Eastern Front: The Eastern Front on
1 July 1941 already is descending into savagery. According to the diary of Marie Vassiltchikov in Berlin, a returning soldier from the front, Burchard of Prussia, describes the fighting as "absolutely beastly." Burchard reports that neither side is taking many prisoners and fighting is heavy everywhere.
In the Far North, German troops taking part in Operation Platinum Fox (part of Operation Silver Fox) experience their first real failure of the campaign, though it is a minor one. The 2nd Mountain Division fails to break through Soviet defenses on the Rybachy Peninsula and face such determined resistance that they have to go onto the defensive themselves. Army of Norway commander General Dietl decides to switch some units from 2nd Mountain Division down to support the 3rd Mountain Division, which is struggling against strong Soviet defenders to reach the Litsa River.
The Germans and Finns launch Operation Arctic Fox (Unternehmen Polarfuchs) at midnight. Finnish 6th Division opens the offensive, crossing the border in the direction of Salla. The German 6th SS Mountain Division (Nord) soon follows. The defending Soviet forces of Soviet 14th Army (General Valerian A. Frolov) put up a fierce defense and the offensive gets nowhere.
In the Army Group North Sector, the Soviet troops are in full retreat from the Dvina River. They plan to make a stand on the Stalin Line in Estonia. The German panzers, however, have been ordered to consolidate their position and await the infantry before making any further advances. Once the Germans are able to resume their forward movement, the next objective is Leningrad. German troops do make some ground and take Riga, Latvia.
In the Army Group Center sector, Soviet Western Front commander General Eremenko begins forming a defensive line on the Berezina River. He orders the 13th Army to fall back between Borisov, Brodets, and Kholkolnitza, and the 4th Army to cover the river line from Brodets to Svisloch and Bobruisk. The Stavka rushes the 1st Moscow Motor Rifle Division west from Moscow to Borisov to anchor the line. The problem, though, is that - contrary to Hitler's 29 June stop order - General Guderian's 2nd Panzer Group already is in Bobruisk and across the river, and today seizes Berezina. In addition, the 4th Panzer Division has seized a railway bridge at Svisloch.
In the Army Group South Sector, the Soviets are in full retreat again after making a brief stand during the Battle of Brody. General Popel, who only a few days ago excited the entire Red Army with the recapture of Dubno, is forced to break out to the east after a halfhearted attempt to relieve him by a regiment of 22nd Mechanized Corps fails. Panzer Group 1 continues on the offensive, but the Soviet counterattacks have decimated its strength and its remaining panzers have lost much of their initial striking power.
The Axis attack in this sector expands when the German 11th Army, Romanian 3rd Army, and Romanian 4th Army cross the Prut River into the Bessarabia and Bukovina regions of Moldova.
 |
| British Commonwealth Troops enter Palmyra, 1 July 1941. |
Syrian/Lebanon Campaign: British Habforce, marching west from Iraq, has been banging at the gates of the Vichy French base at Palmyra for the past week. The French position at Palmyra has been well-defended, but British forces are multiplying while the Vichy French are running low on supplies. Today, the 10th Indian Division (Major-General Slim) crosses the border from Iraq with the objective of advancing toward the coast and joining the advance on Beirut.
Defending Vichy 2nd Light Desert Company tries to retake Sukhna from the Arab Legion, but the French are soundly defeated and forced to surrender themselves (80 men and 6 armored cars). This imperils the French flank of Palmyra and causes them to begin rethinking their ability to hold the important base there. British troops essentially capture Palmyra, though the official surrender is not made today.
Off the coast, the Vichy French have a small supply convoy approaching heading for Beirut. The RAF attack with Albacore torpedo bombers and sink 2778-ton French freighter St. Didier in the Gulf of Adalia. This causes the accompanying freighter, 2536-ton Chateau Yqem, to head back to France.
 |
| Romanian officers at the bridge over the Pruth River, 1 July 1941 (Federal Archives, B 145 Bild-F016198-38). |
European Air Operations: The RAF scores a success during one of its many raids over Brest against the large German warships there. A force of 52 bombers scores a hit on heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen during the night with an armor-piercing bomb that destroys the control center in the heart of the ship. There are 60 men killed and 40 others wounded. This puts the Prinz Eugen out of action for the rest of 1941.
RAF Fighter Command conducts Circus missions over France and points north. The RAF loses several planes, including two British Stirling bombers making their first operational sortie.
Battle of the Baltic: Soviet freighter Imanta runs aground in the eastern Gulf of Finland and is a total loss.
