Thursday 1 May 1941
It is now necessary to fight hard for Crete, which seems soon to be attacked heavily, and for Malta as a base for flotilla actions against the enemy's communications with Libya.Churchill sends a much briefer cable to his Middle East Commander, General Archibald Wavell, merely appending his cable to Cunningham and noting "Feel sure you are waiting to strike a blow." An old sea dog, Churchill naturally favors the Royal Navy over the army, but it also is clear from his communications that he hates to lavish praise on Wavell (and his subordinates) for what are likely personal reasons.
Italian airborne troops continue occupying the Greek islands of Cephalonia, Ithaca, and Zante.
Iraqi War: The Iraqis have demanded that the British at Habbaniya Airfield west of Baghdad surrender. The British do not reply. The ultimatum will expire in the early morning hours of 2 May. The British prepare to sortie out of their airfield fortress against the Iraqis, who have set up 28 artillery pieces on a plateau overlooking the airfield to the south. There are small Iraqi attacks near the airfield at Rutba. Air Vice-Marshal Harry Smart is instructed personally by Churchill to defend his position: "If you have to strike, strike hard. Use all necessary force."
 |
| The May Day parade in Kuibyshev on May 1, 1941 (Vladimir Samartsev). |
The Luftwaffe sinks British freighter Europa and ammunition transporter Malakand during the raid on Liverpool.
Churchill's secretary, John Colville, notes in his diary after a tour of the area that "Plymouth has been cruelly laid waste in the last fortnight." The Luftwaffe has attacked Plymouth for five nights running, but at least the attacks had lessened in severity as they continued. Now, it is Liverpool's turn. The War Cabinet minutes note that it is "disturbing" that "the Press had drawn attention to an unofficial nightly exodus from Plymouth into surrounding districts." The same pattern is likely to occur in Liverpool.
The Luftwaffe combines the day and night fighter commands into a unified command structure, but FLAK units remain independently controlled by local air headquarters (Luftgaukommandos). Colonel Josef Kammhuber is in charge of coordinating FLAK, searchlight and radar units and is a genius at creating an organization (though a bit shakier on overall military strategy). Kammhuber is in the process of coordinating Reich air defenses into a unified structure later known as the Kammhuber Line. This works fairly well under the circumstances that prevail during the early part of the war.
RAF Bomber Command conducts a sweep off the Dutch coast with 22 planes, but there are no incidents.
Ofw. Erich Rudorffer of I./JG 2, with nineteen aerial victories, is awarded the Ritterkreuz.
U-103 (Viktor Schütze), on its fourth patrol, is off the coast of West Africa when it torpedoes and sinks 1494 ton British freighter Samsø. This is the start of a string of success in the area for U-103. The Samsø sinks slowly, taking 50 minutes, and only one crewman perishes. The rest of the crew makes it to Los Island, French Guinea, on 3 May.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 329-ton minesweeping trawler Jean Frederic off Start Point. There is one death. Another ship, 200-ton balloon barrage vessel Saturnus, is declared a total loss due to damage sustained. Both vessels have Dutch crews.
British 2950-ton freighter Sea Fisher hits a mine and is beached with the assistance of two tugs. The ship is given temporary repairs and eventually makes it to Middlesborough on 5 May.
Royal Navy patrol boat 534-ton Loch Oskaig captures 3317-ton French freighter Cap Cantin near the entrance to the Mediterranean and takes it to Gibraltar.
Royal Navy patrol boat Cavina captures 6466-ton Italian tanker Sangro, a blockade runner, in the same general vicinity as the Loch Oskaig's capture.
Royal Navy patrol boat HMS Corinthian captures 350-ton French three-masted schooner Martin Pecheur. The ship is sent to Gibraltar with a prize crew.
Royal Navy destroyer HMS Juno sustains damage when a depth charge explodes prior to launch. One man is killed and 15 others are wounded.
Portugues schooner Santa Quitéra founders off the Grand Banks. All 40 men are rescued.
Royal Navy destroyers HMS Adrias and Haydon are laid down.
USN submarine USS Grenadier is commissioned, and light fleet carrier USS Independence is laid down, along with destroyers Bancroft, Beatty, Endicott, Kendrick, Laub, McCook and Tillman.
U-163 and U-164 are launched, and U-568 is commissioned. At this stage of the war, increases to the U-boat fleet are far outpacing losses.
 |
| Maurine Zollman, a John Powers model (photo by John Rawlings). |
The following Italian infantry, meanwhile, which was supposed to follow the panzer in, is still dealing with isolated Australian outposts that have been overrun but still refuse to surrender. Overall, the battle is trending toward the British, but they have lost ground when they have very little to spare. Operations are hampered during the morning by fog. This combat operation, incidentally, is sometimes called the Battle of Ras el Medauar.
The Luftwaffe, of course, fiercely supports the German attack. Hans-Joachim Marseille, escorting German Stuka dive bombers to Tobruk, shoots down his 10th and 11th kills, two British Hurricane fighters.
