Monday 16 February 1942
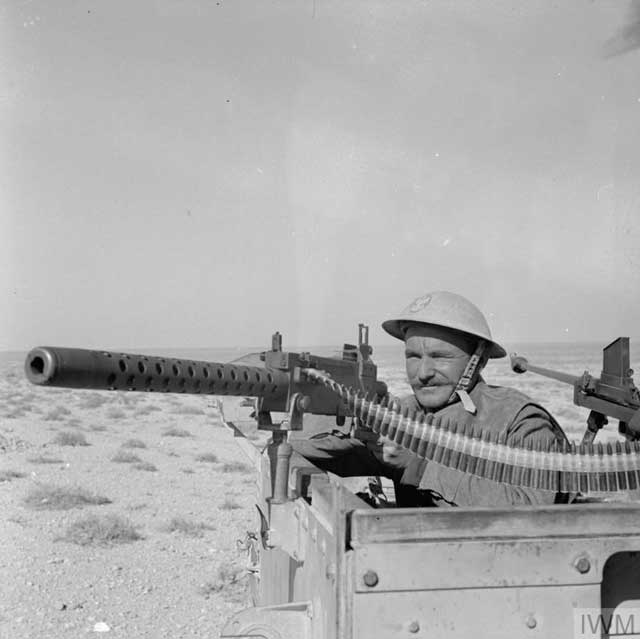 |
| "These pictures were taken at the extreme forward positions around Carmuset er Regem (Karmusat ar Rijam) area near Gazala, show infantry and artillery units of the Polish Independent Carpathian Rifles Brigade facing German and Italian forces." 16 February 1942. © IWM (E 8413). |
In Burma, the bitter battle at Bilin River continues. The 17th Indian Infantry Division is the only large Allied formation between the Japanese and Rangoon, and the fate of Burma hangs in the balance. The two understrength Japanese infantry divisions making the attack, the 33d and 55th, are well-trained in jungle warfare and can operate independently of motor transport. The Allied troops, on the other hand, are deficient in those areas. The Japanese maintain pressure on the British garrisons but also stealthily send units through the jungle to cut off the British lines of communication. Army Commander General Hutton comes forward to see how things are going and is dismayed. The Bilin River at that time of year is dry and little more than a sandy ditch, offering little defensive aid. The Sittang River to the rear is much more useful defensively. He gives Brigadier Sir John George Smyth, V.C., commander of the 17th, permission to withdraw.
Japanese planes attack an Allied convoy bound for Timor. It is led by US Navy heavy cruiser USS Houston and the destroyer USS Peary. The planes score no hits, but near-misses kill two men and injure 18 others. After this incident, the convoy is rerouted to Darwin, Australian, thereby virtually abandoning any hope of holding a position on Timor.
 |
| The Daily Mirror of 16 February 1942 reports the loss of Singapore, announced in a radio address by Prime Minister Winston Churchill the previous night. |
 |
| Time Magazine, 16 February 1942, has Soviet Marshal Shaposhnikov on the cover. |
European Air Operations: During the day, RAF No. 88 and 226 Squadrons send eight Boston bombers on anti-shipping operations off the Dutch coast. This is a new mission for the Boston bombers, their first regular one. This mission does not result in any ships attacked or bombers lost.
After dark, RAF Bomber Command sense 37 Hampden and 12 Manchester bombers to lay mines in the Frisian Islands. One Hampden and one Manchester fail to return. Another 18 Wellingtons hit different targets in northern Germany with eight planes bombing Bremen, seven bombing Aurich, two bombing Oldenburg, and one bombing Wilhelmshaven. Two bombers hit Schipol Airfield at Amsterdam and Soesterberg Airfield near Utrecht. The British also send 11 bombers to drop leaflets over France. One British tactic at this stage is simply to spread out their attacks in order to maximize their nuisance value, as every raid requires that city's tired workers to get out of bed and troop down to shelters. Some raids force all of the Reich's workers to do so because it is unclear where the bombers will strike. In some ways, this is more useful to the British war effort than the actual effects of the bombs dropped.
 |
| U-156 (foreground) and U-507 (background) in September 1942 during the Laconia incident. |
In a very rare direct attack by Reich forces on land targets in the Western Hemisphere, U-156 (Kptlt. Werner Hartenstein), on its second patrol out of Lorient, attempts to shell Aruba. Hartenstein orders the crew to use the 37 mm (1.46 inch) deck gun to fire on the important oil refinery installation on the island. However, through sheer negligence, the two-man gun crew forgets to remove the water plug from the gun barrel. This causes the shell to explode within the barrel and throw shrapnel everywhere. The explosion kills the triggerman, Matrosengefreiter Heinrich Büssinger, and causes the gunnery officer standing nearby, II WO Leutnant zur See Dietrich von dem Borne, to lose his right leg. This disaster does not cause Hartenstein to abandon his attack, however. He orders the crew to saw off the shattered portion of the barrel, and they pump 16 rounds at the refinery. The shortened barrel, however, is not as accurate as it otherwise might be at long range, so only two shells are reported to hit the target. They cause a dent in an oil storage tank and a hole in a house. After this, Hartenstein sets a course for another part of the island.
