Monday 2 June 1941
 |
| Victims and fellow townspeople of Kondomari, Crete are herded to the site of hostage executions, 2 June 1941 (Franz Peter Weixler, Federal Archive). |
Anglo-Iraq War: Jamil al-Midfai is named Prime Minister of Iraq on 2 June 1941. In Baghdad, the "Farhud" attacks continue against the Jewish Quarter. While the instigation and causes of the Farhud are subject to debate, but what is known for certain is that it ends today during the afternoon. It is unknown exactly how many deaths result from the Farhud, but estimates range from 100-1000, wich larger numbers of wounded.
Regent Abdul Illah (Abdullah) ends the Farhud riots, according to the Iraqi Commission Report, when he orders forces loyal to him into Baghdad. They use machine guns to kill many rioters. Another version of events is that the British are the ones that restore order. The two versions may be reconciled by assuming that the Regents ask the British to restore order, but that is unclear. In any event, hundreds of people on both sides of the Farhud - rioters and Jewish victims - perish. This incident begins the gradual elimination of the centuries-old Jewish presence in Baghdad.
In Syria, Vichy French forces claim to shoot down a British Blenheim reconnaissance plane over Syria-Lebanon.
European Air Operations: RAF Bomber Command attacks the Ruhr River Valley of Germany with 44 bombers.
RAF Bomber Command sends 9 Blenheims of 2 Group, 105 Squadron to raid the Kiel Canal. This includes the naval barracks at Friedrichskoog and various villages along the canal. The RAF planes sink two small ships that block the canal for ten days.
RAF Bomber Command also sends bombers of 107 Squadron to raid the region between the Ems and the Elbe.
RAF Bomber Command also targets the liner Europe, tied up at Bremerhaven.
RAF Bomber Command sends 150 aircraft to attack Dusseldorf and 25 aircraft to attack Duisburg overnight.
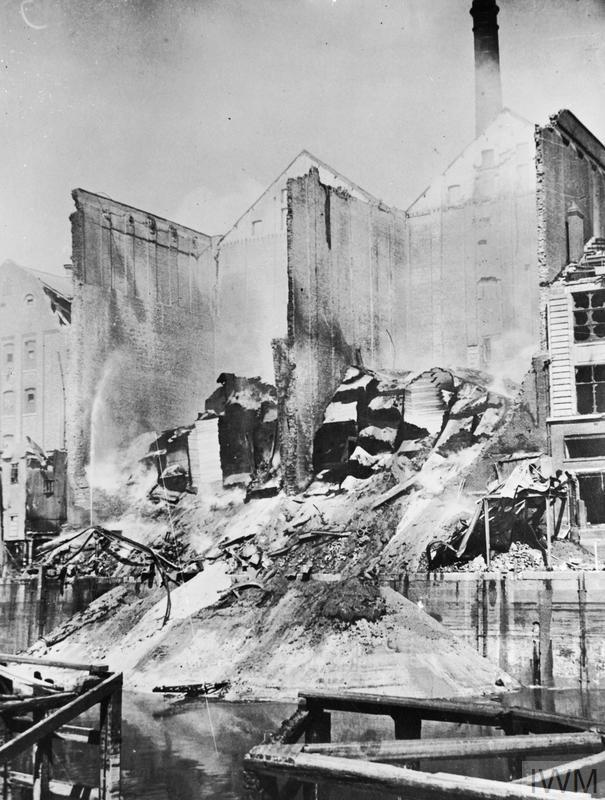
The Luftwaffe attacks Manchester during the night of 1-2 June, killing 70 and injuring 86. This is the Manchester Blitz.
The Luftwaffe bombs Park Grove, Hull. This is Hull's fiftieth raid of the war. There are 27 killed and 11 wounded, and the tragedy is that the "all clear" mistakenly had sounded and the victims had just exited their shelters.
The RAF shoots down a Junkers Ju 88A northeast of Tynemouth at 22:29. There are two deaths, and two crewmen become POWs.
East African Campaign: East African 22nd Infantry Brigade begins crossing the Omo at Sciola in Galla-Sidamo.
