May 10, 1941, is one of the most bizarre days during World War II. The idea of a leading member of one nation willingly placing himself, without conditions, under the power of his country's opponent is virtually unprecedented in world history. What makes the day even curiouser is that the motivations and purpose behind this strange decision also are murky and subject to interpretation.
Anglo/Iraq War: The Germans begin setting in motion Operation Iraq, their planned intervention in Iraq. The objective is to fly troop transports to Mosul in Junkers Ju 52s. Today, the first planes set out, escorted by Bf 110s of the 4th group of the 76th Zerstorergeschwader 76 (Destroyer Wing) under Lt. Col. Holbein, from Greece to Rhodes. The elongated route goes mainland Greece-Rhodes-Aleppo-Damascus-Mosul, and each stage will require a day's flight. The entire project under Luftwaffe General Felmy is a rushed job, and the pilots do not have maps and the planes have not been modified for desert conditions.
At Fort Rutbah in Iraq, the advance elements of Arab Legion which have been shadowing the fortress while the RAF bombs it receive some ground reinforcements. The No. 2 Armoured Car Company RAF has arrived, and Squadron Leader Michael Casano, in command, attacks the defending Iraqis. The action is inconclusive, but the 40 Iraqi armoured cars which had arrived recently withdraw as RAF Blenheim bombers continue bombing the fort. After dark, the entire Iraqi Fort Rutbah garrison withdraws.
 |
| Damage in London from the 10 May 1941 raid. |
European Air Operations: The RAF announces that a Dutch bomber squadron operated using RAF planes for the first time during the night of 9/10 May. They attacked a Luftwaffe base at Kristiansund in southern Norway.
Tonight marks the culmination of the London Blitz. A massive force of 570 Luftwaffe planes pounds the docklands area of London and the City of London. The Luftwaffe likes to time its London raids to natural phenomena such as moonless nights for maximum effect, and this raid occurs during an ebb tide which hampers firefighting efforts. The bombers drop 700 metric tons of high explosives and 2393 incendiary bombs. Despite upgraded fire prevention measures instituted following the great incendiary raids of late 1940, the bombs cause over 2000 fires of varying sizes.
Among the downtown areas hit is the House of Commons, the roof of Westminster Hall and the top of Victoria Tower. In the City of London, the Tower of London and the Mint are set afire. In the port, the bombs sink small (4 ton) Safari and Miss England, (5 ton) Royal Navy auxiliary vessels Altais, Comet I, and Faislane, and (6-ton) Igloo, Jake II and Nomad III. Damaged during the raid are 4241-ton British freighter Tower Field and 1438 ton sludge vessel Henry Ward.
Overall, there are 3000+ casualties from the raid (around 1500 deaths), and some consider this the worst Luftwaffe raid against England during the entire war. It also, fortunately for the British, is the last mass raid against London of the war, though smaller raids continue for the next several years.
While the raid is an undoubted success in the sense that it causes a lot of damage, there also is a very bad omen for the Luftwaffe. It loses 21-27 planes (accounts vary) during the night, a massive and unsustainable number that reflects vastly improved British night fighter and anti-aircraft fire. This equals the number of planes the Luftwaffe lost during the great day raids of the fall of 1940 which caused its turn toward night raids. Raids in London are becoming too costly in general when easier pickings will soon be available in the East.
RAF Bomber Command attacks coastal targets (18 aircraft) during the day and Hamburg (119 aircraft) and Berlin (23 aircraft) during the night.
 |
| Damage to the Houses of Parliament following the raid of 10 May 1941. |
East African Campaign: Having completed their capture of the Falagi Pass, Indian troops advance toward 11,400 foot Mount Gumsa. This is garrisoned by Italian troops and supposedly guards the key point of Amba Alagi from the east. However, the Italians immediately withdraw from the mountain after sunset and join the main force in Amba Alagi.
The 1st South African Brigade arrives at Amba Alagi after a long march. The Italian stronghold now is encircled, and the British plan a set-piece attack.
In the Gold Coast, the 24th Infantry Brigade captures Italian positions at Wadara in Galla-Sidamo.
Battle of the Atlantic: Operation Primrose, the capture of U-110, ends today with the sinking of the U-boat while under tow during a storm. It is unclear if this is intentional, but subsequent histories often will claim that it was in order to hide the fact that the submarine was captured and the extremely important Enigma Code Machine and codebooks retrieved.
