Wednesday 7 May 1941
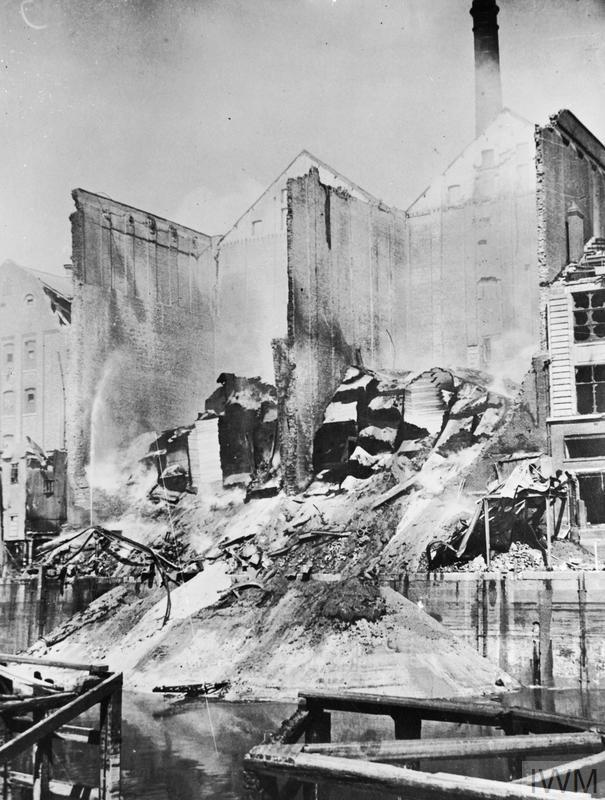 |
| "Smouldering grain cascades slide into the river at Hull after the raid on the night of 7/9 May 1941." © IWM (HU 660). |
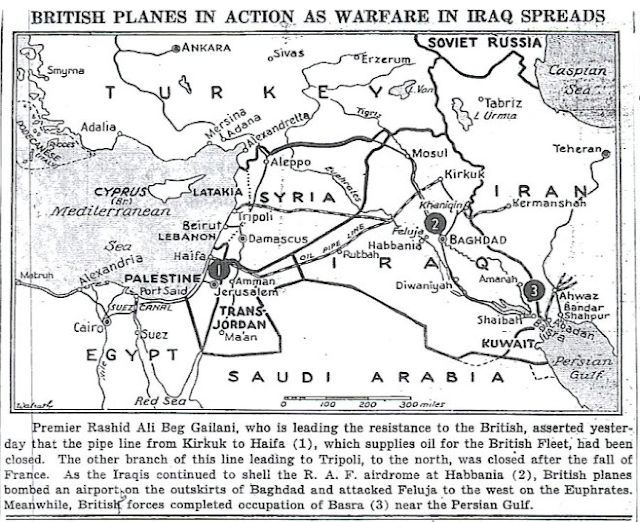
The British troops at Habbaniya continue pushing the Iraqi troops back toward Baghdad. Further south, the Indian 20th and 21st Brigades sortie out of the port of Basra and attack nearby port Ashar. Brigadier Slim arrives at Basra as chief of staff to General Edward Quinan.
The Italians have some planes in Iraq, and today they score a rare success when they damage 176-ton British tanker barge Safiyeh in the Persian Gulf. The barge is towed to Abadan for repairs.
Both sides are planning to send reinforcements - the Germans via Viche-held Syria - but the British have troops already on the march and already are having success on the ground in Iraq.
The Germans send Fritz Grobba to Iraq to become their official representative in Baghdad.
 |
| One of 50 Guy Mk IA armored cars, seen here during anti-invasion exercises in Southern Command, 7 May 1941. It sports a 15 mm Besa MG. |
The May Blitz on Liverpool and Merseyside continues for a seventh consecutive (and last) night. The entire dock area is destroyed or still in flames. A hit on a school shelter kills 160 people, and a hospital sees 60 patients and staff perish.
There is more destruction in the harbor, too. Destroyer HMS Hurricane takes a direct hit and sinks, but fortunately, it is in shallow water and is raised and returned to service by January 1942. Destroyer Viscount and CAM ship Maplin also are damaged by the ship, with the Viscount also out until January 1942. 43 ton flat Ellesbasnk sinks at Stanley Dock, and 201-ton tug Hornby also is sunk, but later raised and returned to service. Other ships hit at Liverpool:
- 46-ton sailing barge Ida Burton (sunk)
- 4672-ton British freighter Clan Macinnes (damaged).
