Abstract
Purpose
The appearance of the 2019 novel coronavirus (Covid-19), for which there is no treatment or a vaccine, formed a sense of necessity for new drug discovery advances. The pandemic of NCOV-19 (novel coronavirus-19) has been engaged as a public health disaster of overall distress by the World Health Organization. Different pandemic models for NCOV-19 are being exploited by researchers all over the world to acquire experienced assessments and impose major control measures. Among the standard techniques for NCOV-19 global outbreak prediction, epidemiological and simple statistical techniques have attained more concern by researchers. Insufficiency and deficiency of health tests for identifying a solution became a major difficulty in controlling the spread of NCOV-19. To solve this problem, deep learning has emerged as a novel solution over a dozen of machine learning techniques. Deep learning has attained advanced performance in medical applications. Deep learning has the capacity of recognizing patterns in large complex datasets. They are identified as an appropriate method for analyzing affected patients of NCOV-19. Conversely, these techniques for disease recognition focus entirely on enhancing the accurateness of forecasts or classifications without the ambiguity measure in a decision. Knowing how much assurance present in a computer-based health analysis is necessary for gaining clinicians’ expectations in the technology and progress treatment consequently. Today, NCOV-19 diseases are the main healthcare confront throughout the world. Detecting NCOV-19 in X-ray images is vital for diagnosis, treatment, and evaluation. Still, analytical ambiguity in a report is a difficult yet predictable task for radiologists.
Method
In this paper, an in-depth analysis has been performed on the significance of deep learning for Covid-19 and as per the standard search database, this is the first review research work ever made concentrating particularly on Deep Learning for NCOV-19.
Conclusion
The main aim behind this research work is to inspire the research community and to innovate novel research using deep learning. Moreover, the outcome of this detailed structured review on the impact of deep learning in covid-19 analysis will be helpful for further investigations on various modalities of diseases detection, prevention and finding novel solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), viral diseases persist to instigate and cause a serious risk to public health by altering themselves. Over the past years, many pandemic viruses have killed millions of humans like smallpox (Henderson, 2009) and Spanish influenza (Spreeuwenberg et al., 2018). Various pandemics have been witnessed such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Pandemic SARS, 2003), H1N1 influenza (Pandemic H1N1, 2009), and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) (Pandemic MERS, 2012) in the years 2003, 2009, and 2012, respectively. SARS-COV and MERS-COV which are initiated from the reservoirs of animals are the two extremely pathogenic human coronaviruses (H-CoV’s) that caused distressing mortality in the twenty-first century. Coronaviruses are the large, encircled RNA viruses that belong to the subfamily of Orthocoronavirinae and division of a Coronaviridae family (Bhardwaj et al., 2017). Coronaviruses are categorized into four generations: alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), and delta (δ). Here mammals were contaminated through α and β, and birds were contaminated through γ and δ, respectively (Paules et al., 2020). Coronavirus was initially recognized in the past 1930 when a brutal respiratory virus of domestic chickens was depicted to be affected by the infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) (Estola, 1970). Later, H-CoV’s were identified in 1960.
A new pathogenic H-CoV was out broke in December 2019 and was identified in Wuhan, China (World Health Organization, 2020). Wuhan city with more than 11 million populations is the most heavily populated city in central China. Wuhan city is well-known for selling a variety of live animals such as marmots, bats, poultry, and snakes, and most of the cases were interlinked to this wholesale seafood market (Andersen et al., 2020). The clinical features of anonymous pneumonia are very much related to those of growing pneumonia like dyspnea, fever, dry cough, and bilateral lung penetrates on imaging. Later, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) specialists confirmed it as new coronavirus pneumonia (NCP) which was originated by novel coronavirus after producing an examination of models gathered from the throat swab on 7 January 2020 (Huang et al., 2020a). Consequently, the virus was named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (Lai et al., 2020), and the World Health organization (WHO) has named the disease as Covid-19 on 11 February 2020 (World Health Organization, 2020a). After 17 January 2020, NCOV-19 was frequently raised in the foremost areas of China and crossed more than 7000 cases which make their government take strict actions to avoid the spreading of this harmful virus. On 30 January 2020, WHO declared the pandemic as the NCOV-19 widens to 18 countries by the human-to-human spread. The main cause of spreading this NCOV-19 is not acquiring exact information regarding previous stage symptoms. This has led to a situation where individuals do not know that they were infected and traveled with nil knowledge about the dissemination of disease. So, extensive screening of people at busy places such as bus stations, railway stations, and airlines is needed to inhibit the spread of the disease. It desires several analyzing equipment united with thermal sensors, artificial intelligence (AI) (van der Schaar and Alaa, 2020), and machine learning (ML) (Yan et al., 2020). As early diagnosis of the disease is the only way to control the spread of Covid-19, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is considered as one of the standard methods for diagnosing NCOV-19 (Xu et al., 2020). Time and small sensitivity cannot assemble the standard of classifying fast-rising active cases, and it turned as one of the main drawbacks of RT-PCR. Moreover, fighting against this NCOV-19 is a huge challenge faced by both doctors and research scientists. Early recognition plays a major role in the diagnosis of NCOV-19 and can enhance long-term endurance rates. Medical imaging is an extremely significant method for early recognition and diagnosis of NCOV-19. But, manual analysis of a huge number of medical images can be time-consuming and tedious and effortlessly causes mistakes and human bias. So, X-ray images and computer tomography (CT) were used to support doctors in inferring medical images to advance their effectiveness.
