Friday 6 February 1942
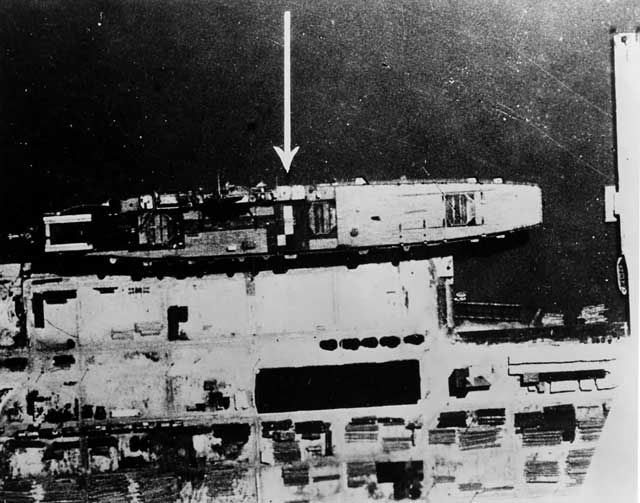 |
| RAF reconnaissance photo showing Graf Zeppelin at Gotenhafen (Gdynia), 6 February 1942 (U.S. Naval History and Heritage Command NH 78306). |
Battle of the Pacific: A Carley float is spotted near Flying Fish Cove, Christmas Island and recovered on 6 February 1942. This island is run by employees of the Christmas Island Phosphate Company, Lt. The float contains a body clothed in a white boiler suit which is buried but not identified, as the staff is preparing to evacuate (which is done by 23 February 1942). This random occurrence begins a mystery that continues into the 21st Century, as some people believe that the float and body came from lost Australian cruiser HMAS Sydney, sunk on 19 November 1941. Since there were no survivors of that ship's encounter with German raider Kormoran and no bodies were ever recovered, this would be the only remains ever found from the doomed ship. The body is exhumed and examined in 2006 with inconclusive results. This remains under review by the Australian government and a great deal of effort, time, and thought has been expended on the human remains. They also have been the foundation of various conspiracy theories, such as that the German machine-gunned any survivors of the Sydney (there is no proof of this aside from interpretations about the state of the remains). This is one of the longest-lasting investigations stemming from World War II.
On 6 February 2021, the Australian government announced that DNA testing has proven that the body was, in fact, a deceased crewman from HMAS Sydney. His name was Able Seaman (AB) Thomas Welsby Clark, a native of Brisbane.
General Tomoyuki Yamashita, General Office Commanding 25th Army, is safely ensconced in the royal palace directly across the strait from Singapore. The British know he is there, but do not shell the palace out of respect for the feelings of the local people. Yamashita's presence there serves multiple purposes, including suggesting to the British that the major Japanese invasion of Singapore will come in the eastern portion of the strait near the destroyed causeway. Yamashita summons his officers at 11:00 and gives them the plan of attack. He plans a feint in the northeast on the night of 7 February, when he will have the ceremonial Imperial Guards Division take Palau Ubin Island opposite Chang in the northeast of Singapore. On the 8th, the 5th and 18th Divisions will mount the main invasion in northwest Singapore. The more perceptive British strategists in Singapore, such as British chief engineer Brigadier Ivan Simson, divine this plan and warn Lieutenant General Ernest Percival, General Officer Commanding Malaya Command, that the danger lies in the northwest. Percival, however, is convinced that the attack will occur in the east, which provides a more direct route to the heart of Singapore, and continues reinforcing that area.
After dark, the Australian 22nd Brigade sends three small patrols across the strait to Johor. The Japanese spot one of them, sinking its ship and kill the commander. The other patrols manage to gather intelligence about Japanese troop concentrations. The Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army, supported by Australian troops, sink and kill a Japanese patrol that was attempting to cross the Strait for similar purposes.
