Friday 15 August 1941
 |
| Heinrich Himmler looks at a young Soviet prisoner during an official visit to a prisoner-of-war camp in the vicinity of Minsk, Belarus on 15 August 1941. The Soviet POWs have been told to sit, and this one has refused. He could be shot for his disobedience (and perhaps was). This picture is sometimes misidentified as showing a different visit by Himmler to a concentration camp with the prisoner identified as a famous British office, but that does not seem to be the case. (US Holocaust Memorial Museum, courtesy of National Archives and Records Administration, College Park, MD). |
Eastern Front: A very common theme in German recollections of Operation Barbarossa is the unexpected weight of Soviet military resistance. This is the case on 15 August 1941 at the highest levels, as OKH Chief of Staff General Franz Halder notes in the war diary that "It appears" that the 16th Infantry Division has run into "a larger enemy group than expected" at Cherson (Kherson), Ukraine. He notes that the "advance" is "held up as a result." It is easy to read into such writings a sense of bewilderment as to where all these Soviet troops are coming from. They are stopping the panzers from Finland to the Black Sea every time it seems an opening has been found, and nobody has a good explanation of why - it was supposed to be easier than this.
In the Far North sector, the Finns and Germans are stopped cold in their attempts to seize Murmansk and the Murmansk railway, but the Soviet position in the Karelian Isthmus is falling apart. The Finns are tightening their grip on the northern half of the lake, which is important because the Soviets are using the lake to supply many of their units, and any loss of control also could imperil shipping of supplies to Leningrad (though that is not necessary - yet) near its southern tip. Towns in Karelia have outsized importance because there are so few of them, and they control the few roads through the dense forests. The Soviets continue to demonstrate their difficulties operating in the dense forests and marshy areas of Karelia that they displayed during the Winter War (and which, incidentally, German troops share).
The Soviets send in the fresh 265th Division over the lake, but Finnish 10th Division mauls it in battle near Lake Ladoga today, encircling the hapless Soviets. Nearby, Finnish I Corps (2nd, 7th, and 19th Divisions) takes Sortavala on the northern fringes of Lake Ladoga (7th Division under Colonel Svensson enters first). The defending Soviet 168th Rifle Division has nowhere to run except the forests, and its only hope of survival is a seaborne rescue. The Finns take 540 Soviet prisoners, but many escape into the woods. It is a double-whammy in one day that drastically undermines the Soviet grasp on the lake.
In the Army Group North sector, the Germans of I Corps supported by VIII Air Corps take Novgorod at the northern tip of Lake Ilmen after a vicious struggle. With difficulty, 16th Army is retaining its hold on Staraya Russa at the lake's southern tip. They now can use the lake to form a solid defensive barrier - although the Wehrmacht going on the defensive is not the plan. The Soviet breakthrough south of Staraya Russa is stopped. Hitler, concerned by the breakthrough, orders reinforcements sent in from all sides, which Halder in his diary notes is "that old mistake" of overreacting to a perceived threat and thereby allowing the 2-4 Soviet divisions to "tie up three to four German Divisions."
Field Marshal von Leeb of Army Group North asks for more troops. Hitler hears of this, calls von Leeb in for a conference, and orders the transfer to von Leeb of a panzer division and two motorized divisions from General Hoth's Panzer Group 3. Field Marshal von Bock of Army Group Center, Halder records in the war diary, is "furious" and warns that this means his army group will have to go over to the defensive.
In the Army Group Center sector, the German high command continues to debate whether or not to give up the "lightning rod" position at Yelnya. The German advance continues at Rogachev, but the going is slow elsewhere, though XII and XIII Corps appear in good shape to link up soon with XXXII Corps north of Gomel and trap some more Soviet soldiers.
In the Army Group South sector, the Romanians continue their pause in their attack on Odessa as they bring forward forces. The German 6th Division of 11th Army runs into strong resistance at Nikolayev, and Soviets in a pocket near Kanev on the Dneipr are refusing to surrender. The Soviets at Nikolayev, while fighting a ferocious rearguard action and fooling the Germans into thinking they are making a stand there, continue evacuating while covered by naval forces.
The Red Air Force sends 15 bombers to raid Berlin, but they cause little damage.