Soviet minesweeper T-299 Imanta hits a mine and sinks off Saaremaa, Estonia.
Soviet submarine M-81 hits a mine and sinks on the Laine Bank, off Vormsi, Estonia.
Soviet auxiliary minesweeper M-3134 hits a mine and sinks off Libau.
 |
| Kapitänleutnant Klaus Scholtz of U-108. |
Battle of the Atlantic: U-108 (Kptlt. Klaus Scholtz), on its third patrol out of Lorient and operating south of Greenland and about 500 nautical miles (930 km, 580 miles) north of the Azores, torpedoes and sinks 2486-ton weather ship Toronto City. There are no survivors. After this, U-108 responds to orders from the U-boat command, which has received a report on the location of Convoy OG-66 from a Luftwaffe Focke-Wulf Fw-200 Condor of I,/KG.40, and sails to intercept the convoy.
The Focke-Wulf 200 Condor which reports the presence of Convoy OG-66 bombs 3133-ton Royal Navy armed boarding vessel HMS Malvernian. The Malvernian's crew abandons ship and it later sinks after being bombed by Luftwaffe aircraft on 11 July. There are 57 survivors and 107 deaths.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 1262-ton British freighter Homefire northeast of Cromer. There are two deaths.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 1177-ton British freighter Highwood and 4098-ton freighter Jamaica Planter at Barry. The two ships are in drydock, so they can't sink. There is one death on the Highwood.
British 211-ton fishing trawler Strathgairn hits a mine and sinks about 20 miles southwest of Barra Head. There are five deaths and six survivors.
British 86-ton drifter Devon County hits a mine in the Thames Estuary and sinks. There are three deaths.
Royal Norwegian Torpedo Boat HNoMS MTB 5 suffers an engine explosion in port in the UK and is a total loss. There are four deaths.
The Venezuelan government seizes interned 1153-ton German freighter Durazzo and renames it Pampero.
The Soviet Navy orders six submarines to patrol off of northern Norway.
German raiders Atlantis and Orion meet in the South Atlantic north of the island of Tristan da Cunha and refuel from supply ship Anneliese Essberger. Atlantis then departs for the Indian Ocean and thence the Pacific.
Convoy SC-36 departs from Sidney bound for Liverpool.
Royal Navy tug HMS Canute is commissioned and submarine Sportsman and minesweeping trawler Liscomb are laid down.
US submarine USS Blackfish and minesweeper Starling are laid down.
U-131 (Korvettenkapitän Arend Baumann) is commissioned, U-159 is launched, U-185, U-447, U-448, U-468, U-520, U-621 and U-622 are laid down.
 |
| Sir Claude Auchinleck (1884-1981) (Cecil Beaton), new British Middle East Commander on 1 July 1941. |
Battle of the Mediterranean: General Claude Auchinleck arrives from India and takes command of the British Middle East Command. General Archibald Wavell, having fallen from grace following the failure of Operation Battleaxe in June, replaces Auchinleck in India. Winston Churchill makes his displeasure clear to Wavell by appointing Oliver Lyttelton as Minister of State resident in the Middle East, removing some of Wavell's new authority.
Following his successful occupation of Libya and defensive victories over the British Army, German General Erwin Rommel receives a promotion to General of Tank Forces (General der Panzertruppe).
Royal Navy corvette HMS Hyacinth runs aground four miles south of Famagusta. Going to its aid, corvette Erica also suffers damage. The Hyacinth eventually is refloated (on 5 July) and makes it to Alexandria for repairs.
Operation Substance, a Royal Navy convoy of six freighters, makes it to Malta with 65,000 tons of supplies.
Some RAF Bristol Blenheims based at Malta bomb the Spanish Port Mole at Tripoli and others attack Homs, North Africa. At Homs, the bombers cause some damage along the coast road such as knocking out a truck.
The Luftwaffe attacks Alexandria during the night with 16 bombers.
Battle of the Black Sea: Soviet destroyer Bystry hits a mine off Sevastopol. The captain beaches the ship to avoid sinking.
Battle of the Pacific: German raider Komet has been sailing in company with minelayer Adjutant (the renamed Norwegian whaler POL IX captured on 14 January 1941 by German raider Pinguin). Near the Chatham Islands, Adjutant experiences engine trouble and is scuttled.