Over the initiating of the pandemic, medical centers in China had inadequate testing tool kits, which are in addition generating a high speed of false-negative results, so physicians are persuaded to make an analysis only on clinical as well as chest CT results (Bernheim et al., 2020). CT and x-ray images are broadly utilized for the detection of NCOV-19. Many researchers affirmed that uniting medical image features by laboratory outcomes may assist in the early recognition of NCOV-19 (Ozturk et al., 2020). Radiologic images attained from NCOV-19 cases include practical information for diagnostics. Applications of machine learning (ML) techniques for the usual diagnosis in the medicinal field have newly achieved recognition by becoming an additional device for doctors (Litjens et al., 2017). Various machine learning (ML) methods were used to recognize infected people with adapted characteristics. Machine learning algorithms such as multilayer perceptron and Naive Bayes are used in the detection of tumor (Sharma et al., 2014). Initially, the images are preprocessed using preprocessing techniques. Then, feature extraction is performed by utilizing a gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM). Finally, the classification of images has been done using multilayer perceptron and Naive Bayes algorithms. From the results, it is noted that both multilayer perceptron and Naive Bayes algorithms attain an accuracy of 98.6% and 91.6% in the detection of tumor. The approaches of machine learning such as support vector machines (Haller et al., 2012), multivariate logistic regression (Huertas-Fernandez et al., 2015), and artificial neural networks (Hamilton et al., 2006) have been utilized in the classification of Parkinson’s disease. All these approaches have attained accuracies above 90% in the classification of disease. Therefore, techniques of ML have been broadly exploited in the experimental diagnosis, due to the accessibility of a huge number of quick devices for the assortment, examinations, and storage of large-sized information. ML methods can be effectively utilized in various healthcare applications such as disease discovery, recognition, diagnosis, drug manufacturing, medical image analysis, smart management of health records, and many more (Bhardwaj et al., 2017). As machine learning techniques are used in the diagnosis and forecasting of disease, they can also be used to determine the disease patterns (Singh et al., 2018). Therefore, distinct approaches of machine learning such as support vector machine, regression, random forest, and k-means have been effectively utilized in handling the present global pandemic. Though ML has proved its efficiency at the categorization of health records, noticing a disease, collecting data, etc., still some of the systematic methods have not been utilized yet due to several disadvantages like the irregularity of data, heterogeneity, deficiency of recognizing tools, temporal dependency, not utilizing complete medical datasets, etc. (Rekha Hanumanthu, 2020). To stabilize these drawbacks, feature engineering is approached by acquiring the benefits of human ingenuity. However, these weaknesses have been complicated by several health principles that are consumed in the simplification of information. There can be a state where some medicinal works require to be implied in abnormal ways. This difficulty can be determined by exemplifying the health composition in the improvised method. Still, the recent models cannot be forecasted by supervised models. Yet, representation learning can be unproblematic to extort necessary data while generating predictors.
