Monday 9 June 1941
 |
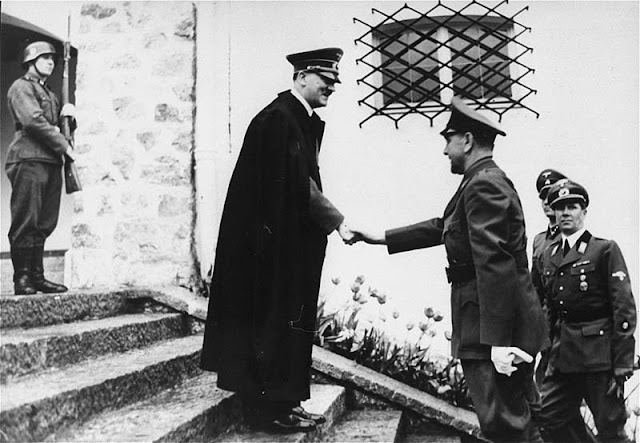
| Adolf Hitler greets Croatian strongman Ante Pavelić at the Berghof, 9 June 1941 (US Holocaust Memorial Museum). |
The 420 Commandos (British No. 11 (Scottish) do land - but in daylight. This deprives them of the element of surprise, a key advantage of Commando forces. They arrive in three different places, and the French barely notice them because they are fighting the advancing Australians. Subsequently, the Commandos under Lieutenant Colonel R.L. Pedder (Highland Light Infantry) serve as infantry and take heavy casualties (including Pedder himself, who is replaced by Geoffrey Keyes). By dint of hard fighting, the Commandos and some Australian troops of the 2/16 Australian Brigade do land on the other side of the river by using canvas boats. Australian engineers immediately begin building a pontoon bridge, which they complete after midnight.
The French use armored cars to counterattack the bridgehead, but the Commonwealth troops hold their position. The war then becomes active out at sea. Vichy French destroyers Valmy and Guépard sortie to bombard the British troops in the bridgehead. It is one of the few times during the war when British troops face naval bombardment (which turns out to be quite inaccurate).
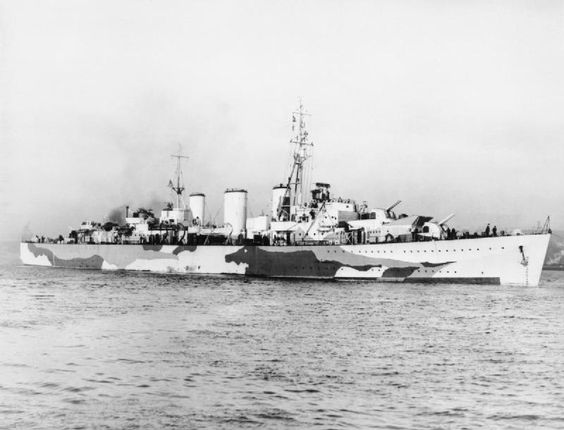
The Royal Navy quickly responds by sending destroyer HMS Janus, followed by New Zealand light cruiser HMNZS Leander and. Destroyers HMS Kandahar and Kimberley are nearby bombarding the Khan Bridge, and they also sally against the Vichy French destroyers. The Australian shore-based artillery also fires at the attacking French ships.
Faced with overwhelming firepower, the French ships withdraw to Beirut, chased by destroyers Hotspur, Isis, and Jackal. However, before they go, the French ships damage two of the British ships, destroyers Janus and Jackal, the former badly. Janus must be towed to Haifa by Kimberley, taking two British ships out of the fray. Jackal, only slightly damaged by one shell strike, stays in service.
French submarine Caiman is operating off the Syrian coast. It attacks British light cruiser HMS Phoebe. However, the attack fails and the Phoebe is undamaged. The incident induces the British to withdraw their ships to Haifa.
Elsewhere, Australian troops capture Fort Khiam but are stopped there. Free French 1st Infantry Brigade and 2nd Infantry Brigade advance to Kissoue south of Damascus.
The Luftwaffe, as in Iraq, has a very minimal presence in Lebanon and Syria. The Vichy French, though, have a formidable array of new fighters, including the new Dewoitine D.520. The RAF sends Gloster Gladiators from Amman to support the advancing British trips on the road to Damascus.
The outcome of the day's fighting is that the advancing Commonwealth troops are slightly behind schedule but still crossed the river. The road to Tyre, and beyond to Beirut, is now accessible.
