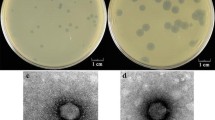
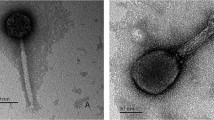
Summary
Bacteriophage T12 is the prototype phage carrying the streptococcal erythrogenic toxin A (speA) gene. To examine more closely the phages involved in lysogenic conversion, we examined 300 group A streptococcal strains, and identified and isolated two new phages that carry the speA gene. The molecular sizes of these phage genomes were between 32 and 40 kb, similar to that of phage T12 (35 kb). However, as ascertained by restriction analysis, the physical maps of the new phage genomes were different from phage T12 and from each other. Hybridization analysis also showed that all of these phages were only partially related to one another and the speA gene was always located close to the phage attachment site. Additionally, colony hybridization showed that whereas phage T12 or one of its close relatives is the most common phage associated with the group A streptococci, phage 49 has a much stronger association with the speA gene. A defective phage was also found following pulsed field gel electrophoresis of total phage DNA. This phage appears to be a resident of strain T253c and is found only following induction of a T253c lysogen. Restriction enzyme analysis of the isolated defective phage DNA suggests that it is the source of the submolar amounts of DNA previously found in association with phage T12 digestion patterns. Additionally, the defective phage may serve as the site of integration of the speA gene-carrying phages described above.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando K, Kurauchi K, Nishimura H (1930) Studies on the “toxins” of hemolytic streptococci. III. On the dual nature of the Dick toxin. J Immunol 18:223–255
Barksdale L, Garmise L, Rivera R (1961) Toxinogeny in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol 81:527–540
Betley MJ, Mekalanos JJ (1985) Staphylococcal enterotoxin A is encoded by phage. Science 229:185–187
Colon-Whitt A, Whitt RS, Cole RM (1979) Production of an erythrogenic toxin (streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin) by a nonlysogenized group-A streptococcus. In: Parker MT (ed) Pathogenic streptococci. Reedbooks Ltd., Chertsey, Surrey, pp 64–65
Dick GF, Dick GH (1924) Etiology of scarlet fever. J Am Med Assoc 82:301–302
Frobisher M, Brown JH (1927) Transmissible toxigenicity of streptococci. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 41:167–173
Gaworzewska E, Colman G (1988) Changes in the pattern of infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Epidem Inf 100: 257–269
Goshorn SC, Schlievert PM (1989) Bacteriophage association of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. J Bacteriol 171:3068–3073
Holmes RK (1976) Characterization and genetic mapping of non-toxinogenic (tox) mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol 19:195–207
Hooker SB, Follensby EM (1934) Studies on scarlet fever. II Different toxins produced by hemolytic streptococci of scarlatinal origin. J Immunol 27:177–193
Inoue K, Iida H (1971) Phage-conversion of toxigenicity in Clostridium botulinum type C and D. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 24:53–56
Johnson LP, Schlievert PM (1983) A physical map of the group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin bacteriophage T12 genome. Mol Gen Genet 189:251–255
Johnson LP, Schlievert PM (1984) Group A streptococcal phage T12 carries the structural gene for pyrogenic exotoxin type A. Mol Gen Genet 194:52–56
Kjems E (1948) Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. 2. Adsorption, lysogenization, and one-step growth experiments. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 42:56–66
Lakshmidevi G, Davidson BE, Hillier AJ (1988) Circular permutation of the genome of a temperate bacteriophage from Streptococcus cremoris BK5. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:511–519
Murphy JR, Papenheimer AM, deBroms ST Jr (1974) Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:11–15
Nida SK, Ferretti JJ (1982) Phage influence on the synthesis of extracellular toxins in group A streptococci. Infect Immun 36:745–750
Novick RP, Khan SA, Murphy E, Iordanescu I, Edelman J, Krolewski J, Rush M (1980) Hitchhiking transposons and other mobile genetic elements and site specific recombination systems in staphylococci. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 45:67–76
O'Brien AD, Newland JW, Miller SF, Holmes RK (1984) Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science 226:694–696
Pitcher DG, Saunders NA, Owen RJ (1989) Rapid extraction of bacterial genomic DNA with guanidium thiocyanate. Lett Appl Microbiol 8:151–156
Sambrook J, Frisch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Haber laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Spanier JG, Cleary PP (1983) A restriction map and analysis of the terminal redundancy in the group A streptococcal bacteriophages SP24. Virology 130:502–513
Stevens FA, Dochez AR (1924) Studies on the biology of Streptococcus. III Agglutination and absorption of agglutinin with Streptococcus scarlatinae. J Exp Med 40:253–262
Stevens DL, Tanner MH, Winship J, Swarts R, Ries KM, Schlievert PM, Kaplan E (1989) Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med 321:1–7
Watson DW (1960) Host-parasite factors in group A streptococcal infections. Pyrogenic and other effects of immunologic distinct exotoxins related to scarlet fever toxins. J Exp Med 111:255–284
Weeks CR, Ferretti JJ (1984) The gene for type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) is located in bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun 46:531–536
Weeks CR, Ferretti JJ (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin gene from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun 52:144–150
Yu CE, Ferretti JJ (1989) Molecular epidemiologic analysis of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene (speA) in clinical Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Infect Immun 57:3715–3719
Zabriskie JB (1964) The role of temperate bacteriophage in the production of erythrogenic toxin by group A streptococci. J Exp Med 119:761–779
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, CE., Ferretti, J.J. Molecular characterization of new group A streptococcal bacteriophages containing the gene for streptococcal erythrogenic toxin A (speA). Molec. Gen. Genet. 231, 161–168 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293833
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293833