Thursday 5 June 1941
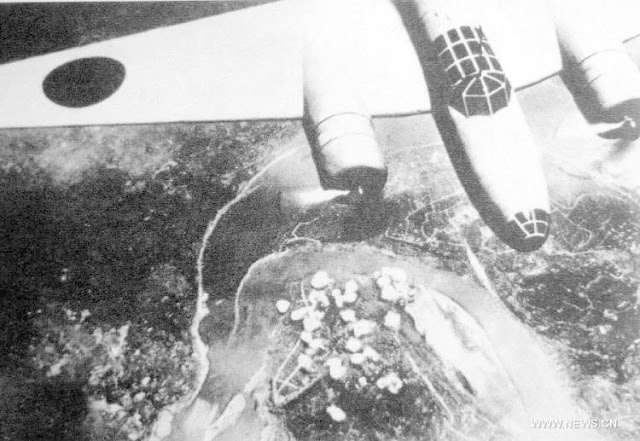 |
| The Japanese bombing Chungking. |
The Vichy French bomb the Transjordanian capital of Amman.
The British Middle East Command is ironing out the details of its planned invasion of Syria, Operation Exporter. General Maitland Wilson, who is planning the operation, will command the initial stages of the operation from the King David Hotel in Jerusalem. Then, he will hand off the direction of operations to Major-General John Lavarack of the 1st Australian Corps once Damascus and Beirut have fallen and the campaign effectively has been decided.
Brigadier Sydney Rowell, chief of operations of the Corps, argues that control of operations should vest in the local commanders from the start, but Thomas General Blamey, on Middle East Commander General Archibald Wavell's staff in Cairo, overrules him. The British feel, from intelligence information gathered from French defectors, that the invasion of Syria will be a simple affair, and Blamey wants to "not rock the boat." Rowell and Blamey have a lack of respect for each other which rapidly is turning personal.
Rowell and headquarters for the 1st Australian Corps move to Nazareth in anticipation of the invasion.
The Royal Navy continues re-deploying its ships to support the invasion of Syria. Anti-aircraft cruiser HMS Coventry and destroyers Hero and ISIS leave Alexandria. They are to rendezvous with troopship Glengyle at Port Said, which is to embark on invasion troops.
In Iraq, the British occupy Kirkuk.
 |
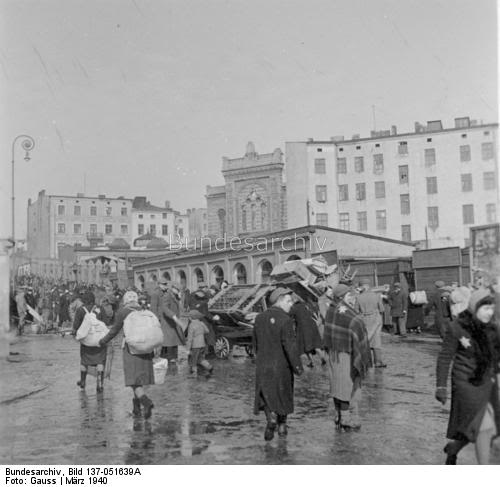
| Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler arrives at Lodz Ghetto (Litzmannstadt) on 5 June 1941. He is in a BMW 355 bearing his standard "SS-1" plates. Visible (grey hair) is Mordechai Chaim Rumkowski, the “leader” of the Jewish community. Himmler is on an inspection tour of the manufacturing process at the camp (they make uniforms and other items). Karl Wolff, Himmler's Chief Adjutant, is visible, as is Ghetto Administrator Hans Biebow (face at extreme left, over the shoulder of the political officer). Poland at this time is a beehive of activity due to the looming start of Operation Barbarossa. |
Luftwaffe ace Heinz Wiest (six victories) of JG 51 perishes in a flying accident.
East African Campaign: East African 22nd Infantry Brigade captures over 1000 Italian troops near the Omo River at Sciola in Galla-Sidamo.
 |
| Heavy cruiser ORP Burza H-73 seen off Bangor, Ireland, 5 June 1941. |
U-48 (Kptlt. Herbert Schultze), on its 12th patrol out of Kiel in the Atlantic midway between Ireland and St. John's, torpedoes and sinks 6054-ton British tanker Wellfield. There are 8 deaths and 34 survivors. The survivors are picked up by Norwegian freighter Heina.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 3540-ton British coal hulk Himalaya at Portland, Dorset.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 73-ton Royal Navy balloon barrage drifter Lavinia L. off Sheerness. There is one death.
