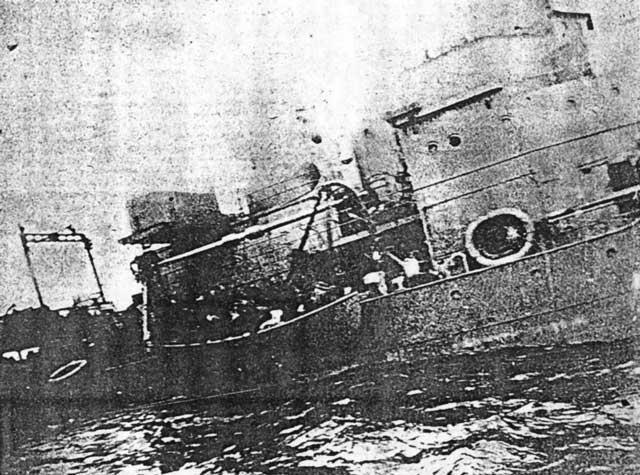
Monday 23 February 1942
 |
| U-751 arrives at St. Nazaire, 23 February 1942 (Sheep, Federal Archive Picture 101II-MW-3691-05). |
 |
| The 23 February 1942 Adelaide, Australia, The Advertiser highlights Japanese losses off Bali. The truth is far grimmer, but people would rather read positive stories. |
Early in the morning of the 23rd, six B-17s in two flights of 3 of the Kangaroo Squadron (435th Bomb Squadron of the 19th Bomb Group) based at Garbutt Field, Townsville, Australia, bomb the Japanese fortress at Rabaul. This is the first such bombing mission. Only two of the bombers actually drop their bombs. One of these two B-17s is "Swamp Ghost." Due to weather and mechanical issues, only one bomber actually hits the target. "Swamp Ghost" has mechanical issues that prevent its bomb bay doors from opening on its first run, so it makes another pass and successfully drops its bombs. However, this second pass exposes "Swamp Ghost" to ground fire. It takes heavy damage (121 bullet holes) which forces its crew to crash-land in a swamp eight miles from the northern Papua New Guinea coast.
The "Swamp Ghost" crew survives an arduous six-week trek out of the swamp. The plane is left there virtually intact until being rediscovered by Australian Army troops in a helicopter in 1972. In 2006, "Swamp Ghost" is removed from the swamp by cargo helicopter and currently is on display in Hangar 19 at Ford Island in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii.
 |
| Comrade Stalin is on the front page of the Moscow Bolshevik for 23 February 1942. |
European Air Operations: The RAF has a fairly light day of activity, sending only 23 Hampdens to drop mines off Wilhelmshaven and Heligoland, as new commander General Arthur "Bomber" Harris gets familiar with his forces. Harris has a mandate to turn the RAF as an instrument of vengeance against the Reich by launching terror raids against population centers rather than focusing on military targets as has been the case to date.
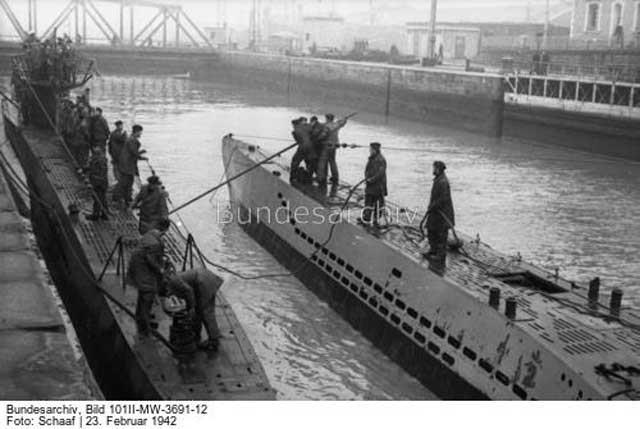 |
| U-751 arrives at St. Nazaire, 23 February 1942. It is tieing up inboard of U-85 (right). (Sheep, Federal Archive Picture 101II-MW-3691-12). |
U-129 (Kptlt. Asmus Nicolai Clausen), on its fourth patrol out of Lorient, has a big day northeast of Barima, Venezuela. Attacking at 01:20, the submarine sinks 1754-ton Canadian freighter George L. Torian (15 deaths, 4 survivors). At 04:43, it spots and sinks 5658-ton US freighter West Zeda (all 35 survive). Then, at 15:04, Clausen torpedoes and sinks 1904-ton Canadian freighter Lennox (2 deaths and 18 survivors). All of these ships are independents, as convoys have not yet been organized this far south.
 |
| HMAS Ping Wo. A 3105-ton Chinese river steamer, Ping Wo is used on 23 February 1942 to tow the disabled HMAS Vendetta from the Javan port of Tanjung Priok to Fremantle, Western Australia. This is part of the general evacuation of Java. The tow to Fremantle takes 62 days, or 72 days if you count an additional tow to Port Phillip Bay (Royal Australian Navy). |
U-161 (Kptlt. Albrecht Achilles), on its second patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 7001-ton US freighter Lihue about 275 miles west of Martinique. Lihue is another independent, which U-boat captains have found are easy targets. U-161 surfaces after hitting the Lihue with a single torpedo at 06:43 and engages in a brief gun duel with the freighter before submerging again and waiting for it to sink. All 45 men on board survive.
 |
| The 23 February 1942 Life magazine features guns at the Brooklyn Navy Yard on the cover. |
British/Australian Relations: After urgent demands by Australian Prime Minister John Curtin, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill confirms that the Australian 6th and 7th Divisions which are at sea will be returned to Australia for the defense of the homeland.