General Wavell, from his headquarters in Cairo, is quick to put out a press release about the defense of Tobruk which is refreshingly candid for a military communique. He notes:
An extremely violent battle ignited Wednesday night around Tobruk. After a vigorous bombardment lasting several hours, German and Italian infantry attacked the Tobruk fortifications, deploying heavy tanks and flamethrowing tanks simultaneously. Early this morning another attack ensued by large numbers of German Stuka dive bombers which dropped heavy calibre bombs on the defence installations. Until 10:00 A.M. the British garrison succeeded in preventing any breach in the Tobruk defences. After that, a strong panzer force successfully penetrated the outer perimeter along a 2-mile front. British and Australian troops are at this moment engaged in hand-to-hand fighting in the defensive installations outside the city.The presence of flamethrower tanks at this early stage of the war is a bit unusual, as the Wehrmacht and British did not become enamored with them until later. They apparently are Italian L3 tanks of the Ariete Division, small tanks that tow their flamethrower fuel in a separate armored trailer.
The RAF attacks shipping in the Benghazi harbor and sinks 1533-ton Italian freighter Serdica.
HMS Upholder torpedoes and sinks German freighter Arcturus just south of the Kerkennah Islands, Tunisia. This is part of a convoy returning from North Africa to Italy.
HMS Upholder also torpedoes and sinks German freighter Leverkusen in the same vicinity as the Arcturus south of the Kerkennah Islands.
Two Royal Navy submarines go missing in the Mediterranean during this general period of time - HMS Undaunted (operating near Tripoli) and Usk (the Strait of Sicily). Causes of their loss are unknown. Submarine Truant has sustained damage from minelaying and is sent from Malta to Gibraltar.
German 1819-ton freighter Larissa hits a mine and sinks in the Gulf of Volos.
Winston Churchill orders another operation to run an aircraft carrier into the Mediterranean from Gibraltar and fly off some Hawker Hurricanes to Malta. Such operations have had mixed success to date, with losses of several planes that apparently ran out of fuel. This projected operation is tentatively slated for late May at the earliest.
At Malta, the Luftwaffe attacks continue, and the attacks include bombings and minelaying. The Germans sink 1373-ton freighter Polinice, but the ship is later raised for salvage. There is one civilian death. HMS Jersey hits a mine in Valetta Harbor and later sinks during a raid.
The Italian Navy sends a large force, including three light cruisers, to lay mines north of Tripoli.
 |
| The 1 May 1941 cover of "The Shadow" magazine. |
German Military: Generalleutnant August Krakau takes command of the German 7th Mountain Division, replacing Robert Martinek. Kapitän zur See Friedrich Hüffmeier took command of cruiser Köln.
US Military: Rainbow 5, the plan for US military responses to an attack, is completed by the Joint Army-Navy Board. It calls for a defensive strategy that entails the surrender of the Philippines. Admiral Hart in the Philippines, acting on optimistic advice from the Navy Department, tells his staff that they will have at least two days of warning prior to the outbreak of hostilities. Commander H D Linder, RNethN arrives in Manila to serve as Hart's liaison with the powerful Dutch naval forces in the East Indies (Indonesia).
Admiral Ernest J. King takes command of the Atlantic Fleet.
Lieutenant Colonel William P. T. Hill takes command of the newly built Marine Barracks of New River, North Carolina.
Japanese Military: Aircraft carrier Kaga is put in drydock in Sasebo for refit, while freighter Kasuga Maru begins conversion to an escort carrier at the same port.
 |
| The May Day parade in Moscow, 1 May 1941. |
The Red Army is ready, in the interests of the socialist state, to ward off every blow struck by the imperialists. The international situation is full of unexpected events. In such a situation the Red Army must step up its defensive readiness.The German military attache in Moscow notes that the Red Army has begun calling up recruits in the lowest age cohort six months earlier than usual. The Soviets also orders that foreign diplomats may no longer travel freely, but must be escorted.
British Military: General Percival leaves Great Britain to take up his new command in Singapore by air. It is a risky passage via Gibraltar, Malta, Egypt, and India.
 |
| US War Bonds go on sale today. |
Visiting Australian Prime Minister Robert Menzies confides in his diary that he is "desperately afraid of the future in Great Britain." Menzies is scheduled to return home on 3 May, but notes that Lord Beaverbrook "thinks [it] absurd that I should go back to Australia!" There is definite sentiment among those opposed to Churchill's conduct of the war that Menzies would be a good replacement for Churchill as Prime Minister of Great Britain.