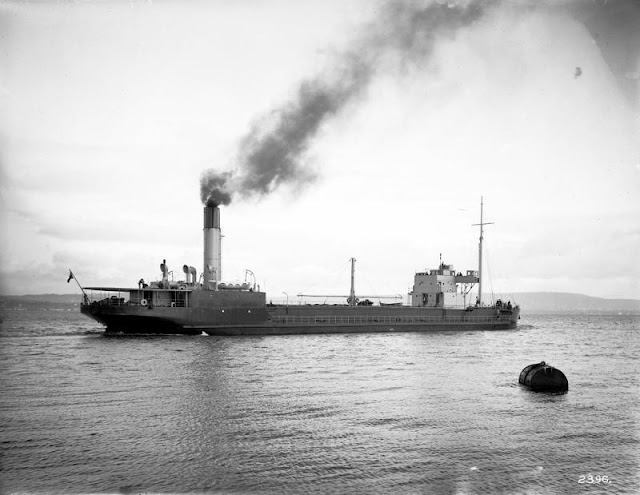 |
| SS Oranjestad, sunk by U-156 on 16 February 1942. |
 |
| SS San Nicholas, sunk by U-502 on 16 February 1942. |
- 2395-ton British freighter Tia Juana (17 dead, nine survivors)
- 2650-ton Venezuelan freighter Monagas (five dead, 26 survivors)
- 2391-ton British freighter San Nicolas (seven deaths, 19 survivors).
U-67 (Kptlt. Günther Müller-Stöckheim), on its third patrol out of Lorient, damages 3177-ton Dutch tanker Rafaela one mile north of Willemstad, Curaçao. The ship is towed to port but there it breaks in two and sinks. Rafaela later is raised, repaired, and returned to service.
 |
| SS Ramapo, sunk by U-108 on 16 February 1942. |
U-564 (Kptlt. Reinhard Suhren), on its fourth patrol out of La Pallice, uses its 88 mm deck gun to damage independent British tanker Opalia about 300 miles northwest of Bermuda. U-564 fires all 83 rounds in its inventory but does not succeed in sinking the tanker, hitting it with only three rounds. The tanker makes it to port and suffers only three injured men due to shell splinters.
 |
| SS Pedernales sinking, 16 February 1942. |
War Crimes: While Singapore fell on 15 February 1942, echoes from that defining moment continue to reverberate throughout the region. In the final days before its capture, Singapore refugees sought any means of escape that they could find. Since the Japanese possessed the only airfield and there were no more large ships willing to make the dangerous passage, that meant overloaded small craft, basically anything that could float. One of those ships was the Sarawak royal yacht Vyner Brooke, which carried wounded soldiers and 65 members of the Australian Army Nursing Service from the 2/13th Australian General Hospital. Also on board the 1670-ton vessel were many civilians and assorted other refugees. This results in the Bangka Island Massacre.
 |
| The NY Times for 16 February 1942 is full of very accurate news about the deteriorating situation for the Allies in the Pacific Theater of Operations. |
British Military: The British form the 10th Army under Lieutenant-General E.P. Quinan. Its responsibilities are Iran and Iraq. Quinan has been the commander of Iraqforce and is famous for his attention to detail (a "spit and polish" officer), something that is extremely prized in a peacetime army but not so much in chaotic war conditions.
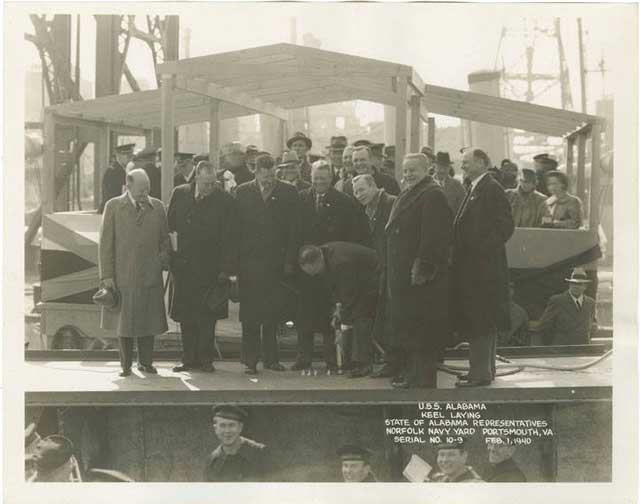 |
| Dignitaries and sailors attending the launch of USS Alabama, 16 February 1942 (US Navy). |
The USAAF Fifth Air Force continues organizing its forces. HQ 49th Pursuit Group (Interceptor) and 7th Pursuit Squadron (Interceptor) transfer from Melbourne to Bankstown, Australia with P-40s. The 8th Pursuit Squadron (Interceptor) transfers from Melbourne to Canberra, also with P-40. The air echelon of the 16th Bombardment Squadron, 27th Bombardment Group, transfers from Brisbane to Batchelor with A-24s. The ground echelon remains trapped on Bataan.