Other Luftwaffe attacks occur on Tynemouth Borough in Northumberland, West Hartlepool, Hartlepool and Billingham in Co Durham and Middlesbrough in Yorkshire. The attacks are not large - Hartlepool is bombed by nine planes - but they stretch out British air defenses and cause a lot of pain and suffering and damage to property.
The Luftwaffe continues attacking British shipping elsewhere as well, sinking 260-ton minesweeping trawler Susarion east of Humber Light Vessel and 96-ton naval drifter Gowan Hill at the port of Greenock. Also sunk at Greenock is 106-ton British freighter Bluestone (everyone survives).
The RAF conducts a Roadstead Operation to Gravelines. After dark, Bomber Command sends 15 bombers against the U-boat pens at St. Nazaire and another 89 bombers against the port of Brest. There also are attacks by 16 planes against coastal targets.
RAF ace Douglas Bader shoots down a Bf 109 during the day and also claims another probable.
The first B-17 Flying Fortress in RAF service arrives in Great Britain at RAF Watton. RAF No. 90 Squadron, a World War I unit, is reformed to handle the heavy bombers, which soon will relocate to West Raynham.
East African Campaign: The situation at Amba Alagi temporarily settles down into garrison duty as the Allied forces await the arrival of reinforcements.
 |
| HMS Somali in a prewar 1939 photo. The Somali captured German weather ship Munchen on 7 May 1941. |
Italian submarine Enrico Tazzoli spots 4310-ton Norwegian freighter Ferlane a few hundred miles off of Guinea Bissau and sends it to the bottom. Everybody aboard survives.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 12-ton fishing trawler Waterlily at Bessom Creek, West Mersea (near Clacton-on-Sea).
British 72-ton steam barge Kineenan hits a mine and sinks at Liverpool. All five men aboard are killed.
U-93 (Kptlt. Claus Korth) is on its fourth patrol near Greenland when it has an incident involving its machine gun. Three men are wounded, but the U-boat continues its patrol.
Two Italian submarines, Archimede and Guglielmotti, complete the long journey from Eritrea when they arrive in Bordeaux.
Convoy OB 319 departs from Liverpool.
Royal Navy corvette HMS Mignonette is commissioned.
Destroyer USS Woolsey is commissioned (Lt. Commander William H. Von Dreele).
U-352 is launched, U-260 and U-662 are laid down.
The pace at sea is picking up, though. Operation Tiger, which left Gibraltar on the 6th, continues steaming toward Alexandria. The transports carry tanks, but the more important tank personnel are still sent on the much longer, but safer, route around South Africa.
Royal Navy cruiser HMS Ajax and destroyers Havock, Hotspur and Imperial are passing by Benghazi to meet the Tiger convoy when they detour to bombard the city. They sink Italian freighters Capitano Cecchi and Tenace.
The Luftwaffe attacks Tobruk Harbor and scores some successes. Sunk is minesweeper Stoke, while minesweeping whaler Svana is damaged by a near miss.
The Luftwaffe raids Suda Bay, the center of British operations on Crete. They damage 1545-ton Greek freighter Tanais, which the Germans later raise and return to service.
The Germans are still consolidating their hold on mainland Greece. The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 1216-ton Greek freighter Katina P. at Astakos on the west coast.
Italian 2939 ton freighter Pascoli hits a mine and sinks near Saseno (Sazan) Island (near Vlore).
Churchill allows General Freyberg, commander in Crete, to receive actual Ultra decrypts of German wireless transmissions using the Enigma code machine. These decrypts show in real-time that the Luftwaffe is planning an aerial assault by paratroopers. However, the Secret Intelligence Service cautions Freyberg not to act on the Ultra decrypts unless and until he received independent verification of their contents so that the Germans would not suspect a security breach. Freyberg dutifully complies, and thus does not rearrange his defenses from the beaches to prospective aerial landing zones at Maleme Airfield and elsewhere despite having a very clear picture of how the battle will develop.