Battle of the Atlantic: U-147 (Oblt. Eberhard Wetjen), operating in the Northwest Approaches on its third patrol, attacks Convoy OB-329. It torpedoes and damages 4996-ton Belgian freighter Mokambo. The Mokambo makes it to the Clyde in tow. However, Royal Navy destroyer HMS Wanderer and corvette Periwinkle attacks and sinks U-147 with a depth charge attack. There are 24-26 deaths - the entire crew - on U-147.
U-108 (Kptlt. Erich Hilsenitz), on its third patrol out of Lorient, spots Convoy OB-327 in the mid-Atlantic. It torpedoes and sinks 7628-ton freighter Michael E, which happens to be the first catapult aircraft merchant (CAM) ship. There are four deaths on the Michael E. The ship has no time to launch its fighter plane, but the pilot manages to survive the sinking along with 61 others. It is an inauspicious debut of the CAM ship force.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages Royal Navy submarine HMS P.32 off Finisterre. P.32 is able to continue on to Gibraltar, though its batteries are damaged and it is unable to submerge.
Royal Navy escort ship Hartland (formerly a US Coast Guard cutter) collides with 646-ton British freighter Welsh Coast. The Hartland makes it to Falmouth for repairs and a scheduled refit.
Dutch submarine O.14 is involved in a collision. The submarine makes it to Grangemouth for repairs that take a month.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 2477-ton British freighter Beaumanoir in Robin Hood's Bay. The ship is taken under tow, but the Luftwaffe returns and sinks the Beaumanoir.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 4749-ton British freighter Prince Rupert City north of Loch Eriboll, Scotland. There are four deaths.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 197-ton Belgian trawler John 90 miles southeast of Inglos Hofdi. Everyone survives.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 2183 ton British freighter Thorpebay about six miles from Coquet Lighthouse, Northumberland. The Thorpebay makes it back to the Tyne for repairs.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 195-ton British trawler Ben Screel east of Dunstanburgh Castle, Northumberland. Ben Screel makes it back to the Tyne for repairs.
Finnish 5417 ton freighter Kasteholm hits a mine and sinks northeast of the Faroe Islands. There is one death, the rest of the crew makes it to Tórshavn, Faroe Islands.
Canadian minesweeper (former Norwegian whale factory ship) HMCS Suderøy V is commissioned, minesweeper Caraquet is launched, minesweepers Grandmère and Vegreville are laid down.
US escort aircraft carrier USS Long Island (AVG-1) is commissioned (Commander Donald B. Duncan) at Newport News, Virginia. The Long Island is a conversion from cargo ship SS Mormacmail.
Royal Navy minelayer Plover lays minefield BS.57 in the English Channel.
Convoy OB 330 departs from Liverpool.
Battle of the Mediterranean: The Wehrmacht High Command issues a communique:
The British War Cabinet discusses the future of Cyprus, which it believes may be next on Hitler's agenda in the Mediterranean. The Greek government would like to set up its capital in Cyprus, and there is some support within the British government for ceding the island to Greece for that purpose. The Cabinet concludes that the entire matter should be left to postwar peace settlement discussions.
Navy 353-ton whaler HMT Kos XXII attempts to make a run from Crete to Alexandria but sinks along the way. Royal Navy HMS LCT 16 also is sunk by the Luftwaffe off Canea, Crete.
Royal Navy submarine Clyde fires a torpedo at an Italian freighter off Terranova but misses.
In Malta, the British notice a new, large incendiary bomb being used by the Italian bombers. The anti-aircraft defenses claim to have shot down a Junkers Ju 52 transport off the coast.
War Crimes: Pursuant to a standing order of temporary Crete commander General Kurt Student (sanctioned by Hermann Goering), German paratroopers (Fallschirmjäger) decide to settle some scores with the local population. Four trucks full of soldiers from the III Battalion of Luftlande-Sturm-Regiment 1 under the command of Oberleutnant Horst Trebes arrive at the village of Kondomari. The Germans force all civilians into the town square and then pick out male hostages. The 23-60 men are taken to a nearby olive grove and executed. The whole event is filmed by a Wehrmacht war correspondent, Franz-Peter Weixler, who secretly opposes the action.
Other Fallschirmjäger troops surround the village of Alikianos. The Germans take 42 men from the village to a churchyard and execute them. Other civilians are executed at Agia (12 men shot) and Kyrtomado (25 men shot).