It is a very good day for U-556 (Kptlt. Herbert Wohlfarth), on its first patrol out of Kiel and part of Wolf Pack West. It is stalking Convoy OB-318 before dawn when it attacks 4986-ton British freighter Aelybryn. The Aelybryn is disabled but ultimately makes it to port under tow with only one death.
A few hours later, U-556 torpedoes and sinks 4861-ton freighter Empire Caribou. There are 11 survivors and 34 deaths.
In the evening, U-556 then torpedoes and sinks 5086-ton Belgian freighter Gand. There are 43 survivors, with one man killed and another wounded.
Royal Navy boarding vessel HMS Hilary captures 5719-ton Italian tanker Gianna M. north of the Azores. The Hilary escorts the captured ship to join convoy HG 61, which is bound for Belfast. The Gianna M. will be renamed Empire Control and used by the British.
Convoy HX 126 departs from Halifax, Convoy SL 74 departs from Freetown bound for Liverpool.
Minesweeper HMAS Bendigo (Lt. Commander James A. R. Patrick) is commissioned.
U-86 and U-374 are launched.
 |
| Damage on Carlisle Street W1 following the 10 May 1941 Luftwaffe raid. The damage here included the complete destruction of Carlisle House, the headquarters of the British Board of Film Censors. |
Battle of the Mediterranean: Winston Churchill remains upset about the "bottleneck" at Takoradi airfield, the key transit hub on the 3700-mile route across Africa to supply Cairo with planes. He tells Air Chief Marshal Sir Charles Porter that "A regular flying-boat service should be established to bring back pilots which are accumulating in Egypt." He emphasizes that "Speed is essential, as from every side one gets information of the efforts the enemy is making." One of those "sides," of course, is Churchill's top-secret Ultra decryption service.
Churchill is upset about the entire Middle East Command. His dissatisfaction with Middle East Commander General Archibald Wavell is well known, and he is prone to venting his feelings both to Wavell directly and to the War Cabinet. Anthony Eden recalls in his subsequently published diary "The Reckoning" that today Churchill "was in favor [at the War Cabinet meeting] of changing [Indian Commander] Auchinleck and Wavell about." However, Eden notes there is a rare moment of disagreement about this within Churchill's cabinet of "yes men" (Australian Prime Minister Robert Menzies' scathing term for them). Eden writes that "I have no doubt that Archie [Wavell] has a better mind, but one does not know how he is bearing the strain." For the moment, the War Cabinet dissuades Churchill from making a change, which would seriously disrupt British strategy in the region at a critical juncture.
Churchill's prime grievance against Wavell is that he is not using his forces efficiently and basically has accumulated an army of slackers who lack aggressive spirit. In Wavell's defense, he has shown great tactical and strategic judgment, such as being skeptical of Churchill's obsession with trying to defend Greece against the advice of Menzies and others. The garrisoning of Greece, and then the evacuation in Operation Demon, was accomplished with great skill and few unnecessary losses. Considering that Great Britain's lifeline to India and control of East Africa and the eastern Mediterranean hinges upon control of Egypt, being conservative with the stretched British forces there could also be deemed quite prudent.
Operation Tiger continues to steam east through the Mediterranean. The Luftwaffe or Regia Aeronautica bomb and damage destroyer HMS Fortune. A large force of Royal Navy destroyers from the force bombard Benghazi at sunset. Royal Navy gunboat Ladybird bombards Gazala during the night.
The Luftwaffe sinks a motor launch, ML 1011, which is crossing from Suda Bay to Sphakia Bay.
At Benghazi, Royal Navy submarine Triumph torpedoes and sinks Italian banana boat Ramb III. The Italians will raise the Ramb III and return her to Trieste for repairs.
Following discussions with Benito Mussolini, General Friedrich Paulus departs from Rome to Berlin. He will not return to the southern theater of operations, which his wife believes is not the place for him to make his reputation. Upon his arrival in Berlin, he reiterates his previous assessments that General Rommel is reckless and must be watched closely.
