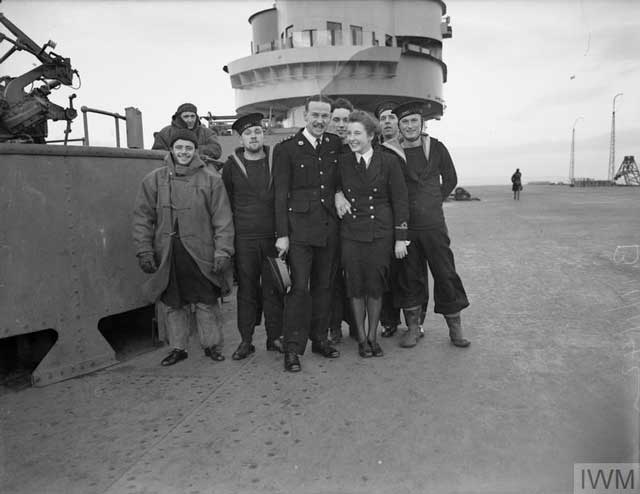
Wednesday 11 June 1941
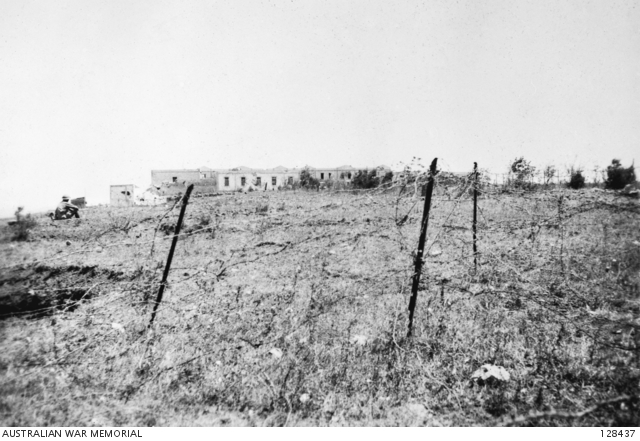 |
| "Lebanon. 11 June 1941. Fort Merdjayoun in the town of Merdjayoun, which was occupied by French forces before being captured on 11 June 1941 by elements of the 7th Australian Division AIF. The town was then occupied by 2/33rd Battalion, a cavalry unit and a battery of artillery in a defensive role." (Australian War Memorial 128437). |
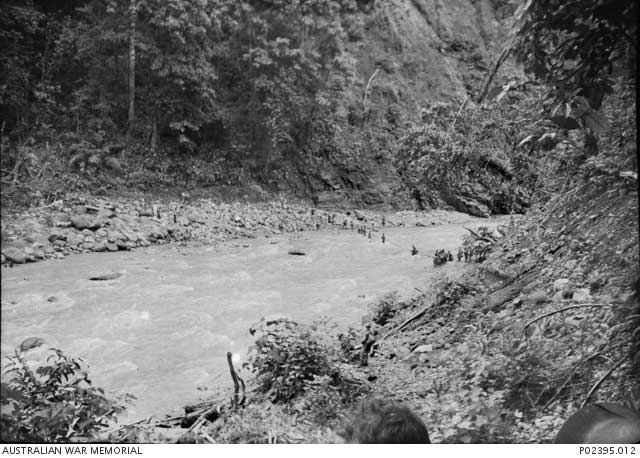
Syrian/Lebanon Campaign: The Australian 21st Brigade continues marching north from Tyre toward Sidon as part of Operation Exporter on
11 June 1941. Further inland, the Australian 25th Brigade takes Merdjayoun (Merjayun). The Australians, feeling confident, leave only a skeleton force to hold Merdjayoun and send the bulk of the 25th Brigade north to attack Jezzine.
Free French 1st Infantry Brigade and 2nd Infantry Brigade attack Kissoue south of Damascus. The Vichy French, however, are massing large forces to block the Commonwealth troops' advances.
A French Dewoitine D.520 shoots down a British Curtiss Tomahawk. It is the only Tomahawk that the RAF loses during the campaign.