European Air Operations: RAF Bomber Command takes the day and night off after several maximum efforts in recent days, most famously the daylight raid on Cologne power station on 12 August. RAF Bombers - the ones that make it back - struggle in before dawn from their raids on Hannover, Brunswick, and Magdeburg.
The Luftwaffe raids northeastern England in small raids by individual bombers. One bomb land on a house killing all seven people inside, including five boys aged 6-14. Another bomb lands on a house nearby and kills a 64-year-old widow and apparently others in the house. Other houses also are destroyed. The night's events prove that even "pinprick" attacks can cause large numbers of casualties, especially considering that the British public has been lulled into a false sense of security since the end of large-scale Luftwaffe raids in May.
David Bensusan-Butt, a civil servant in the War Cabinet Secretariat and an assistant of Winston Churchill's friend Lord Cherwell, completes his report based on analysis of RAF bombing missions. The report is not circulated until 18 August, but the reports are obvious at a glance and can be summarized in a phrase: RAF bombing is wildly inaccurate and only rarely hits the actual target. The Butt Report's results are explosive (no pun intended) and will lead to major changes in RAF bombing strategy. Churchill takes a few days to think about the findings before releasing them to the War Cabinet and RAF.
Battle of the Baltic: The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks Soviet reefer Kretinga in the Gulf of Finland. All 24 crew perish.
Soviet 441-ton minesweeper T-202/Buy hits a mine and sinks off Cape Yuminda, Suursaari (Hogland Island), Finland. The mine was laid by German S-boats.
German 542-ton freighter Memelland hits a mine and sinks south of Helsinki.
Battle of the Atlantic: Royal Navy light cruiser HMS Despatch stops 3667-ton German freighter Nordeney northeast of the Amazon Estuary. Like many crews of blockade runners, the German crewmen scuttle the ship and become prisoners.
US Navy aircraft carrier USS Yorktown leads a neutrality patrol out of Bermuda. US battleship Arkansas (BB-33) ends its own neutrality patrol when it returns to Hampton Roads.
Convoy Dervish, a supply mission bound for Archangel, Soviet Union, stops briefly at Scapa Flow before heading toward its next port of call in Reykjavik, Iceland.
German raider Orion, back in the Atlantic following a lengthy sojourn in the Indian Ocean, arrives in Spanish territorial waters and disguises itself as Spanish freighter Contramestre Casado.
Convoy ON-7 departs from Liverpool, Convoy SL-84 departs Freetown bound for Liverpool. Convoy WS-8C (Exercise Leapfrog) is canceled and the ships return to the Clyde.
U-165, U-334, and U-377 are launched, U-233 is laid down.
Battle of the Mediterranean: The RAF bombs and sinks 400-ton Italian freighter Adua in the Gulf of Sirte.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Thrasher attacks German freighter Ankara in Mandri Channel, Greece, but misses.
Royal Navy battleship arrives at Suez and proceeds toward Alexandria now that its battle-damage from the Crete campaign has been repaired in Durban. It sails in company with four destroyers, anti-aircraft ship Coventry, and troopship Glengyle.
Operation Guillotine, the British reinforcement of Cyprus, continues with Australian light cruiser HMAS Hobart arriving in Famagusta with three other ships and unloading troops there.
Royal Navy destroyers Kandahar and Kimberley make the nightly supply run to Tobruk and return safely to Alexandria before dawn breaks on the 15th. Destroyers Hasty and Jaguar make the run after dark.
At Malta, Royal Navy submarine Osiris arrives safely carrying supplies. RAF No. 105 Squadron sends 5 Blenheims (two lost) to attack Benghazi. Early on the 16th, they claim to destroy one tanker, damage another and leave two other ships damaged.
Soviet submarine L-5 lays a minefield off Sulina, Romania.
Soviet gunboats Krasnaya Armeniya and Krasnaya Gruziya give fire support to Soviet ground troops at Grigorevka and Spridovka, Odessa, Ukraine.
The Soviets scuttle submarine S-39, under construction at Nikolayev, Ukraine, to prevent its capture.
Battle of the Pacific: Soviet 2607-ton freighter Tungus sinks from an unexplained cause between Vladivostok and the La Perouse Strait. Several Soviet ships have sunk in the Vladivostok region recently from "friendly" mines.