Royal Navy 505-ton trawler Ash hits a mine and sinks in the Thames Estuary. There are some men wounded, but everybody survives.
British 6278-ton freighter Myrmidon hits a mine in the Crosby Channel. The Myrmidon makes it back to Liverpool. Eventually, it heads to New York for complete repairs.
Royal Navy destroyer Matabele hits a submerged object off Barrow. It has to return to Barrow for repairs and is out of service until August. With so many vessels being sunk all around Great Britain, underwater hazards not marked on charts are multiplying and becoming a serious problem.
The Royal Navy continues landing ground reinforcements in Iceland. This month, an infantry battalion and artillery battalion arrive. The British occupation presence is rapidly building to a total of 25,000 men. The Icelandic government remains officially neutral but offers no resistance to the British. The British build numerous facilities at Reykjavik and elsewhere, including No. 30 General Hospital and No. 50 General Hospital. The British are preparing to hand off occupation duties to the United States, but that process has not yet begun.
Canadian corvettes HMCS Buctouche (Lt. William W. Hackney) and Sherbrooke (Lt. Commander Eric G. M. Donald) are commissioned.
U-573 (Kptlt. Heinrich Heinsohn) is commissioned in Kiel.
The Kriegsmarine places an ambitious order for 102 new U-boats to be built. Germany only has so much steel, most imported from Scandinavia, and the army and navy both need what is available for their projects. Thus, there is constant competition for steel allotments, which is a symptom of a larger issue facing the Reich.
 |
| Fiat CR-42-Falco 161 Gruppo CT Stormo Autonom 164a 164 5 MM7475, Rhodes, June 1941. |
Royal Navy submarine HMS Triumph encounters three small Italian ships in the Gulf of Sirte along the coast southeast of Misrata. Using its deck gun, Triumph sinks escorting Italian gunboat Valoroso, 245-ton freighter Frieda and 244-ton freighter Trio Frassinetti.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Unique (Lt. A.F. Collett, RN), on its 9th war patrol, makes a daring intrusion into Lampedusa Harbor early in the morning. At 08:22, it torpedoes and sinks 736-ton Italian freighter Arsia inside Lampedusa Harbor. Collett has to fire two torpedoes because the first at 07:53 misses and hits the shore just astern of the ship. There are no casualties. Shrapnel from the Arsia damages 275-ton freighter Egusa and small fishing boat Giuseppe Padre (two casualties). Some sources place this as occurring on 3 June, and that Unique arrives back at Malta today.
Operation Rocket is in progress. This is another in a regular series of operations from Gibraltar to fly fighter aircraft to Malta. Aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal and Furious carry Hawker Hurricanes, escorted by battlecruiser Renown and six destroyers. The two carriers, leading two separate groups, intend to fly off 43 Hurricanes once they are within range of Malta.
At Alexandria, Royal Navy submarine HMS Rorqual departs with a load of supplies for Malta. These trips take almost a week now because of the Luftwaffe's control over the skies now that Crete is in German hands. Australian destroyers HMAS Vendetta and Voyager also depart, carrying supplies to Tobruk. Vendetta and Voyager complete the journey after dark, quickly unloading and returning to Mersa Matruh before dawn.
The British reinforce Cyprus with Australian troops. The Germans, however, have their eyes fixed on the East and no longer are interested in more island adventures in the Mediterranean.
At Malta, the military government sends the War Office a warning that the island is not prepared to withstand a Luftwaffe invasion using airborne troops, as on Crete. The cable notes that local air superiority has been lost. On the bright side, the cable bravely states that "Malta is in a much better position to stand up to it than was Crete." The problem is that the risk of airborne landings requires defenses inland, while the danger of seaborne landings requires troops guarding the beaches. The British forces on Malta have insufficient troops to guard against both possibilities simultaneously. The cable concludes with a request for three squadrons of fighters (meaning an additional squadron to add to the two already present), two infantry battalions and additional artillery.
 |
| The Evening Star, Washington, D.C., 5 June 1941. |
Dutch/French Relations: The government of the Dutch East Indies closes the Karimata Strait and Sunda Strait to Vichy French vessels. The French in Indochina is completely dominated by Japanese Imperial forces.