Journalist Alan Moorehead talks to captured Vichy French soldiers and gets a surprise: their morale is excellent. He reports that the French say that they are resisting the British invasion fiercely because they are professional soldiers and the attack was unprovoked. Another factor is that Germany essentially is holding their relatives in metropolitan France hostage. There also is an element of simple Gallic pride, as the French soldiers feel that the British look down on them ("like the Italians") for losing France to Hitler.
In other words, the French are resisting not just for pragmatic reasons, but for pride. However, the silver lining is that, once the defending French soldiers prove their point about their ability to resist, they eventually will give in to the inevitable and surrender. There is some hard fighting left before that can happen, though.
 |
| A Curtiss Tomahawk of 3 Squadron at Lydda (Lot), 11 June 1941 (via Mike Mirkovic). |
European Air Operations: During the day, RAF Bomber Command sends 25 aircraft to bomb Bremerhaven, but 19 turn back due to Reich air defenses. The British, like the Luftwaffe before them, are gradually coming to the realization that daylight bombing raids are extremely costly.
RAF Fighter Command sends fighters on Rhubarb and Roadstead operations. RAF 11 Group (12 planes of RAF No. 74 Squadron and 12 of No. 609 Squadron escort five Blenheim bombers of 16 Group) conducts a Roadstead operation that targets a tanker defended by flak-ships off Dunkirk. The pilots report scoring a hit on the tanker, but there is no verification from German records. Luftwaffe Oblt. Johannes Seifert of 3./JG 26 downs a Hurricane from RAF No 248 Squadron during daylight action.
After dark, RAF Bomber Command raids the industrial Ruhr River Valley, the Rhineland, Hamburg, and Bremen. The weather is good, and the British will continue attacking the Ruhr for the next 19 nights. They put 98 bombers over Dusseldorf and 80 over Duisburg. RAF Bomber Command also sends 24 aircraft to Boulogne and 20 bombers on minelaying missions.
The Luftwaffe drops leaflets over East Anglia, as it did during the summer of 1940, and sends planes across Great Britain. These tout German successes in the Atlantic and they warn, with some credibility, that further resistance to the Reich will mean starvation throughout the British Isles.
East African Campaign: The Indian 15th Punjab Regiment of the Indian 3rd Battalion completes the capture of Assab, which essentially just means checking the town for any Italian stragglers. The entire Red Sea now is clear of Axis influence, and soon American freighters will be able to cross it to deliver supplies to British forces in Egypt.
(Kraupa; Tuskany; Duskamp, Federal Archive
Bild 101II-MW-3509-30).
 |
| "France, Saint-Nazaire.- Admiral Karl Doenitz on the quay in front of incoming U-boat U-93, the crew standing on the U-boat deck in anticipation of the award of the Knight's Cross to Lieutenant Claus Korth, U-93's commander. |
Battle of the Atlantic: U-79 (Kptlt. Wolfgang Kaufmann), on its first patrol out of Kiel, is operating west of Iceland when it torpedoes and sinks 1524 ton Norwegian freighter Havtor. There are six deaths and 14 survivors.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 2056-ton British freighter Moorwood near 19C Buoy north of Whitby. Everyone survives.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 3178-ton British freighter Baron Carnegie just east of St. Davids in St. George's Channel. There are 25 deaths (16 are listed as "missing" but never are found). British 1358-ton freighter Seine takes Baron Carnegie in tow, but Baron Carnegie sinks north of Fishguard.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages 2842-ton British freighter Westburn a few miles north of Skinningrove off Hartlepool. Taken in tow, the Westburn arrives in Hartlepool later in the day.
Royal Navy submarine H.32 grounds in the Clyde. After it frees itself, H.32 goes to Ardrossan for repairs.
The Kriegsmarine makes a rare fleet maneuver (the Royal Navy, by comparison, keeps its ships constantly in motion). This is Operation Sommerreise (Summer Journey). The Germans send heavy cruiser Lutzow (damaged during the invasion of Norway), light cruisers Emden and Leipzig, and destroyers Eckhold, Galster, Lody, Z.23, and Z.24 to Norway. The plan is for Lutzow to break out into the Atlantic and be joined there by sister ship Admiral Scheer.
