Wednesday 11 March 1942
 |
| HMS Naiad, sunk in the Mediterranean on 11 March 1942. |
General Jonathan Wainwright now commands in Luzon, though MacArthur has indicated that he intends to continue to control operations through proxies. Wainwright commands roughly 95,000 Allied forces on Bataan and Corregidor. The Japanese commander, General Homma, is under firm orders from Tokyo to resume his offensive and evict the remaining Allied forces from the Philippines.
 |
| A US Army M2A4 light tank in British service, 11 March 1942. © IWM (H 17816). Many of these tanks served in Burma. |
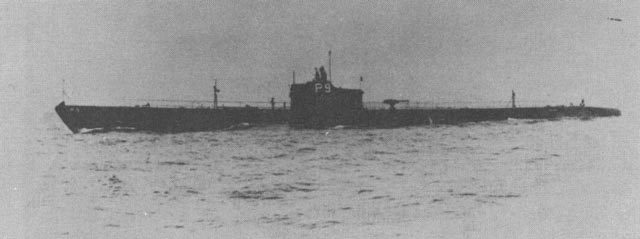 |
| USS Pollack (SS-180). Among its achievements was being among the first three US submarines on war patrol during World War II, the first to reach Japanese waters, and the first to get a confirmed victim (USS Pollack SSN 603). |
Japanese submarine I-2, operating off West Sumatra, torpedoes and sinks 4360-ton British passenger/cargo vessel SS Chilka. There are seven dead and at least three survivors.
US 4932-ton passenger/cargo ship SS Mount McKinley grounds off Unimak Island, Aleutians and is wrecked. Everyone survives.
 |
| PB2Y-3 at Noumea Harbor New Caledonia March 11, 1942 (USAF). |
European Air Operations: After several days of full-strength raids, the RAF takes a day off to recuperate.
 |
| Fukushu Maru, sunk on 11 March 1942. |
U-701 (Kptlt. Horst Degen), on its second patrol out of St. Nazaire, torpedoes and sinks 507-ton Royal Navy trawler HMT Stella Capella about 12 miles southeast of Vattarnes Lighthouse, Iceland. The trawler is heading to Stornoway to repair its defective anti-submarine equipment. All 33 men on board perish.
U-94 (Oblt. Otto Ites), on its third patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 1630-ton Norwegian freighter Hvoslef about two miles east of Fenwick Island off Delaware Bay. There are six dead and three injured men who required hospitalization out of 14 survivors.
Italian submarine Enrico Tazzoli (Cmdr Carlo Fecia di Cossato) sinks 3628-ton Panamian transport SS Cygnet about four miles east of Dixon's Light, San Salvador Island, Bahamas. Cossato uses his deck gun in addition to a torpedo, apparently to economize on torpedoes during a successful patrol far from his base. All 30 men aboard survive.
German E-boat S-70 torpedoes and sinks 951-ton British collier SS Horseferry off Sheringham. There are 10 deaths.
 |
| "Survivors of HMS NAIAD onboard HMS JERVIS." 11 March 1942. © IWM (A 8389). |
Malta comes under the jurisdiction of Commander in Chief Middle East Forces. Naval and RAF garrisons are under command of Commander in Chief Mediterranean and Air Officer Commanding in Chief, respectively. Lieutenant General Sir William Dobbie, Governor of Malta, remains commander in chief, but his days are numbered. The Axis has been pounding the island relentlessly in recent weeks and Winston Churchill is casting about for a replacement for Dobbie. There are some highly placed individuals who believe that Dobbie is a bit too religious and fatalistic.
 |
| Italian police at a conference in Berlin (Oranienburg), 11 March 1942 (Federal Archive Bild 121-1080). |
Anglo/Indian Relations: Following closely on President Roosevelt's cable suggesting political reform in India, Prime Minister Churchill issues a statement in which he agrees to negotiations with Indian leaders, including the Indian Congress Party, and appoints Sir Stafford Cripps as the negotiator. Cripps will leave on 22 March. Churchill's main goal is India's full participation in the war effort. For this, he embraces the "Draft Declaration" which contemplates self-government after the war. Sending Cripps is a calculated move by Churchill, who views him as a political rival and calculates that failure in India will damage Cripps.
Brazil: President Getúlio Vargas issues a decree reiterating his authority to declare war or impose a state of national emergency. Brazilians are worried about U-boat attacks in the Caribbean and are preparing to seize Axis nationals and their property.
American Homefront: In Omaha, Nebraska, 11-year-old Warren Buffett buys his first shares of stock (Buffett sometimes gives a date of 12 March 1942). They are three shares of Cities Service preferred stock. Being underage, he must use his father's brokerage account. The purchase consumes all of the money Buffett has saved since age 6. "I went all in," Buffett reminisced in February 2019. "I had become a capitalist, and it felt good."
 |
| "Li'l Abner" comic strip by Al Capp from 11 March 1942. |
March 1942
March 1, 1942: Second Battle of Java Sea
March 2, 1942: Huge Allied Shipping Losses at Java
March 3, 1942: Japan Raids Western Australia
March 4, 1942: Second Raid On Hawaii
March 5, 1942: Japan Takes Batavia
March 6, 1942: Churchill Assaults Free Speech
March 7, 1942: British Defeat in Burma
March 8, 1942: Rangoon Falls to Japan
March 9, 1942: Japanese Conquest of Dutch East Indies
March 10, 1942:US Navy attacks Japanese Landings at Lae
March 11, 1942: Warren Buffett's First Stock Trade
March 12, 1942: Japan Takes Java
March 13, 1942: Soviets Attack In Crimea Again
March 14, 1942: The US Leans Toward Europe
March 15, 1942: Operation Raubtier Begins
March 16, 1942: General MacArthur Gets His Ride
March 17, 1942: MacArthur Arrives in Australia
March 18, 1942: Japan Attacks In Burma
March 19, 1942: Soviets Encircled on the Volkhov
March 20, 1942: "I Shall Return," Says MacArthur
March 21, 1942: Germans Attack Toward Demyansk
March 22, 1942: Second Battle of Sirte
March 23, 1942: Hitler's Insecurity Builds
March 24, 1942: Bataan Bombarded
March 25, 1942: Chinese Under Pressure in Burma
March 26, 1942: Win Or Die, Vows MacArthur
March 27, 1942: The Battle of Suusari
March 28, 1942: The St. Nazaire Commando Raid
March 29, 1942: The Free Republic of Nias
March 30, 1942: Japanese-Americans Off Bainbridge Island
March 31, 1942: Japanese Seize Christmas Island
2020





