Wednesday 27 August 1941
 |
| U-570 is captured by a Royal Navy anti-submarine warfare trawler on 27 August 1941. This picture was shot by an Allied plane circling the U-boat. |
In central Iran, the 10th Indian Infantry Division is hindered more by the rough terrain than by the defenders. Defenders in the town of Gilan-e-Gharb put up a spirited resistance, but it is soon overcome. This opens the Pai Tak Pass, which leads toward Tehran. The retreating Iranians cut down some trees across the road and dynamite it in places, slowing the British down but not stopping them.
In the northwest, the Soviets face stiffer opposition, but overcome it with the aid of Red Air Force bombers and utter ruthlessness (along with taking a lot of casualties of their own). The Iranians retreat on Ramsar and hope to make a stand there. In the northeast, the Soviets invading from Turkmenistan SSR have a real battle against Iran's 9th Infantry Division at Mashhad and Khorasan province. The Soviets have been stopped for three days at the frontier, but the Iranians have taken heavy casualties and their hold on Mashhad is becoming tenuous.
Australian sloop HMAS Yarra captures 4901-ton Italian freighter Hilda at Banda Addas. The Iranian crew sets Hilda on fire, but the British put them out. Royal Navy tug Sydney Thubron tows Hilda to Karachi, where it is converted into a Royal Navy repair ship.
In Tehran, everyone can see how things will turn out. The Prime Minister resigns and German nationals look for escape routes. Mohammad Ali Foroughi becomes the new Prime Minister, but everyone knows that it won't be for long.
 |
| Members of the ground crew paint victory bar number 44 on the rudder of Erich Schmidt`s "Yellow 11," Surash, Bf 109F, 27 August 1941. |
The Germans are beginning to formulate a plan for taking Kyiv. General von Sodenstern, Chief of Staff at Army Group South, cautions that Sixth Army must not become "locked" with the Soviet defenders, but instead should circle around the city to the east and cut off its supplies and escape route. This is extremely wise counsel that the same Sixth Army would have been well to heed exactly a year later at Stalingrad.
In the Far North sector, the Finns mount major attacks on the Soviet-held port of Hango in southwest Finland by both land and sea. The heavily fortified Soviets, though, are well-provisioned and the small beachhead is heavily armed. The Soviets resist the assaults.
The Finnish Light Brigade T, 12th Division, and 18th Division continue pursuing the Soviet 43rd, 115th, and 123rd Rifle Divisions near the Vuoksi River. Finnish troops are spreading out all across the Karelian Isthmus, cutting off Viipuri tightening their grip on the shore of Lake Ladoga. However, despite being experts at forest warfare, they are having difficulty drawing tight lines to hem in the retreating Soviets because the terrain offers too many chances to escape unseen.
Northeast of Nurmi Lake, a bloody battle develops between Finnish XXXVI Corps and fleeing Soviet troops. A German SS battalion fails to close a pincer at the narrows at Kayrala in the morning, allowing Soviets to escape on foot without any equipment. The Axis troops quickly regroup, and XXXVI Corps sends some Finnish troops to the Wehrmacht's 169th Division while attaching three SS battalions to the Finnish 6th Division. The Axis troops hurry toward the town of Allakurtti along a road and a railway line, but the Soviets get there ahead of them and prepare fortified positions. The Soviets fight for their lives and manage to hold their line sufficiently for most of their troops to escape.