The British, of course, keep very close tabs on German warships. They learn today from Ultra decrypts about Operation Sommerreise and begin preparing a response. The Admiralty brings the Home Fleet to one hour's notice.
Convoy OB-334 departs from Liverpool.
U-130 (K.Kapt. Ernst Kals) is commissioned at Kiel.
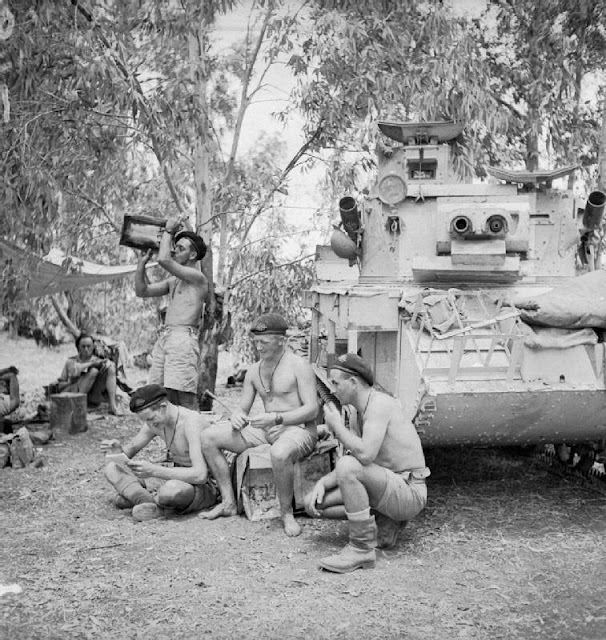 |
| "The crew of an Australian Vickers Light Tank Mk VI works on their vehicle during the advance into Syria, 11 June 1941."(© IWM (E 3149E)). |
Battle of the Mediterranean: British troops under General O'Moore Creagh prepare for the upcoming Operation Battleaxe, scheduled to begin on 15 June. On the other side, newly appointed commander of the 15th Panzer Division General Walter Neumann-Silkow is more worried about his supply situation than the enemy, as his panzers are running low on petrol.
Royal Navy submarine Taku (Lt. Commander Edward C.F. Nicolay) torpedoes and sinks 1600-ton German freighter Tilly L.M. Russ in Benghazi Harbor.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Torbay rams and sinks a caique about 15 miles south of Mitylene (Lesbos). The caique is being used as a troop transport, there is an unknown number of casualties.
The RAF attacks Benghazi and sinks Italian naval trawlers Mario Bianco and Cirene.
At Malta, the Luftwaffe drops bombs between Ta Qali and Mosta, as well as eight east of Valletta. A much larger attack of an estimated 22 Axis aircraft is spotted 30 miles north of the island but turns back when the RAF scrambles fighters.
Convoy BA-3 departs from Karachi bound for Aden.
Battle of the Pacific: Captured whaler Adjutant with prize crew departs German raider Komet for minelaying operations in New Zealand waters.
Anglo/US Relations: President Roosevelt agrees to occupy Iceland with US troops. While there is no danger of combat in Iceland, this will free up 25,000 British troops who have been unopposed, though not invited, by the Icelandic government. Iceland is critically important to the Allies for protection of their cross-Atlantic convoys, as both ship and air patrols emanating from there cover a large area that U-boats are using with great success.
 |
| Vickers Light Tank Mk VI with Australian crew during the advance into Syria, 11 June 1941. |
Japanese/Dutch Relations: While the Germans have conquered The Netherlands, the Dutch East Indies remain a powerful force in the Pacific. Not only do the Dutch there possess a strong navy, but they also control raw materials that the Japanese need. Today, however, the Japanese accept defeat in their attempts to lock up more oil and other supplies. This is another skirmish in a trade battle that has broken out across the globe, with the Axis and Allies vying to "lock-up" sources of supply of strategic commodities such as oil and tungsten.
Japanese/Soviet Relations: The Japanese and Soviets, who recently reached an agreement regarding the border in Manchuria, expand their economic relations.