Allied Relations: The United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand reach an agreement (Master Mutual Aid Agreement) regarding the conduct of the war in the Southwest Pacific.
 |
| On Malta, sailors draw their rum rations. "Wherever they find themselves the ratings draw their issue. In this case on the top of the RN Signal Station at Valletta Palace." 23 February 1942. © IWM (A 9244). |
USAAF General Ira C. Eaker establishes the headquarters of his VIII Bomber Command at Daws Hill Lodge, High Wycombe, Buckinghamshire, England.
Major General Lewis H Brereton, Commanding General USAAF 5th Air Force, departs from Australia to India. ABDA Vice Commander Major General George H. Brett assumes control of 5th Air Force Operations in Brereton's absence. Brett today flies from Java back to Australia as part of a broader evacuation of the island. Brereton's mission in New Delhi, India, is to begin to organize the new Tenth Air Force, which includes preparation for the famous "Hump" Airlift to China.
 |
| U-123 (28-year-old German Captain Reinhard Hardegen) returns to Lorient after a successful patrol off the east coast of the United States, February 1942 (Dietrich, Federal Archive Bild 101II-MW-3983-23). |
Italian Homefront: It is a day of speeches by leaders around the world, and that includes Benito Mussolini. In Rome, he gives a typical lengthy speech during which he states:
We call bread, bread and wine, wine, and when the enemy wins a battle it is useless and ridiculous to seek, as the English do in their incomparable hypocrisy, to deny or diminish it.Mussolini is expressing a common theme of the Axis leaders that the world media is not giving due credit for their successes, a refrain also heard often from Hitler. Of course, the media they are concerned about is the Western media, and it is difficult to imagine them saying anything positive about Axis successes.
 |
| President Roosevelt during his fireside chat on 23 February 1942. While the chat is only broadcast over the radio, FDR asks listeners to pull out a map - then gestures during his speech toward the places that he is talking about on his own map (Libary of Congress). |
We have most certainly suffered losses – from Hitler's U-Boats in the Atlantic as well as from the Japanese in the Pacific – and we shall suffer more of them before the turn of the tide. But, speaking for the United States of America, let me say once and for all to the people of the world: We Americans have been compelled to yield ground, but we will regain it. We and the other United Nations are committed to the destruction of the militarism of Japan and Germany. We are daily increasing our strength. Soon, we and not our enemies will have the offensive; we, not they, will win the final battles; and we, not they, will make the final peace."
Roosevelt also quotes Thomas Paine's refrain that "these are the times that try men's souls," and adds "tyranny, like Hell, is not easily conquered." This period following the fall of Singapore is an emotional low point of the war for the Allies, but FDR's frankness helps morale.
President Roosevelt's Executive Order 9066, which authorizes the internment of anyone of Japanese ancestry, arrives at Lt. General John L. Dewitt's West Coast headquarters of the Western Defense Command. He is now free to intern practically anyone he sees fit.
 |
| On 23 February 1942, USAAF Boeing B-17E Flying Fortress (41-2446) ditched in Agaiambo swamp, Papua New Guinea after running out of fuel. It was rediscovered in 1972 and removed from the swamp in 2006. Swamp Ghost is now on display in the Pacific Aviation Museum Pearl Harbor. |
February 1942
February 1, 1942: The US Navy Strikes Back
February 2, 1942: Germans Recovering in Russia
February 3, 1942: Japanese Shell and Bomb Singapore
February 4, 1942: Battle of Makassar Strait
February 5, 1942: Empress of Asia Sunk
February 6, 1942: The Christmas Island Body
February 7, 1942: The Double-V Campaign
February 8, 1942: Japan Invades Singapore
February 9, 1942: French Liner Normandie Capsizes
February 10, 1942: US Car Production Ends
February 11, 1942: Tomforce Fails on Singapore
February 12, 1942: The Channel Dash
February 13, 1942: Japanese Paratroopers In Action
February 14, 1942: RAF Orders Terror Raids
February 15, 1942: Japan Takes Singapore
February 17, 1942: Indian Troops Defect to Japanese
February 18, 1942: Battle of Badung Strait
February 19, 1942: FDR Authorizes Internment Camps
February 20, 1942: O'Hare the Hero
February 21, 1942: Crisis in Burma
February 22, 1942: Bomber Harris Takes Over
February 23, 1942: Bombardment of Ellwood, California
February 24, 1942: US Raid on Wake Island
February 25, 1942: Battle of Los Angeles
February 26, 1942: Gneisenau Eliminated
February 27, 1942: Battle of Java Sea
February 28, 1942: Battle of Sunda Strait
2020