 |
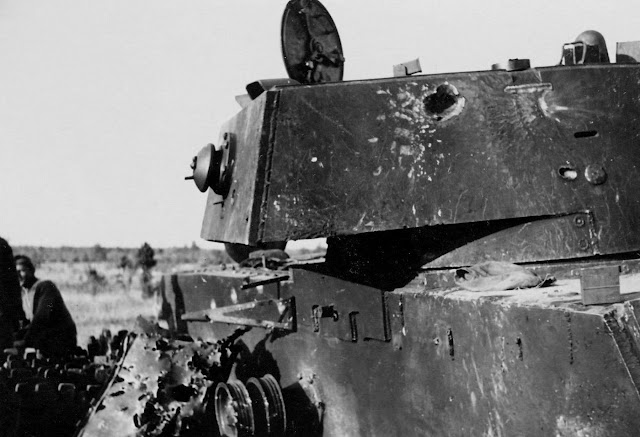
| Finnish soldiers examine a disabled Soviet tank, 27 August 1941 (SA-Kuva). |
In the Army Group Center sector, Panzer Group 3 recaptures Velikie Luki after Soviet counterattacks. Group Stumme at Velikie Luki prepares for a drive on Toropets. General Stumme reports to headquarters that his troops have captured 34,000 Soviet soldiers and 300 guns of 22nd Army. German 250th Infantry Division, the Spanish Blue Division, begins marching on foot from the Polish border to Smolensk. General Guderian's Panzer Group 2 expands its bridgehead south of the Desna River at Novgorod-Seversk, but the going is slow both for the Panzer Group and Second Army which is also moving toward Kyiv.
In the Army Group South sector, the Germans complete their movement of an assault battalion and ten heavy artillery battalions to assist the Romanians in a resumption of the attack on Odessa. The Soviets have little chance of prevailing but have been ordered to fight to the end. Hitler and Mussolini tour areas behind the front lines and meet with army leaders. In what may be a related incident, the leader of Panzer Group 2, General Paul von Kleist, is mentioned in the Wehrmachtbericht, one of the Reich's highest honors.
Soviet bombers hit Koenigsberg during the night.
 |
| Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini in Stępina during their inspection tour, 27 August 1941. |
European Air Operations: During the day, the RAF sends 13 Blenheim bombers on Circus operations to Lille and St. Omer. However, the missions are recalled.
After dark, RAF Bomber Command sends 91 bombers (35 Hampdens, 41 Wellingtons, and 15 Whitleys) against favorite target Mannheim. The bombers must overcome ground haze and cause only moderate damage, damaging 13 buildings and injuring 13 people at a hotel. The RAF loses 7 Wellingtons and a Whitley when the planes return to England, apparently due to bad weather.
In addition, the RAF sends 2 Wellingtons to bomb Boulogne, 2 Wellingtons to bomb Dunkirk, and 17 Hampdens on minelaying operations in the Frisians. There are no losses.
Pilot Officer William R. Dunn, an American pilot flying a Spitfire Mk II with RAF No. 71 "Eagle" Squadron, downs two Bf 109 Fs. Dunn, who also got the squadron's first confirmed victory on 21 July 1941, thereby becomes the first American ace of World War II. Dunn is wounded in the right leg in the action and, after recovery, becomes an instructor.
 |
| German troops manhandling an artillery piece. The arrow points to a German soldier using a captured SVT 38/40 rifle (screen capture from Die Deutsche Wochenschau, 27 August 1941). |
The Soviet Baltic Fleet evacuates Tallinn, Estonia in a maximum effort of over 200 vessels. The ships head toward Kronstadt, Kotlin Island near Leningrad. There are four separate convoys and a Soviet main covering force commanded by Vice Admiral V.F. Tributs. Prior to leaving, the Soviets scuttle a number of vessels, including:
- sailing ship Juno
- sailing ship Kodu
- sailing ship Leidus
- sailing ship Minnalaid
- sailing ship Delphin
- sailing ship Kihelkonna
- 185-ton freighter Salmi
- 403-ton freighter Saturn.