These incidents will be included in charges of war crimes made after the war against General Student and others.
German/Italian Relations: Hitler and Mussolini unexpectedly meet at the Brenner Pass. It is their first meeting since 20 January 1941, their third at the Brenner Pass, and their fifth conference since the start of the war. Also attending the meeting are German Foreign Minister Joachim Ribbentrop and Italian Foreign Minister Count Galeazzo Ciano. Exactly what is said at this private meeting has been the subject of much conjecture and debate.
It is believed that Mussolini urges a joint strategy against Great Britain in the Mediterranean, which Hitler rejects. This would jibe with Kriegsmarine Admiral Raeder's "peripheral strategy" which has been working well to date.
According to Joseph Goebbels, Hitler tells Mussolini about Operation Barbarossa at this meeting. However, Ciano writes in his diary, "The general impression is that for the moment Hitler has no precise plan of action." If Hitler does tell Mussolini, the latter does not tell even his closest government cronies. The official communique simply states that the meeting lasted for several hours and was cordial.
After the meeting, Mussolini - who has a tendency to disparage the Germans after such meetings, but not Hitler personally - supposedly says:
German/Vichy French Relations: Pursuant to the Paris Protocols, the Vichy French government grants the Reich the use of port facilities in Bizerte, Tunis (Tunisia). While this is farther from the Libyan front, it also is closer to Naples than Tripoli. This makes Bizerte ideal for quick and relatively safe convoys across the Tyrrhenian Sea for items that are not time-critical. However, for the time being, only non-military supplies are allowed through the port.
Anglo/Turkish Relations: The Turkish government informs the British government that it prefers to remain neutral and declines a request to join an invasion of Vichy French Levant.
Anglo/US Relations: The US Army-Navy Board officially adopts the U.S.-British Commonwealth joint Basic War Plan, or, as it later became known, Rainbow Five. In the event of a worldwide conflict, the plan is for the Allies to make their priority defeating Italy and Germany first. As for Japan, the Allied "strategy, in the Far East will be defensive" because "the United States does not intend to add to its present military strength" there. Rainbow Five basically foresees the loss of the Philippines. However, no plans are made for evacuating the Americans in the islands.
US Military: Cryptanalyst Joseph Rochefort reports to the main US Navy building at Pearl Harbor, Territory of Hawaii for his new duty as head of the cryptanalysis section.
Australian Military: The RAAF established its No. 3 Base Stores Depot at Spring Hill.
Channel Islands: Hitler is worried about the defense of the islands. He asks to have maps of them brought to him.
China: The Chinese (commander of the Chinese 3rd PG, Lo Ying-Teh) decline a shipment of Hawk 81A (P-40C) fighter aircraft. They thus become the property of Claire Chennault’s Flying Tigers.
Holocaust: The Vichy French government orders a census of Jews. It also bans Jews from holding public office.
American Homefront: Henry Louis "Lou" Gehrig passes away in Riverdale, the Bronx, New York from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), an incurable neuromuscular disorder later referred to in North America as Lou Gehrig's disease. Mayor Fiorella La Guardia ordered flags in New York to be flown at half-staff. His remains are interred at Kensico Cemetery in Valhalla, New York. At the time of his death, Gehrig - "The Iron Horse" - holds the record for the number of consecutive games played, 2130, which will not be broken until 1998.
Chief Justice of the United States Charles Evans Hughes informs President Roosevelt that he will be retiring effective July 1.
Former 1936 Presidential candidate Alf Landon gives a speech at the commencement of Simpson College in Indianola, Iowa. He urges caution and deliberation before going to war. Landon notes, in reference to the rush to war:
Future History: Walter Stacy Keach Jr. is born in Savannah, Georgia. Keach goes on to a renowned acting career, which includes the CBS television series Mickey Spillane's Mike Hammer and The New Mike Hammer from 1984 to 1987. Stacy Keach continues to act as of this writing, including serving as the narrator for the CNBC series "American Greed" and hosting "The Twilight Zone" radio series.
