Iran Invasion: A ceasefire is in effect in Iran as new Prime Minister Mohammed Foroughi discusses a settlement with the British and Soviets. A key question is what happens to German and Italian nationals present in Tehran. Foroughi basically agrees with the Allies that all Axis nationals should be handed over to the Allies and the German, Italian, Romanian, and Hungarian legations expelled. However, the decision is up to Reza Shah, and he prefers to allow them the Axis nationals and their families to escape.
The negotiations take on a weird slant because Foroughi fundamentally opposes Reza Shah's rule (Foroughi had been dismissed from a previous appointment as prime minister in 1935 due to family connections with an anti-reform riot in Mashhad). Basically, Foroughi views an Allied takeover as "liberation" from Reza Shah. Thus, in effect, Foroughi simply wants to surrender, let the Allies have whatever they want, and doesn't care what happens to Reza Shah or the Axis nationals. At least on his end, it is not an adversarial negotiation.
Reza Shah has different goals. He thus becomes the major stumbling block to a quick settlement, being the only one who wants to protect some semblance of Iranian sovereignty. The issue becomes critical because the Soviets have no time to waste and simply want to occupy the half of the country allocated to them and get back to fighting the Germans. They also are eager to open up as quickly as possible an "Iranian corridor" for Allied supplies safe from Axis submarines and Luftwaffe attacks. The British are more patient because the Qajar dynasty has served their interests over the years, but the Soviets are in a better position to take Tehran - which gives their wishes a little more emphasis.
 |
| Finnish troops fire a mortar, 29 August 1941 (SA-Kuva). |
Eastern Front: In his war diary, OKH Chief of Staff General Franz Halder confesses that "We still have no clear idea what the enemy is up to." This is the truest statement of the war. Halder notes in his entry total casualties for Operation Barbarossa through 13 August 1941:
- Wounded: 9,516 officers and 277,472 NCOs and soldiers
- Killed: 3,874 officers and 79,643 NCOs and soldiers
- Missing: 362 officers and 18,957 NCOs and soldiers
Total casualties to date are 389,924, or 11.4% of the initial strength of the Eastern Army.
In the Far North sector, Soviet forces at Viipuri (Vyborg) receive orders to retreat. Finnish 4th and 8th Infantry Divisions march into the city unopposed. One of the first things that the Finnish troops do is to raise a flag (actually, since they can't find a flag, they use a soldier's shirt) over the medieval castle's main tower. The flag that flew over the tower when the Finns handed the city over to the Soviets at the end of the Winter War is soon found and raised again (the flag is now in the central War Museum at Helsinki).
The Soviet troops are gone, but they remain intact and undefeated. They also have left many "presents" for the Finns throughout Viipuri in the form of boobytraps and time bombs. The news of the capture (or, recapture) electrifies the nation and is probably the happiest day of the entire war for the people of Finland. The Finns also make further advances in the direction of Leningrad, capturing Terioki, which is about 30 miles north of the city. They also cut the railroad running to Leningrad along the northwestern shore of Lake Ladoga. All of these successes, however, only bring the moment of truth closer in which they will have to tell the Germans that they will not attack Leningrad.
In the Army Group North sector, German troops complete the occupation of Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. Elsewhere, the front is relatively quiet due to poor weather. German troops are approaching the outer line of Leningrad's fortifications, but progress is slow all across the front. General Halder notes hopefully that "The Finns are making encouraging progress on Leningrad from the north." He does not realize yet that Field Marshal Mannerheim has no intention of actually attacking the city.
In the Army Group Center sector, General Guderian's Panzer Group 2 is counterattacked from both the west and east as he tries to break out from his bridgehead across the Desna River. General Halder, however, has no sympathy, noting in his diary that:
It is all Guderian's own fault. He devised this plan of attack and even the most naive enemy could not be expected to stand by passively while an enemy flank is pounding past his front.