In the Philippines, the Japanese attack the US Army I Corps sector in the western half of the Bataan Peninsula. Their aim is to relieve two dwindling Japanese pockets just south of the Allied Main Line of Resistance (MLR). The Japanese attack gets within 800 years (meters) of the main pocket but then are stopped by elements of the 11th Division, Philippine Army. This Japanese wedge in the MLR becomes known as the "Upper Pocket," though this is a misnomer because it is not technically a pocket (though it is isolated by the river at its back). Further north, in Manila Bay, the US continues to hold isolated islands where Fort Drum and Fort Frank are located. The Japanese begin shelling these islands today from artillery positioned along the south shore of the Bay in the vicinity of Ternate.
The Allies continue to believe that the Bataan Peninsula can be held indefinitely. There is little sense of urgency, though everyone understands the seriousness of the battles underway. Thus, staff officers worry more about supplies and reinforcements there rather than an evacuation. Today, the Engineer, United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE), submits to G-4 (logistics), USAFFE, a detailed list of requested supplies for Bataan to be shipped "to whatever supply point may be most advantageous." This includes, among other things, camouflage nets, truck radiators, barbed wire, chemicals, paper, mapping and aerial reconnaissance supplies, construction supplies such as acetylene bottles, paintbrushes, and explosives for demolition work. The Engineer recommends that the supplies be sent on three ships so that some get through despite losses. There is nothing wrong with the list and it certainly comports with the army's basic requirements. However, its underlying premise is that the US presence on Bataan is stable and likely to last for a long time since, even if approved, these items would take months to procure and ship.
Fierce air battles continue over Burma. At about 10:00, the American Volunteer Group (AVG) destroys four Nakajima Ki-27, Army Type 97 Fighters near Rangoon. Japanese forces are infiltrating across the Salween River but are not yet in a position to mount a major attack to dislodge the Indian defenders there.
The gradual Japanese occupation of the Netherlands East Indies continues as a detachment lands at Gorontalo on Minahassa Peninsula, west of Menado, on Celebes Island. Japanese bombers attack Palembang P1 Airfield on Sumatra at 1100 hours. During the attack, they shoot down two Blenheim bombers and four Hawker Hurricanes and destroy two Buffaloes on the ground. The Dutch receive reconnaissance reports of Japanese naval forces concentrating near the Anambas Islands. Agents in French Indochina report the presence of a Japanese airborne division which is prepared for action.
Eastern Front: The Germans have avoided disaster by reopening supply lines to the Fourth Army and other large formations that were isolated by the Soviet counteroffensive around Moscow in December and January 1942. However, large forces remain surrounded at Kholm and Demyansk and there are no plans to relieve them anytime soon. Instead, the Germans have decided to supply them by air in the first sustained airlift in military history. Hitler is solidly behind this idea, though his underlings sometimes advise him that the planes could be better used elsewhere and the pockets are unsustainable. The airlift is hampered by the absence of airfields, so many of the supply efforts must be made by airdrops. These drops are not always accurate, and fierce battles develop as both sides attempt to recover the crates in the contested fringe areas. Overall, though, the airlift idea works, though life inside the pockets is grim and the defenses barely hold. The Red Army also has troops behind German lines, most notably south of Rzhev, and they, too, survive only with airlifts. There Germans are astonished to see the Red Air Force transports landing within view and in all kinds of weather.
European Air Operations: The RAF resumes operations after a mid-winter break. During the day, it sends 33 Hampden and 13 Manchester bombers to lay mines in the Frisian Islands. The British lose one Hampden.
RAF Bomber Command also sends 57 Wellington and 3 Stirling bombers to attack the German naval base at Brest. The cloudy weather prevents precision bombing and only 21 bombers report dropping their bombs on the target. If the raid has any significance, it is to stimulate German plans for Operation Cerberus, the Channel Dash scheduled for four days before the new moon on 11 February 1942.