Amid the diverse techniques of representation learning, a deep learning (DL) method plays a vital role, is proven as an easy method, and is created by the composition of many nonlinear variations. DL techniques are the superior exact models due to the deep architectural design for managing huge medical datasets such as segmentation of biomedical images and categorization of various cancer types and brain anomalies. Several features like the absence of human interference in feature mining, high performance, and unuse of engineering profits made DL techniques more useful and popular over the ML methods. DL, which is a well-known study field of AI, allows the formation of end-to-end methods to attain assured consequences with input data, with no requirement of manual feature extraction (LeCun et al., 2015). DL is quickly becoming an important technology in image or video classification and recognition. DL has been utilized in numerous applications like natural language and speech recognition. The structural design of DL can also be employed in several fields of computer vision and image processing that include the capability to hold constant learning systems and intricate data with shared qualities. One benefit of DL is that it can produce high-level attribute depiction directly from the raw images. DL improves a health organization to identify superior results, expand infection scope, and implement significant immediate medical images (Lundervold & Lundervold, 2019). The forecast for NCOV-19 with DL plays a critical role. Several researchers have used DL in clinical diagnosis and attained better outcomes. Examples include recognition of tumor classification, prostate segmentation, nodule classification, etc. with the DL techniques. DL techniques have been used successfully in solving many problems that include skin cancer classification (Codella et al., 2017), brain disease classification (Talo et al., 2019), lung segmentation (Souza et al., 2019), breast cancer detection (Celik et al., 2020), arrhythmia detection (Yıldırım et al., 2018), and fundus image segmentation (Tan et al., 2017). Various researches proved that the methods of DL have been utilized in the categorization as well as the study of deadly diseases on radiography. The major distinctiveness like better performance, deficiency of human contribution in quality extraction, and detection made the DL techniques more competent and popular for the prediction of different types of disease. As intelligent computing approaches have been immensely utilized in inhibiting the spread of diseases, the current Covid-19 pandemic is also seeking the support of intelligent computing approaches in developing more efficient forecasting and prediction models to control the spread of Covid-19. The rapid growth of the Covid-19 pandemic has required the need for knowledge in this area. This has enlarged attention in enhancing the automatic recognition systems based on AI methods. It is a difficult task to afford professional clinicians to each hospital due to the incomplete number of radiologists. So, easy, precise, and efficient AI techniques may be cooperative to defeat this crisis and offer appropriate assistance to patients.
Keeping in view, an effort has been put forward towards the survey of various DL techniques for Covid-19 in a broad spectrum. Apart from the methodologies, the impact on the consideration of types of data for Covid-19 research, popularity statistics of DL in solving Covid-19 problems, measures taken to cope up with Covid-19, etc. have been deeply analyzed. This is the first ever survey paper made on the state-of-the-art DL methodologies on Covid-19 as per the standard search databases. This article will be a drop of radiance for further research on DL with Covid-19 in the upcoming future. This paper has been organized in the following manner. The procedure and keyword search strategy for collecting literature data related to DL techniques are represented in Section 2. Section 3 describes all the deep learning techniques used to resolve several issues of Covid-19. Section 4 depicts the types of problems resolved by using deep learning methods. Section 5 describes the critical perspectives that are observed from this research work. Section 6 discusses various challenges, and Section 7 concludes this research work by depicting some future directions.
Systematic literature review procedure
In this section, the procedure followed to collect literature data related to Covid-19 for DL is depicted. In order to filter exact related data, a systematic paper inclusion procedure is followed like collecting review articles, research articles related to DL for Covid-19. To screen unrelated papers, articles not related to DL but Covid-19 related, inaccessible abstracts, etc. are excluded. Moreover, the keyword search strategy and paper segregation strategy are depicted in the following subsections.
Keyword search strategy
For our current study, in order to find out the exact related papers, advanced benchmark online databases such as IEEE Xplore, Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Springer have been selected. Some keywords have been applied to retrieve papers from the database. From keyword search, many keyword-related term papers are found. Henceforth, the exact related papers, i.e., deep learning–based methods, are filtered. Filters are applied in advanced search, and the exact methodology of keyword search has been depicted in Table 1.
Paper segregation strategy
From the keyword search strategy, we found 76 papers related to the study. Afterward, we found some issues of Covid-19 such as screening, identification, classification, diagnosis, detection, as well as prediction and separated the papers based on issue wise accordingly. The paper segregation strategy has been depicted in Table 2.