 |
| Chinese packed tight into a Chungking air-raid shelter. Could the air could in such an enclosed space possibly be enough for all those people? Well... the Chinese sadly found out it wasn't enough. |
US Government: President Roosevelt's administration requests funding of $10.4 billion in army defense spending in the fiscal year 1942 (which begins in September 1941). This is a vast sum for the time, especially with the country still supposedly at peace.
 |
| Chinese packed tight into a Chungking air-raid shelter. |
 |
| Damage from the Chungking air raid of 5 June 1941 (Mel Jacoby). |
 |
| Some people trampled in Chungking during the 5 June 1941 raid (Mel Jacoby). |
 |
| A casualty carried out of a Chungking shelter following the raid of 5 June 1941 (Mel Jacoby). |
Holocaust: Japanese luxury ocean liner Hikawa Maru departs from Yokohama for Vancouver carrying Jewish refugees from Europe. This is a continuation of a very roundabout escape route used by small numbers of Jews during the first two years of the war.
 |
| HMS Ariguani (F 105) in the Clyde, 5 June 1941. Ariguani is a Fighter Catapult Ship (FSC) that embarks a Fulmar, visible on the left. |
Greek Homefront: Greek Prime Minister-in-exile Emmanouil Tsouderos makes a radio broadcast from Alexandria to occupied Greece. He states in part:
Unite as one man more closely than ever around our national symbols, around our flag and our heroic King. Keep your heads high as men who have been victorious. Do not trust the enemy; and have confidence in the final victory. Help each one of you, with every means at your disposal in order that we may achieve the final victory. Help our country to overcome the present misfortunes until the glorious day of liberation of a Greece great and new.Greek resistance to the occupying German troops is heightening due to recent atrocities committed against civilians on Crete at Kandanos and elsewhere.
 |
| HMS Roxborough is seen off Bangor, Ireland, on 5 June 1941. |
Future History: Spalding Rockwell Gray, actor, and writer, is born in Providence, Rhode Island. He begins a theatrical career in New York in the late 1960s, and vaults to celebrity status with the film version of his classic monologue "Swimming to Cambodia" in 1987. The film, among other things, features Gray describing his quest for his "perfect moment." Gray, already a supporting actor, goes on to various film roles. Spalding Gray passes away in 2004, apparently by suicide following a car crash in Ireland. He is buried in Oakland Cemetery, Sag Harbor, New York.
Martha Argerich is born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. She becomes one of the top classical pianists in the world. She also is famous in medical circles for surviving malignant melanoma in the 1990s following experimental treatment at the John Wayne cancer institute in Santa Monica, California. As of 2018, her cancer remains in remission and she continues to give recitals.
Stuart Watkins is born in Newport, Wales. He becomes a top Welsh international rugby union wing. Watkins begins his rugby career at Cross Keys before switching to his home town of Newport in 1963.
Robert Kraft is born in Brookline, Massachusetts. He becomes Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of The Kraft Group and owner of NFL team the New England Patriots.
 |
| Beechcraft F-2 Expeditor reconnaissance aircraft near Ninilchik, Alaska, June 5, 1941 (3:35PM, USAAC photo). |
June 1941
June 1, 1941: Farhud Pogrom
June 2, 1941: Massacres on Crete
June 3, 1941: Kandanos Massacre
June 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes Away
June 5, 1941: Death in Chungking
June 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar Order
June 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at Pessac
June 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and Lebanon
June 9, 1941: Litani River Battle
June 10, 1941: British Take Assab
June 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond Russia
June 12, 1941: St. James Agreement
June 13, 1941: Lützow Damaged
June 14, 1941: Latvian June Deportations
June 15, 1941: Operation Battleaxe
June 16, 1941: The Old Lion
June 17, 1941: British Spanked in North Africa
June 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its Back
June 19, 1941: Cheerios Introduced
June 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air Force
June 21, 1941: Damascus Falls
June 22, 1941: Germany Invades Russia
June 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes Havoc
June 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius Fall
June 25, 1941: Finland Declares War
June 26, 1941: Bombing of Kassa
June 27, 1941: Encirclement At Minsk
June 28, 1941: Minsk Falls
June 29, 1941: Brest Fortress Falls
June 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top Ace
2020

