Spy Stuff: German spy Josef Jakobs, who parachuted into Britain on the night of 31 January/1 February 1941, is executed by firing squad at the Tower of London. This is the last execution in the Tower of London - to date. Jakobs is given this "honor" - and Germans do consider it more dignified to be shot than hanged - because, unlike most spies, he is a member of the Wehrmacht.
In Tokyo, Richard Sorge sends a message to Moscow stating that the Japanese have decided not to attack the Soviet Union. Sorge's messages are taken much more seriously now following his successful warning of Operation Barbarossa.
Anglo/US/Soviet Relations: President Roosevelt and Prime Minister Churchill send a joint message to Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin. The message reads in part that it is time to discuss "long term policy" at a special conference:
US Military: The US Navy commissions Palmyra Island Naval Air Station. Although widely separated from the other islands in the chain, Palmyra Atoll is part of the Hawaiian Island chain. It has been under naval jurisdiction since 1934, codified by Executive Order 8616. US control of part of the atoll is legally disputed by private parties throughout the war (and ultimately overturned by the US Supreme Court), but that does not affect NAS Palmyra Island. The government has plans to dredge a ship channel, lay roads and causeways, and even build new islands.
Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson gives a radio address in which he goes through various aspects of the international situation, such as the bases obtained as leases from Great Britain recently. He remarks in all seriousness that an invasion of the United States by Axis troops "would be no playboy affair."
Japanese Military: Japanese 8360-ton seaplane tender Sanyo Maru completes its conversion and is attached to the Sasebo Naval District. It embarks six Type 0 Mitsubishi F1M2 “Pete” scout float biplanes and two Type O Aichi E13A1 "Jake" three-seat reconnaissance floatplanes, with two Type 95 Nakajima E8N2 "Dave" two-seat reconnaissance float biplanes in reserve.
The Imperial Japanese Navy fits AMC Hokoku Maru with searchlights and equipment for handling floatplanes. She will carry one Type 94 Kawanishi E7K2 “Alf” floatplane and one spare plane.
The IJN requisitions 5181-ton freighter Hide Maru for use as an ammunition ship, 10,383-ton tanker Kuroshio Maru, and 5350-ton freighter Bangkok Maru as a specialty cruiser.
The IJN commissions 6795-ton salvage vessel Yamabiko Maru.
US Government: Having returned to the United States from Placentia Bay, Newfoundland, President Roosevelt spends a quiet day fishing from presidential yacht USS Potomac (AG-25) in Pulpit Harbor, Penobscot Bay, Maine. Fishing, of course, was the cover story used during his absence from public view during the Atlantic Conference.
British Government: On his way back to England from the Atlantic Conference aboard battleship HMS Prince of Wales, Prime Minister Churchill stops for a day at Iceland.
German Government: Over dinner, Hitler relaxes with friends and goes into one of his monologues about whatever topic has crossed his mind during the day. Today, because there has been a high-profile murder in Berlin, the topic is the penal system. This does give some insight into the Reich's justice system:
Holocaust: Following the successful institution of the practice in the former Yugoslavia, Reich Commissioner for Eastern Territories Heinrich Lohse in Minsk decrees that Jews must wear the Yellow Star of David. This actually includes two yellow badges, one on the chest and one on the back. He also orders that Jews are not to own radios or automobiles. Jews also are prohibited from using public accommodations such as trains, parks, and theaters.
Reichsfuhrer-SS Heinrich Himmler visits Minsk and witnesses the execution of Jews at a nearby concentration camp. In company with SS General Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski and adjutant Karl Wolf Himmler also inspects an insane asylum. Bach-Zalewski claims to have told Himmler that using firing squads for euthanasia damages the shooters psychologically. Himmler orders them to try using dynamite on the inmates instead, which later is done with poor results. After exhausting these choices, they try gas.
In the town of Roskiskis on the Lithuanian-Latvian border, locals riot and institute a pogrom against Jews that ultimately claims an estimated 3200 lives.
At Kovno, Lithuania, surviving Jews who have survived earlier purges are forced into the suburban Ghetto in Viliampole.
The German authorities at Riga, Latvia establish a Jewish ghetto.