Deep learning methods for Covid-19
In this section, various deep learning methods applied for solving the issues of Covid-19 have been mentioned. The types of deep learning methods used are recurrent neural network (RNN) (Zahangir Alom et al., 2020), convolutional neural network (CNN) (Apostolopoulos et al., 2020), generative adversarial network (GAN) (Zhavoronkov et al., 2020), long short-term memory (LSTM) (Patankar, 2020), and auto-encoder-decoder (Amyar et al., 2020). Many types of CNN such as multiple CNN (Apostolopoulos et al., 2020), inception residual CNN (IRCNN), and modified CNN (Heidari et al., 2020) have been successfully utilized for resolving Covid-19 issues. Also, various other DL methods such as DenseNet (Elasnaoui & Chawki, 2020), InceptionV3 (Horry et al., 2020), Visual Geometry Group (VGG) (Horry et al., 2020), MobileNet (Toğaçar et al., 2020), ResidualNet (ResNet) (Kuo et al., 2020), and SqueezeNet (Ucar & Korkmaz, 2020) have also been used for resolving various problems of Covid-19 like diagnosis and classification, etc. These methods have been depicted in Fig. 1.
CNN
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are multilayered, feed-forward NNs which utilize perceptions for supervised learning and to dissect information. It is utilized primarily with visual information. The enormous headways in profound learning are expected partially to an energizing utilization of CNNs in an opposition held in 2012. The accomplishment of a profound convolutional design called AlexNet, which was the reason for the ILSVRC (ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition), was the essential purpose behind altogether quickened exploration in the field of profound learning in the course of recent years. Be that as it may, CNNs are not restricted to the recognition of images. Those used to be applied in analytics of text data. They can also be used with other data, if those are depicted in graphical format with the help of CCNs (chart convolutional networks).
Rajaraman et al. (Rajaraman et al., 2020) have introduced a method of detecting NCOV-19 in chest X-rays with the help of CNN. The authors have considered the datasets such as the RSNA CXR dataset, pediatric CXR dataset (Kermany et al., 2018), as well as Twitter Covid-19 CXR dataset. Accuracy, sensitivity, precision, etc. are used as performance metrics. Based on the experimentation, 99.01% of the accuracy rate has been obtained in identifying NCOV-19. The risk of automatically categorizing pulmonary diseases along with X-ray images of the emerged NCOV-19 has been considered by Apostolopoulos et al. (Apostolopoulos et al., 2020). The authors have used an efficient variant of CNN named MobileNetV2 and a dataset with 3905 X-ray images. They have considered several DL methods: AlexNet, VGGNet16, VGGNet19, GoogleNet, and ResNet50. Accuracy, sensitivity, and precision are considered as performance metrics to categorize X-ray images having pulmonary diseases. Based on the experimentation, 99.18% of classification accuracy has been obtained. Rahimzadeh and Attar (Rahimzadeh & Attar, 2020) have proposed a technique of deep CNN for identifying NCOV-19 from X-ray images, respectively. They utilized Xception, ResNet50V2, and concatenated network which are advanced DL techniques for their study. As CNNs are reciprocal to image data, the authors have applied the enhanced CNN model on 42 infected patients X-ray having Covid-19 and 180 X-ray images with pneumonia. True positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN), and false negative (FN) are considered as the evolution metrics. They considered the dataset having 11,302 images. Based on the experimentation, the authors have concluded that an accuracy of 99.56% has been attained. Likewise, several researches related to Covid-19 is being initiated day-by-day and already some research investigations to resolve problems related to Covid-19 have been implemented. Some of the CNN methods used for resolving Covid-19 problems have been mentioned in Table 3.
Moreover, many other DL methods (variations of CNN) have also been applied to tackle Covid-19 issues, and those researches have been mentioned in Table 4.
RNN
A recurrent neural network (Williams et al., 1986) is intended to perceive an informational index’s successive credit and use examples to foresee the following likely situation. It is a ground-breaking way to deal with handling successive information like sound, time arrangement information, and composed regular language. Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) is utilized to prepare the system alongside backpropagation. In contrast to conventional systems, where sources of inputs as well as outputs are autonomous of one another. In RNN, the hidden layer jams consecutive data from past advances. This implies the yield from a prior advance is taken care of, as the contribution to a present advance, utilizing similar loads, and inclination over and over for forecast purposes. The layers are then joined to make a solitary intermittent layer. These criticism circles process consecutive information, permitting data to continue, as in memory, and illuminate the final outcome. RNNs are layered to process the data in two ways: feed-forward (to process information) and input circles utilizing backpropagation (circling data once more into the system). RNNs are not quite the same as feed-forward systems, since feed-forward systems acknowledge each info and give one yield in turn. This coordinated imperative does not exist with RNNs, which can allude to past guides to frame the expectations dependent on their implicit memory.