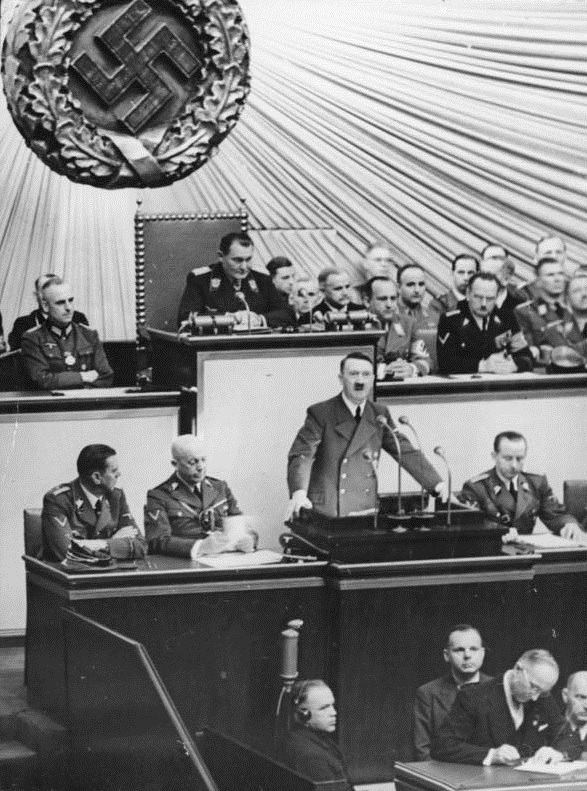
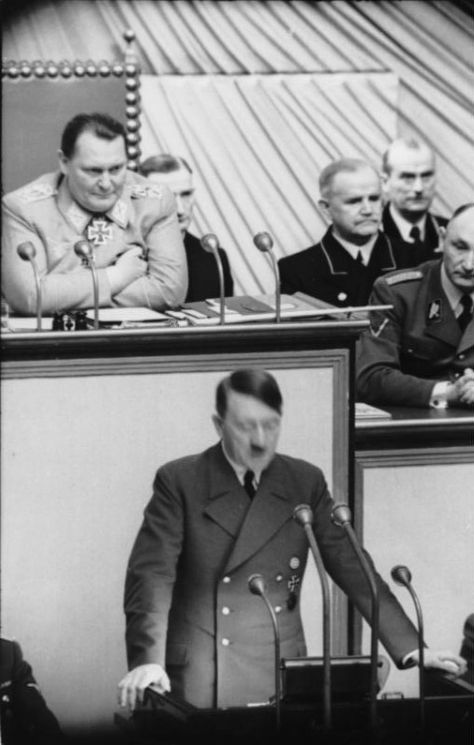
During his speech to the House of Commons (see below), Winston Churchill states that:
The loss of the Nile Valley and the Suez Canal and the loss of our position in the Mediterranean, as well as the loss of Malta, would be among the heaviest blows which we could sustain.Basically, Churchill confirms the wisdom of German Admiral Raeder's "peripheral strategy" which so far has worked well and still retains a lot of promise.
At Malta, there are several air raid alerts. The planes attack Luqa Airfield and some other military positions, and the RAF loses two Hurricanes when the planes collide (one pilot killed).
Lord Gort arrives at Gibraltar as the new Governor and Commander-in-Chief.
 |
| The front page of the New York Daily News, 7 May 1941. |
Spy Stuff: In an unusual incident, the Royal Navy has diverted three light cruisers (HMS Birmingham, Edinburgh, and Manchester) from their coverage of minelaying Operation SN 9A to seek out a German weather ship off Iceland. This is Operation EB, and it succeeds when the cruisers capture 306-ton German weather ship Munchen. The weather ship is taken to Thorshavn.
Capturing the German ship itself, though, is not the real prize. Among other things, quick action by men on destroyer Somali recovers valuable Enigma codes from the Munchen. Such codes can be extremely valuable so long as the Germans don't know they have been broken because Kriegsmarine Enigma operators are extremely careful and it is difficult to break their codes otherwise. Such codes also typically remain in effect for extended periods.