- minelayer Amur (blocking ship)
- 696-ton freighter Gamma (blocking ship)
- 80-ton tugboat Virre (blocking ship)
- 160-ton freighter Alar (blocking ship)
- freighter Diana (blocking ship)
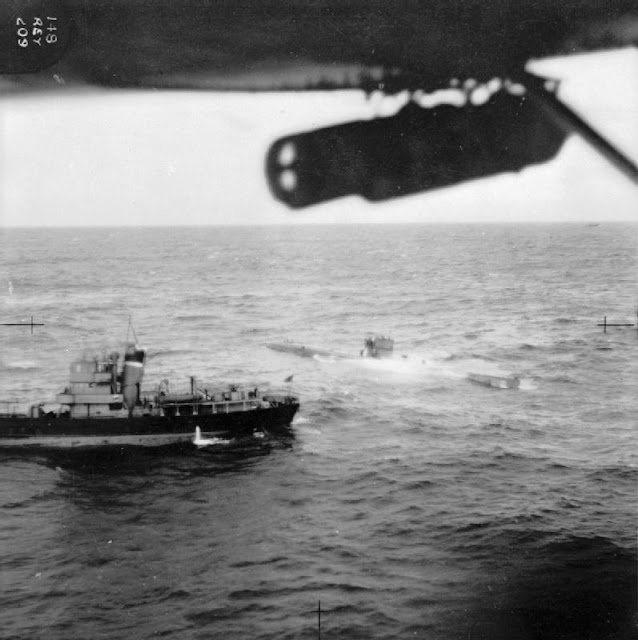 |
| An RAF Catalina takes a picture of U-570 surrendering to a British Royal Navy ship, 27 August 1941. |
U-557 (KrvKpt. Ottokar Arnold Paulssen), on its third patrol operating out of Lorient, has a big day. It torpedoes and sinks several ships of Convoy OS-4 west of Ireland and south of Iceland:
- 4414-ton Norwegian freighter Segundo (seven deaths, 27 survivors)
- 6303-ton British freighter Saugor (59 deaths, 23 survivors)
- 4736-ton British freighter Tremoda (32-35 deaths, 18-21 survivors )
- 4954-ton British freighter Embassage (39 deaths, 3 survivors).
There is a tragedy on HMS Lulworth when Canadian seaman Lt. C.A. Keeler jumps off the ship to rescue a female survivor from 439-ton Norwegian freighter Ingria of Convoy OS-4. Both are lost at sea and their bodies are never found. Keeler receives the Albert Medal posthumously.
The German 6th Destroyer Division, based at Kirkenes, Norway, already is suffering from combat and the elements. After only six weeks in Northern Norway, destroyers Richard Beitzen and Hermann Schoemann must return to German for repairs. This leaves only two destroyers to patrol the northern convoy routes - right when activity is starting to ramp up with British supply missions to Murmansk and Archangel.
US Battleship USS Mississippi (BB-41) departs from Hampton Roads, Virginia on a neutrality patrol. American Task Group TG-2.5, led by aircraft carrier Yorktown, arrives at Bermuda to conclude a neutrality patrol. Royal Navy battleship Rodney departs from Bermuda and joins American Task Force TG2.6 to search for a reported Kriegsmarine cruiser in the North Atlantic (reported by Canadian AMC Prince David).
Convoy ON-10 departs from Liverpool.
Royal Navy destroys Rotherham and corvettes Eglantine and Soroy are commissioned, destroyer Aldenham and submarine Traveler are launched.
 |
| "A soldier of the Polish Independent Carpathian Rifles Brigade with his monkey mascot onboard one of the Royal Navy destroyers on the way from Alexandria to Tobruk, 27 August 1941." © IWM (E 5050). |
While en route from Naples to Tripoli, an Italian convoy is attacked. Royal Navy submarine Urge (Lt Cdr Tomkinson) torpedoes 497-ton Italian freighter Aquitania, but Aquitania is able to return to Trapani, Sicily at reduced speed. Italian torpedo boat Clio counterattacks Urge and damages the British submarine. Two other Royal Navy submarines, Unbeaten and Utmost, also attack ships in the area but miss.
Royal Navy submarine Triumph (Cdr Woods) captures and then sinks an Italian fishing boat off the Furano River, Sicily.