Einsatzcommando 3 executes 425 Jewish men, 19 Jewish women, and 17 non-Jews in Vilnius.
American Homefront: Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer releases "Life Begins for Andy Hardy." Directed by George B. Seitz, this is the 11th installment of the "Andy Hardy" series starring Mickey Rooney and Lewis Stone. It is memorable as the last installment of the Andy Hardy series to feature Judy Garland as Miss Betsy Booth. As with all of the Andy Hardy films, it turns a tidy profit. Counting domestic and overseas revenues, "Life Begins for Andy Hardy" nets MGM $1.324 million.
In Major League Baseball, there is a rare forfeit at Griffith Stadium in Washington. There is a rain delay in the 7th inning and the umpire orders the infield covered. This is standard practice, but ... it doesn't happen because the ground crew can't be located. The umpire then adjudges the field unplayable and calls it in favor of the home team Senators because they are leading 6-3. However, after an appeal by the Red Sox, the American League forfeits the game to the Red Sox 1-0 because the home team is responsible for the care of the playing field.
Benny Goodman records "Elmer's Tune" in Chicago for Columbia (36359), four days after Glenn Miller records his version for Bluebird Records. Goodman uses his new "girl singer," known as Peggy Lee (real name Norma Deloris Egstrom). It is Lee's first recording with the Benny Goodman Orchestra and apparently her first recording ever. While Miller's version goes to number one on the Billboard chart in December, Goodman's and Lee's version does not chart - but it begins a very long and productive career for Miss Peggy Lee.
Future History: Donald Eugene Ulrich is born in Olympia, Washington. As Don Rich, he becomes a top country musician in the early 1960s and helps to develop the Bakersfield sound. Rich backs singer Buck Owens as a member of The Buckaroos until his untimely death in a motorcycle accident in 1974 at the age of 1932.
August 1941
August 1, 1941: More Executions on Crete
August 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement Closes
August 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces Euthanasia
August 4, 1941: Hitler at the Front
August 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk
August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the Arctic
August 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb Berlin
August 8, 1941: Uman Pocket Captured
August 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia Bay
August 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over Berlin
August 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in Life
August 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter Announced
August 13, 1941: The Soybean Car
August 14, 1941: The Anders Army Formed
August 15, 1941: Himmler at Minsk
August 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270
August 17, 1941: Germans in Novgorod
August 18, 1941: Lili Marleen
August 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 Destruction
August 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad Begins
August 21, 1941: Stalin Enraged
August 22, 1941: Germans Take Cherkassy
August 23, 1941: Go to Kiev
August 24, 1941: Finns Surround Viipuri
August 25, 1941: Iran Invaded
August 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the Desna
August 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate Tallinn
August 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets Savaged
August 29, 1941: Finns take Viipuri
August 30, 1941: Operation Acid
August 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No
2020
In the Far North sector, the Finns and Germans are stopped cold in their attempts to seize Murmansk and the Murmansk railway, but the Soviet position in the Karelian Isthmus is falling apart. The Finns are tightening their grip on the northern half of the lake, which is important because the Soviets are using the lake to supply many of their units, and any loss of control also could imperil shipping of supplies to Leningrad (though that is not necessary - yet) near its southern tip. Towns in Karelia have outsized importance because there are so few of them, and they control the few roads through the dense forests. The Soviets continue to demonstrate their difficulties operating in the dense forests and marshy areas of Karelia that they displayed during the Winter War (and which, incidentally, German troops share).
 |
| Soviets surrendering while playing a merry tune. "The last of the surrendered Russian soldiers translate their joy through the accordion." - Sortavala, 15 August 1941. |
 |
| Original caption: "Private Heino Jauhiainen... who singlehandedly took 25 Russians prisoner during the Ontrosenvaara sweep." - 15 August 1941. |
Field Marshal von Leeb of Army Group North asks for more troops. Hitler hears of this, calls von Leeb in for a conference, and orders the transfer to von Leeb of a panzer division and two motorized divisions from General Hoth's Panzer Group 3. Field Marshal von Bock of Army Group Center, Halder records in the war diary, is "furious" and warns that this means his army group will have to go over to the defensive.
