Thursday 21 August 1941
Let us, like one man, rise to the defense of our city, of our homes and families, our freedom and honor. Let us do our sacred duty as Soviet patriots in our relentless struggle against a hated and ruthless enemy, let us be vigilant and merciless in dealing with cowards, panic-mongers, and deserters, let us establish the strictest revolutionary discipline in our city. Armed with such iron discipline and Bolshevik organization, let us meet the enemy and throw him back.Among other things, the Appeal is notable for its references to "Soviet patriotism" - a concept that the Soviets will quickly replace with calls to protect "Mother Russia," a much more compelling concept. Soviet citizens see phrases like "iron discipline" and shudder.
In the evening, Stalin calls Zhdanov and Voroshilov and berates them. He asks why they had set up the aktiv without first asking his permission, and why Zhdanov and Voroshilov themselves were not actually members of it (presumably so that they could control it). They replied lamely that the council would help with the defense of the city, which did not mollify Stalin at all.
Stalin immediately orders a "review" of the Council for the Defense of Leningrad and that its membership should be "revised" to include Voroshilov and Zhdanov. He also officially rebukes the two men for forming worker "battalions" with inadequate weapons and orders that new leaders of these battalions - selected by the Kremlin - be installed.
Stalin's reaction seems excessive until you remember that the previous Russian revolution - the one that installed him as its dictator - began in Leningrad. Having the city cut off by the Germans means it cannot be supplied and thus is at risk, but it also means that Stalin himself has no direct control over it. This raises all sorts of unpleasant possibilities for the Kremlin in general and Stalin in particular. Stalin's chief of police, Lavrentiy Beria, has his ear at this time and is feeding Stalin's innate paranoia about disloyalty and insurrections that stem from Stalin's own rise to power.
 |
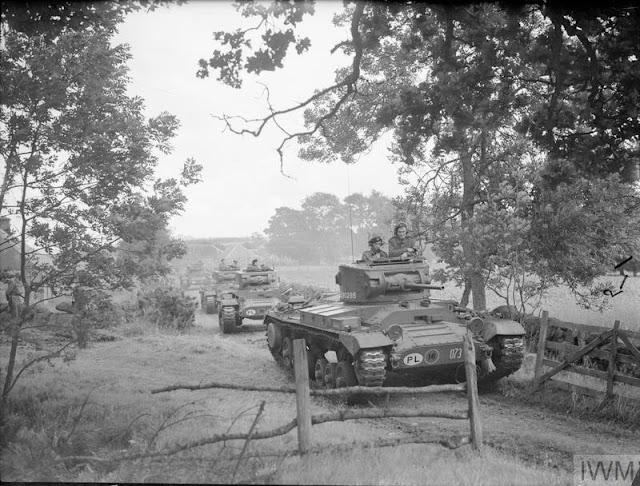
| "A Valentine Mark III tank (T 1290288) of the 2nd Battalion, 1st Tank Regiment (1st Polish Corps) on exercise in Scotland, 21 August 1941. Photograph taken during General Alan Brooke's visit to the Scottish Command." (© IWM (H 12987)). |
The proposal by the army for the continuation of the operations in the east, dated 18.8, do not meet with my approval. I order the following: The principal objective that must be achieved before the onset of winter is not the capture of Moscow, but rather in the south the occupation of the Crimea and the industrial and coal region of the Donets, together with the isolation of the Russian oil regions in the Caucasus. In the north, the encirclement of Leningrad and the union with the Finns.General Franz Halder, who also sees Moscow as the best objective, writes in his diary, "It [this Hitler directive] is decisive for the outcome of the campaign." General Alfred Jodl, chief of operations at OKW, quickly instructions Commander of the Army Field Marshal von Brauchitsch to focus on seizing the Crimea and the materials-rich areas in the south. The only important objective in the north is Leningrad, and Moscow is a secondary objective.
In the Far North sector, the Finnish General Headquarters orders IV Corps (Lt. Gen. Lennart Oesch) to begin pursuing the retreating Soviets toward Viipuri. This is a day earlier than planned, and the change is due to the Finns noticing that the Soviets have left. The overall intent is to take Viipuri and all of western Karelian Isthmus.