Operation Guillotine, the British reinforcement of Cyprus, continues today with the departure from Port Said of Australian sloop HMAS Parramatta and transport Salamaua. The ships proceed to Famagusta, arriving on the 29th, and then return to Alexandria to conclude the operation.
The Luftwaffe attacks Tobruk, and a Junkers Ju-87 Stuka sinks 245-ton whaler Skudd III. There are three deaths immediately, another man dies later of wounds, and two sailors are missing. An additional six men are wounded.
Luftwaffe ace Hans-Joachim Marseille shoots down a Hurricane fighter near Gambut, Libya.
There is an invasion alert on Gozo beach at Malta due to reports of Italian torpedo boats in the area. However, there is no invasion.
 |
| USS North Carolina firing her forward 16" guns during trials, 26-27 Aug 1941. |
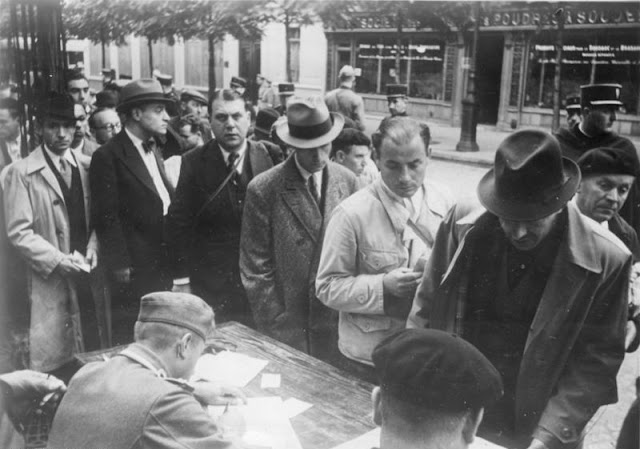
The incident hardens the Vichy government's resolve to eliminate dissent within its zone. It arrests political opponents and simply calls them "communists" to justify the arrests regardless of their true political affiliations.
Laval, shortly after being shot, prevents the Germans from immediately shooting Collette. He tells the German officer who has apprehended the shooter, "Don't do that. You do not know how the French will react like I do." Laval is not particularly popular in France despite being a long-time politician and former head of the government, so he has no illusions that the public will support his ordering instant executions by the occupying army. However, Collette is not let go - he will go on trial, be sentenced to death, have his sentence commuted by Petain, and then be sent to a succession of French prisons and ultimately Mauthausen concentration camp.
Collette, despite his own arduous path for the duration of the war and murky motives, becomes something of a symbol for the French Resistance. He survives the war, publishes a book, "I Shot Laval," in 1946, and dies in 1995.
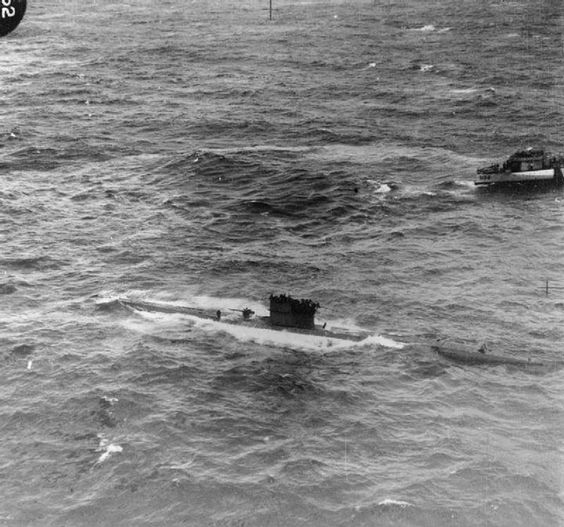 |
| U-570 is captured by the Royal Navy, 27 August 1941. |
In Washington, D.C., Dusko Popov meets with FBI Chief J. Edgar Hoover. Popov is a putative spy for the Germans who is a double agent for the Allies. Popov has in his possession a list of questions given to him to ask about which prominently features Pearl Harbor, Hawaii - the main base of the US Pacific Fleet. Hoover, however, sees no significance in these questions.