Battle of the Atlantic: Operation Paukenschlag (Drumbeat) continues off the east coast of the United States with the arrival of the second wave of U-boats. The first wave of the operation sank 25 Allied ships in 25 days. The most successful U-boat was U-123, which sank nine ships. This next wave of the attack will, when it is completed, replace the original six U-boats with 15 submarines. The US Navy is overstretched and has not yet established a convoy system along the coast. The U-boats throughout the war enjoy their greatest success against "independents" and thus find great success with unescorted freighters and tankers which often are illuminated by cities behind them along the shore which are brightly lit.
U-82 (Kptlt. Siegfried Rollmann), on its third patrol out of La Pallice, France, has sunk three ships of 19,307 tons on this patrol in the western Atlantic and is returning to France when it runs out of luck. After spotting Convoy OS-18 northeast of the Azore Islands (Rollmann informs his superiors of this and he is ordered to shadow the convoy), Rollmann is spotted by Royal Navy escorts sloop Rochester (L50) and corvette Tamarisk. They combine to sink U-82, and there are no survivors of the crew of 34 to add further details. With a total of 51,859 tons of cargo shipping sunk and one warship of 1190 tons sunk, along with damaging a 1999-ton freighter, U-82 is one of the more successful U-boats of World War II.
U-107 (Kptlt. Harald Gelhaus), on its fifth patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 3431-ton US freighter Major Wheeler in the Atlantic while en route from Fajardo, Puerto Rico to Philadelphia carrying 4,611 pounds of sugar. The ship sinks by the stern within two minutes. All 35 men aboard perished.
U-106 torpedoes, shells, and sinks 10,107-ton refrigerated cargo liner Opawa MV about 400 miles northeast of Bermuda. There are 56 deaths and 15 survivors, including master Captain W.G. Evans.
In an incident that is sometimes reported as happening on either 5 or 6 February 1942, U-109 (Kptlt Bleichrodt) torpedoes and sinks 3530-ton Panamian freighter SS Halcyon. Search and rescue take place on 6 February 1942. A search plane finds the wreckage and directs British tanker British Prestige to the area. It spends the day hunting down and rescuing 27 survivors, one 73 years old.
Battle of the Mediterranean: On land, the two sides settle down to garrison duties, the British on the Gazala Line and the Axis forces around Mechili.The Afrika Korps under Lieutenant General Erwin Rommel advance of 350 miles past Benghazi has been a bonanza for the Wehrmacht, as the British have not only abandoned their own supplies but also previously abandoned German supplies such as ammunition that the British did not have time to remove.
On Malta, planes of RAF No. 21 Squadron (Blenheim IV) is flying off the island of Filfla when some Bf 109s of JG 53 appear and shoot down three Blenheims. Lt. Hans, Oblt. Wittmeyer, Lt. Herbert Soukup, and Oblt. Helmut Belser all claim victories.
Arab/Axis Relations: Amin al-Husseini, the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, travels from Germany to Italy and confers with Benito Mussolini in Rome. Husseini, who previously has conferred with Hitler and other top German leaders, feels that they have a common enemy in the British, who he sees as protecting the Jewish people in the Middle East. It is a very fine point and perhaps a point without much of a distinction, but while Hitler and his cronies want to exterminate the Jewish people, Husseini only wants to destroy Zionism and expel all Jewish people from what he considers to be Arab lands. The Axis powers hope that Husseini can raise troops against the Allies and rise up in a giant Jihad against them throughout the Middle East. Husseini is willing to do this, but he has virtually no military power, only somewhat shaky moral authority and popular influence.
Allied Relations: The first meeting of the military leaders of the United Kingdom and the United States, the Combined Chief of Staff, takes place in Washington, D.C.
designates certain areas as Naval Coastal Frontiers. This includes the Eastern, Gulf, Caribbean, Panama, Hawaiian, Northwest, Western, and Philippine Sea Frontiers.
A USAAF P-40 Kittyhawk piloted by 2nd Lieutenant Oscar W. A. Handy (0-425080) of the 3rd Pursuit Squadron (Provisional) crashes at Darwin, Northern Territory. Handy survives.