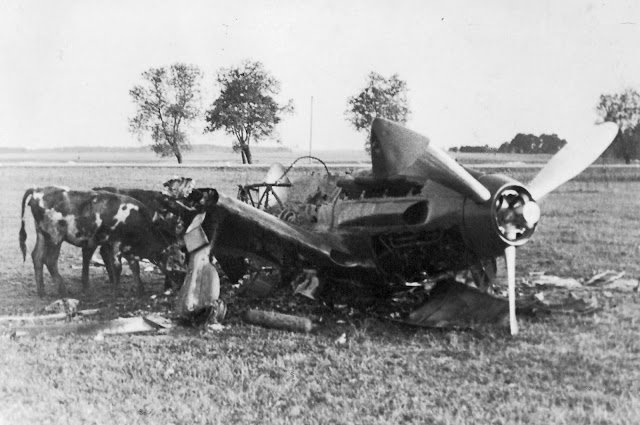 |
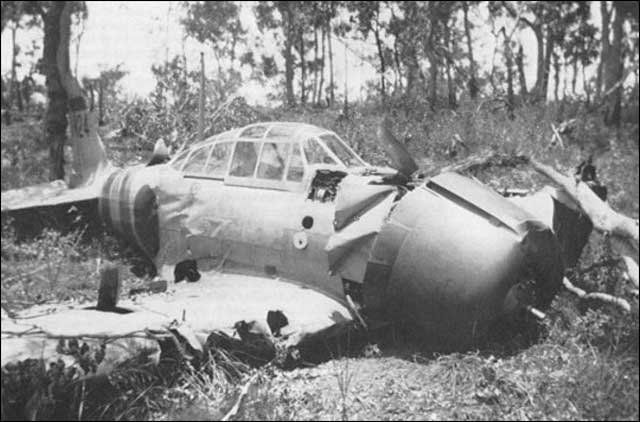
| A Soviet AF Mig 3 destroyed on the ground during Operation Barbarossa, 1941. |
Propaganda: The OKW issues a communique about recent air battles:
In the course of June 30 the Luftwaffe once again inflicted annihilating blows on the Soviet-Russian bomber and fighter formations. On June 30, the enemy lost 280 aircraft in all, 216 of them in aerial combats. German fighter wings led by [air ace] Lt. Col. Molders and by Major Trautloff particularly distinguished themselves during the fighting by shooting down 110 and 65 planes respectively. At Dunaburg [Daugavpils in Latvia] the Trautloff Fighter Wing succeeded in destroying all 40 planes of a Soviet attack group. The Molders Fighter Wing gave equally impressive proof of the superiority of the German Luftwaffe in the region east of Minsk and Bobruisk, where large numbers fo enemy formations sought to disrupt the movements of the advancing German troops. Of the approximately 100 attacking fighters and bombers, the Molders Fighter Wing destroyed 80. In the battle Lt. Col. Molders won his 82nd aerial victory, Captain Joppien his 52nd.
Molders now is not only the leading air ace of World War II but of all time, having topped the victory total of Baron von Richthofen during World War I.
While the Germans are outwardly confident about the Luftwaffe's successes, in reality, the size of the Red Army's air fleet has come as a shock. The Luftwaffe literally has destroyed thousands of Soviet planes, but this does not seem to have cut very far into their supply. It now is becoming clear that the Soviet Red Air Force had a magnitude of planes greater than was thought before the start of Operation Barbarossa. Today, the Soviet Naval Air Unit 401 IAP begins using new MiG-3 fighters and down four Bf 109 fighters - a very rare success by the Red Air Force over the Luftwaffe at this stage of the war.
This continuing numerical challenge, in fact, is a realization setting in with the Germany Army as well, as they have destroyed thousands of tanks, but the Soviet defense is stiffening, not deteriorating. The Germans comfort themselves with the truth that their tactics at this stage of the war are superior to those of the Soviets.
German/Croatian Relations: Germany accepts an offer by Croatia to supply a division of troops under German command for service in the Soviet Union.
Vichy French/Soviet Relations: The Petain government freezes all Soviet assets in France.
 |
| A pre-war USAAF B-24A in flight. Note the prominent neutrality markings on the nose, wings, and fuselage). |
Anglo/US Relations: The fledgling North Atlantic air ferry route takes a major step forward. A Consolidated B-24A bomber of the USAAF Air Corps Ferrying Command flies from Bolling Field at Washington D.C. to Montreal and Newfoundland and then to Prestwick, Scotland.
Anglo/Canadian Relations: Canadian leader Mackenzie King, in London, presents British Prime Minister Winston Churchill with the Canadian "Torch of Victory."