At Malta, Governor Dobbie praises the people of Malta for their support of the war effort and suggests that the government in London should issue a statement of thanks. He also requests 4000 rifles for the defense of the island; the rifle shortage has become an issue throughout the Middle East Command. The RAF loses a Beaufighter (two deaths) which was sent up to intercept a flight of Ju-52 transports flying from Sicily to North Africa.
 |
| Damage to the Westminster Abbey high altar (the roof has collapsed) following the attack of 10 May 1941. |
POWs: British Lieutenant Anthony "Peter" Allan, held at the Oflag IV-C "officer's" prisoner of war camp at Colditz Castle, escapes. He hides in a straw mattress being removed from the camp by French laborers who know he is in it but do not give him away. Allan was sent to Sonderlager (high-security prison camp) Colditz because he already had escaped from another POW camp but then had been recaptured. Allan originally was captured at St. Valery in June 1940 by General Rommel's 7th Panzer Division. Allan intends to head to Poland but instead is given a lift to Vienna by a friendly (and clueless) SS officer. He ultimately will be recaptured and returned to Colditz to spend the next three months in solitary confinement.
Anglo/German Relations: Around 2:30 p.m., German Deputy Fuhrer Rudolf Hess, second in succession to Adolf Hitler, leaves a personal letter for Adolf Hitler and says goodbye to his wife Ilse. He then has his driver take him and his adjutant from his villa in the Munich suburb of Harlaching to the Messerschmitt aircraft factory at Augsburg. After making flight preparations for his personal Bf 110, Hess at 5:45 p.m. takes off and takes a northwesterly course to Bonn, where he then tracks the Rhine River all the way to the coast. Crossing the West Frisian islands, he veers north, then to the northwest again.
Hermann Goering, head of the Luftwaffe, is alerted to the flight and orders Adolf Galland, head of JG 26, to intercept him. However, Galland's fighters are based too far to the south and are unable to find Hess. Berlin Radio broadcasts a cryptic alert at 8 p.m. that "Party member Hess had left on Saturday for a light form which he had not yet returned." That the Luftwaffe knows about Hess' flight on the 10th makes Adolf Hitler's surprised reaction to the flight on the morning of the 11th suspect.
Once he reaches the right latitude, Hess turns the craft due west past the final piece of land and heads toward the Northumbrian coast. Hess, concerned about being intercepted, descends to wavetop level and proceeds with skill. At RAF Fighter Command, the commanding officer responds to word that an unidentified fighter has been spotted and fighters vectored toward it by shouting, "For God's sake, tell them not to shoot him down!" Hess has taken care of that by descending, however, thereby evading the three RAF Spitfires far above.
The RAF pilots never see him, so Hess continues flying west, remaining at the treetop level and heads toward his destination: Dungavel. However, he overflies his destination in the blacked-out north, reaches the Firth of Clyde, and then turns back in confusion. At around 10:25 p.m., his fuel tanks empty, Rudolf Hess bails out and operates his parachute, watching his Messerschmitt glide on and then crash and burst into flames not far away.
Proving himself a fairly adept navigator as well as pilot, Hess lands in Eaglesham, only a dozen miles from his destination, in a Scottish field. Hess is, as he recalls later, elated and triumphant that he has made, despite his regret at not meeting the Military Intelligence officers and Service Agents waiting for him at his destination nearby.
Scottish Lanarkshire farmer David McLean, meanwhile, has seen many warplanes overflying his farm during the war, so the notion of a pilot bailing out nearby is hardly unexpected. Hearing the plane and then observing the descending parachute, McLean grabs a pitchfork and approaches the figure laying nearby on the ground. Unable to make out even whose side the man is on, McLean asks, "Are ye a Nazi enemy, or are ye one o' ours?" Hess replies, "Not Nazi enemy; British friend."
McLean takes Hess into his farmhouse, which Hess accomplishes with difficulty because he has wrenched his ankle during his landing in the dark. In the kitchen, McLean's mother makes tea (which Hess refuses), and Hess tells McLean that he is Alfred Horn and that he was flying to meet with the Duke of Hamilton, the owner of the great Dungavel estate. Soon some local Home Guardsmen (Jack Paterson and Robert Gibson), and Hess tells them that he is Alfred Horn, just come from Germany and trying to land at the Duke's private airfield. "Please tell the Duke of Hamilton that I have arrived."