Halder's real beef with Guderian is lingering anger over the latter's failure to convince Hitler to focus on Moscow rather than Kyiv. Halder is correct about tactics, of course, as a lateral movement along the front does, invariably, invite a flank attack. Guderian is struggling toward Konotop, the first stop on his way to a junction with Panzer Group 1 to the east of Kyiv.
In the Army Group South sector, the Soviets encircled at Odessa mount a fierce counterattack. They manage to push back the Romanian 4th, 11th, and 1st Army Corps in the area of Gnileakovo and Vakarzhany and give themselves a little breathing room. The Axis forces, however, remain in control and prepare to resume their own attacks on the 30th.
 |
| Spitfire MkIIB, UZ-N, P8342, after the sortie on 29 August 1941. Sgt Machowiak shot down a Bf109 on that flight, in return being shot up himself - note visibly damage empennages. |
European Air Operations: Weather is poor throughout the day and night, so not as much is accomplished as the RAF probably wished. During the day, the RAF sends 6 Blenheim bombers on a Circus mission to Hazebrouck and one to Dusseldorf. There are no losses, but the bombers achieve very little because out of all seven bombers, only one releases its bombs over its target (Hazebrouck).
After dark, RAF Bomber Command mounts raids on perennial favorites Frankfurt and Mannheim. It is a big night, with a maximum effort in the air. RAF raids still do not match the size of Luftwaffe raids at their peak, but RAF bombers tend to be larger than Luftwaffe bombers with larger bomb loads, so just looking at raw numbers of bombers can be deceptive.
Against Frankfurt, RAF Bomber Command sends 143 bombers (73 Hampdens, 62 Whitleys, 5 Halifaxes, and 3 Manchesters). This is the first 100-bomber raid on Frankfurt. The targets are railway installations and the harbor area. This raid is the first in which an Australian squadron, No. 455 (Squadron Leader French) participates. Two Hampdens and a Whitley are lost. Due to the poor weather accuracy is impossible, and the results reflect this. Some lucky hits damage a gasworks, but most of the bombs drop either aimlessly on vacant ground or on some houses. There are 8 deaths, 7 in a single house that is hit.
Against Mannheim, RAF Bomber Command sends 94 Wellington bombers, of which two are lost. The weather affects results here as well, with only minor and scattered damage. There is one injury.
Attacks on the French coast have become training exercises as much as real attacks due to their close proximity and the ease of locating the targets. Tonight, five Wellington bombers attack Le Havre without loss.
 |
| RAF Spitfire forced to make an emergency landing after air-to-air combat, Westende, 29 August 1941. (Photo CegeSoma, N° 12.999). |
Battle of the Baltic: The Baltic is littered with sinking and sunk Soviet ships from the evacuation convoys that left Tallinn. Destroyer Yakov Sverdlov, damaged on the 28th, goes under today, having been mined along with many other ships off Cape Juminda. Overall, about 30 of 200 Soviet vessels have been lost in one of the greatest naval disasters of the war.
Luftwaffe Junkers Ju-88s from II/KG77 and KGR806 return to the attack today after having had great success on the 28th. They again attack the Soviet convoys, now off Suursaari (Hogland Island). They hit several Soviet ships:
- 3974-ton freighter VT-543/Vtoraya Pyatiletka (beached)
- 1207-ton freighter VT-550/Siaulia (beached)
- 5920-ton repair ship Serp I Molot (beached)
- 2675-ton Soviet transport Tobol (sunk)
- freighter VT-523/Kazakhstan (makes it to Kronstadt)
VT-523/Kazakhstan barely makes it to port, and only does so after disembarking 2300 out of 5000 fleeing troops on board at Steinskar. The beached ships usually are destroyed quickly by the Luftwaffe, but at least most of the passengers can reach the shore.