In the Army Group Center sector, the German high command continues to debate whether or not to give up the "lightning rod" position at Yelnya. The German advance continues at Rogachev, but the going is slow elsewhere, though XII and XIII Corps appear in good shape to link up soon with XXXII Corps north of Gomel and trap some more Soviet soldiers.
In the Army Group South sector, the Romanians continue their pause in their attack on Odessa as they bring forward forces. The German 6th Division of 11th Army runs into strong resistance at Nikolayev, and Soviets in a pocket near Kanev on the Dneipr are refusing to surrender. The Soviets at Nikolayev, while fighting a ferocious rearguard action and fooling the Germans into thinking they are making a stand there, continue evacuating while covered by naval forces.
The Red Air Force sends 15 bombers to raid Berlin, but they cause little damage.
 |
| Soviet prisoners who are taken at Sortavala, including female soldiers, 15 August 1941 (SA-Kuva). |
The Luftwaffe raids northeastern England in small raids by individual bombers. One bomb land on a house killing all seven people inside, including five boys aged 6-14. Another bomb lands on a house nearby and kills a 64-year-old widow and apparently others in the house. Other houses also are destroyed. The night's events prove that even "pinprick" attacks can cause large numbers of casualties, especially considering that the British public has been lulled into a false sense of security since the end of large-scale Luftwaffe raids in May.
David Bensusan-Butt, a civil servant in the War Cabinet Secretariat and an assistant of Winston Churchill's friend Lord Cherwell, completes his report based on analysis of RAF bombing missions. The report is not circulated until 18 August, but the reports are obvious at a glance and can be summarized in a phrase: RAF bombing is wildly inaccurate and only rarely hits the actual target. The Butt Report's results are explosive (no pun intended) and will lead to major changes in RAF bombing strategy. Churchill takes a few days to think about the findings before releasing them to the War Cabinet and RAF.
 |
| "Handley Page Halifax Mark I Series 1, L9530 MP-L, of No 76 Squadron RAF undergoing maintenance at Middleton St George, County Durham. L9530 was shot down while attacking Magdeburg on 15 August 1941." © IWM (CH 3393). |
Soviet 441-ton minesweeper T-202/Buy hits a mine and sinks off Cape Yuminda, Suursaari (Hogland Island), Finland. The mine was laid by German S-boats.
German 542-ton freighter Memelland hits a mine and sinks south of Helsinki.
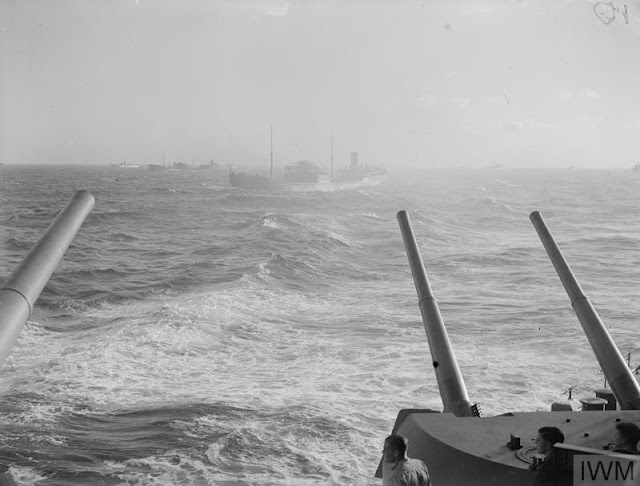 |
| "Ships of the convoy as seen from HMS PRINCE OF WALES." This is taken during the voyage home of Winston Churchill aboard Prince of Wales on 15 August 1941 when the battleship joins a convoy heading for England. © IWM (A 4955). |
US Navy aircraft carrier USS Yorktown leads a neutrality patrol out of Bermuda. US battleship Arkansas (BB-33) ends its own neutrality patrol when it returns to Hampton Roads.
Convoy Dervish, a supply mission bound for Archangel, Soviet Union, stops briefly at Scapa Flow before heading toward its next port of call in Reykjavik, Iceland.
German raider Orion, back in the Atlantic following a lengthy sojourn in the Indian Ocean, arrives in Spanish territorial waters and disguises itself as Spanish freighter Contramestre Casado.