US/Icelandic Relations: The US and Iceland reach an agreement whereby US troops will replace British troops which are "occupying" Iceland - with the Icelandic government's tacit support.
 |
| Chiang Kai-shek, Madame Chiang, and Claire Lee Chennault. |
US/Chinese Relations: The American Volunteer Group (AVG), more familiarly known as the Flying Tigers, is officially formed under Claire Chennault. In actual fact, pilots flying with the AVG are employed with a shell corporation, the Central Aircraft Manufacturing Company (CAMCO). Their mission is to defend Burma, China, and Burma Road.
Chinese/German/Italian Relations: Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang government in Chungking breaks relations with Germany and Italy. The reason is their recognition of those countries of the Japanese puppet government of General Wang Chingwei in Nanking. Kai-shek recalls his ambassador in Berlin and charge d'Affaires in Rome.
The Axis powers are still trying to cajole the Japanese into striking north into the Soviet Union, but the Japanese high command has decided its future lies to the south. However, many Germans in the theater of operations feel that the Axis should ally with the Nationalist government because they are both fighting against communism.
Soviet/Chinese Relations: The Soviets, no doubt hearing of China's sudden issues with the Axis, propose an alliance.
German Military: Field Marshal List, with little to do in the Balkans, is made Southeast Commander.
Soviet Military: General of the Army Dmitry Pavlov, recently relieved of command of Western Front, is arrested. The charges run the gamut from cowardice to willful abandonment of positions - basically, everything that he can be charged with under Articles 58-1b, 58-11 RSFSR Criminal Code. Pavlov's entire staff is charged, too. The penalty is death, and while no trial has been held, everyone knows the outcome.
Vnukovo Airport opens southwest of Moscow.
British Military: The British Special Air Service forms under Colonel David Stirling.
 |
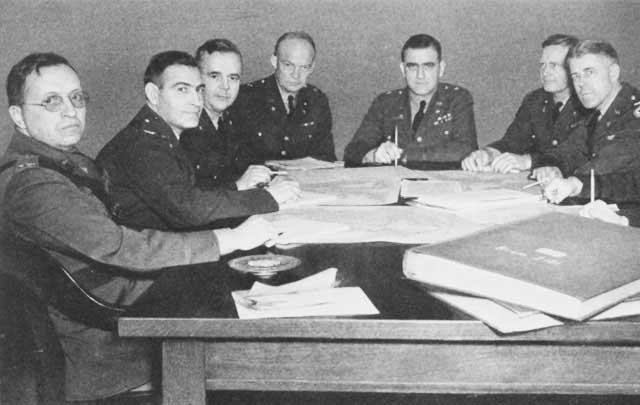
| Colonel Dwight Eisenhower, right, in 1941 during the Louisiana Maneuvers. (Robertson Collection). |
US Military: The US Navy establishes Naval Coast Frontiers in the North Atlantic, Southern, Caribbean, Panama, Pacific Southern, Pacific Northern, Hawaiian, and Philippine. The US Army Air Force establishes Patrol Wing 7 at Argentia, Newfoundland. The US Coast Guard sets up the Northeast Greenland Patrol, which begins patrols for U-boats.
US Navy escort carrier USS Long Island executes the first landing, takeoff, and catapult launching from an escort aircraft carrier.
All men aged 21 (those born on or before July 1, 1920) and over must register for the draft.
Colonel Dwight D. Eisenhower becomes chief of staff to General Walter Krueger, Commander of the Third Army, at Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas. His first major duty will be to oversee the Louisiana Maneuvers, a series of U.S. Army exercises held around Northern and Western-Central Louisiana, including Fort Polk, Camp Claiborne, and Camp Livingston. These maneuvers also will feature the talents of Omar Bradley, Mark Clark, Lesley J. McNair, Joseph Stilwell and George Patton, Jr.
Holocaust: The massacre of 25 Polish professors in the city of Lwów (modern-day Lviv, Ukraine) begins. The professors apparently are those who actively cooperated with the Soviet authorities during the Soviet occupation of late 1939-June 1941. However, there is no indication that the professors acted in a political fashion during the occupation.
 |
| Pervitin, manufactured at the Temmler factory. It became quite popular in the Reich among all classes of people as a pick-me-up. |
German Homefront: The German government classifies Pervitin (aka Methamphetamine) as a restricted substance under the Opium Law. The OKW, though, is so impressed by the substance's properties that it already has ordered 10 million capsules for distribution to the Wehrmacht. The Pervitin pills have been shown to keep troops alert and energized under trying circumstances. The pills are to be distributed first to Luftwaffe pilots who need to stay alert during long missions, but ultimately will spread throughout the Army, too. Unlike some phony "Vitamin pills" being given to the troops (so that
Reichsmarschall Hermann Goering can get kickbacks), these pills pack a punch.
