Abstract
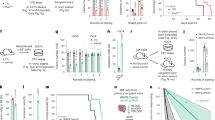
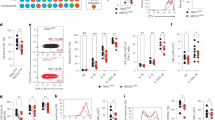
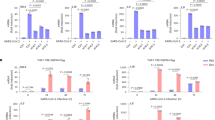
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein (vFLIP) K13 is a potent activator of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway. In this study, we show that infection with KHSV and ectopic expression of K13, but not its NF-κB-defective mutant, suppressed the expression of CXCR4. Suppression of CXCR4 by KSHV and K13 was associated with upregulated expression of miR-146a, a microRNA that is known to bind to the 3′-untranslated region of CXCR4 mRNA. Reporter studies identified two NF-κB sites in the promoter of miR-146a that were essential for its activation by K13. Accordingly, ectopic expression of K13, but not its NF-κB-defective mutant or other vFLIPs, strongly stimulated the miR-146a promoter activity, which could be blocked by specific genetic and pharmacological inhibitors of the NF-κB pathway. Finally, expression of CXCR4 was downregulated in clinical samples of KS and this was accompanied by an increased expression of miR-146a. Our results show that K13-induced NF-κB activity suppresses CXCR4 through upregulation of miR-146a. Downregulation of CXCR4 expression by K13 may contribute to KS development by promoting premature release of KSHV-infected endothelial progenitors into the circulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn GO, Brown JM . (2009). Role of endothelial progenitors and other bone marrow-derived cells in the development of the tumor vasculature. Angiogenesis 12: 159–164.
Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, Chow KY, Harriague J, Moepps B et al. (2005). The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 280: 35760–35766.
Baxter A, Brough S, Cooper A, Floettmann E, Foster S, Harding C et al. (2004). Hit-to-lead studies: the discovery of potent, orally active, thiophenecarboxamide IKK-2 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 2817–2822.
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A, Berahovich R, Miao Z et al. (2006). A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med 203: 2201–2213.
Cameron JE, Yin Q, Fewell C, Lacey M, McBride J, Wang X et al. (2008). Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular microRNA miR-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways. J Virol 82: 1946–1958.
Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM et al. (1994). Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science 266: 1865–1869.
Chaudhary PM, Jasmin A, Eby MT, Hood L . (1999). Modulation of the NF-kappa B pathway by virally encoded death effector domains-containing proteins. Oncogene 18: 5738–5746.
Chaudhary PM, Nicholas J . (2008). Molecular biology of human herpesvirus 8 neoplasia. In: Nicholas J, Jeang K-T, Wu T-C (eds). Human Cancer Viruses. Principles of Transformation and Pathogenesis. Karger: Basel. pp 186–210.
Chugh P, Matta H, Schamus S, Zachariah S, Kumar A, Richardson JA et al. (2005). Constitutive NF-kappaB activation, normal Fas-induced apoptosis, and increased incidence of lymphoma in human herpes virus 8 K13 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 12885–12890.
Ciufo DM, Cannon JS, Poole LJ, Wu FY, Murray P, Ambinder RF et al. (2001). Spindle cell conversion by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: formation of colonies and plaques with mixed lytic and latent gene expression in infected primary dermal microvascular endothelial cell cultures. J Virol 75: 5614–5626.
Dorak T . (2006). Real Time PCR. Taylor & Francis: Oxford, 333pp.
Dourmishev LA, Dourmishev AL, Palmeri D, Schwartz RA, Lukac DM . (2003). Molecular genetics of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) epidemiology and pathogenesis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67: 175–212.
Flore O, Rafii S, Ely S, JJ OL, Hyjek EM, Cesarman E . (1998). Transformation of primary human endothelial cells by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Nature 394: 588–592.
Grossmann C, Podgrabinska S, Skobe M, Ganem D . (2006). Activation of NF-kappaB by the latent vFLIP gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is required for the spindle shape of virus-infected endothelial cells and contributes to their proinflammatory phenotype. J Virol 80: 7179–7185.
Guasparri I, Keller SA, Cesarman E . (2004). KSHV vFLIP is essential for the survival of infected lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 199: 993–1003.