Holocaust: Gross-Rosen concentration camp (German: Konzentrationslager Groß-Rosen), set to become one of the largest camps, becomes an independent camp. It is in Groß-Rosen, Lower Silesia, Germany (later Rogoznica, Poland). Gross-Rosen had been begun in the summer of 1940 as a satellite camp of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp.
 |
| SS Karsik (formerly the German Soneck), 1 May 1941, a well-traveled 2191 ton ship of World War II (Australian War Memorial, ID Number: 303479) |
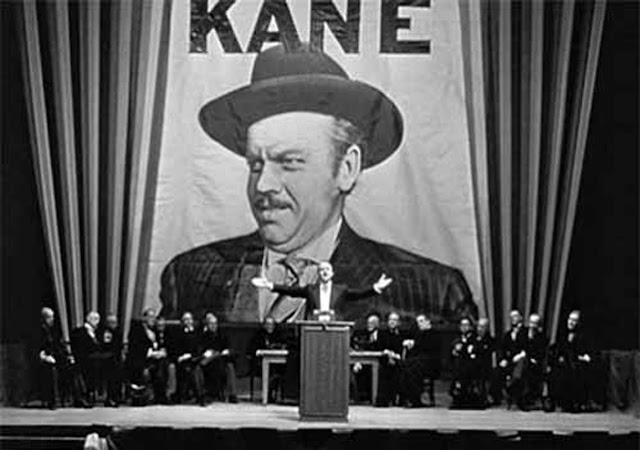
US Homefront: Orson Welles' "Citizen Kane" is released in the US, with its world premiere at the Palace Theater in New York. It will be nominated for nine Academy Awards and win for Best Original Screenplay (Welles and Herman Mankiewicz). The making of "Citizen Kane" is an oft-retold saga all of its own, with William Randolph Hearst repeatedly trying to quash its release to no avail. "Citizen Kane" is widely regarded as one of the best films ever made, and can fairly be said to the high point of Welles' long and inventive career. Audience reception upon its release, however, is muted.
The Esposito Brothers, who stand accused of murder near the Empire State Building, are convicted of two counts of murder after one minute of deliberation. A photographer happened to be nearby and captured stunning images of the incident. The brothers' attempt to plead insanity as their defense fails. However, the case greatly expands the use of the insanity defense.
General Mills introduces its new cereal Cheerioats. The name eventually will become Cheerios, and the cereal remains a steady seller for many decades.
US Defense Savings Bonds and Stamps, better known as war bonds, go on sale.
April 1941
April 1, 1941: Rommel Takes Brega
April 2, 1941:Rommel Takes Agedabia
April 3, 1941: Convoy SC-26 Destruction
April 4, 1941: Rommel Takes Benghazi
April 5, 1941: Rommel Rolling
April 6, 1941: Operation Marita
April 7, 1941: Rommel Takes Derna
April 8, 1941: Yugoslavia Crumbling
April 9, 1941: Thessaloniki Falls
April 10, 1941: USS Niblack Attacks
April 11, 1941: Good Friday Raid
April 12, 1941: Belgrade and Bardia Fall
April 13, 1941: Soviet-Japanese Pact
April 14, 1941: King Peter Leaves
April 15, 1941: Flying Tigers
April 16, 1941: Battle of Platamon
April 17, 1941: Yugoslavia Gone
April 18, 1941: Me 262 First Flight
April 19, 1941: London Smashed
April 20, 1941: Hitler's Best Birthday
April 21, 1941: Greek Army Surrenders
April 22, 1941: Pancevo Massacre
April 23, 1941: CAM Ships
April 24, 1941: Battle of Thermopylae
April 25, 1941: Operation Demon
April 26, 1941: Operation Hannibal
April 27, 1941: Athens Falls
April 28, 1941: Hitler Firm about Barbarossa
April 29, 1941: Mainland Greece Falls
April 30, 1941: Rommel Attacks
May 1941
May 1, 1941: British Hold Tobruk
May 2, 1941: Anglo-Iraq War
May 3, 1941: Liverpool Hammered
May 4, 1941: Hitler Victory Speech
May 5, 1941: Patriots Day
May 6, 1941: Stalin In Command
May 7, 1941: May Blitz
May 8, 1941: Pinguin Sunk
May 9, 1941: U-110 Captured
May 10, 1941: Hess Flies Into History
May 11, 1941: The Hess Peace Plan
May 12, 1941: Tiger Arrives Safely
May 13, 1941: Keitel's Illegal Order
May 14, 1941: Holocaust in Paris
May 15, 1941: Operation Brevity
May 16, 1941: Blitz Ends
May 17, 1941: Habbaniya Relieved
May 18, 1941: Croatia Partitioned
May 19, 1941: Bismarck at Sea
May 20, 1941: Invasion of Crete
May 21, 1941: Robin Moore Sinking
May 22, 1941: Royal Navy Destruction Off Crete
May 23, 1941: Crete Must Be Won
May 24, 1941: Bismarck Sinks Hood
May 25, 1941: Lütjens' Brilliant Maneuver
May 26, 1941: Bismarck Stopped
May 27, 1941: Bismarck Sunk
May 28, 1941: Crete Lost
May 29, 1941: Royal Navy Mauled Off Crete
May 30, 1941: Sorge Warns, Stalin Ignores
May 31, 1941: British Take Baghdad
2020