Other German aircraft are in operation and hit additional ships in the Soviet evacuation convoys:
- 2317-ton transport VT-581/Lake Lucerne (sunk)
- Soviet transport Sigulda (sunk off Lavansaari Island)
- 2414-ton transport VT-529/Skrunda (damaged near Suursaari, sinks on the 30th)
- Soviet transport VT-520/Evald (sunk off Mohni Island)
- 1423-ton transport VT-563/Atis Kronvaldis (sunk off Lavansaari Island)
- 1791-ton VT-546/Ausma (sunk off Lavansaari Island)
- 206-ton transport VT-537/Ergonauts (sunk off Lavansaari Island)
In addition, another Soviet ship, transport VT-501/Balhash, hits a mine off of Lavansaari Island and sinks. Estonian 1879-ton transport Naissaar has especially bad luck. First, it hits a mine east of Mohni Island, Estonia, then the Luftwaffe finds it and sinks it.
There are scenes of chaos. For example, fully loaded 2026-ton passenger ship/freighter Vironia, bombed and damaged on the 28th, is taken in tow by Saturn. However, then Saturn hits a mine and has to release the tow. In the early morning hours of the 29th, Vironia drifts into a mine off Cape Juminda and sinks within five minutes. There are 1300 deaths.
The Soviets know that a disaster is happening offshore, of course, and organize a rescue operation composed of anything that floats on Suursaari. They sail out under the command of Captain G. Svayskov in a dozen old minesweepers, a division of patrol boats, six motor torpedo boats, eight submarine chasers, two tugs, four motorboats, two cutters, and rescue ship Meteor. It is a motley collection, but the ships float and manage to rescue 12,160 Soviet troops who otherwise would drown. Soviet submarine SHCH-322 accompanies the rescue ships but is lost at sea - presumably due to hitting a mine in the same minefield off Juminda Point.
The Germans and Finns know about the Soviet disaster as well. Finnish minelayers add another 24 mines to Minefield Juminda. After dark, German 5th R-Boat Flotilla adds another 32 mines between Minefield Juminda and Finnish Minefield Valjarvi - just in case the Soviets get wise to the location of the Juminda minefield (after losing over 30 ships there) and decide to try to sidestep it.
 |
| Naissaar, sunk in the Baltic by the Luftwaffe on 29 August 1941. |
Battle of the Atlantic: Royal Navy destroyer HMS St. Mary's collides with 3244-ton troopship Royal Ulsterman while operating with Convoy SD-10 to the west of Scotland. St. Mary's requires repairs in Greenock and then Liverpool that lasts until 15 December.
Italian blockade runners 6420-ton Himalaya and 5869-ton Africana reach the Gironde River after their journey from Brazil.
The Royal Navy and US Neutrality patrols have been fruitlessly searching for a reported German heavy cruiser in the North Atlantic for several days. However, today an RAF reconnaissance plane spots the three known German cruisers in the Atlantic - Scharnhorst, Gneisenau, and Prinz Eugen - in port at Brest.
Convoy OG-73 departs from Liverpool bound for Gibraltar, Convoy HX-147 departs from Halifax bound for Liverpool.
 |
| Members of the Australian Militia based at Wallgrove, New South Wales, enlist in the army during a recruitment rally in Sydney on 29 August 1941 (Sun News/The Sydney Morning Herald). |
Battle of the Mediterranean: Operation Treacle concludes as Royal Navy destroyers HMS Griffin and Havock bring the last batch of Polish troops into Tobruk and carry the final group of Australians out. The ships return safely to Alexandria without incident in the early hours of the 30th.
An Italian convoy three troopships (Neptunia, Oceania, and Victoria) departs from Naples for Tripoli by way of Sicily. Royal Navy submarine Urge fires a torpedo at Victoria off Capri but misses. It alerts the Admiralty about the tempting targets, which dispatches fellow submarines Upholder and Ursula from Malta.
Another Italian convoy departs from Tripoli bound for Naples. So, there will be a lot of targets for the British over the next 48 hours.