Convoy ON-7 departs from Liverpool, Convoy SL-84 departs Freetown bound for Liverpool. Convoy WS-8C (Exercise Leapfrog) is canceled and the ships return to the Clyde.
U-165, U-334, and U-377 are launched, U-233 is laid down.
 |
| "The Prime Minister with Hermann Jonasson, Prime Minister of Iceland." This is during a brief stop-over by Churchill in Reykjavik on 15 and 16 August 1941 following the Atlantic Conference. © IWM (A 4992). |
Royal Navy submarine HMS Thrasher attacks German freighter Ankara in Mandri Channel, Greece, but misses.
Royal Navy battleship arrives at Suez and proceeds toward Alexandria now that its battle-damage from the Crete campaign has been repaired in Durban. It sails in company with four destroyers, anti-aircraft ship Coventry, and troopship Glengyle.
Operation Guillotine, the British reinforcement of Cyprus, continues with Australian light cruiser HMAS Hobart arriving in Famagusta with three other ships and unloading troops there.
Royal Navy destroyers Kandahar and Kimberley make the nightly supply run to Tobruk and return safely to Alexandria before dawn breaks on the 15th. Destroyers Hasty and Jaguar make the run after dark.
At Malta, Royal Navy submarine Osiris arrives safely carrying supplies. RAF No. 105 Squadron sends 5 Blenheims (two lost) to attack Benghazi. Early on the 16th, they claim to destroy one tanker, damage another and leave two other ships damaged.
Soviet submarine L-5 lays a minefield off Sulina, Romania.
Soviet gunboats Krasnaya Armeniya and Krasnaya Gruziya give fire support to Soviet ground troops at Grigorevka and Spridovka, Odessa, Ukraine.
The Soviets scuttle submarine S-39, under construction at Nikolayev, Ukraine, to prevent its capture.
Battle of the Pacific: Soviet 2607-ton freighter Tungus sinks from an unexplained cause between Vladivostok and the La Perouse Strait. Several Soviet ships have sunk in the Vladivostok region recently from "friendly" mines.
Spy Stuff: German spy Josef Jakobs, who parachuted into Britain on the night of 31 January/1 February 1941, is executed by firing squad at the Tower of London. This is the last execution in the Tower of London - to date. Jakobs is given this "honor" - and Germans do consider it more dignified to be shot than hanged - because, unlike most spies, he is a member of the Wehrmacht.
In Tokyo, Richard Sorge sends a message to Moscow stating that the Japanese have decided not to attack the Soviet Union. Sorge's messages are taken much more seriously now following his successful warning of Operation Barbarossa.
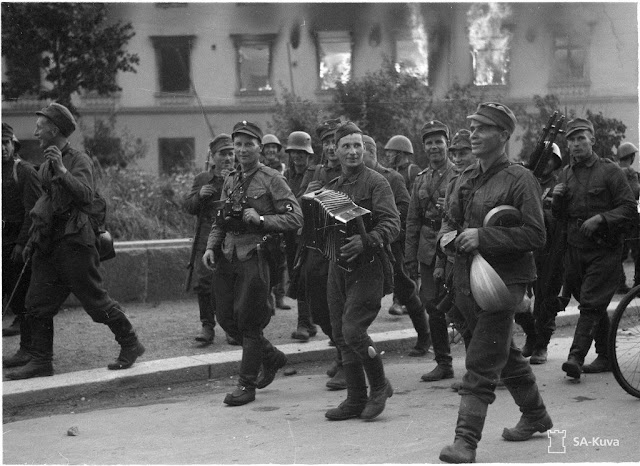 |
| Surrendered Soviet troops playing the accordion and singing as they march into captivity in Sortavala, 15 August 1941 (SA-Kuva). |
In order that all of us may be in a position to arrive at speedy decisions as to the apportionment of our joint resources, we suggest that we prepare for a meeting to be held at Moscow, to which we would send high representatives who could discuss these matters directly with you.The President and PM also note that they will continue to send supplies (as in the current Operation Dervish) pending Stalin's response. As with virtually all messages sent by the western allies to Stalin, he does not respond directly, but only through intermediaries.