The defending Soviet troops of 43rd, 115th, and 123rd Rifle Divisions by now have escaped from their exposed positions further north and have fallen back on the city. This has improved the overall Soviet chances of holding a line north of Leningrad at the narrow part of the Karelian Isthmus. The Finnish II Corps and 18th Division, assisted by other units, continue consolidating their bridgehead over the Vuoksi River. The Soviets plan to swing the 115th and 123rd Rifle Divisions over to counterattack them in order to establish a solid line on the Vuoksi. The Finns take Kexholm (Käkisalmi, Priozersk) on the northeast shore of Lake Ladoga.
 |
| "Valentine Mark III tanks of the 2nd Battalion, 1st Tank Regiment (1st Polish Corps) on exercise in Scotland. Photograph was taken during General Alan Brooke's visit to the Scottish Command." 21 August 1941 (© IWM (H 12994)). |
In the Army Group Center sector, the Soviets retreat from Gomel after a fierce defense and several unsuccessful counterattacks. German Panzer Group 2 (General Guderian) continues advancing south between Bryansk and Gomel toward Kyiv. Soviet 24th Army continues attacking the German "lightning rod" position at Yelnya throughout the day, but Red Army General Rakutin finally receives Stavka permission to stop his attacks until he gets reinforcements and replacements.
German 1.SS-Infanterie-Brigade (mot.) Leibstandarte der SS Adolf Hitler (Obergruppenfuhrer Sepp Dietrich) captures Kherson (Cherson). Sixth Army continues pursuing the retreating Soviet 5th Army, and LI Corps establishes a crossing of the Dneipr at Okuminovo, north of Kyiv.
General Hoth completes a refit of Panzer Group 3. He notes the following strengths:
- Panzer Division 7: 45%
- Panzer Division 12: 45%
- Panzer Division 19: 60%
- Panzer Division 20: 49%
 |
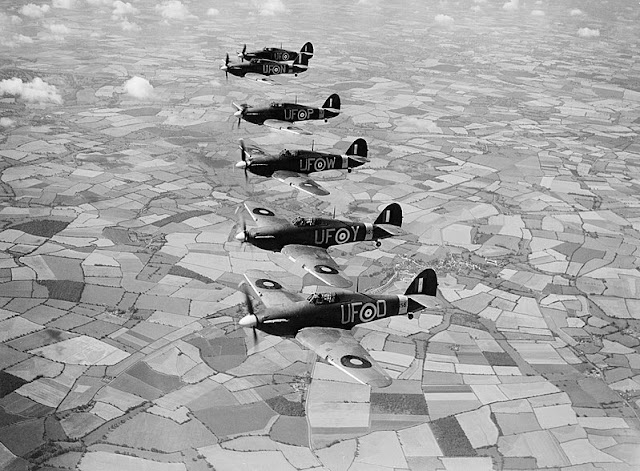
| "Airacobra Mark I, AH577, of No. 601 Squadron RAF based at Duxford, Cambridgeshire, in flight. This aircraft was coded UF-M and was for a time the personal aircraft of the Squadron's Commanding Officer." 21 August 1941 (© IWM (CH 3711)). |
An RAF Hurricane Mk. IIB on a delivery flight, S/n Z5070, crash-lands at Athboy, County Meath. The Irish Army Air Corps repairs the damaged plane and puts it into service as the Corps' sixth fighter (the others are three Gloster Gladiator Mk. Is, another Hurricane Mk. IIB, and a Hurricane Mk. X).
 |
| "Airacobra Mark I, AH576 ‘UF’, of No. 601 Squadron RAF, on the ground at Duxford, Cambridgeshire. The aircraft was detached to Reid & Sigrist Ltd for trials on 7 September, following which it was to have been returned to the Squadron (hence the proprietary application of the unit code letters and squadron badge on the fin), but was written off on 5 October 1941." 21 August 1941 (© IWM (CH 3723)). |
Admiral Tributs' plan is based on aerial reconnaissance showing that the Germans have all of their troops in the front lines and none in reserve. He believes that any quick thrust to the east into the rear of their lines approaching Leningrad might catch them off guard. The plan is imaginative and daring and is better than anything else being considered. However, Stalin apparently is worried about a new, growing power block centered around Leningrad that is outside of his control due to the intervening presence of the Wehrmacht. The official reason given for turning it down is that it would be too difficult to assemble sufficient forces.