Anglo/Soviet Relations: Sir Stafford Cripps, ambassador to Moscow, returns to London for consultations. Cripps is England's point man for the Soviet Union because he is a committed Socialist with decidedly Marxist leanings and works well with the Russians. Cripps' departure in the face of all the warnings he has been receiving about a prospective attack by Germany leaves Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin very suspicious about what Winston Churchill is planning.
German/US Relations: Brazilian steamer Ozorio rescues the last eleven survivors from the US freighter SS Robin Moor (Captain E. W. Meyers). The Robin Moor was sunk in the South Atlantic on 21 May by U-69 (Kapitänleutnant Jost Metzler) while carrying contraband aircraft parts bound for the British in the Middle East. The sinking has become a major diplomatic incident, but not sufficiently for the United States to declare war.
 |
| Bomb damage in Belfast at Ravenscroft Avenue, East Belfast looking toward the Hollywood Arches (11 June 1941). |
Japanese Military: At an army/navy conference, the new chief of the Imperial Japanese Naval General Staff, Admiral Osami Nagano, comes out forcefully as a supporter of Nanshin-ron. This is the southeastern expansion of the Empire of Japan at the expense of the current colonial powers there. While Nanshin-ron has been official Japanese national policy since the promulgation of the Toa shin Shitsujo (New Order in East Asia) in1936 at the "Five Ministers Conference," everybody knows this means war with Great Britain, the Netherlands East Indies, the Vichy French in Indochina, and the native powers in the region such as Thailand and Burma. Nagano wants to expand to the southeast before the United States completes its "two-ocean" construction plans.
Nagano, however, remains opposed to war with the United States if it can possibly be avoided. He takes a very dim view of Admiral Yamamoto's plans to attack Pearl Harbor. However, almost everyone else in the top tier of the Japanese military prefers to strike the United States while it remains relatively weak in the Pacific.
US Military: Battleship USS Arizona departs from Pearl Harbor, Hawaii for Long Beach, California.
Soviet Military: Soviet General Georgi Zhukov continues quietly building up forces in the European portion of the Soviet Union. He orders the transfer of some Red Army units from Transbaikal to the Kyiv region. However, Zhukov remains bound by Premier Joseph Stalin's wishes to do nothing to provoke the Germans.
 |
| Two related German paratroopers (Fallschirmjäger) who have survived Operation Mercury meet in Canea, Crete, 11 June 1941 (Federal Archive Bild 183-H25246). |
German Military: Adolf Hitler issues
Fuhrer Directive No. 32, "Preparations For The Period After Barbarossa." The directive turns out to have no effect on anything aside from planning but does offer insight into Hitler's mindset on the eve of Operation Barbarossa.
As he is wont to do, Adolf Hitler begins making plans for operations far in the future that depend on operations closer in time to turn out as planned. So, today he tasks the OKW Operations Staff led by General Alfred Jodl with working up plans for the period after the Soviet Union is conquered.
Hitler notes pointedly that, "The main efforts of the armaments industry can be diverted to the Navy and Airforce." The Reich armaments sector takes this to heart, and begin to view the production of shells and other munitions as a low priority. This will have baleful consequences for the Wehrmacht late in 1941 and in 1942 as Soviet resistance proves fiercer than expected.
Hitler demonstrates in Directive No. 32 that he views Operation Barbarossa more as a temporary pause in other operations already on the docket than a major, long-term undertaking. So, he anticipates implementing Operation Felix, the planned seizure of Gibraltar. His thinking is revealed when he orders the capture of Tobruk in "about November," when the Afrika Korps can be "brought to the highest possible efficiency in personnel and equipment." This, presumably, would only be possible after the Wehrmacht can redirect forces from the conquered Soviet Union.
Interestingly, Hitler barely mentions Operation Sea Lion, the proposed invasion of England, in Directive No. 32, and only in passing. He notes that preparations for the invasion would "serve the double purpose of tying down English forces at home and of bringing about a final English collapse through a landing in England." He is more interested, however, in a resumption of the "Siege of England," which can be undertaken "with the utmost intensity" only
after the Soviet Union is beaten.