The 178th Signal Company is constituted at Camp Shelby, Mississippi. It will serve with distinction in the Rhineland in 1944 and Vietnam in the 1960s.
British Military: In a typical wartime accident, a Bristol Blenheim on a training mission crashes into a tree after taking off from Hinton-in-the-Hedges. The only man aboard, Sgt William Everard-Smith of 13 OTU RAF, is buried at Chorley (St. Gregory) Roman Catholic Churchyard nearby. These crashes happen through pilot error, strained maintenance servicing, poor visibility, and other factors that are not as pronounced during peacetime.
Hermann Goering's position as plenipotentiary of the Four Year Plan, which destroy attempts at coordination toward efficiency. While Goering continues in this position and is allowed to continue building his personal empire primarily centered in Austria and the Balkans, Todt is given sweeping new powers over the wartime economy. This is a tacit recognition by Hitler that final victory is going to take more time than originally thought and the Reich has to prepare for a long and arduous war.
Egypt: Under intense pressure from the British (British ambassador Sir Miles Lampson has surrounded the royal palace with tanks in the "Abdeen Palace incident"), King Farouk organizes a new Wafd (nationalist) government. He appoints Mostafa El-Nahas to the position of Prime Minister. Nahas has a reputation for being corrupt (as just one example, he is accused of forcing landowners to sell him prime property), but he is acceptable to the British because his pecuniary motivations outweigh any pro-Axis sympathies that he may or may not have. He also was one of the signers of the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty of 1936, which indicates some willingness to work with the British, though (long after the war) he later denounces that treaty during a low-point in Egyptian-British relations.
American Homefront: Monogram Pictures releases "Law of the Jungle" (1942), a wartime thriller directed by Jean Yarbrough about German spies in British Rhodesia, Africa.
February 1942
February 1, 1942: The US Navy Strikes Back
February 2, 1942: Germans Recovering in Russia
February 3, 1942: Japanese Shell and Bomb Singapore
February 4, 1942: Battle of Makassar Strait
February 5, 1942: Empress of Asia Sunk
February 6, 1942: The Christmas Island Body
February 7, 1942: The Double-V Campaign
February 8, 1942: Japan Invades Singapore
February 9, 1942: French Liner Normandie Capsizes
February 10, 1942: US Car Production Ends
February 11, 1942: Tomforce Fails on Singapore
February 12, 1942: The Channel Dash
February 13, 1942: Japanese Paratroopers In Action
February 14, 1942: RAF Orders Terror Raids
February 15, 1942: Japan Takes Singapore
February 17, 1942: Indian Troops Defect to Japanese
February 18, 1942: Battle of Badung Strait
February 19, 1942: FDR Authorizes Internment Camps