Soviet planes attack the German 3rd Ferry Battalion which is ferrying troops in Riga Bay in company with two Soviet destroyers. Some small Soviet ships, including freighter Leeni, hit mines and sink in German Minefield Juminda between Hogland Island (Suursaari) to Reval, Estonia.
Soviet destroyers Artem and Surovyi hit and damage German gunboat SAT-1 Ost in the Baltic. The gunboat's skipper manages to beach the boat, and it is later salvaged. There is one death.
 |
| "Six Hurricane Mk IIBs of 'B' Flight, No. 601 Squadron RAF based at Duxford, Cambridgeshire, flying in starboard echelon formation near Thaxted, Essex." 21 August 1941 (© IWM (CH 3517)). |
In a companion operation to Operation Dervish, today at 22:00 Force K leaves Hvalfjord bound for operations against coal fields in Bergensburg, Norway, with part of the force proceeding on to Archangel. The voyage to Archangel is planned to take ten days.
The Royal Navy is conducting submarine patrols along the Arctic sea route. Submarine HMS Trident launches an attack on a Norwegian tanker and an accompanying Kriegsmarine artillery training ship off the northern coast of Norway but misses.
The Soviets also are active along the northern sea routes. Soviet submarine M-172 (Lt Cdr Israel Fisanovich) makes a daring entrance into the Liinakhamari fjord but misses when it attacks German freighter Monsun docked at the Pechenga pier (some accounts state that he sinks a ship).
While laying a minefield about 50 km off Jæderens Point/Egerö, southeastern Norway, Free French submarine Rubis (Lt Cdr Rousselot) attacks two freighters but misses. It does sink 4360-ton Finnish freighter Hogland with one of the mines that it lays. Rubis itself is damaged when two torpedoes misfire and explode just after leaving the submarine. Rubis eventually makes it to Dundee for repairs. The Germans order the 11th Minesweeping Flotilla to the area to clear the minefield.
During a Luftwaffe attack on Southampton, the Germans bomb and sink French drifter Gloria in Excelsis Deo. The drifter later is raised and repaired.
A Luftwaffe Focke-Wulfe Fw-200 Condor spots Convoy OG-71 and radios its position.
Convoy HX-146 departs from Halifax bound for Liverpool.
Royal Navy destroyer HMS Laforey (G-99, Captain Reginald M. J. Hutton) is commissioned.
Canadian minesweeper HMCS Grandmere is launched at Montreal.
US submarine USS Gato is launched.
U-376 (Oblt. Friedrich-Karl Marks), U-435 (Kptlt. Hans-Henrich Giessler), and U-584 (Kptlt. Joachim Deecke) are commissioned, U-174 is launched.
 |
| HMS Taku at Malta ca. August 1941. |
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 311-ton Egyptian freighter El Fath at Famagusta. There are four deaths.
British 10,893-ton freighter Durham, which arrived at Malta during Operation Substance, departs from Malta toward Gibraltar without an escort. A fast ship, it perhaps is counting on the distraction caused by Force H. Durham hits a mine west of Pantelleria Island, but eventually makes it to Gibraltar for repairs.
Operation Treacle, the replacement of the Australian 18th Infantry Brigade at Tobruk with troops of the Polish Carpathian Brigade, continues. Destroyers Griffin, Jackal, and Kandahar carry the troops.
Early in the morning, around 06:30, the Luftwaffe (Junkers Ju-88 aircraft of III/LG.1) hits and damages destroyer Nizam returning from an Operation Treacle run. Nizam, which is hit north of Bardia, is taken under tow until it regains engine operation. Nizam makes it back to Alexandria under its own power.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Taku arrives at Malta with supplies from Alexandria.
Ten Wellington bombers based on Malta damage buildings and port infrastructure at Tripoli Harbor.
Three Italian aircraft make low-flying attacks on Hal Far and the Safi dispersal area. A dogfight with Hurricanes ensues. A Bofors crew guarding the area claims to make some hits on one of the attackers.
Battle of the Pacific: German 5098-ton freighter Odenwald leaves Yokohama, Japan for Bordeaux, France. Japanese 5019-ton freighter Teisen Maru, formerly German Ursula Rickmers, arrives at Tokyo successfully after her first charter trip carrying coal and lumber from Kushiro, Hokkaido to Nagoya, Japan.
German/Spanish Relations: The Spanish Blue Division (250th Infantry Division) begins moving to the Eastern Front south of Leningrad.