Zahangir Alom (Zahangir Alom et al., 2020) has anticipated a new methodology for the identification of NCOV-19 by using recurrent NNs (RNNs) (Mooney, 2020), as well as Covid-19 (Cohen, 2020) is the considered datasets by the authors that are having both X-ray and CT images, respectively. The authors have considered several performance metrics such as TP, FP, and accuracy rate. It was noticed that the proposed method attains accuracy rates of 84.67% and 98.78% for CT and X-ray images, respectively. Punn et al. (Punn et al., 2020) have introduced a method to use the DL techniques for pandemic analysis. The authors have considered the data from the Johns Hopkins University dashboard. Deep neural network (DNN), RNN, support vector regression (SVR), and polynomial regression (PR) are the several techniques that are used by the authors. It takes time series data as the input. Based on the experimentation, the authors have attained the PR model as the better model among others in terms of root-mean-square error (RMSE).
LSTM
Long short-term memory (Sepp Hochreiter & Schmidhuber, 1997) is a sort of RNN that permits deep RNNs to be prepared without making pitches that update loads become flimsy. Data patterns can be put away in memory for progressively expanded timeline with the capacity to specifically review or erase information. It utilizes backpropagation but is prepared to learn grouping information utilizing memory squares associated into layers rather than neurons. As the data is handled through the layers, the design can include, expel, or adjust information variance. LSTM is one of the most appropriate methods for classification and prediction dependent on time arrangement information, presenting superior outcomes for different issues (Sherstinsky, 2018). These empower information researchers to make profound models utilizing huge stacked systems and handle complex succession issues in ML more proficiently.
Patankar (Patankar, 2020) has developed a novel method for the discovery of drug to resolve the issue of Covid-19 in the year 2020. The author has used LSTM-RNN as a proposed methodology, and for performance analysis, they have utilized fingerprint data. A good rate of drug discovery has been obtained with the proposed method. Ayyoubzadeh et al. (Ayyoubzadeh et al., 2020) have developed a modern method for the prediction of Covid-19 in the year 2020. The authors developed LSTM as a proposed methodology and have utilized text data in order to assess performance. A good prediction rate has been obtained with the proposed method. Bandyopadhyay and Dutta (Bandyopadhyay & Dutta, 2020) have developed a modern method for the prediction of Covid-19 using text data. The authors have proposed LSTM based RNN, GRU (gated recurrent unit)-based RNN, as well as LSTM-GRU-RNN for predicting Covid-19. From the experimental analysis, it is observed that LSTM-GRU-RNN outperformed among others. Pal et al. (Pal et al., 2020) have developed an LSTM-based NN method for the prediction of Covid-19 using text data. A good prediction rate has been obtained by using the proposed method.
GAN
Generative adversarial networks (Goodfellow et al., 2014) are one of the deep learning unsupervised algorithms. Whenever a training dataset is given to GAN as input, they automatically detect data patterns present in the dataset, so that they produce novel data by self-learning process. They imitate any dataset through minor dissimilarities. The network structure of GAN consists of two nets trenching one another; hence, it is expressed as adversarial. They utilize two associate models such as generator and discriminator in which a generator is used to create novel data instances and a discriminator discriminates original data with counterfeit data. They are repetitive, and this repetitive behavior leads them to be stronger with each repetition. GANs have the ability to confine and replicate dissimilarities, generate images, produce fine data, as well as convert data on a given dataset.