Australian Military: Following the tragic losses suffered by their troops in Singapore, the Australian Chiefs of Staff recommend that "if possible, all Australian forces now under order to transfer to the Far East from the Middle East should be diverted to Australia." This indirectly is hurting the Allied situation in the Middle East, where Australian and New Zealand troops have carried much of the burden against General Erwin Rommel's Afrika Korps. However, the Australians rightly fear the seemingly unstoppable Japanese advance southward towards them.
 |
| A Dr. Seuss political cartoon published on 16 September 1942 shows Hitler and Tojo as thieves leading stolen cattle out of barns marked "Pearl Harbor," "Singapore," and "Maginot Line." Tojo says to Hitler, "Funny... Some people never learn to keep their barn doors locked." PM Magazine, Dr. Seuss Collection, MSS 230. Special Collections & Archives, UC San Diego Library. |
Hungarian Government: Regent Admiral Horthy's party pushes a bill through the legislature which establishes a vice-regency. The bill gives Horthy the right to nominate his own candidate. In practical effect, this bill seeks to establish a de facto dynasty for the Horthy family, though there remains widespread disagreement within the government of automatic succession. In due course, Horthy nominates his son, Istvan Horthy, as vice-regent. This is considered by many, including leaders of the fascist Arrow-Cross Party, as an affront to the Reich, as Istvan is known to be "no friend" of the Third Reich and Hitler does not think very highly of him. However, at this point, the Germans do not want to "rock the boat" far behind the front lines and wish enthusiastic Hungarian participation in the coming summer offensive which they believe will be decisive. So the fascists, at least for the time being, accept this development.
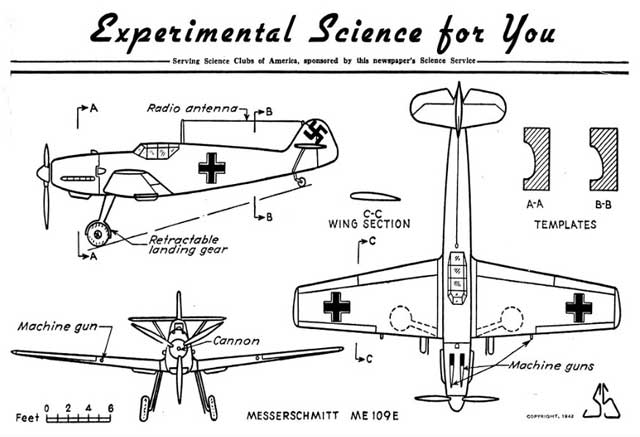 |
| The San Bernardino County California Sun Newspaper, February 16, 1942, gives instructions for building your very own Luftwaffe fighter. |
Holocaust: Heinrich Himmler issues a decree regarding German objectives behind the lines in the East. He directs that "Polonized Germans" - ethnic Germans in Poland who are resistant to Germanization - be resettled in "Old Reich territory" to complete their "re-Germanization." Anyone who resists is to be sent to a concentration camp. Meanwhile, "German farmers, laborers, civil servants, merchants, and artisans" are to be resettled in former Poland in order to create "a living and deep-rooted bastion of German people." The ultimate aim is to replace the native population of Poland with a reliably "German" one and force the native population to become truly German. Ruthless measures are approved for this process, including the confiscation of property, land, and assets.
 |
| Newsweek magazine for 16 February 1942 highlights the growing use of female labor in wartime factories. |
 |
| Life magazine, 16 February 1942, highlights soldier-civilian relations. |
February 1942
February 1, 1942: The US Navy Strikes Back
February 2, 1942: Germans Recovering in Russia
February 3, 1942: Japanese Shell and Bomb Singapore
February 4, 1942: Battle of Makassar Strait
February 5, 1942: Empress of Asia Sunk
February 6, 1942: The Christmas Island Body
February 7, 1942: The Double-V Campaign
February 8, 1942: Japan Invades Singapore
February 9, 1942: French Liner Normandie Capsizes
February 10, 1942: US Car Production Ends
February 11, 1942: Tomforce Fails on Singapore
February 12, 1942: The Channel Dash
February 13, 1942: Japanese Paratroopers In Action
February 14, 1942: RAF Orders Terror Raids
February 15, 1942: Japan Takes Singapore
February 17, 1942: Indian Troops Defect to Japanese
February 18, 1942: Battle of Badung Strait
February 19, 1942: FDR Authorizes Internment Camps
February 20, 1942: O'Hare the Hero
February 21, 1942: Crisis in Burma
February 22, 1942: Bomber Harris Takes Over
February 23, 1942: Bombardment of Ellwood, California
February 24, 1942: US Raid on Wake Island
February 25, 1942: Battle of Los Angeles
February 26, 1942: Gneisenau Eliminated
February 27, 1942: Battle of Java Sea
February 28, 1942: Battle of Sunda Strait
2020
