US/Japanese Relations: Ambassador Nomura sends a message to Tokyo indicating that President Roosevelt is seriously interested in the resumption of negotiations. Nomura even provides a sample response to Tokyo for its consideration.
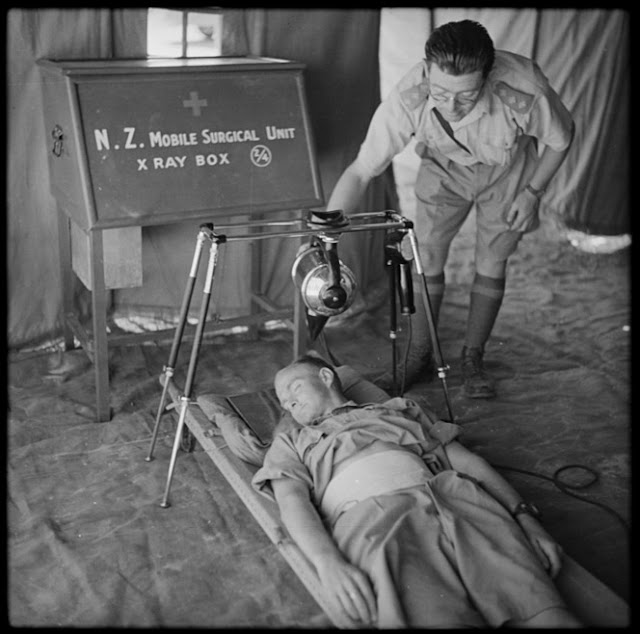 |
| Demonstration of a New Zealand Mobile Surgical Unit’s portable X-ray machine. Taken in Egypt, 21 August 1941, by an official war photographer. |
Japanese Military: The Imperial Japanese Navy requisitions 5350-ton cargo ship Saigon Maru for use as an auxiliary cruiser and also requisitions 2681-ton freighter Senko Maru.
US Government: President Roosevelt gives Congress a "copy" of the Atlantic Charter agreement recently reached with Winston Churchill in Canada. As Roosevelt later notes:
There isn't any copy of the Atlantic Charter, so far as I know. I haven’t got one. The British haven’t got one. The nearest thing you will get is the [message of the] radio operator on Augusta and Prince of Wales. That's the nearest thing you will come to it. ... There was no formal document.Roosevelt briefs Congress on the agreement, summarizing its points, stating in part:
Finally, the declaration of principles at this time presents a goal which is worth while for our type of civilization to seek. It is so clear cut that it is difficult to oppose in any major particular without automatically admitting a willingness to accept compromise with Germans; or to agree to a world peace which would give to Reich domination over large numbers of conquered nations. Inevitably such a peace would be a gift to Hitlerism to take breath--armed breath--for a second war to extend the control over Europe and Asia to the American Hemisphere itself.The statement concludes:
It is also unnecessary for me to point out that the declaration of principles includes of necessity the world need for freedom of religion and freedom of information. No society of the world organized under the announced principles could survive without these freedoms which are a part of the whole freedom for which we strive.
It is around this date that a newspaper reporter coins the term "Atlantic Charter" to refer to the agreement.
China: Japanese bombers sink two Chinese gunboats, the “Jiangxi” and “Jiangkun,” at Bazhong, Sichuan Province, China.
China: Japanese bombers sink two Chinese gunboats, the “Jiangxi” and “Jiangkun,” at Bazhong, Sichuan Province, China.