The Royal Navy begins patrols of the Straits of Gibraltar, hunting for any U-boats making the passage. This patrol involves destroyers Vimy, Midette, and Wild Swan, and corvettes Campanula, Wallflower, Campion, and Hydrangea, along with a couple of motor launches (ML-170 and ML-172).
British freighters Deucalion (7516 tons) and Farndale arrive safely at Gibraltar after sailing from Malta. The Admiralty has stopped any further such independent journeys due to the danger.
Fifteen Wellington bombers based on Malta raid Tripoli, reporting hits on both ships and shore targets. The RAF conducts daily raids on the North African coast, but the British do not publicize these raids because they want to keep the Germans confused as to their source.
Royal Australian Air Force pilot Clive Caldwell, in a P-40 “Tomahawk” of No. 250 Squadron, is flying northwest of Sidi Barrani when he is jumped by two Bf 109E-7s. They badly damage Caldwell's Tomahawk and wound him in the back, left shoulder, and leg. However, he manages to maneuver into position to shoot one of the planes down (the wingman of Luftwaffe ace Leutnant Werner Schroer, who watches in bemusement) and nurse his flaming plane back to base. It is incidents such as this that give him the nickname "Killer Caldwell" (a nickname he despises) and make him the top Allied ace in North Africa and of any pilot flying a P-40. Caldwell finishes the war with 28 total victories: 20 German/Italian and 8 Japanese.
Battle of the Black Sea: The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 5117-ton freighter Kamenets-Podolsk between Kerch, Crimea, and Sevastopol.
 |
| German Soldier's Newspaper WACHT IM SÜDOSTEN from August 29, 1941. |
Special Operations: Operation Gauntlet, the raid on Spitzbergen and its associated activities, continues. Today, 21,517-ton HMT Empress of Canada offloads the 1800 Russian coalminers that it evacuated from Spitzbergen to two Soviet ships that meet it off the Dvina lightship. Empress of Canada then returns to Spitzbergen to join light cruiser HMS Aurora, carrying 200 Free French escaped prisoners of war who managed to make it across the lines.
RAF Bomber Command conducts its first flights in support of Resistance groups. RAF No. 138 Squadron of No. 3 Group, newly formed, is based at Newmarket and conducts the operations. These are clandestine operations, and that extends to opaque records available about how many planes are sent, where they go, and what they do. Typically, the missions are made by Lysanders or other light aircraft that can land in fields and quickly take off again after accomplishing whatever they were sent to do. This typically involves dropping agents by parachute, picking up or leaving small packages, or landing in a remote spot during the night to pick up a returning agent or downed RAF crew.
 |
| Henri Honoré d'Estienne d'Orves, a member of the French Resistance executed on 29 August 1941. |
Partisans: The count Henri Honoré d'Estienne d'Orves, codenamed "Jean-Pierre Girard," and 25 other members of the French resistance network "Nemrod" are executed at dawn at the Fort du Mont Valérien. They were betrayed by their radio operator, Alfred Gaessler, who became a double agent. Henri Honoré d'Estienne d'Orves, an associate of Charles de Gaulle and a leader of the group, is buried in Verrières-le-Buisson. The Germans advertise the executions throughout Paris as an "example," and this leads other Frenchmen to join the Resistance.
US/Japanese Relations: Both the Japanese and the Americans wish to keep their negotiations out of the press for a variety of reasons. These include the effect on public opinion in Japan and the reactions of their allies. This has led to some unhelpful incidents, such as Winston Churchill making bellicose statements directed at Japan during a radio address, but, on the whole, it has succeeded. Today, however, some cracks appear in the curtain of secrecy. The New York Times prints a story that notes the meeting between Ambassador Nomura and President Roosevelt on the 28th, and the Japanese release some details from the diplomatic note given to Roosevelt at that meeting. The Japanese accuse the Americans of publicizing the meeting in order to alienate them from their German and Italian allies - who are completely oblivious to the negotiations - tell Nomura that henceforth he must consult with the Foreign Office before releasing any public statements.
