Abstract
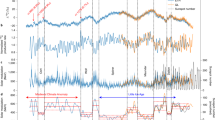
Solar activity alternates between active and quiet phases with an average period of 11 years, and this is known as the Schwabe cycle. Additionally, solar activity occasionally falls into a prolonged quiet phase (grand solar minimum), as represented by the Maunder Minimum in the 17th century, when sunspots were almost absent for 70 years and the length of the Schwabe cycle increased to 14 years. To examine the consistency of the cycle length characteristics during the grand solar minima, the carbon-14 contents in single-year tree rings were measured using an accelerator mass spectrometer as an index of the solar variability during the grand solar minimum of the 4th century BC. The signal of the Schwabe cycle was detected with a statistical confidence level of higher than 95 % by wavelet analysis. This is the oldest evidence for the Schwabe cycle at the present time, and the cycle length is considered to have increased to approximately 16 years during the grand solar minimum of the 4th century BC. This result confirms the association between the increase of the Schwabe cycle length and the weakening of solar activity, and indicates the possible prolonged absence of sunspots in the 4th century BC as during the Maunder Minimum. Theoretical implications from solar dynamo theory are discussed in order to identify the trigger of prolonged sunspot absence. A possible association between the long-term solar variation around the 4th century BC and terrestrial cooling in this period is also discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H.D.: 1959, Astrophys. J. 130, 364.
Babcock, H.W.: 1961, Astrophys. J. 133, 572.
Barber, K.E., Langdon, P.G.: 2007, Quat. Sci. Rev. 26, 3318.
Beer, J., Tobias, S., Weiss, N.: 1998, Solar Phys. 181, 237.
Berggren, A.M., Beer, J., Possnert, G., Aldahan, A., Kubik, P., Christl, M., Johnsen, S.J., Abreu, J., Vinther, B.M.: 2009, Geophys. Res. Lett. 36(11), L11801.
Berner, K.S., Koc, N., Divine, D., Godtliebsen, F., Moros, M.: 2008, Paleoceanography 23, 2.
Bronk Ramsey, C.: 2008, Quat. Sci. Rev. 27(1 – 2), 42.
Bronk Ramsey, C., van der Plicht, J., Weninger, B.: 2001, Radiocarbon 43, 381.
Charbonneau, P., Dikpati, M.: 2000, Astrophys. J. 543, 1027.
Choudhuri, A.R., Karak, B.B.: 2009, Res. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 953.
Desprat, S., Goni, M.F.S., Loutre, M.F.: 2003, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 213, 63.
Dikpati, M., Charbonneau, P.: 1999, Astrophys. J. 518, 508.
Eddy, J.A.: 1976, Science 192, 1189.
Geel, B.V., Buurman, J., Waterbolk, H.T.: 1996, J. Quat. Sci. 11(6), 451.
Gil Garcia, M.J., Ruiz Zapata, M.B., Santisteban, J.I., Mediavilla, R., Lopez-Pamo, E., Dabrio, C.J.: 2007, Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 16, 241.
Godwin, H.: 1962, Nature 195, 984.
Goslar, T.: 2003, PAGES News (Past Global Changes) 11(2 – 3), 12.
Hale, G.E., Nicholson, S.B.: 1925, Astrophys. J. 62, 270.
Hale, G.E., Ellerman, F., Nicholson, S.B., Joy, A.H.: 1919, Astrophys. J. 49, 153.
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M., Reichmann, E.J.: 2002, Solar Phys. 211, 357.
Hathaway, D.H., Nandy, D., Wilson, R.M., Reichmann, E.J.: 2003, Astrophys. J. 589, 665.
Hotta, H., Yokoyama, T.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 709, 1009.
Hoyt, D.V., Schatten, K.H.: 1998, Solar Phys. 179, 189.
Karak, B.B.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 724, 1021.
Kota, J., Jokipii, J.R.: 1983, Astrophys. J. 265, 573.
Leighton, R.B.: 1964, Astrophys. J. 140, 1547.
Masarik, J., Beer, J.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12099.
Matsuzaki, H., et al.: 2007, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 259(1), 36.
Maunder, E.W.: 1890, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 50, 251.
Miyahara, H., Yokoyama, Y., Masuda, K.: 2008, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 272, 290.
Miyahara, H., Masuda, K., Muraki, Y., Furuzawa, H., Menjo, H., Nakamura, T.: 2004, Solar Phys. 224, 317.
Miyahara, H., Kitazawa, K., Nagaya, K., Yokoyama, Y., Matsuzaki, H., Masuda, K., Nakamura, T., Muraki, Y.: 2010, J. Cosmol. 8, 1970.
Nagaoka, S., Kawano, K., Ito, Y., Okuno, M., Nakao, T., et al.: 1998, In: Nakamura, T. (ed.) Summaries of Researches Using AMS at Nagoya University IX, The Nagoya University Center for Chronological Research, Nagoya, 260.
Nakamura, T., Niu, E., Oda, H., Ikeda, A., Minami, M., et al.: 2000, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 172, 52.
Pinnegar, C.R., Mansinha, L.: 2004, Signal Process. 84, 1167.
Plunkett, G., Swindles, G.T.: 2008, Quat. Sci. Rev. 27, 175.
Reimer, P.J., Baillie, M.G.L., Bard, E., Bayliss, A., Beck, J.W., et al.: 2004, Radiocarbon 46, 1029.
Reimer, P.J., Baillie, M.G.L., Bard, E., Bayliss, A., Beck, J.W., et al.: 2009, Radiocarbon 51, 1111.
Richards, M.T., Rogers, M.L., Richards, D.St.P.: 2009, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 121, 797.
Schwabe, S.H.: 1843, Astron. Nachr. 20, 283.
Siegenthaler, U., Beer, J.: 1988, Secular Solar and Geomagnetic Variations in the Last 10,000 Years, Kluwer Academic, Boston, 315.
Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A., Schüssler, M., Fligge, M.: 2002, Astron. Astrophys. 396, 1029.
Stockwell, R.G., Mansinha, L., Lowe, R.P.: 1996, IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(4), 998.
Stuiver, M.: 1991, Quat. Res. 35, 1.
Stuiver, M., Braziunas, T.F.: 1988, Secular Solar and Geomagnetic Variations in the Last 10,000 Years, Kluwer Academic, Boston, 245.
Stuiver, M., Braziunas, T.F.: 1989, Nature 338, 405.
Stuiver, M., Polach, H.A.: 1977, Radiocarbon 19, 355.
Stuiver, M., Quay, P.D.: 1980, Science 207, 11.
Stuiver, M., Reimer, P.J., Bard, E., Beck, J.W., Burr, G.S., et al.: 1998, Radiocarbon 40, 1041.
Swindles, G.T., Plunkett, G., Roe, H.M.: 2007, J. Quat. Sci. 22(7), 667.
Usoskin, I.G., Sokoloff, D., Moss, D.: 2009, Solar Phys. 254, 345.
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 471, 301.
Watari, S.: 2008, Space Weather 6, 12.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the staff of the Center for Chronological Research, Nagoya University and the staff of the Micro Analysis Laboratory Tandem Accelerator, University of Tokyo. This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B:22340144) by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan. The authors thank the anonymous referee for many useful comments and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaya, K., Kitazawa, K., Miyake, F. et al. Variation of the Schwabe Cycle Length During the Grand Solar Minimum in the 4th Century BC Deduced from Radiocarbon Content in Tree Rings. Sol Phys 280, 223–236 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0045-2