To identify NCOV-19 in chest X-ray images, deficiency of standard datasets, Loey et al. (Loey et al., 2020) have introduced a GAN-related deep transfer learning model. The authors have used advanced technologies like AlexNet, VGGNet16, VGGNet19, GoogleNet, and ResNet50. They have taken chest CT images as input and found GAN as the most used technique. They considered a dataset having 307 images that belong to four several kinds of classes: pneumonia bacterial, Covid-19, and normal and pneumonia virus, respectively. The robustness of the projected technique has been raised as the over-fitting risks were resolving by the GAN. Based on the experimentation, the proposed approach has effectively detected NCOV-19 even in the deficiency of datasets and got 100% accuracy in testing. Zhavoronkov et al. (Zhavoronkov et al., 2020) have developed GAN and used it for the screening of drugs with the help of text data. Accuracy, recall, etc. have been used as performance metrics, and reliable outcomes have been observed based on experimentations. Waheed et al. (2020) have developed a novel approach for the detection of Covid-19. The authors have developed the GAN method, and for performance evaluation, a dataset having CXR images has been considered. Advanced accuracy has been obtained with the incorporation of GAN. Khalifa et al. (Khalifa et al., 2020) have introduced a method of identifying a pneumonia chest X-ray with modified deep transfer learning for a partial dataset. The authors have developed an advanced technology named generative adversarial network (GAN) along with ResNet18. They have considered X-ray images as input and found GAN as a perfect methodology for creating CT images. They considered a dataset that is having 5863 chest X-ray images. They selected different DL methods such as VGGNet16, GoogleNet, AlexNet, and ResNet50 to identify CT images. Sensitivity, accuracy, precision, etc. are considered as classification metrics. Based on the experimental results, the model has outperformed with a 99% accuracy rate. Classical information augmentations with CGAN with deep transfer learning for NCOV-19 identification in partial CT images have been proposed by Loey et al. (Loey et al., 2020a). The authors have used 5 various deep CNN-based models such as AlexNet, VGGNet16, VGGNet19, GoogleNet, and ResNet50 for the study to recognize the NCOV-19-affected patients with chest CT radiograph images. Sensitivity, specificity, precision, accuracy, and F1-score are considered performance metrics. Their experimental results proved that 82.91% accuracy was found and attained a high performance in ResNet50 among others.
Auto-encoder-decoder
Auto-encoders are immediate appropriation neural networks that reestablish the contribution at the yield (Kramer, 1991). Inside they have a concealed layer, which can be a code that depicts the model. They are intended to not have the option to precisely duplicate the contribution to the yield. As a rule, they are constrained inside the component of the code or fined for enactment inside the code. The information is reestablished with mistakes due to coding misfortunes; however, so on lessen them, the network is compelled to search out bowed pick the premier significant highlights.
Amyar et al. (Amyar et al., 2020) have developed a modern deep learning approach for the classification as well as segmentation of Covid-19 in CT images. The authors have proposed an encoder having 10 convolutional layers along with two decoders having 10 convolutional layers for segmentation purposes. They have also utilized MLP (multi-layered perceptron) for classification purposes. For analyzing the performance, a dataset having 1044 patients as data has been considered. The encoder takes CT images as input; further, the decoder can reconstruct the image with the first decoder. False-positive rate, true-positive rate, as well as accuracy have been utilized as performance metrics. Reliable outcomes have been obtained with the proposed technique. Khobahi et al. (Khobahi et al., 2020) have developed a DL methodology for the identification of Covid-19. The authors have developed an encoder-decoder method of classification, and a dataset having CT CXR image has been utilized for analyzing the proposed architecture. Accuracy, precision, recall rates, etc. have been considered as evaluation metrics, and an accuracy of 93.5% has been obtained for identifying Covid-19.
Types of Covid-19 problems resolved by DL
In this section, various Covid-19 problems resolved by DL techniques have been mentioned and explained in an analytical manner. The problems related to Covid-19 infection are basically categorized as diagnosis, forecasting, and classification. Various models using DL approaches have been developed to resolve the distinct problems of Covid-19.