Overall, Tokyo is pleased with the slight movement in negotiations that resulted from Nomura's visit with Roosevelt. However, Nomura is instructed to avoid any meetings on US soil - which apparently does not include Hawaii or Alaska - and that a meeting at sea would be acceptable, too.
French/Laotian/Japanese Relations: A final agreement, the Franco-Laotian Treaty of Protectorate, puts the finishing touches on the brief border war earlier in 1941 between Thailand and French Indochina. Vichy French Admiral Jean Decoux, Governor-General of Indochina and King Sisavang Vong of Louangphrabang sign the agreement. This affirms the status of Laos as a protectorate of Vichy, recognizes the transfer of territory to Thailand, and adds the provinces of Vientiane, Xiangkhoang, and Louang Namtha to Laos. Japan acts as the "honest broker" in the negotiations.
Japanese Military: The Imperial Japanese Navy requisitions 10,439-ton freighter Hokoku Maru. The IJN also begins converting 8691-ton Hoyo Maru and 5350-ton freighter Bangkok Maru, the former into an auxiliary tanker and the latter into an armed merchant cruiser.
US Military: Jack Heyn enlists in the United States Army Air Corps in Omaha, Nebraska. Heyn becomes a top war photographer, memorializing events in the Pacific Theater.
 |
| New Prime Minister Arthur Fadden at Parliament House, 29 August 1941. |
Australian Government: Arthur Fadden of the Country Party officially becomes Australia's 13th Prime Minister. Former Prime Minister Robert Menzies, who resigned due to lack of support within his own party, stays on as Minister for Defense Coordination.
 |
| Members of the Serbian State Guard, an organization founded on 29 August 1941. |
Serbian Homefront: General Milan Nedic is chosen to lead the Germans' revamped puppet government, the Government of National Salvation. This succeeds the Commissioner Government. The completes the partition of Serbia. Nedic institutes the Serbian State Guard, a paramilitary organization designed to maintain control within the puppet state. The Serbian State Guard assists in executions at the Banjica Concentration camp in Belgrade.
 |
| Fire on Main Street in Middletown, Connecticut causes damage to five companies and injures five men. The State Police and National Guard are called to help put out the fire. |
American Homefront: Charles Lindbergh addresses an America First rally in Oklahoma City. He warns that Great Britain could turn against the United States "as she has turned against France and Finland." Montana Senator Burton K. Wheeler speaks next and chastises Great Britain for its treatment of India, stating:
If our interventionists want to free a country from the dominion of another country, we ought to declare war on Great Britain to free India. I have never seen such slavery as I saw in India a few years ago.
Lindbergh and Wheeler are fighting against the tide, as Gallup public opinion polling suggests that more of the public is beginning to accept President Roosevelt's interventionist policies.
"Sun Valley Serenade," starring Sonja Henie, Milton Berle, and Glenn Miller, goes into wide release. It features "Chattanooga Cho Choo," which is the top record of 1941 and sells a million copies. Originally, "Chattanooga Choo Choo" was the B side to "I Know Why," but radio Deejays simply flipped the disc over and played the song that they preferred. The song is inducted into the Grammy Hall of Fame in 1996. "Chattanooga Choo Choo" features skiing scenes that help with recruitment for the embryonic 10th Mountain Division stationed at Camp Hale, Colorado.
Paramount Pictures releases "Flying Blind," a war comedy/action film starring Richard Arlen and Jean Parker. This is a typical entry from Pine-Thomas Productions which costs very little to make ($90,000) but returns big profits (gross of $500,000+). The film has some interesting stock aerial footage, such as of a Lockheed 12A Junior Electra, Boeing 247, and Douglas DC-3.