Special Operations: Operation Gauntlet continues in Spitzbergen without any interference from the Germans. The Norwegians are sending the Germans in mainland Norway false weather reports of fog which keep away Luftwaffe reconnaissance flights by Wettererkundungsstaffel (Wekusta 5). The Canadians settle in and continue destroying mining equipment and coal dumps in the midnight sun. The Germans don't know anything is amiss, so they continue sending colliers to pick up loads of coal - which the Canadians gladly seize.
Applied Science: Winston Churchill approves the MAUD Committee's suggestion that an atomic bomb should be developed:
Although personally, I am quite content with the existing explosives, I feel we must not stand in the path of improvement, and I therefore think that action should be taken in the sense proposed by Lord Cherwell.The Americans already are working toward an atomic bomb, and also have reached the same conclusions as Churchill based on their reading of the same MAUD Report.
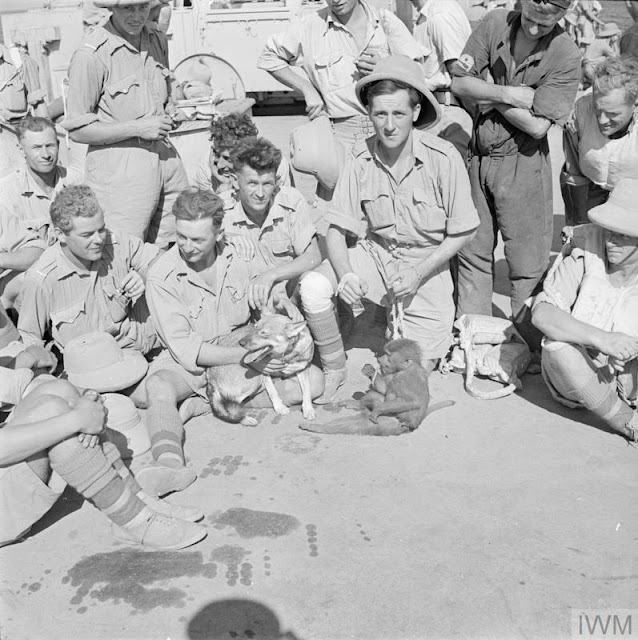 |
| "Soldiers of the Polish Independent Carpathian Rifles Brigade getting their mascot pets, a monkey and a dog, used to each others company, 27 August 1941. Photograph was taken on board of one of the Royal Navy destroyers on the way from Alexandria to Tobruk." (© IWM (E 5051)) |
to discuss from a broad standpoint all important problems between Japan and America covering the entire Pacific area, and to explore the possibility of saving the situation.In a sign of things to come, the Japanese embassy staff has difficulty completing the translation of Prince Konoye's message in time for Nomura's meeting with the Secretary of State - even though they have the message a full day in advance. Thus, Nomura must deliver the message only partly in writing and partly orally. Hull denies Nomura's request to see President Roosevelt immediately but says he will try to set up a meeting in the morning.
The Director of the American Bureau for Japanese Foreign Affairs, Mr. Terasaki, delivers a statement intended for US Ambassador Joseph Grew. It demands that the US tankers bound for Vladivostok be recalled or, if that is impossible, be rerouted to avoid passing through the Straits of Saya and Tsugaru. The Japanese note says that Imperial Japan resents supplies being sent through Japanese waters to the USSR, which may later use those supplies against Japan.