Diagnosis of Covid-19
ML and DL techniques have developed many solutions in the medical domain, and now they are being utilized to fight against the NCOV-19, whereas the AI community is functioning intensively on distributing applications that can assist to hold the results of the pandemic with the help of DL methods. These DL methods are still at an infant phase, and it will obtain time before the consequences of such procedures are evident. Some researchers have used DL techniques like CNN to diagnose Covid-19 using CXR as well as CT images, and reliable outcomes have been obtained (El-Din Hemdan et al., 2020; Razzak et al., 2020; Ezzat & Ella, 2020). The diagnosis of NCOV-19 with DL includes patients’ lungs x-rays and categorizes the X-ray as NCOV-19 infected or not infected. DL image scrutiny equipment can be enhanced to sustain radiologists in the quantification, triage, and trend assessment of the data. Gozes et al. (Gozes et al., 2020) have majorly carried the study by RADLogics. The main motive behind their study is to create an AI-based mechanical CT image diagnosis equipment to attain high accurateness in the identification of NCOV-19-positive patients and observe them during treatment. The authors have provided a timely investigation of patients by distributing the quantitative measurements. It was found to introduce a Corona Score that constantly measures the development of the infection over time. To detect the infection, the authors have initially segmented the lung sections of the CT scans with a U-Net design that was trained on 6150 images. The abnormalities of NCOV-19 were identified from the divided lung images with the pre-trained ResNet50 2D CNN on the ImageNet dataset. Based on the experimentation, the authors have reported two points: either having high sensitivity (98.2% sensitivity and 92.2% specificity) or high specificity (96.4% sensitivity and 98% specificity). The diagnosis of Covid-19 infection includes the detection, prediction of severity, and screening of drugs.
The Alibaba Research Academy (DAMO Academy) (Alibaba, 2020) in early February has approached with an AI-based resolution that can identify NCOV-19 with an accuracy of 96% within 20 s. The network acquires the patient’s CT scan as input as well as output whether the symptoms of NCOV-19 have been shown or not. More than 5000 trained samples were adjusted in this model and were arranged in more than 26 hospitals in China. This procedure has been used to diagnose 30,000 cases so far. Their group has also urbanized an NLP solution that relies on pre-trained techniques for analyzing health reports of NCOV-19 in search of a treatment (Shan et al., 2020). Currently, this model is widely using and testing for text investigation of health records and epidemiological study by centers of disease controls (CDCs) in several areas in China.
DL models can be useful for the prediction of the severity of the patients. Due to the fast spread of NCOV-19, doctors are facing high complexity in the NCOV-19 analysis. Generally, the prediction of patients’ severity will take the mortality rate and medical route for identifying serious cases from severe cases. Yan et al. (Yan et al., 2020a) have used 2779 electronic patient reports comprising of their health conditions from 10 January to 18 February in China. Data preprocessing, splitting, and training are included, where the authors introduced all the medical measurements in data preprocessing and added two new labels named survival and death. The information was separated into 70% and 30% for training as well as testing purposes in the data splitting phase. Multi-tree XGBoost algorithm was selected by the authors in the training phase to forecast the patient’s severity by utilizing the input data. Based on the experimentation, the authors have concluded that the model was outperformed better results by attaining accuracy of 90% in early identification, early intrusion, as well as the lessening mortality rate in highly affected NCOV-19 patients.
AI is not only helpful for analyzing NCOV-19 but also used for drug screening. Many research teams in China made a study of how DL can assist in finding the medicine faster than conventional methods. Researchers are trying to discover a vaccine to treat this pandemic. More than 30 agents were discovered by the research including natural products and western as well as traditional medicines that might have potential effectiveness against NCOV-19 (Dong et al., 2020). A few of these agents have been rapidly tested in clinical investigations and illustrated preliminary effectiveness against NCOV-19. Many researchers were capable to detect potential vaccines for NCOV-19 by conducting drug screening.
Classification
According to medical research, it was found that people who are experiencing NCOV-19 have various respiratory patterns. Due to this, the East China Normal University researchers have combined with organizational researchers to expand a DL-based algorithm that can assist in the screening, predicting, and diagnosing affected patients based on the breathing issues. DL has been widely utilized in the field of respiratory pattern recognition. Cho et al. (Cho et al., 2017) have exploited the CNN to attain the classification of deep breathing. Similarly, Kim et al. (Kim and Han 2019) have utilized 1D CNN to categorize the respiratory signals projected by the radars into four types. Thus, the categorization of respiratory signals extorted by the noncontact measurement scheme with the help of DL is a study of great significance. Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2020c) have used a GRU NN with attention and bidirectional machines to categorize six clinically major respiratory patterns (eupnea, tachypnea, bradypnea, biots, Cheyne-Stokes, and central apnea) with a depth camera. The authors have developed a respiratory simulation technique for producing simulated information and attained current world information with a depth camera. Based on the experimentation, the authors have concluded that the anticipated technique can categorize the six stated respiratory patterns with an accuracy of 94.5%, precision of 94.4%, recall of 95.1%, and F1-score of 94.8%, respectively. CT imaging is vital for evaluation, staging, and diagnosis of Covid-19 infection. For quantification and to decrease the CT scan diagnosis time, investigators have built a model with DL techniques to measure the lung infection that is caused by NCOV-19 (Shan et al., 2020). The major reason behind their study is to enhance a DL-based technique for the quantification as well as mechanical segmentation of the infected areas and the overall lungs from CT scans. The authors have improved a VB-NET network (Milletari et al., 2016). They declared that their projected model was quicker than the real V-NET due to its bottleneck structure. Their system was trained on 249 NCOV-19 patients and confirmed with 300 latest NCOV-19 patients.