Charles Robert Watts is born in Kingsbury, London. He becomes a talented drummer and, in mid-1962, meets Brian Jones, Ian "Stu" Stewart, Mick Jagger and Keith Richards. In January 1963, Watts joins The Rolling Stones, which goes on to become one of the top rock groups of all time. As of this writing, he continues to be a member of the group despite having experienced some health problems.
June 1941
June 1, 1941: Farhud Pogrom
June 2, 1941: Massacres on Crete
June 3, 1941: Kandanos Massacre
June 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes Away
June 5, 1941: Death in Chungking
June 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar Order
June 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at Pessac
June 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and Lebanon
June 9, 1941: Litani River Battle
June 10, 1941: British Take Assab
June 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond Russia
June 12, 1941: St. James Agreement
June 13, 1941: Lützow Damaged
June 14, 1941: Latvian June Deportations
June 15, 1941: Operation Battleaxe
June 16, 1941: The Old Lion
June 17, 1941: British Spanked in North Africa
June 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its Back
June 19, 1941: Cheerios Introduced
June 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air Force
June 21, 1941: Damascus Falls
June 22, 1941: Germany Invades Russia
June 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes Havoc
June 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius Fall
June 25, 1941: Finland Declares War
June 26, 1941: Bombing of Kassa
June 27, 1941: Encirclement At Minsk
June 28, 1941: Minsk Falls
June 29, 1941: Brest Fortress Falls
June 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top Ace
2020
Regent Abdul Illah (Abdullah) ends the Farhud riots, according to the Iraqi Commission Report, when he orders forces loyal to him into Baghdad. They use machine guns to kill many rioters. Another version of events is that the British are the ones that restore order. The two versions may be reconciled by assuming that the Regents ask the British to restore order, but that is unclear. In any event, hundreds of people on both sides of the Farhud - rioters and Jewish victims - perish. This incident begins the gradual elimination of the centuries-old Jewish presence in Baghdad.
In Syria, Vichy French forces claim to shoot down a British Blenheim reconnaissance plane over Syria-Lebanon.
 |
| German troops choose which hostages to execute in Kondomari, Crete, 2 June 1941 (Franz Peter Weixler, Federal Archive). |
RAF Bomber Command sends 9 Blenheims of 2 Group, 105 Squadron to raid the Kiel Canal. This includes the naval barracks at Friedrichskoog and various villages along the canal. The RAF planes sink two small ships that block the canal for ten days.
RAF Bomber Command also sends bombers of 107 Squadron to raid the region between the Ems and the Elbe.
RAF Bomber Command also targets the liner Europe, tied up at Bremerhaven.
RAF Bomber Command sends 150 aircraft to attack Dusseldorf and 25 aircraft to attack Duisburg overnight.
The Luftwaffe attacks Manchester during the night of 1-2 June, killing 70 and injuring 86. This is the Manchester Blitz.
The Luftwaffe bombs Park Grove, Hull. This is Hull's fiftieth raid of the war. There are 27 killed and 11 wounded, and the tragedy is that the "all clear" mistakenly had sounded and the victims had just exited their shelters.
The RAF shoots down a Junkers Ju 88A northeast of Tynemouth at 22:29. There are two deaths, and two crewmen become POWs.
East African Campaign: East African 22nd Infantry Brigade begins crossing the Omo at Sciola in Galla-Sidamo.
 |
| Victims at Kondomari, Crete lining up for their executions, 2 June 1941 (Franz Peter Weixler, Federal Archive). |
U-108 (Kptlt. Erich Hilsenitz), on its third patrol out of Lorient, spots Convoy OB-327 in the mid-Atlantic. It torpedoes and sinks 7628-ton freighter Michael E, which happens to be the first catapult aircraft merchant (CAM) ship. There are four deaths on the Michael E. The ship has no time to launch its fighter plane, but the pilot manages to survive the sinking along with 61 others. It is an inauspicious debut of the CAM ship force.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages Royal Navy submarine HMS P.32 off Finisterre. P.32 is able to continue on to Gibraltar, though its batteries are damaged and it is unable to submerge.
Royal Navy escort ship Hartland (formerly a US Coast Guard cutter) collides with 646-ton British freighter Welsh Coast. The Hartland makes it to Falmouth for repairs and a scheduled refit.