February 20, 1942: O'Hare the Hero
February 21, 1942: Crisis in Burma
February 22, 1942: Bomber Harris Takes Over
February 23, 1942: Bombardment of Ellwood, California
February 24, 1942: US Raid on Wake Island
February 25, 1942: Battle of Los Angeles
February 26, 1942: Gneisenau Eliminated
February 27, 1942: Battle of Java Sea
February 28, 1942: Battle of Sunda Strait
2020
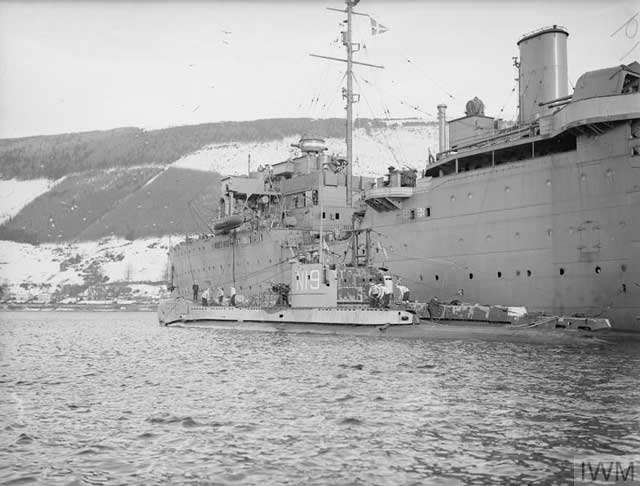 |
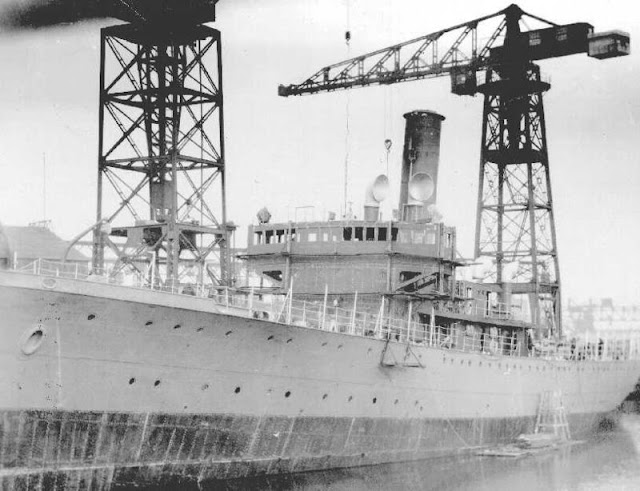
| "HMS UTMOST alongside the depot ship HMS FORTH." 6 February 1942 (© IWM (A 7726)). |
After dark, the Australian 22nd Brigade sends three small patrols across the strait to Johor. The Japanese spot one of them, sinking its ship and kill the commander. The other patrols manage to gather intelligence about Japanese troop concentrations. The Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army, supported by Australian troops, sink and kill a Japanese patrol that was attempting to cross the Strait for similar purposes.
In the Philippines, the Japanese attack the US Army I Corps sector in the western half of the Bataan Peninsula. Their aim is to relieve two dwindling Japanese pockets just south of the Allied Main Line of Resistance (MLR). The Japanese attack gets within 800 years (meters) of the main pocket but then are stopped by elements of the 11th Division, Philippine Army. This Japanese wedge in the MLR becomes known as the "Upper Pocket," though this is a misnomer because it is not technically a pocket (though it is isolated by the river at its back). Further north, in Manila Bay, the US continues to hold isolated islands where Fort Drum and Fort Frank are located. The Japanese begin shelling these islands today from artillery positioned along the south shore of the Bay in the vicinity of Ternate.
 |
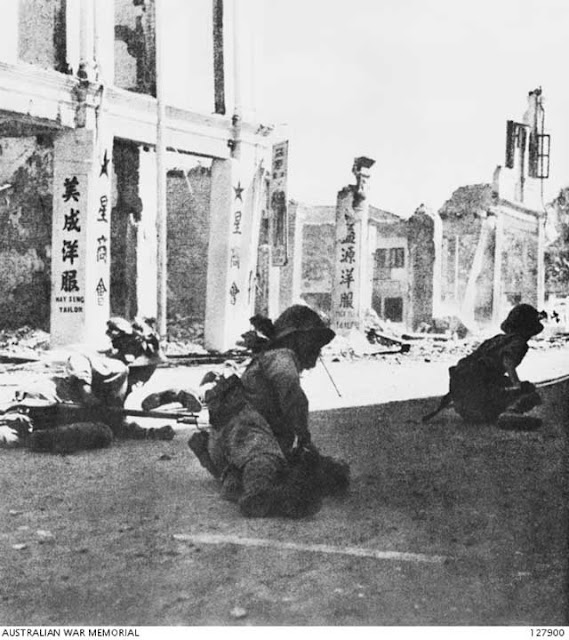
| The New York Times publishes on page 8 what it describes as the "First Pictures of Japanese Entering Manila." |
 |
| USS Downes (DD-375). "Being floated out of Pearl Harbor Navy Yard's Drydock # 1, while under salvage on 6 February 1942. Light-colored patches cover areas of severe damage to her hull. She had been bombed and burned out during the Japanese attack on 7 December 1941. U.S. Naval History and Heritage Command Photograph." NH 54557. |
The gradual Japanese occupation of the Netherlands East Indies continues as a detachment lands at Gorontalo on Minahassa Peninsula, west of Menado, on Celebes Island. Japanese bombers attack Palembang P1 Airfield on Sumatra at 1100 hours. During the attack, they shoot down two Blenheim bombers and four Hawker Hurricanes and destroy two Buffaloes on the ground. The Dutch receive reconnaissance reports of Japanese naval forces concentrating near the Anambas Islands. Agents in French Indochina report the presence of a Japanese airborne division which is prepared for action.