US Military: The US Navy commissions Palmyra Island Naval Air Station. Although widely separated from the other islands in the chain, Palmyra Atoll is part of the Hawaiian Island chain. It has been under naval jurisdiction since 1934, codified by Executive Order 8616. US control of part of the atoll is legally disputed by private parties throughout the war (and ultimately overturned by the US Supreme Court), but that does not affect NAS Palmyra Island. The government has plans to dredge a ship channel, lay roads and causeways, and even build new islands.
Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson gives a radio address in which he goes through various aspects of the international situation, such as the bases obtained as leases from Great Britain recently. He remarks in all seriousness that an invasion of the United States by Axis troops "would be no playboy affair."
Japanese Military: Japanese 8360-ton seaplane tender Sanyo Maru completes its conversion and is attached to the Sasebo Naval District. It embarks six Type 0 Mitsubishi F1M2 “Pete” scout float biplanes and two Type O Aichi E13A1 "Jake" three-seat reconnaissance floatplanes, with two Type 95 Nakajima E8N2 "Dave" two-seat reconnaissance float biplanes in reserve.
The Imperial Japanese Navy fits AMC Hokoku Maru with searchlights and equipment for handling floatplanes. She will carry one Type 94 Kawanishi E7K2 “Alf” floatplane and one spare plane.
The IJN requisitions 5181-ton freighter Hide Maru for use as an ammunition ship, 10,383-ton tanker Kuroshio Maru, and 5350-ton freighter Bangkok Maru as a specialty cruiser.
The IJN commissions 6795-ton salvage vessel Yamabiko Maru.
US Government: Having returned to the United States from Placentia Bay, Newfoundland, President Roosevelt spends a quiet day fishing from presidential yacht USS Potomac (AG-25) in Pulpit Harbor, Penobscot Bay, Maine. Fishing, of course, was the cover story used during his absence from public view during the Atlantic Conference.
British Government: On his way back to England from the Atlantic Conference aboard battleship HMS Prince of Wales, Prime Minister Churchill stops for a day at Iceland.
German Government: Over dinner, Hitler relaxes with friends and goes into one of his monologues about whatever topic has crossed his mind during the day. Today, because there has been a high-profile murder in Berlin, the topic is the penal system. This does give some insight into the Reich's justice system:
The greatest vice of our penal system is the exaggerated importance attached to a first sentence. Corporal punishment would often be much better than a term of imprisonment. In prison and in penitentiary establishments, the delinquent is at too good a school. The old lags he meets there teach him, first that he was stupid to be caught, and secondly to do better next time. All that his stay in prison amounts to in the end is only an uninterrupted course of instruction in the art of doing wrong. In such a case, I see no sense in a long trial, with all its formalities, to study the question of responsibility or irresponsibility. In my view, whether responsible or not, the author of that crime should disappear.It turns out that Hitler is not a big fan of due process.
 |
| Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski gives a speech in Minsk on the occasion of a visit by Heinrich Himmler, 15 August 1941. |
Reichsfuhrer-SS Heinrich Himmler visits Minsk and witnesses the execution of Jews at a nearby concentration camp. In company with SS General Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski and adjutant Karl Wolf Himmler also inspects an insane asylum. Bach-Zalewski claims to have told Himmler that using firing squads for euthanasia damages the shooters psychologically. Himmler orders them to try using dynamite on the inmates instead, which later is done with poor results. After exhausting these choices, they try gas.
In the town of Roskiskis on the Lithuanian-Latvian border, locals riot and institute a pogrom against Jews that ultimately claims an estimated 3200 lives.
At Kovno, Lithuania, surviving Jews who have survived earlier purges are forced into the suburban Ghetto in Viliampole.
The German authorities at Riga, Latvia establish a Jewish ghetto.
Einsatzcommando 3 executes 425 Jewish men, 19 Jewish women, and 17 non-Jews in Vilnius.