The two Guardsmen take Hess to their local headquarters. Soon, a crowd gathers. A dozen Home Guardsmen soon arrive to stand watch, and when the Military Intelligence and Secret Service agents arrive to pick Hess up, they are skeptical. Only when a regular army unit arrives as a backup for the Military Intelligence and Secret Service men do the locals release "Alfred Horn" to their custody. They drive Hess to the Maryhill Barracks near Glasgow.
The timing of the flight, supposedly chosen by Hess' astrologer, serendipitously (apparently) occurs during the Luftwaffe's biggest raid of the war against London. This could be counted upon to draw RAF air defenses to the south while Hess sneaks in from the north. Naturally, there are many unanswered questions about this incident, not least how the British knew to expect Hess. The flight comes to be known as a "peace mission," though why such would be attempted in this fashion is unfathomable. However improbable, this begins one of the strangest tales of World War II, one that will have reverberate not just in the days and weeks and years, but even decades, to come.
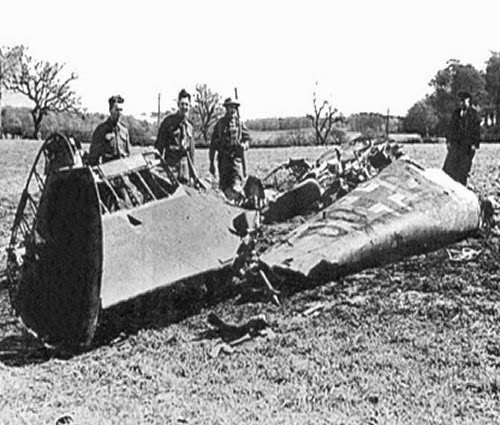 |
| Pieces of the Rudolf Hess plane gathered together in Scotland following his 10 May 1941 flight. |
Anglo/Irish Relations: Churchill sends Alfred Duff Cooper a memo stating that "Eire has repudiated the status of a Dominion... It may well be that force will have to be used." His concern is Royal Navy access to Irish ports, a burgeoning issue due to the recent Luftwaffe success in bombing the northern British ports such as Liverpool and Hull.
Anglo/US Relations: Churchill cables President Roosevelt to thank him for allowing RAF pilots to train in the United States. "We have made active preparations and the first 550 of our young men are now ready to leave." General Henry "Hap" Arnold, the head of the US Army Air Corps, originally made the offer, which Churchill calls "unexpected and very welcome." Naturally, training a warring country's soldiers is hardly commensurate with true neutrality, but such distinctions long ago were discarded by the United States.
Bulgarian/Japanese Relations: Bulgaria becomes one of the few countries to establish diplomatic relations with the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo.
 |
| Damage in London from the 10 May 1941 Luftwaffe raid. |
British Military: The 200th Beaufighter is completed just as its predecessors complete their biggest victory of the war to date over London.
German Military: An experimental rocket - not jet - engine with the designation RII-203 is tested on a ground stand. Calculations show that it would reach a speed of 623 mph. The engine uses hydrogen peroxide, which the Germans call T-Stoff, oxidized by a potassium permanganate solution they call Z-Stoff. These mix in a combustion chamber and fuel a steam generator. The engine etches a distinctive purple exhaust flame behind it. Now that the engine has been shown to work, the Luftwaffe designers work on creating an airframe around it. This project ultimately, after many delays and setbacks, will result in the Me 163, but that is far in the future.
Italian Military: The Italian Navy at La Spezia takes delivery of midget submarines CB-3, CB-4, CB-5, and CB-6 from Caproni.
Japanese Military: Vice Admiral Toshio Shimazaki become chief of staff at the port of Makio on the Pescadores Islands, Taiwan.
British Government: Churchill urges Chancellor of the Exchequer Sir Kingsley Wood to remove restrictions on pensions that give widows full pension rights only to those soldiers killed while on duty, whereas those whose husbands are killed while on leave - even by enemy action - get nothing. Removing this distinction, he writes, "would remove what seems to me to be a well-founded grievance."
Philippines: Ernest Hemingway, visiting Manila on his way back to the US from his China trip, gives the officers an informal briefing about events in Asia. He displays (in hindsight) an extremely accurate perception of coming events in the region, including his conclusion that Japan was on the verge of war with the US and that the Nationalist Chinese and Chinese Communists were on the verge of fighting each other as much as they were allegedly fighting the Japanese together. The US officers on the base are all recently arrived from the States, so have little idea of the realities of the theater. Robbie Robertson, recently the head of the 3d Pursuit Squadron and waiting for a return to the US aboard the USAT Washington, makes an appointment for Hemingway to brief the Philippines Department's intelligence service and air officer on the 12th.
