Sunday 12 May 1940
 |
| German tanks in the Ardennes, May 1940 (Blucher Federal Archive). |
Allied Headquarters: General Gamelin, the Commander-in-Chief of the French forces, has his headquarters at Vincennes on
12 May 1940. He has no radio and notes that he does not even have a radio - so he has "no idea" where the front lies.
German Headquarters: Heinz Guderian is in command of German XIX Armeekorps (as he was during the Polish campaign) at Sedan. He favors an aggressive stance and proposes enlarging his bridgehead across the Meuse (he has 3 intact bridges) to 20 km (12 miles) deep. His superior, General Ewald von Kleist, orders him to be more cautious and limit his penetration to 8 km (5 miles). Hitler is wary of the tanks outrunning the infantry and seems to envisage a static campaign with a definite, unchanging front forming - as in his own experiences during World War I.
Western Front: The Dutch are making valiant defensive efforts at key points, but overall are being pushed back into their Fortress Holland defensive zone between Rotterdam and Amsterdam.
The Germans advancing near Tilburg run into the French 7th Army and there is heavy fighting. The German advance continues.
The German Army Group A, led by Panzer Group Kleist, advances through the Ardennes and reaches Sedan without serious opposition. The column of military vehicles stretches back to the German border. This is the first German intrusion on French soil.
The French form up on the opposite bank with artillery support. The artillery shells Sedan during the night. The importance of Sedan is not the city itself, but the entry it provides to the heart of France. Its capture in 1870 essentially decided the Franco-Prussian war.
North of Sedan, the Germans are on the Meuse at Dinant. General Rommel's 7th Panzer Division is on the riverbank and he personally scouts out a way to cross it.
The Germans send a three-man scouting part to see if Fort Kornwerderzand at the Afsluitdijk is defended. The fort opens fire and kills two of the three men. The Germans decide to take the fort, beginning with Luftwaffe strikes.
The first tank battle of the campaign erupts between General René Prioux’s 2d French armored divisions (confusingly, Corps de Cavalerie) and the 3d and 4th Panzer Divisions at the Gembloux Gap. The 4th Panzer Division assaults toward Hannut, which protects the 6th Army's flank. They engage 25 French tanks and destroy 7 of them for no losses. The Germans probe toward Tirlemont, drawing Allied forces there while continuing toward Hannut. The French attempt a flank attack, which fails, and the German panzers run into a French strongpoint at Crehen.
The French are forced to retreat to Medorp after breaking out of an encirclement. They also abandon Hannut. In the evening, the Germans renew the attack and force the French strongpoint at Wansin to withdraw, but the rest of the French line holds. The outcome is a tentative French victory for having stopped the German advance, even if only temporarily. The French Somua S35 and Hotchkiss H35 tanks are good equipment, though they have their faults. They outclass the German Panzer Is and IIs, though the Panzer IIIs are more of a match.
The German 18th Army captures Eindhoven and continues pushing forward.
At Grebbeberg, the German 207th Infantry Division, supported by the SS Brigade Der Fuhrer, directly attacks the hill that dominates the defense. After an artillery barrage of several hours, the SS Brigade attacks. The SS men take an 18th Century fort, the Hoornwerk. This provides a wedge into the Dutch battle line, whose other guns cannot fire sideways. Dutch counterattacks fail. Obersturmbannführer (Lieutenant Colonel) Hilmar Wäckerle, contrary to orders, moves his battalion forward, penetrates the Dutch line, and gets surrounded - but holds on. The Dutch bring up reinforcements and plan a flank attack on the Germans. It is a confusing situation, but the Germans have the initiative - if they can rescue the impetuous Wäckerle.
German 6th Army pushes across the Albert Canal toward Gembloux.
The German 9th Panzer division is heading to the Moerdijk bridges over Hollands Diep estuary. They are still held by German paratroopers. These bridges, 10 miles south of Rotterdam, prevent the Allies from reinforcing Rotterdam.
The Allies have occupied the Dyle Line with the French 1st Army, 7th Army, 9th Army, and the British Expeditionary Force. The BEF is in position in Belgium.
The Allies hold a conference near Mons, including French Defense Minister Daladier, General Georges, General Billotte, British General Pownall, and Belgian King Leopold.
 |
| Fokker C.5RR 645 of III-2 LvR at Middenmeer after an emergency landing on 12 May 1940 (Photo: collection Nederlands Instituut voor Militaire Historie). |
European Air Operations: Fairey Battle light bombers of No. 12 Squadron attack the Veldwezelt bridge over the Albert Canal. The Germans have brought up anti-aircraft batteries to protect the bridge, which survives with damage.