Labbaye C, Spinello I, Quaranta MT, Pelosi E, Pasquini L, Petrucci E et al. (2008). A three-step pathway comprising PLZF/miR-146a/CXCR4 controls megakaryopoiesis. Nat Cell Biol 10: 788–801.
Liu L, Eby MT, Rathore N, Sinha SK, Kumar A, Chaudhary PM . (2002). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein physically associates with and persistently activates the Ikappa B kinase complex. J Biol Chem 277: 13745–13751.
Matta H, Chaudhary PM . (2004). Activation of alternative NF-kappa B pathway by human herpes virus 8-encoded Fas-associated death domain-like IL-1 beta-converting enzyme inhibitory protein (vFLIP). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9399–9404.
Matta H, Mazzacurati L, Schamus S, Yang T, Sun Q, Chaudhary PM . (2007a). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) oncoprotein K13 bypasses TRAFs and directly interacts with the I\{kappa\}B kinase complex to selectively activate N. J Biol Chem 282: 24858–24865.
Matta H, Punj V, Schamus S, Mazzacurati L, Chen AM, Song R et al. (2008). A nuclear role for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded K13 protein in gene regulation. Oncogene 27: 5243–5253.
Matta H, Sun Q, Moses G, Chaudhary PM . (2003). Molecular genetic analysis of human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein-induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 278: 52406–52411.
Matta H, Surabhi RM, Zhao J, Punj V, Sun Q, Schamus S et al. (2007b). Induction of spindle cell morphology in human vascular endothelial cells by human herpesvirus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13. Oncogene 26: 1656–1660.
Moore PS, Chang Y . (2001). Molecular virology of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356: 499–516.
Moses AV, Fish KN, Ruhl R, Smith PP, Strussenberg JG, Zhu L et al. (1999). Long-term infection and transformation of dermal microvascular endothelial cells by human herpesvirus 8. J Virol 73: 6892–6902.
Moses AV, Jarvis MA, Raggo C, Bell YC, Ruhl R, Luukkonen BG et al. (2002). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced upregulation of the c-kit proto-oncogene, as identified by gene expression profiling, is essential for the transformation of endothelial cells. J Virol 76: 8383–8399.
Motsch N, Pfuhl T, Mrazek J, Barth S, Grasser FA . (2007). Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces the expression of the cellular microRNA miR-146a. RNA Biol 4: 131–137.
Naranatt PP, Krishnan HH, Svojanovsky SR, Bloomer C, Mathur S, Chandran B . (2004). Host gene induction and transcriptional reprogramming in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8)-infected endothelial, fibroblast, and B cells: insights into modulation events early during infection. Cancer Res 64: 72–84.
Pellet C, Kerob D, Dupuy A, Carmagnat MV, Mourah S, Podgorniak MP et al. (2006). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viremia is associated with the progression of classic and endemic Kaposi's sarcoma. J Invest Dermatol 126: 621–627.
Perry MM, Moschos SA, Williams AE, Shepherd NJ, Larner-Svensson HM, Lindsay MA . (2008). Rapid changes in microRNA-146a expression negatively regulate the IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. J Immunol 180: 5689–5698.
Poole LJ, Yu Y, Kim PS, Zheng QZ, Pevsner J, Hayward GS . (2002). Altered patterns of cellular gene expression in dermal microvascular endothelial cells infected with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Virol 76: 3395–3420.
Punj V, Matta H, Schamus S, Chaudhary PM . (2009a). Integrated microarray and multiplex cytokine analyses of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13 affected genes and cytokines in human blood vascular endothelial cells. BMC Med Genomics 2: 50.
Punj V, Matta H, Schamus S, Yang T, Chang Y, Chaudhary PM . (2009b). Induction of CCL20 production by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: role of viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13-induced NF-\{kappa\}B activation. Blood 113: 5660–5668.
Raggo C, Ruhl R, McAllister S, Koon H, Dezube BJ, Fruh K et al. (2005). Novel cellular genes essential for transformation of endothelial cells by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Cancer Res 65: 5084–5095.