Palestine: Winston Churchill sends Viscount Cranborne a note saying that "I have always been most strongly in favor of making sure that the Jews have proper means of self-defense for their Colonies in Palestine." He instructs Cranborne to help them.
China: The Japanese North China Front Army remains on the offensive, while the Imperial Air Force raids Chungking again.
 |
| The Salvation Army building collapses in Queen Victoria Street, City of London, as a result of the Luftwaffe raid of 10 May 1941. |
Belgian Homefront: "The Strike of 100,000" takes place in Belgium. Led by Julien Lahaut, head of the Belgian Communist Party, the workers seek a wage increase. The strike originates at the Cockerill Steel Works in Seraing, eastern Belgium. This is the first anniversary of Fall Gelb (Case Yellow), the German invasion of Belgium and the Netherlands. While popularly known as a strike by 100,000, it is estimated that 70,000 workers participate. It is a brief strike that obviously has some nationalistic implications, and the Germans agree to 8% wage gains. The Germans display very strained tolerance for communists during this period due to the alliance with the Soviet Union.
American Homefront: Australian Prime Minister Robert Menzies, recently arrived in Washington from England via Canada, discusses the situation in the United States at length with Walter Lippman, the respected columnist at the NY Times. Menzies concludes that:
General American sentiment is on our side, but the moral arguments of cowardice and short-range self-interest are being directed by [Herbert] Hoover, [Senator Burton] Wheeler, [Charles] Lindbergh & Co. to the mothers and possible draftees.
Menzies worries that the American public is not being properly told that the war is about their future as much as that of the actual combatants. He calls President Roosevelt's failure to properly shape public opinion in this regard "disturbing."
Menzies meets with Roosevelt for an hour and calls him "older and more tired" than he recalls, but their conversation "most vigorous." Menzies also says that Roosevelt is "jealous" of Churchill's "place in the center of the picture" and that Roosevelt is "
not [emphasis in original] an organizer - very like Winston - and co-ordination of effort is not conspicuous." Reflecting on his meeting with Secretary of State Cordell Hull, Menzies concludes that Hull and the rest of the Cabinet is "for
war" [emphasis in original], but Roosevelt "trained under Woodrow Wilson in the last war," is awaiting a provocation. Menzies calls FDR's campaign promises to keep the US out of the war "foolish."
In San Francisco, soldiers hold a musical benefit show to raise funds for recreational purposes. This is a symptom of very low funding of the military during this period.
At the Preakness, Whirlaway is the winner.
 |
| Carefree times on Goat Island, Australia, 10 May 1941 (Adelie Hurley). |
May 1941 May 1, 1941: British Hold TobrukMay 2, 1941: Anglo-Iraq WarMay 3, 1941: Liverpool HammeredMay 4, 1941: Hitler Victory SpeechMay 5, 1941: Patriots DayMay 6, 1941: Stalin In CommandMay 7, 1941: May BlitzMay 8, 1941: Pinguin SunkMay 9, 1941: U-110 CapturedMay 10, 1941: Hess Flies Into HistoryMay 11, 1941: The Hess Peace PlanMay 12, 1941: Tiger Arrives SafelyMay 13, 1941: Keitel's Illegal OrderMay 14, 1941: Holocaust in ParisMay 15, 1941: Operation BrevityMay 16, 1941: Blitz EndsMay 17, 1941: Habbaniya RelievedMay 18, 1941: Croatia PartitionedMay 19, 1941: Bismarck at SeaMay 20, 1941: Invasion of CreteMay 21, 1941: Robin Moore SinkingMay 22, 1941: Royal Navy Destruction Off CreteMay 23, 1941: Crete Must Be WonMay 24, 1941: Bismarck Sinks HoodMay 25, 1941: Lütjens' Brilliant ManeuverMay 26, 1941: Bismarck StoppedMay 27, 1941: Bismarck SunkMay 28, 1941: Crete LostMay 29, 1941: Royal Navy Mauled Off CreteMay 30, 1941: Sorge Warns, Stalin IgnoresMay 31, 1941: British Take Baghdad2020