British Homefront: The government announces that coal deliveries will be restricted to once per month. In practice, this only affects businesses.
American Homefront: The National Broadcasting Company (NBC), which has been broadcasting off-and-on since 1939, broadcasts a Brooklyn Dodgers vs. Philadelphia Phillies baseball game, followed by 1935 drama "Death from a Distance" starring Lola Lane and Russell Hopton, over NBC station WNBT in New York City. This is considered the start of full commercial television service in the United States. The broadcast includes the first paid television advertisement over the new medium, a spot for the Bulova watch company (which costs the company $9). There are still very few television sets in New York, so very few people see the broadcast.
Joe DiMaggio of the New York Yankees extends his club-record hitting streak. He gets hits in both ends of a doubleheader against the Boston Red Sox at Yankee Stadium. The second game is shortened by rain, and DiMaggio needs the benefit of a questionable call by official scorer Dan Daniel (Red Sox third baseman makes a bad throw to first on a grounder) to extend his hitting streak to 44 games. This ties the major league consecutive game hitting streak set by right fielder Willie Keeler of the Baltimore Orioles in 1897.
Future History: Rodrigue Gabriel Gilbert is born in Montreal, Canada. He plays in the National Hockey League from 1960-1978 and is inducted into the Hockey Hall of Fame in 1982. Gilbert plays for the New York Rangers throughout his career and eventually has his number 7 retired by the team. During the time of this writing, Rod Gilbert remains active with his Garden of Dreams Foundation.
 |
| Washington National Airport (later Reagan National), 1 July 1941 (Library of Congress LC-USF33-021029-M1). |
June 1941 June 1, 1941: Farhud PogromJune 2, 1941: Massacres on CreteJune 3, 1941: Kandanos MassacreJune 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes AwayJune 5, 1941: Death in ChungkingJune 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar OrderJune 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at PessacJune 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and LebanonJune 9, 1941: Litani River BattleJune 10, 1941: British Take AssabJune 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond RussiaJune 12, 1941: St. James AgreementJune 13, 1941: Lützow DamagedJune 14, 1941: Latvian June DeportationsJune 15, 1941: Operation BattleaxeJune 16, 1941: The Old LionJune 17, 1941: British Spanked in North AfricaJune 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its BackJune 19, 1941: Cheerios IntroducedJune 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air ForceJune 21, 1941: Damascus FallsJune 22, 1941: Germany Invades RussiaJune 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes HavocJune 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius FallJune 25, 1941: Finland Declares WarJune 26, 1941: Bombing of KassaJune 27, 1941: Encirclement At MinskJune 28, 1941: Minsk FallsJune 29, 1941: Brest Fortress FallsJune 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top AceJuly 1941July 1, 1941: US TV Broadcasting StartsJuly 2, 1941: MAUD ReportJuly 3, 1941: Stalin SpeaksJuly 4, 1941: Pogroms in Eastern EuropeJuly 5, 1941: Germans on ScheduleJuly 6, 1941: Australians Attack DamourJuly 7, 1941: US Marines in IcelandJuly 8, 1941: Flying Fortresses In ActionJuly 9, 1941: British Take DamourJuly 10, 1941: Sword and Scabbard OrderJuly 11, 1941: Cease-fire in Syria and LebanonJuly 12, 1941: Anglo/Russian Assistance PactJuly 13, 1941: Uprising in MontenegroJuly 14, 1941: Katyusha Rocket Launchers in ActionJuly 15, 1941: Smolensk FallsJuly 16, 1941: Stalin's Son CapturedJuly 17, 1941: Heydrich Orders Mass ExecutionsJuly 18, 1941: Twin Pimples RaidJuly 19, 1941: V for VictoryJuly 20, 1941: The Man Who Wouldn't ShootJuly 21, 1941: Moscow in FlamesJuly 22, 1941: Soviet Generals ExecutedJuly 23, 1941: Secret Plan JB 355July 24, 1941: Operation SunriseJuly 25, 1941: US Naval AlertJuly 26, 1941: Italian E-Boat Attack on MaltaJuly 27, 1941: MacArthur ReturnsJuly 28, 1941: Auschwitz ExterminationsJuly 29, 1941: Rescue From CreteJuly 30, 1941: Raid on Petsamo and KirkenesJuly 31, 1941: Final Solution Order2020