 |
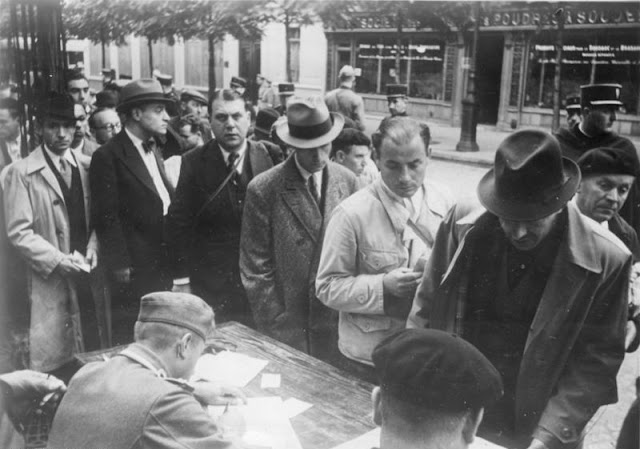
| "After the occupation of France by the fascist German Wehrmacht, the German racial laws are also enforced here. The arrest of Jews in Paris in August 1941." (Federal Archive, Bild 183-B10923). |
After direct orders from Sixth Army Commanding General Walther von Reichenau, German 295th Division participates to some extent in the killing of about 90 Jewish children who have been abandoned and locked in a school at Bila Tserkva. The incident is notable for many reasons, including a direct protest to the army by two Wehrmacht chaplains about the killings which delayed it by a day. Oberst (Lieutenant-Colonel Helmuth Groscurth) has put his own career in jeopardy by forwarding the protest of the chaplains to the army headquarters. Technically, SS units are under army control, so the army has the final say on who is killed and who is not. Catholic Father Ernst Tewes, one of the two chaplains (the other being Lutheran Pastor Gerhard Wilczek), later comments:
All those we wanted to save were shot. Because of our initiative it just happened a few days later than planned.Reichenau is put out by the entire affair. He writes in response to the request:
The conclusion of the report in question contains the following sentence: "In the case in question, measures against women and children were undertaken which in no way differ from atrocities carried out by the enemy about which the troops are continually being informed." I have to describe this assessment as incorrect, inappropriate and impertinent in the extreme. Moreover, this comment was written in an open communication which passes through many hands. It would have been far better if the report had not been written at all.There is no question that the regular army participated to some extent in the killings aside from Reichenau's order. A witness, an SS soldier, recalled later that the regular army dug the trench into which the children fell after being shot. Exactly who shot the children is unclear. Ukrainians unhappily watch the executions.
A concentration camp at Jasenovac, Croatia becomes operational.
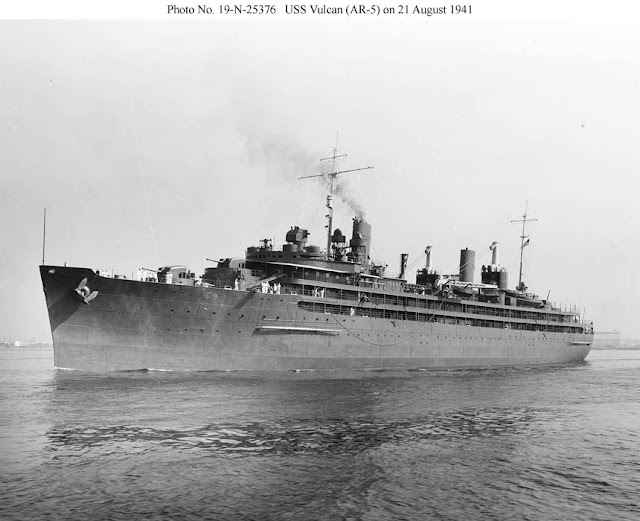 |
| Repair ship USS Vulcan (Commander Leon S. Fiske, AR-5) near the Philadelphia Navy Yard, 21 August 1941 (Photo No. 19-N-25376 Source: U.S. National Archives, RG-19-LCM). |
Paramount Pictures film "World Premiere" is released. It stars John Barrymore, Frances Farmer, Ricardo Cortez, and Sig Ruman. It is a comedy about the machinations behind releasing an anti-Hitler film.
 |
| A German sentry in France with his BMW R75 motorcycle (colorized). |
August 1941
August 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement Closes
August 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces Euthanasia
August 4, 1941: Hitler at the Front
August 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk
August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the Arctic
August 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb Berlin
August 8, 1941: Uman Pocket Captured
August 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia Bay
August 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over Berlin
August 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in Life
August 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter Announced
August 13, 1941: The Soybean Car
August 14, 1941: The Anders Army Formed
August 15, 1941: Himmler at Minsk
August 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270
August 17, 1941: Germans in Novgorod
August 18, 1941: Lili Marleen
August 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 Destruction
August 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad Begins
August 21, 1941: Stalin Enraged
August 22, 1941: Germans Take Cherkassy
August 23, 1941: Go to Kiev
August 24, 1941: Finns Surround Viipuri
August 25, 1941: Iran Invaded
August 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the Desna
August 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate Tallinn
August 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets Savaged
August 29, 1941: Finns take Viipuri
August 30, 1941: Operation Acid
August 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No
2020