Dutch submarine O.14 is involved in a collision. The submarine makes it to Grangemouth for repairs that take a month.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 2477-ton British freighter Beaumanoir in Robin Hood's Bay. The ship is taken under tow, but the Luftwaffe returns and sinks the Beaumanoir.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 4749-ton British freighter Prince Rupert City north of Loch Eriboll, Scotland. There are four deaths.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 197-ton Belgian trawler John 90 miles southeast of Inglos Hofdi. Everyone survives.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 2183 ton British freighter Thorpebay about six miles from Coquet Lighthouse, Northumberland. The Thorpebay makes it back to the Tyne for repairs.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 195-ton British trawler Ben Screel east of Dunstanburgh Castle, Northumberland. Ben Screel makes it back to the Tyne for repairs.
Finnish 5417 ton freighter Kasteholm hits a mine and sinks northeast of the Faroe Islands. There is one death, the rest of the crew makes it to Tórshavn, Faroe Islands.
Canadian minesweeper (former Norwegian whale factory ship) HMCS Suderøy V is commissioned, minesweeper Caraquet is launched, minesweepers Grandmère and Vegreville are laid down.
US escort aircraft carrier USS Long Island (AVG-1) is commissioned (Commander Donald B. Duncan) at Newport News, Virginia. The Long Island is a conversion from cargo ship SS Mormacmail.
Royal Navy minelayer Plover lays minefield BS.57 in the English Channel.
Convoy OB 330 departs from Liverpool.
 |
| German troops line up to execute hostages in Kondomari, Crete, 2 June 1941 (Franz Peter Weixler, Federal Archive). |
The battle for Crete is over. The whole island has been freed from the enemy. Yesterday German troops occupied the last base of the beaten British, the port of Sfakion, capturing 3,000 more prisoners in the process.For once, the Germans understate their achievement - they actually capture more than 3,000 men at Sfakia.
The British War Cabinet discusses the future of Cyprus, which it believes may be next on Hitler's agenda in the Mediterranean. The Greek government would like to set up its capital in Cyprus, and there is some support within the British government for ceding the island to Greece for that purpose. The Cabinet concludes that the entire matter should be left to postwar peace settlement discussions.
Navy 353-ton whaler HMT Kos XXII attempts to make a run from Crete to Alexandria but sinks along the way. Royal Navy HMS LCT 16 also is sunk by the Luftwaffe off Canea, Crete.
Royal Navy submarine Clyde fires a torpedo at an Italian freighter off Terranova but misses.
In Malta, the British notice a new, large incendiary bomb being used by the Italian bombers. The anti-aircraft defenses claim to have shot down a Junkers Ju 52 transport off the coast.
 |
| German troops raise their rifles to execute hostages in Kondomari, Crete, 2 June 1941 (Franz Peter Weixler, Federal Archive Bild 101I-166-0525-39). |
Other Fallschirmjäger troops surround the village of Alikianos. The Germans take 42 men from the village to a churchyard and execute them. Other civilians are executed at Agia (12 men shot) and Kyrtomado (25 men shot).
These incidents will be included in charges of war crimes made after the war against General Student and others.
German/Italian Relations: Hitler and Mussolini unexpectedly meet at the Brenner Pass. It is their first meeting since 20 January 1941, their third at the Brenner Pass, and their fifth conference since the start of the war. Also attending the meeting are German Foreign Minister Joachim Ribbentrop and Italian Foreign Minister Count Galeazzo Ciano. Exactly what is said at this private meeting has been the subject of much conjecture and debate.
It is believed that Mussolini urges a joint strategy against Great Britain in the Mediterranean, which Hitler rejects. This would jibe with Kriegsmarine Admiral Raeder's "peripheral strategy" which has been working well to date.
According to Joseph Goebbels, Hitler tells Mussolini about Operation Barbarossa at this meeting. However, Ciano writes in his diary, "The general impression is that for the moment Hitler has no precise plan of action." If Hitler does tell Mussolini, the latter does not tell even his closest government cronies. The official communique simply states that the meeting lasted for several hours and was cordial.