Australian/Canadian Relations: After an exhausting trip across the Atlantic by flying boat from Portugal to New York, Australian Prime Minister Robert Menzies boards a Douglas bomber and flies up to Ottawa for talks with Canadian leader MacKenzie King. Australia and Canada have a tight relationship because many Australian pilots are being trained in Canada at Empire Air Training Schools in Canada. Menzies gives five speeches and shows films of bomb damage in England.
 |
| View from the Victoria Monument in Derby Square, Liverpool during the May Blitz (Stewart Bale). |
Some have compared Hitler’s conquests with those of Napoleon. It may be that Spain and Russia will shortly furnish new chapters to that theme. It must be remembered, however, that Napoleon’s armies carried with them the fierce, liberating and equalitarian winds of the French Revolution, whereas Hitler’s empire has nothing behind it but racial self-assertion, espionage, pillage, corruption and the Prussian boot.During his remarks, Churchill bashes Leslie Hore-Belisha, the former Secretary of War under Neville Chamberlain. He accuses Hore-Belisha at length and in great detail for not focusing sufficiently on tank development and production. Hore-Belisha, who is present, retorts that Churchill is "indulging in petty recriminations," has not been in that position "for 20 months," and that Churchill has "enjoyed unprecedented powers" since becoming Prime Minister and thus - presumably - should bear the blame for any current deficiencies. The exchange reflects deep worry among the British about the state of their tank forces as compared to the feared panzers.
The House of Commons holds a vote of confidence in the government, and Prime Minister Winston Churchill prevails by 447 to 3. This evidences a slight firming in his overall support despite recent reversals in Libya and Greece.
China: The Battle of South Shanxi, aka the Battle of Jinnan and Zhongtiao Mountains Campaign and the Chungyuan Operation, begins. The Japanese Imperial Army's North China Front Army with six divisions and three brigades under Hayao Tada attacks to secure the Zhongtiao Mountains. The Japanese 3rd Air Group supports ground operations. The Chinese defense is hampered by extreme friction between the separate Nationalist (Kuomintang) and Communist (CPC) forces. The Japanese quickly move to surround the Nationalist Chinese forces, and they call on aid from nearby Communist forces of the 8th Route Army.
Serbia: The Sanski Most revolt continues. Ustaše authorities take prominent hostages at the railway station army barracks to prevent any more attacks on their people. The Germans respond to Ustaše calls for assistance and send 42 soldiers from their base at Prijedor and secure the area of the revolt. However, word has gotten out about the revolt to the surrounding area, and Serbs begin to pour into Tramošnja looking for a fight. The Ustaše kill three Serbs, while the Germans take three casualties. The day ends with Serbs forming a defensive perimeter on the slopes of Kijevska Gora above Sjenokos. The Germans order more troops to the area.
American Homefront: Detroit Tigers baseball star Hank Greenberg, who was drafted on 16 October 1940, is inducted into the US Army and reports to Fort Custer at Battle Creek, Michigan. Greenberg initially was turned down by the draft board (marked 4F) due to "flat feet," but Greenberg requested to be readmitted and ultimately was found fit for military service. He states: "I made up my mind to go when I was called. My country comes first." He trains as an anti-tank gunner and ultimately, with a temporary break in service, will serve for 47 months, the longest of any major league player.
 |
| "Ronald Ford (aged 7) climbs a drainpipe to show that there are no ill effects following his inoculation against diphtheria, which took place the day before (7 May 1941) at Argyle Street School Clinic." © IWM (D 3179). |
May 1941
May 1, 1941: British Hold Tobruk
May 2, 1941: Anglo-Iraq War
May 3, 1941: Liverpool Hammered
May 4, 1941: Hitler Victory Speech
May 5, 1941: Patriots Day
May 6, 1941: Stalin In Command
May 7, 1941: May Blitz
May 8, 1941: Pinguin Sunk
May 9, 1941: U-110 Captured
May 10, 1941: Hess Flies Into History
May 11, 1941: The Hess Peace Plan
May 12, 1941: Tiger Arrives Safely
May 13, 1941: Keitel's Illegal Order
May 14, 1941: Holocaust in Paris
May 15, 1941: Operation Brevity
May 16, 1941: Blitz Ends
May 17, 1941: Habbaniya Relieved
May 18, 1941: Croatia Partitioned
May 19, 1941: Bismarck at Sea
May 20, 1941: Invasion of Crete
May 21, 1941: Robin Moore Sinking
May 22, 1941: Royal Navy Destruction Off Crete
May 23, 1941: Crete Must Be Won
May 24, 1941: Bismarck Sinks Hood
May 25, 1941: Lütjens' Brilliant Maneuver
May 26, 1941: Bismarck Stopped
May 27, 1941: Bismarck Sunk
May 28, 1941: Crete Lost
May 29, 1941: Royal Navy Mauled Off Crete
May 30, 1941: Sorge Warns, Stalin Ignores
May 31, 1941: British Take Baghdad
2020