 |
| Reich Organization Leader Robert Ley speaks at a rally at the Berlin Sports Palace to employees of the Siemens company on 6 February 1942. Behind him is a propaganda poster that reads, "He fights harder! We increase our performance." The Winter Relief is in full swing, a little late but better late than never (Hoffmann, Federal Archive Fig. 183-J00340). |
European Air Operations: The RAF resumes operations after a mid-winter break. During the day, it sends 33 Hampden and 13 Manchester bombers to lay mines in the Frisian Islands. The British lose one Hampden.
RAF Bomber Command also sends 57 Wellington and 3 Stirling bombers to attack the German naval base at Brest. The cloudy weather prevents precision bombing and only 21 bombers report dropping their bombs on the target. If the raid has any significance, it is to stimulate German plans for Operation Cerberus, the Channel Dash scheduled for four days before the new moon on 11 February 1942.
 |
| "Officers and members UTMOST's crew at their action stations in the interior of the submarine. The Commanding Officer, Lieut Cdr R D Cayley, is at the periscope." Taken upon HMS Utmost's arrival at Holy Loch on 6 February 1942 after a year of service in the Mediterranean. © IWM (A 7721). |
 |
| U-82, sunk in the North Atlantic on 6 February 1942. |
 |
| SS Major Wheeler, sunk on 6 February 1942. |
 |
| 10,107-ton cargo liner MV Opawa, sunk on 6 February 1942. |
In an incident that is sometimes reported as happening on either 5 or 6 February 1942, U-109 (Kptlt Bleichrodt) torpedoes and sinks 3530-ton Panamian freighter SS Halcyon. Search and rescue take place on 6 February 1942. A search plane finds the wreckage and directs British tanker British Prestige to the area. It spends the day hunting down and rescuing 27 survivors, one 73 years old.
 |
| British tanker British Prestige (courtesy of Eric Wiberg). |
On Malta, planes of RAF No. 21 Squadron (Blenheim IV) is flying off the island of Filfla when some Bf 109s of JG 53 appear and shoot down three Blenheims. Lt. Hans, Oblt. Wittmeyer, Lt. Herbert Soukup, and Oblt. Helmut Belser all claim victories.
 |
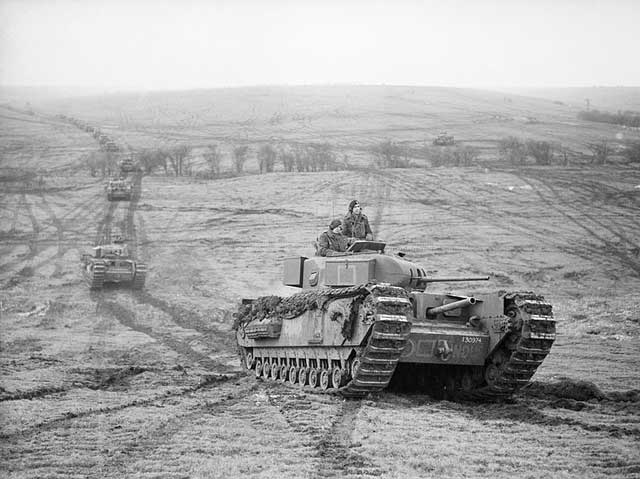
| "The crew of a Crusader tank cleaning the barrel of the 2-pdr gun, 6 February 1942." © IWM (E 8078). |
Allied Relations: The first meeting of the military leaders of the United Kingdom and the United States, the Combined Chief of Staff, takes place in Washington, D.C.
designates certain areas as Naval Coastal Frontiers. This includes the Eastern, Gulf, Caribbean, Panama, Hawaiian, Northwest, Western, and Philippine Sea Frontiers.