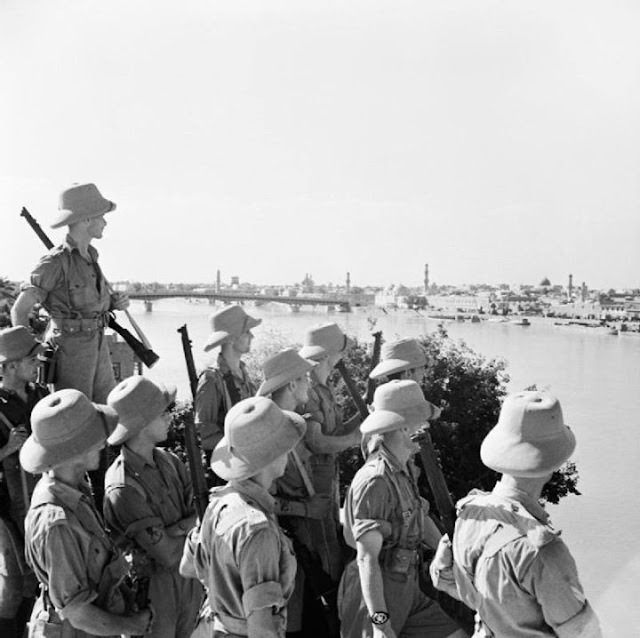 |
| British soldiers looking across the river at Baghdad, 11 June 1941. |
British Military: Major-General Neil Ritchie is sent to the Middle East Command to join the staff of the British Eighth Army in Cairo. His replacement in charge of the British 51st Highland Division is Major General Douglas Neil Wimberley. Wimberley institutes strenuous training routines for future operations - the division is seen as having gotten a bit slack after almost two years of home defense in anticipation of a German invasion that never came.
American Homefront: The President of Fordham University, Rev. Robert I. Gannon, gives a
commencement address at the school entitled "What Will Replace It." The "it" is civilization, and Gannon says in part:
we believe that democracy will rise again, but not until the authority of God is recognized again in public and in private life. Apparently, then, it has fallen our lot to see the end of a civilization.
He notes that whatever the ways of the world, religion will always be there for people. The theme of the address mirrors a growing pessimism in some quarters about the state of the world in 1941.
"Health Lecturer" Russell James is arrested in Minneapolis for practicing healing without a license. He sells a health food product made out of powdered bananas and whey (which does sound pretty healthy). The Hennepin County District Court deliberates for three hours, then finds him not guilty.
 |
| Exterior view of the N. 11 Mikoyan Bread-Baking Plant, Moscow, June 1941 (Meyer, Hannes). |
June 1941 June 1, 1941: Farhud PogromJune 2, 1941: Massacres on CreteJune 3, 1941: Kandanos MassacreJune 4, 1941: Kaiser Wilhelm Passes AwayJune 5, 1941: Death in ChungkingJune 6, 1941: Hitler's Commissar OrderJune 7, 1941: Commandos Strike at PessacJune 8, 1941: British Invade Syria and LebanonJune 9, 1941: Litani River BattleJune 10, 1941: British Take AssabJune 11, 1941: Hitler Thinking Beyond RussiaJune 12, 1941: St. James AgreementJune 13, 1941: Lützow DamagedJune 14, 1941: Latvian June DeportationsJune 15, 1941: Operation BattleaxeJune 16, 1941: The Old LionJune 17, 1941: British Spanked in North AfricaJune 18, 1941: Turkey Turns Its BackJune 19, 1941: Cheerios IntroducedJune 20, 1941: Birth of US Army Air ForceJune 21, 1941: Damascus FallsJune 22, 1941: Germany Invades RussiaJune 23, 1941: A Soviet KV Tank Causes HavocJune 24, 1941: Kaunas and Vilnius FallJune 25, 1941: Finland Declares WarJune 26, 1941: Bombing of KassaJune 27, 1941: Encirclement At MinskJune 28, 1941: Minsk FallsJune 29, 1941: Brest Fortress FallsJune 30, 1941: Mölders Becomes Top Ace2020