Sakakibara S, Pise-Masison CA, Brady JN, Tosato G . (2009). Gene regulation and functional alterations induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ORFK13/vFLIP in endothelial cells. J Virol 83: 2140–2153.
Sarid R, Flore O, Bohenzky RA, Chang Y, Moore PS . (1998). Transcription mapping of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) genome in a body cavity-based lymphoma cell line (BC-1). J Virol 72: 1005–1012.
Schulz TF . (2000). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8): epidemiology and pathogenesis. J Antimicrob Chemother 45 Suppl T3: 15–27.
Sierro F, Biben C, Martinez-Munoz L, Mellado M, Ransohoff RM, Li M et al. (2007). Disrupted cardiac development but normal hematopoiesis in mice deficient in the second CXCL12/SDF-1 receptor, CXCR7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 14759–14764.
Sun Q, Matta H, Chaudhary PM . (2003a). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein protects against growth factor withdrawal-induced apoptosis via NF-kappa B activation. Blood 101: 1956–1961.
Sun Q, Matta H, Lu G, Chaudhary PM . (2006). Induction of IL-8 expression by human herpesvirus 8 encoded vFLIP K13 via NF-kappaB activation. Oncogene 25: 2717–2726.
Sun Q, Zachariah S, Chaudhary PM . (2003b). The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE-inhibitory protein induces cellular transformation via NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 278: 52437–52445.
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D . (2006). NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 12481–12486.
Thome M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Fickenscher H, Meinl E, Neipel F et al. (1997). Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 386: 517–521.
Thurau M, Marquardt G, Gonin-Laurent N, Weinlander K, Naschberger E, Jochmann R et al. (2009). Viral inhibitor of apoptosis vFLIP/K13 protects endothelial cells against superoxide-induced cell death. J Virol 83: 598–611.
Urbich C, Dimmeler S . (2004). Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization and role in vascular biology. Circ Res 95: 343–353.
Williams AE, Perry MM, Moschos SA, Larner-Svensson HM, Lindsay MA . (2008). Role of miRNA-146a in the regulation of the innate immune response and cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 36: 1211–1215.
Williams AE, Perry MM, Moschos SA, Lindsay MA . (2007). MicroRNA expression in the aging mouse lung. BMC Genomics 8: 172.
Xu Y, Ganem D . (2007). Induction of chemokine production by latent Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection of endothelial cells. J Gen Virol 88: 46–50.
Ye FC, Zhou FC, Xie JP, Kang T, Greene W, Kuhne K et al. (2008). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latent gene vFLIP inhibits viral lytic replication through NF-kappaB-mediated suppression of the AP-1 pathway: a novel mechanism of virus control of latency. J Virol 82: 4235–4249.
Zhao J, Punj V, Matta H, Mazzacurati L, Schamus S, Yang Y et al. (2007). K13 Blocks KSHV lytic replication and deregulates vIL6 and hIL6 expression: a model of lytic replication induced clonal selection in viral Oncogenesis. PLoS ONE 2: e1067.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr David Baltimore (California Institute of Technology) for the miR-146a promoter reporter constructs, Dr Parkash Gill for SLK cells, the NIH AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program for CXCR4 antibodies and the Cancer Specimen Resources at the University of California, San Francisco and George Washington University, Washington, for providing patient samples. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA85177 and CA124621) and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punj, V., Matta, H., Schamus, S. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein (vFLIP) K13 suppresses CXCR4 expression by upregulating miR-146a. Oncogene 29, 1835–1844 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.460
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.460
Keywords
This article is cited by
The interplay between EBV and KSHV viral products and NF-κB pathway in oncogenesis
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2020)
HPV16 E6 and E7 upregulate the histone lysine demethylase KDM2B through the c-MYC/miR-146a-5p axys
Oncogene (2018)
Onco-GPCR signaling and dysregulated expression of microRNAs in human cancer
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
miR-146a negatively regulates the induction of proinflammatory cytokines in response to Japanese encephalitis virus infection in microglial cells
Archives of Virology (2017)
MicroRNA analysis in mouse neuro-2a cells after pseudorabies virus infection
Journal of NeuroVirology (2017)