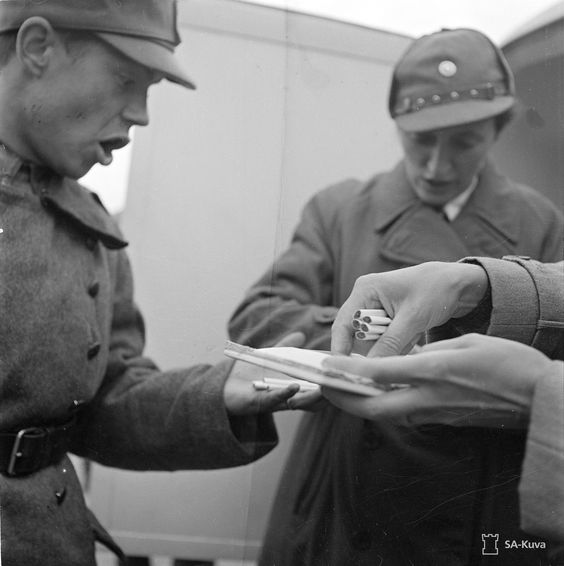 |
| A Finnish soldier receives his cigarette ration, 27 August 1941 (SA-Kuva). |
British Government: Giving in to its usually latent socialistic impulses, the British Government nationalizes the railways for the duration of the conflict. The owners are given £43,000,000 per year as compensation.
China: At Macau, the Japanese issue an ultimatum to the Portuguese administrators of the city: either the city takes a pro-Japanese stance, or the Japanese will block all food imports.
 |
| Hungarian Jews being led to their executions at Kaments-Podolski, 27 or 28 August 1941. |
Soviet Homefront: An Aeroflot Tupolev ANT-6-G2 (TB-3) (CCCP-L1996) crashes into a hill near Kyzyl-Arviat, Turkmenistan. It is carrying cargo on the Tashkent-Ashgabat route, apparently in support of the Soviet invasion of Iran. The pilot apparently cannot find the airport and tries to land in the countryside, but the plane is destroyed and all six crew are killed.
American Homefront: Charlie Root gets his 200th win, the first to do so in Chicago Cubs history, in a 6-4 win over the Boston Braves. Root gave up the famous "called homerun" to Babe Ruth in the 1932 World Series. Root will retire at the end of the season with 201 career victories.
Paramount's "Aloma of the South Seas" premieres. It stars Dorothy Lamour as Aloma and is directed by Alfred Santell. The film, in Technicolor, is later nominated for two Academy Awards for cinematography and visual effects.
Future History: Cesària Évora is born in Mindelo, São Vicente, Cape Verde. She becomes a popular singer and earns the nickname "The Barefoot Diva" due to her penchant for singing without shoes. She passes away on 17 December 2011 in her hometown.
August 1941
August 2, 1941: Uman Encirclement Closes
August 3, 1941: Bishop von Galen Denounces Euthanasia
August 4, 1941: Hitler at the Front
August 5, 1941: Soviets Surrender at Smolensk
August 6, 1941: U-Boats in the Arctic
August 7, 1941: Soviets Bomb Berlin
August 8, 1941: Uman Pocket Captured
August 9, 1941: Atlantic Conference at Placentia Bay
August 10, 1941: Soviet Bombers Mauled Over Berlin
August 11, 1941: Rita Hayworth in Life
August 12, 1941: Atlantic Charter Announced
August 13, 1941: The Soybean Car
August 14, 1941: The Anders Army Formed
August 15, 1941: Himmler at Minsk
August 16, 1941: Stalin's Order No. 270
August 17, 1941: Germans in Novgorod
August 18, 1941: Lili Marleen
August 19, 1941: Convoy OG-71 Destruction
August 20, 1941: Siege of Leningrad Begins
August 21, 1941: Stalin Enraged
August 22, 1941: Germans Take Cherkassy
August 23, 1941: Go to Kiev
August 24, 1941: Finns Surround Viipuri
August 25, 1941: Iran Invaded
August 26, 1941: The Bridge Over the Desna
August 27, 1941: Soviets Evacuate Tallinn
August 28, 1941: Evacuating Soviets Savaged
August 29, 1941: Finns take Viipuri
August 30, 1941: Operation Acid
August 31, 1941: Mannerheim Says No
2020