The RAF sends 38 bombers over Hannut to support the defense of that town, losing 22, and the Arme de l'air sends over 18 new Breguet 693 bombers, losing 8. The Luftwaffe supports the ground operation there with 85 Bf 109s of JG 26, flying 340 sorties during the day. They claim 26 Allied planes for 4 of their own numbers. German anti-aircraft there also claims 25 planes.
The Allies send every available light bomber - some called from Hannut, which thereby loses air support - to attack the Meuse bridges at Sedan. They fail to make any hits and lose 44 percent of their number.
There are Luftwaffe air raids on Rotterdam, including incendiary bombs.
The Luftwaffe attacks and heavily damages Dutch gunboat Friso. It also performs minelaying operations in Belgian waters.
A French pilot, Capt. René Gavoille, reports miles-long Wehrmacht columns in the Ardennes. His superiors are dismissive, calling them "night phantoms." He has spotted Panzer Group Kleist and its 41,140 vehicles on narrow two-lane roads. When he takes off again and takes pictures, they call them "obvious fake tanks."
Adolph Galland, a veteran Luftwaffe ground-attack pilot from the Spanish Civil War, is now a fighter pilot and gains his first aerial victories of the war, destroying three Hurricanes.
Battle of the Atlantic: British ship Roek hits a mine and sinks in the North Sea.
Convoy OA 147 departs from Southend, Convoy OB 147 departs from Liverpool, Convoy HG 30F departs from Gibraltar, Convoy OG 29 forms at Gibraltar, and Convoy HX 42 departs from Halifax.
Norway: The British reinforce Mo i Rana with the British Scots Guards battalion from Harstad. The Germans have troops near Hamnesberget brought in by the seized Norwegian vessel Nord Norge, which the British have sunk (while empty).
Holland: The Dutch Crown Princess, her two daughters Irene and Beatrice, and Prince Bernharddeparts for the UK aboard destroyer HMS Codrington.
Spain: Francisco Franco reaffirms Spain's neutrality.
British Government: The new Chancellor of the Exchequer is Sir Kingsley Wood.
American Homefront: Shirley Temple cancels her film contract with 20th Century Fox and retires (temporarily) - at age 11.
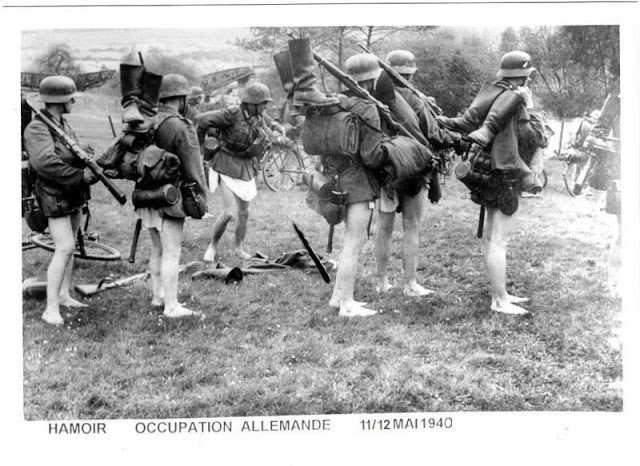 |
| German bicycle troops prepare to cross a river in Belgium by first removing their pants, 11/12 May, 1940. |
May 1940
May 1, 1940: British Leave ÅndalsnesMay 2, 1940: British Depart NamsosMay 3, 1940: Many Norwegians SurrenderingMay 4, 1940: Bader ReturnsMay 5, 1940: HMS Seal SurvivesMay 6, 1940: Allies Focus on NarvikMay 7, 1940: In The Name of God, Go!May 8, 1940: Exit ChamberlainMay 9, 1940: Enter ChurchillMay 10, 1940: Fall GelbMay 11, 1940: Eben Emael SurrendersMay 12, 1940: Germans at SedanMay 13, 1940: Rommel at WorkMay 14, 1940: German Breakout in FranceMay 15, 1940: Holland SurrendersMay 16, 1940: Dash to the ChannelMay 17, 1940: Germans Take BrusselsMay 18, 1940: Germans Take AntwerpMay 19, 1940: Failed French CounterattackMay 20, 1940: Panzers on the CoastMay 21, 1940: Battle of ArrasMay 22, 1940: Attacking Channel PortsMay 23, 1940: British Evacuate BoulogneMay 24, 1940: Hitler's Stop OrderMay 25, 1940: Belgian Defenses CreakingMay 26, 1940: Operation DynamoMay 27, 1940: King Leopold Surrenders May 28, 1940: The Allies Take NarvikMay 29, 1940: Lille FallsMay 30, 1940: Operation FishMay 31, 1940: Peak Day for Dynamo2019