Future History: Robin Douglas Leach is born in Perivale, London. He becomes a reporter for a local paper, then moves on to the Daily Mail at age 18 as a "Page One" reporter. He moves to the United States in 1963 and writes for entertainment magazines such as "People." Robin Leach begins contributing to TV station KABC-TV program AM Los Angeles, interacting with hosts Regis Philbin and Sarah Purcell, and goes on to a variety of other television projects. He is best known for hosting "Lifestyles of the Rich and Famous" from 1984 to 1995. Robin Leach remains a powerful figure in the entertainment industry despite suffering a stroke in November 2017.
Orestes Matacena is born in Havana, Cuba. As a teenager, Matacena joins a resistance group fighting to overthrow Fidel Castro. After emigrating to the United States in 1964, he becomes an American film character actor, writer, producer, and director most known for "The Mask" (1994). Twelve members of the Congress of the United States, House of Representatives, in 1992 award Orestes Matacena commendations for bravery for giving chase to a burglary suspect, apprehending him, and holding him for police.
Sibylle Bergemann is born in Berlin, German Reich. She becomes a top East German photographer and founds the Ostkreuz photography agency in 1990. She becomes a member of the Academy of Arts, Berlin in 1994. She has 12 prints in the public collection of the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. Bergemann passes away on 2 November 2010.
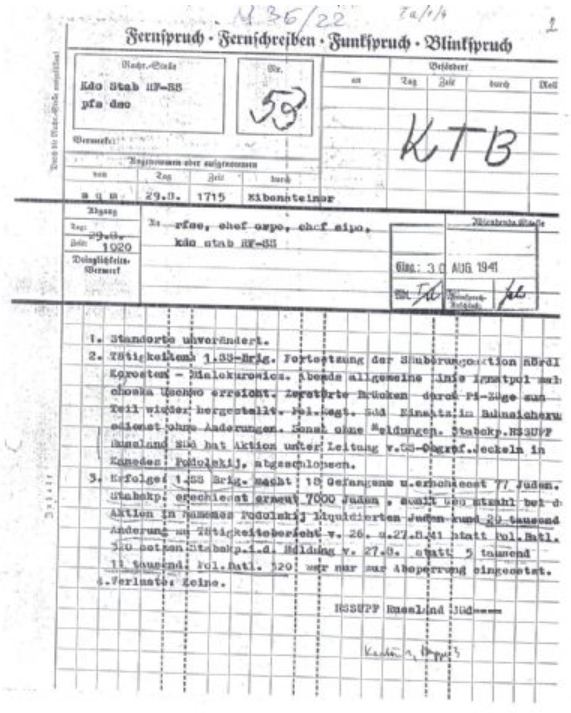 |
| A report by SS-Obergruppenführer Friedrich Jeckeln dated 29 August 1941 which details executions of "about 20,000" Hungarian Jews at the village of Kamenetz-Podolski on 27/28 August 1941. |
August 1941August 1, 1941: More Executions on CreteAugust 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement ClosesAugust 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces EuthanasiaAugust 4, 1941: Hitler at the FrontAugust 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the ArcticAugust 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb BerlinAugust 8, 1941: Uman Pocket CapturedAugust 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia BayAugust 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over BerlinAugust 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in LifeAugust 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter AnnouncedAugust 13, 1941: The Soybean CarAugust 14, 1941: The Anders Army FormedAugust 15, 1941: Himmler at MinskAugust 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270August 17, 1941: Germans in NovgorodAugust 18, 1941: Lili MarleenAugust 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 DestructionAugust 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad BeginsAugust 21, 1941: Stalin EnragedAugust 22, 1941: Germans Take CherkassyAugust 23, 1941: Go to KievAugust 24, 1941: Finns Surround ViipuriAugust 25, 1941: Iran InvadedAugust 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the DesnaAugust 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate TallinnAugust 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets SavagedAugust 29, 1941: Finns take ViipuriAugust 30, 1941: Operation AcidAugust 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No2020