Tuesday 23 April 1940
 |
| French General Georges and Lord Gort inspect a BEF 8-inch Mk VIII howitzer at Bethune, France, 23 April 1940. Most likely that is the 1st Heavy Regiment, Royal Artillery. |
Norway Army Operations: In the evening, the British 15th Brigade arrives at Molde and Andalsnes. Its mission is to support the 148th Brigade, which is under heavy pressure to the south.
At Tretten Gorge on the road north from Lillehammer, the German 196th Infantry Division continues attacking the British 148th Infantry Brigade, inflicting heavy casualties. German artillery is active all morning. The British are trying desperately to hold the river road, but the German panzers are decisive. Three of them break through the British line at 13:00. Mountain troops have scaled the 2165-foot cliff to bypass the British river road defenses. They circle around at at 18:00 begin attacking the British line from the rear.
The British can't hold out and withdraw from Tretten Gorge at 19:00, bombed and strafed on the narrow river road in the Gudbrandsal. Casualties are immense: the British have lost 705 killed, wounded and captured. Only 309 remain fighting. At one point, they take refuge in a railway tunnel and a British officer comments: "700 of us and a bloody train - we're almost suffocating. "We've been stuck here all day with Germans bombing us. One direct hit on the tunnel and we're done for. The train has to keep up steam - choking."
Northeast of Trondheim, the British 146th Infantry Brigade is falling back from Steinkjer under fierce Germans pressure toward its base at Namsos. So far, General de Wiart's troops have lost 19 dead, 42 wounded and 96 missing.
At Hegra Fortress, the Germans continue standing back and lobbing occasional mortar shells at the fort, with Luftwaffe attacks from the nearby airport. Today a few shells destroy one of the fortress' two 7.5 cm positional guns, one of the fortress' command towers and the waterline. The defenders are losing effective ways to strike back.
The Germans are spreading out from Stavanger. At Ogna southeast of Stavanger, the Germans capture the vital bridge, trapping hundreds of troops. The Germans in the area accept the surrender of 1,700 Norwegian troops of the Norwegian 8th Infantry Regiment.
The Polish Podhale Brigade (Chasseurs du Nord) begins moving to Norway.
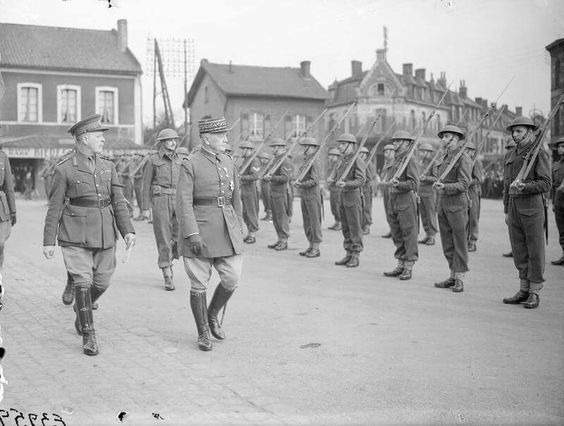 |
| General Georges of the French Army and Lord Gort inspect the Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers at Bethune, France, 23 April 1940. |
The Luftwaffe attacks the British positions at Andalsnes.
The RAF raided Fornebu and Kjeller airports at Oslo, and also Aalborg in northern Denmark for the third night.
The Luftwaffe sent a sweep of Bf 109s over Luxembourg which was met by Hurricanes. No losses on either side.
Battle of the Atlantic: British ship Lolworth hits a mine and sinks in the North Sea.
Kriegsmarine minesweeper M-1302 hits a mine and sinks.
Royal Navy submarine Tetrarch sinks Kriegsmarine vessel UJ-B.
The RAF sends 26 planes on a minelaying operation during the night.
Convoy SL 29 departs from Freetown.
British minesweeping trawler HMS Mangrove (A.E. Johnson) is commissioned.
BEF: The British 46th Infantry Division moves to France.
US/Canadian Relations: President Roosevelt meets with Canadian Prime Minister Mackenzie King in Warm Springs, Georgia.
British Government: Chancellor of the Exchequer John Simon announces a new war budget (classified, of course) which means higher taxes:
- income tax raised to 7s 6d per £;
- higher duties imposed on tobacco and matches, beer and spirits;
- higher postal fees;
- higher telegraph and telephone rates;
- new purchase tax on the way.
Sir Stafford Cripps returns to London after his visits to the USSR, India, and China.
Australia: Coal miners have been on strike since early March, and Prime Minister Menzies reminds them that there's a war on. He states that he may resort to force to reopen the mines.
April 1940
April 1, 1940: Weserubung is a GoApril 2, 1940: British Subs On Alert
April 3, 1940: Churchill Consolidates Power
April 4, 1940: Missed the Bus
April 5, 1940: Mig-1 First Flight
April 6, 1940: Troops Sailing to Norway
April 7, 1940: Fleets At Sea
April 8, 1940: HMS Glowworm and Admiral Hipper
April 9, 1940: Invasion of Norway
April 10, 1940: First Battle of Narvik
April 11, 1940: Britain Takes the Faroes
April 12, 1940: Germans Consolidate in Norway
April 13, 1940: 2d Battle of Narvik
April 14, 1940: Battle of Dombås
April 15, 1940: British in Norway
April 16, 1940: Germans Cut Norway in Half
April 17, 1940: Trondheim the Target
April 18, 1940: Norway Declares War
April 19, 1940: Dombås Battle Ends
April 20, 1940: Germans Advancing in Norway
April 21, 1940: First US Military Casualty
April 22, 1940: First British Military Contact with Germans
April 23, 1940: British Retreating in Norway
April 24, 1940: British Bombard Narvik
April 25, 1940: Norwegian Air Battles
April 26, 1940: Norwegian Gold
April 27, 1940: Allies to Evacuate Norway
April 28, 1940: Prepared Piano
April 29, 1940: British at Bodo
April 30, 1940: Clacton-on-Sea Heinkel
2019