A USAAF P-40 Kittyhawk piloted by 2nd Lieutenant Oscar W. A. Handy (0-425080) of the 3rd Pursuit Squadron (Provisional) crashes at Darwin, Northern Territory. Handy survives.
The 178th Signal Company is constituted at Camp Shelby, Mississippi. It will serve with distinction in the Rhineland in 1944 and Vietnam in the 1960s.
British Military: In a typical wartime accident, a Bristol Blenheim on a training mission crashes into a tree after taking off from Hinton-in-the-Hedges. The only man aboard, Sgt William Everard-Smith of 13 OTU RAF, is buried at Chorley (St. Gregory) Roman Catholic Churchyard nearby. These crashes happen through pilot error, strained maintenance servicing, poor visibility, and other factors that are not as pronounced during peacetime.
Hermann Goering's position as plenipotentiary of the Four Year Plan, which destroy attempts at coordination toward efficiency. While Goering continues in this position and is allowed to continue building his personal empire primarily centered in Austria and the Balkans, Todt is given sweeping new powers over the wartime economy. This is a tacit recognition by Hitler that final victory is going to take more time than originally thought and the Reich has to prepare for a long and arduous war.
 |
| The crew of HMS Utmost hoists the Jolly Roger showing their victories while on patrol after arriving in port at Holy Loch, Scotland, 6 February 1942. |
The attitude of those with near relatives in our Garrison at Rabaul is becoming bitter and hostile at the lack of any news of their sons, brothers and husbands, and of the feeling that is being created that although something could be done to assist them, nothing is being attempted. [NAA A2684/3 Item 749]There indeed are many survivors of the invasion of Rabaul, but little is known about their fate and the vast majority simply disappear without a trace. It is worthwhile to note that Japanese soldiers in some other places at this time of the war (perhaps most notoriously at Hong Kong) have been proven to be torturing and killing prisoners and then burning the bodies to hide their crimes.
American Homefront: Monogram Pictures releases "Law of the Jungle" (1942), a wartime thriller directed by Jean Yarbrough about German spies in British Rhodesia, Africa.
 |
| "Doc Savage," Volume 18, No. 6, February 1942. |
February 1942
February 1, 1942: The US Navy Strikes Back
February 2, 1942: Germans Recovering in Russia
February 3, 1942: Japanese Shell and Bomb Singapore
February 4, 1942: Battle of Makassar Strait
February 5, 1942: Empress of Asia Sunk
February 6, 1942: The Christmas Island Body
February 7, 1942: The Double-V Campaign
February 8, 1942: Japan Invades Singapore
February 9, 1942: French Liner Normandie Capsizes
February 10, 1942: US Car Production Ends
February 11, 1942: Tomforce Fails on Singapore
February 12, 1942: The Channel Dash
February 13, 1942: Japanese Paratroopers In Action
February 14, 1942: RAF Orders Terror Raids
February 15, 1942: Japan Takes Singapore
February 17, 1942: Indian Troops Defect to Japanese
February 18, 1942: Battle of Badung Strait
February 19, 1942: FDR Authorizes Internment Camps
February 20, 1942: O'Hare the Hero
February 21, 1942: Crisis in Burma
February 22, 1942: Bomber Harris Takes Over
February 23, 1942: Bombardment of Ellwood, California
February 24, 1942: US Raid on Wake Island
February 25, 1942: Battle of Los Angeles
February 26, 1942: Gneisenau Eliminated
February 27, 1942: Battle of Java Sea
February 28, 1942: Battle of Sunda Strait
2020





