After the meeting, Mussolini - who has a tendency to disparage the Germans after such meetings, but not Hitler personally - supposedly says:
I wouldn't be at all sorry if Germany in her war with Russia got her feathers plucked.Many believe that the Italians are, indeed, aware of Operation Barbarossa by this date, as evidenced by Italian troop movements in the Balkans.
 |
| The old Salford Royal building in Manchester takes a direct hit on June 2, 1941, with the attack claiming the lives of 14 nurses and their tutor. |
Anglo/Turkish Relations: The Turkish government informs the British government that it prefers to remain neutral and declines a request to join an invasion of Vichy French Levant.
Anglo/US Relations: The US Army-Navy Board officially adopts the U.S.-British Commonwealth joint Basic War Plan, or, as it later became known, Rainbow Five. In the event of a worldwide conflict, the plan is for the Allies to make their priority defeating Italy and Germany first. As for Japan, the Allied "strategy, in the Far East will be defensive" because "the United States does not intend to add to its present military strength" there. Rainbow Five basically foresees the loss of the Philippines. However, no plans are made for evacuating the Americans in the islands.
 |
| Admiral Ernest J. King on the cover of Time magazine, 2 June 1941. |
Australian Military: The RAAF established its No. 3 Base Stores Depot at Spring Hill.
Channel Islands: Hitler is worried about the defense of the islands. He asks to have maps of them brought to him.
China: The Chinese (commander of the Chinese 3rd PG, Lo Ying-Teh) decline a shipment of Hawk 81A (P-40C) fighter aircraft. They thus become the property of Claire Chennault’s Flying Tigers.
Holocaust: The Vichy French government orders a census of Jews. It also bans Jews from holding public office.
 |
| The U.S. Navy troop transport USS West Point (AP-23) under initial conversion and painting at Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock Co., Virginia (USA), 2 June 1941. She was previously SS America. The aircraft carrier USS Hornet (CV-8) is in the background. Note the neutrality markings on West Point's side and the repainting operations (US Navy, National Archives). |
Chief Justice of the United States Charles Evans Hughes informs President Roosevelt that he will be retiring effective July 1.
Former 1936 Presidential candidate Alf Landon gives a speech at the commencement of Simpson College in Indianola, Iowa. He urges caution and deliberation before going to war. Landon notes, in reference to the rush to war:
We find a fatalistic acceptance of the inevitable.He warns that the country runs the risk of falling into "dictatorship, of the right or of the left," due to the "weakening [of] our checks upon the majority."
Future History: Walter Stacy Keach Jr. is born in Savannah, Georgia. Keach goes on to a renowned acting career, which includes the CBS television series Mickey Spillane's Mike Hammer and The New Mike Hammer from 1984 to 1987. Stacy Keach continues to act as of this writing, including serving as the narrator for the CNBC series "American Greed" and hosting "The Twilight Zone" radio series.
Charles Robert Watts is born in Kingsbury, London. He becomes a talented drummer and, in mid-1962, meets Brian Jones, Ian "Stu" Stewart, Mick Jagger and Keith Richards. In January 1963, Watts joins The Rolling Stones, which goes on to become one of the top rock groups of all time. As of this writing, he continues to be a member of the group despite having experienced some health problems.
 |
| USS Long Island (CVE-1) on June 10, 1944, in San Francisco Bay. This photo was taken by NAS Alameda. |
June 1941
June 1, 1941: Farhud Pogrom
June 2, 1941: Massacres on Crete
June 3, 1941: Kandanos Massacre
June 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes Away
June 5, 1941: Death in Chungking
June 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar Order
June 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at Pessac
June 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and Lebanon
June 9, 1941: Litani River Battle
June 10, 1941: British Take Assab
June 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond Russia
June 12, 1941: St. James Agreement
June 13, 1941: Lützow Damaged
June 14, 1941: Latvian June Deportations
June 15, 1941: Operation Battleaxe
June 16, 1941: The Old Lion
June 17, 1941: British Spanked in North Africa
June 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its Back
June 19, 1941: Cheerios Introduced
June 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air Force
June 21, 1941: Damascus Falls
June 22, 1941: Germany Invades Russia
June 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes Havoc
June 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius Fall
June 25, 1941: Finland Declares War
June 26, 1941: Bombing of Kassa
June 27, 1941: Encirclement At Minsk
June 28, 1941: Minsk Falls
June 29, 1941: Brest Fortress Falls
June 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top Ace
2020