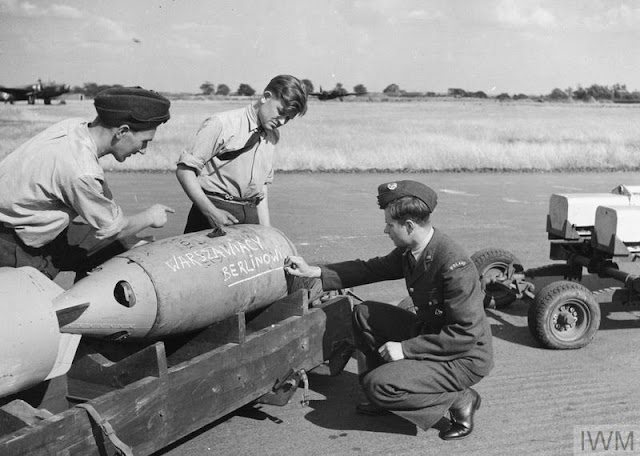 |
| "Groundcrew of a Polish Air Force bomber squadron, very likely of No. 300 Squadron, scribbling their best wishes to the enemy on a bomb at RAF Hemswell, 15 August 1941. The inscription in Polish reads: 'Warszawiacy Berlinowi - From Varsovians to Berlin'." © IWM (HU 111733). |
In Major League Baseball, there is a rare forfeit at Griffith Stadium in Washington. There is a rain delay in the 7th inning and the umpire orders the infield covered. This is standard practice, but ... it doesn't happen because the ground crew can't be located. The umpire then adjudges the field unplayable and calls it in favor of the home team Senators because they are leading 6-3. However, after an appeal by the Red Sox, the American League forfeits the game to the Red Sox 1-0 because the home team is responsible for the care of the playing field.
Benny Goodman records "Elmer's Tune" in Chicago for Columbia (36359), four days after Glenn Miller records his version for Bluebird Records. Goodman uses his new "girl singer," known as Peggy Lee (real name Norma Deloris Egstrom). It is Lee's first recording with the Benny Goodman Orchestra and apparently her first recording ever. While Miller's version goes to number one on the Billboard chart in December, Goodman's and Lee's version does not chart - but it begins a very long and productive career for Miss Peggy Lee.
Future History: Donald Eugene Ulrich is born in Olympia, Washington. As Don Rich, he becomes a top country musician in the early 1960s and helps to develop the Bakersfield sound. Rich backs singer Buck Owens as a member of The Buckaroos until his untimely death in a motorcycle accident in 1974 at the age of 1932.
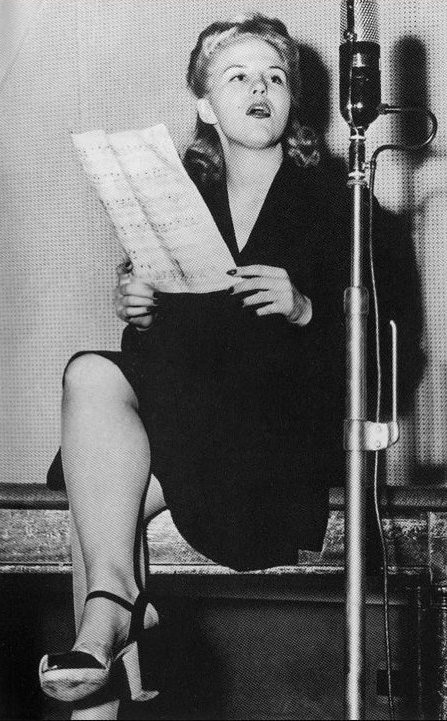 |
| Miss Peggy Lee ca. August 1941. |
August 1941
August 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement Closes
August 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces Euthanasia
August 4, 1941: Hitler at the Front
August 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk
August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the Arctic
August 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb Berlin
August 8, 1941: Uman Pocket Captured
August 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia Bay
August 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over Berlin
August 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in Life
August 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter Announced
August 13, 1941: The Soybean Car
August 14, 1941: The Anders Army Formed
August 15, 1941: Himmler at Minsk
August 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270
August 17, 1941: Germans in Novgorod
August 18, 1941: Lili Marleen
August 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 Destruction
August 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad Begins
August 21, 1941: Stalin Enraged
August 22, 1941: Germans Take Cherkassy
August 23, 1941: Go to Kiev
August 24, 1941: Finns Surround Viipuri
August 25, 1941: Iran Invaded
August 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the Desna
August 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate Tallinn
August 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets Savaged
August 29, 1941: Finns take Viipuri
August 30, 1941: Operation Acid
August 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No
2020