perish later in the prison hospitals from the effects of exposure and beatings. The dead today include 198 Poles, 103 Soviet POWs, 68 Jews, 30 Czechs, 8 Germans, and 2 Yugoslavians.
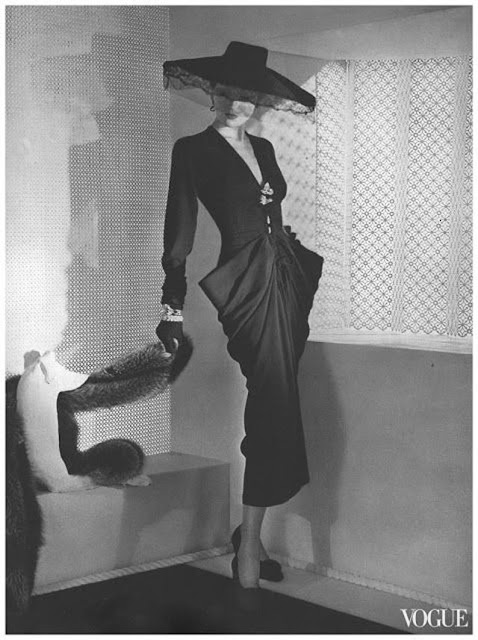 |
| The latest fashion in the 15 March 1942 Vogue, as captured by Horst P. Horst (Horst Bohrmann). |
 |
| A Salvation Army assembly in Newtown, New South Wales, Australia, 15 March 1942 (State Library New South Wales 30906). |
British Homefront: World War I veteran J. R. R. Tolkien, who has attempted to become a World War II cryptographer but failed, is working on a new book. He writes a letter to friend John Kettle on 15 March 1942 in which he discusses "The Hobbit," his book published on 21 September 1937. He goes further, though, and also discusses a new book that he is writing in which:
You will meet the perennial Gandalf again… Bilbo and many other hobbits of Took descent, and also one Sam Gamgee; Tom Bombadil… Trotter the Ranger; Ents (very strange creatures); Elrond, Gollum, and others; and visit the Mines of Moria, the elf-lands of Lothlórien; the Riders of Rohan; the Fortress of Minas Tirith; and come to the final overthrow of the Dark Tower. Or I hope so. And supposing you want to.This will become "The Lord of the Rings," finally published in 1954. It will become one of the best-selling novels ever written, with over 150 million copies sold.
Future History: Mollie Peters is born in Walsham-le-Willows, Suffolk, England. Starting out as a model, she changes her name slightly to Molly Peters and branches out into acting. Film director Terence Young takes an interest in her and casts her as Patricia Fearing, a nurse who takes care of James Bond (Sean Connery") in "Thunderball" (1965). Her final on-screen appearance is in 1968, and Molly Peters passes away on 30 May 2017.
 |
| Maclean's, 15 March 1942. |
March 1942
March 1, 1942: Second Battle of Java Sea
March 2, 1942: Huge Allied Shipping Losses at Java
March 3, 1942: Japan Raids Western Australia
March 4, 1942: Second Raid On Hawaii
March 5, 1942: Japan Takes Batavia
March 6, 1942: Churchill Assaults Free Speech
March 7, 1942: British Defeat in Burma
March 8, 1942: Rangoon Falls to Japan
March 9, 1942: Japanese Conquest of Dutch East Indies
March 10, 1942:US Navy attacks Japanese Landings at Lae
March 11, 1942: Warren Buffett's First Stock Trade
March 12, 1942: Japan Takes Java
March 13, 1942: Soviets Attack In Crimea Again
March 14, 1942: The US Leans Toward Europe
March 15, 1942: Operation Raubtier Begins
March 16, 1942: General MacArthur Gets His Ride
March 17, 1942: MacArthur Arrives in Australia
March 18, 1942: Japan Attacks In Burma
March 19, 1942: Soviets Encircled on the Volkhov
March 20, 1942: "I Shall Return," Says MacArthur
March 21, 1942: Germans Attack Toward Demyansk
March 22, 1942: Second Battle of Sirte
March 23, 1942: Hitler's Insecurity Builds
March 24, 1942: Bataan Bombarded
March 25, 1942: Chinese Under Pressure in Burma
March 26, 1942: Win Or Die, Vows MacArthur
March 27, 1942: The Battle of Suusari
March 28, 1942: The St. Nazaire Commando Raid
March 29, 1942: The Free Republic of Nias
March 30, 1942: Japanese-Americans Off Bainbridge Island
March 31, 1942: Japanese Seize Christmas Island
2020






