The Vichy French assemble forces to defend their colony. General de Verdilhac (Vichy Dep. C-in-C) orders II/6 Battalion French Foreign Legion and 6th Chasseurs d’Afrique (armored) to assemble in Nahr el Awaj area for a counterattack.
 |
| "ORT KHIAM, SYRIA. MEN OF "A" COMPANY, 9TH PLATOON, 2/33 BN WITH A MACHINE GUN LEFT BY THE FRENCH. THEY ARE: LEFT TO RIGHT NX9258 CORPORAL R C CAMPBELL; WX96 SERGEANT A M SWEETAPPLE; NX34870 LIEUTENANT G B CONNOR; AND NX41301 PRIVATE J J WAYTE." The gun is a captured French Hotchkiss MG. They are at Fort Khiam. Fort Khiam (Kiame) fell on 9 June 1941, the day this picture was taken, to the 25th Brigade (Australian War Memorial 008366). |
RAF Bomber Command sends 18 planes on a sweep of the French coast.
East African Campaign: The 3/15th Punjab Regiment in Aden prepare to invade Assab, the last Italian port on the Red Sea, on 10 June. This is Operation Chronometer. Destroyer HMS Dido heads out during the night to bombard the port just before sunrise on the 10th.
 |
| Kapitänleutnant Herbert Kuppisch of U-94, St. Nazaire, France, 9 June 1941 (Buchheim, Lothar-Günther, Federal Archive, Bild 101II-MW-3495-04). |
While U-46 has one more patrol to go, this is its last sinking. During its career, U-46 has sunk 20 merchant ships of 85,792 tons, two auxiliary warships of 35,284 tons, and damaged five other ships (one written off). After its next uneventful patrol, U-46 serves as a training boat with the 26th U-boat Flotilla.
U-101 (Kptlt. Ernst Mengersen), on its 8th patrol out of Lorient in the mid-Atlantic west of Ireland, torpedoes and sinks 1190 ton British freighter Trevarrack. All 45 men onboard perish despite Mengersen seeing three lifeboats launch.
The Luftwaffe (Focke-Wulf Fw 200 aircraft of I Staffeln, Kampfgeschwader 40) bombs and sinks 942-ton British freighter Diana southeast of Iceland. There is one death, the survivors are taken aboard ASW trawler Cape Portland.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 844-ton British freighter Dagmar south of Bournemouth. There are three deaths.
The Luftwaffe (Focke-Wulf Fw 200 aircraft of I Staffeln, Kampfgeschwader 40) bombs and sinks 1894-ton Finnish freighter Fenix west of the Faroe Islands and southeast of Iceland. There is one death.
The Luftwaffe bombs and badly damages 174-ton British freighter Remagio off Bamburgh, Northumberland in the North Sea. The crew abandons the ship, and it drifts ashore. Efforts are made to salvage it, and eventually, it will be refloated and repaired. Some sources place this incident on 8 June.
Belgian 5382-ton freighter Persier, beached during a storm east of Vik in Myrdalur, Iceland in February, breaks her keel while being towed to the Kleppsvik Strand and is beached again.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Urge attacks an Italian freighter northwest of Lampedusa but misses.
The NEF continues expanding its support services at St. John's when auxiliary oiler HMS Clam arrives.
Royal Navy destroyer HMS Zetland (L59) is launched.
Canadian corvette HMCS Saskatoon ( Lt. Joseph S. Scott) is commissioned, minesweepers Canso (North Vancouver) and Granby (Quebec) are launched.
 |
| HMS Zetland (L59), launched at Glasgow, Scotland on 9 June 1941. It later became Norwegian destroyer KNM "Tromsø." |
Spanish 2421 ton freighter Sabina hits a mine and sinks 40 miles (74 km) off Genoa, Italy. Everyone survives.
Royal Navy landing barge SD15 "Leaving" makes it to Sidi Barrani from Crete. It is sailed by an English and Australian crew who stole the craft from the Germans. It is one of the last escape boats from Crete.
In Malta, there is an uproar because they find out there is an Axis informant on the island. Lord Haw-Haw, who makes propaganda broadcasts from Berlin, mentions that gas respirators on Malta feature yellow flaps. The flap is to differentiate British soldiers from enemy invaders who also are wearing gas masks. However, the islanders get some good news when two captured Italian aviators deny that an invasion force is being assembled in Sicily.
RAF fighters shoot down an Italian SM-79 bomber off Malta, and perhaps another, and two others are damaged. The RAF loses a Hurricane.
 |
| Chopping cotton on rented land near White Plains, Greene County, Georgia. The photograph was taken in June 1941 by Jack Delano (original color photo, Library of Congress LC-USF35-599). |
German Military: The Wehrmacht continues assembling along the Soviet border. The Luftwaffe now is transferring planes to forward airfields. Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, remains scheduled to begin on 22 June.
From Berchtesgaden, Hitler issues Fuhrer Directive No. 31, "German Military Organisation in the Balkans." It intends to "establish a clear and unified system of command in the occupied areas of the Balkans." He appoints Field Marshal List, still in the region following his command of German forces during Operation Marita, as the first Commander Armed Forces Southeast. He lists other appointments in the region to be filled by others. The order seeks to ensure the "coordinated defense" of the region, both from external and internal (partisan) threats. He sets the organization and establishment of Crete as the "most urgent task confronting us in the southeast" due to its usefulness to the Luftwaffe. The Italians shall occupy the eastern portion of Crete, but be subordinate to the Wehrmacht. This Directive supersedes Fuhrer Directive No. 29 of 17 May "in so far as it is superseded by the above orders."
Hitler calls his top generals to the Berghof for the final planning of Operation Barbarossa. While the plan is finalized, there remains quite a bit of disagreement about the proper objectives of the advance - Hitler prefers to focus on the southern prong to secure the grain of the Ukraine and Soviet oilfields, while some generals feel that Moscow in the center is the proper objective.
Canadian Military: Leading Airman W. McCulloch of 31 SFTS Kingston, Ontario, is killed when his Battle crashes near Gananoque, Ontario during training.
US Military: The US military terminates plans to occupy the Azores in the event of a German invasion due to military intelligence indicating that Hitler has no plans to invade Spain and Portugal.
 |
| Funeral of Kaiser Wilhelm, 9 June 1941. Leading the dignitaries is Field Marshal August von Mackensen. |
British Homefront: The UK establishes a national Fire Service Council. This results from issues arising during the Blitz from fire services in one town not wishing to help fight fires elsewhere - or only doing so for a price. The 1400 local fire brigades are merged into 32 regional brigades.
commencement address at the Georgia School of Technology in Atlanta. In his speech, entitled "We are Now Nearing the Fateful Hour," Cox states in part:
I have never believed, nor do I now, that the need will come of sending our soldiers overseas. It is machines not men that we must supply.This capsulizes the Isolationist view, that the US should not get entangled in overseas wars, but it is fine to give them the weapons with which to fight.
The Los Angeles Police Department tries to escort a worker across the picket line at North American Aviation in Inglewood, California early in the morning, but that just causes a fight to break out. President Roosevelt, as he has warned he will do, decides to end the strike. He issues Executive Order 8773, instructing the Secretary of War to send in troops. He explains that the strike is "seriously detrimental to the defense of the United States." The US Army (the 3rd Coast Artillery from Ft. MacArthur and two battalions from the 15th Infantry armed with rifles and bayonets) then disperses the picketers. The police arrest about 20 strikers for failing to leave.
U-46, which gets its final victory today, becomes the subject of "Das Boot" (1981), directed by Wolfgang Petersen and starring Jürgen Prochnow, which is based on the novel by Lothar G. Buchheim.
 |
| Benito Mussolini on the cover of Time magazine, 9 June 1941. |
June 1941
June 1, 1941: Farhud Pogrom
June 2, 1941: Massacres on Crete
June 3, 1941: Kandanos Massacre
June 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes Away
June 5, 1941: Death in Chungking
June 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar Order
June 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at Pessac
June 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and Lebanon
June 9, 1941: Litani River Battle
June 10, 1941: British Take Assab
June 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond Russia
June 12, 1941: St. James Agreement
June 13, 1941: Lützow Damaged
June 14, 1941: Latvian June Deportations
June 15, 1941: Operation Battleaxe
June 16, 1941: The Old Lion
June 17, 1941: British Spanked in North Africa
June 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its Back
June 19, 1941: Cheerios Introduced
June 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air Force
June 21, 1941: Damascus Falls
June 22, 1941: Germany Invades Russia
June 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes Havoc
June 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius Fall
June 25, 1941: Finland Declares War
June 26, 1941: Bombing of Kassa
June 27, 1941: Encirclement At Minsk
June 28, 1941: Minsk Falls
June 29, 1941: Brest Fortress Falls
June 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top Ace
2020