Forecasting
The development of disease vigilance systems helps in controlling the spread of the disease. Therefore, the development of accurate forecasting models helps the government and healthcare system to take necessary measures to control the spread of the present Covid-19 pandemic. Forecasting problem has also been resolved with deep learning methods for Covid-19. Huang et al. (Huang et al., 2020) have developed a modern method for the forecast of Covid-19 in China with the use of CNN model. For performance evaluation, a small text dataset having Covid-19 patient samples has been considered, and mean absolute error, root-mean-square error, etc. have been used as evaluation factors. A comparison has been made with benchmark algorithms in literature such as LSTM, MLP, and GRU. A good forecasting rate has been observed with the proposed technique.
Critical analysis
DL method is proficient to train through itself with no assistance, and as a subset of ML, it performs better than ML. DL techniques can be effectively utilized in virtual assistants, fraud identification, personalization, NLP, etc. Usage of DL and ML techniques in the healthcare sector has risen rapidly. Patients’ health condition, heart rate, and blood pressure and some other parameters have been identified while using the techniques of both ML and DL, respectively. An efficient investigation of Covid-19 articles based on DL methods has been made in this study. From the study, it is clear that approaches of DL have been utilized successfully in the analysis of medical images due to some facts including the capability to differentiate among bacteria as well as other pneumonia, removal of rich features from a multimodal medical dataset, early identification of pandemic patterns, and ability to discover several chest CT imaging characteristics. So, DL methods are issuing new possibilities and permitting physicians, researchers, and clinicians to forecast and realize the disease easily. In this section, a systematic review on the type of inputs used, week- and month-wise analysis of research on Covid-19, performance analysis of various advances, type of data used, and many more have been performed.
Analysis on problems resolved and type of inputs used
Purely from the papers obtained from the keyword search, it is observed that many problems of Covid-19 such as diagnosis, classification, and forecasting have been resolved. In this section, we made an analysis on the usage levels of these problems, and this analysis is mentioned in Fig. 2.
Also, we have observed that many forms of data such as image data and text data have been used as inputs for various deep learning models to resolve the issues of Covid-19 like classification. From this observance, we also made an analysis on the usage levels of the type of data used as an input for those deep learning models mentioned in Section 2. This analysis on the type of inputs has been depicted in Fig. 3.
Performance analysis obtained using various DL methods
Due to having more benefits in DL methods such as better performance, managing difficult and multi-models, and feature extractions with no intervention of humans, most of the researchers have focused their concentration on the analysis of Covid-19 with DL methods. Table 5 represents the overall performance of DL methods in the Covid-19 analysis.
Analysis on the types of DL methods used for Covid-19
On the basis of keyword search, we got exactly 76 papers related to DL methods for Covid-19. In this section, an analysis has been made on the usage levels of several types of DL techniques and its applicability on various types of problems. It is noticeable that various methodologies such as CNN as well as other DL methods like DenseNet, InceptionV3, VGG, MobileNet, GoogleNet, and ResNet have been applied. Also, other benchmark methodologies such as GAN, LSTM, and auto-encoder-decoder have also been applied for Covid-19-related problems. This analysis has been depicted in Fig. 4.
From Fig. 4, it is clearly observed that CNNs have been applied more for Covid-19-related issues when compared with others. After CNN, GAN has the second highest usability to be applied for Covid-19. Also, another benchmark method named LSTM has the third highest usage level in solving conflicts of Covid-19. The main reason why these methods have been used is due to the availability of types of data of Covid-19. It is well-known that not all the techniques are fit for every data. We have clearly observed that most of the available datasets of Covid-19 are image datasets. It is proved that CNNs are reciprocal to image data and hence applied on various image data like CXR, CT, etc. They can also be useful for image processing, classification, as well identification due to their behavior like high adaptability. Likewise, RNNs have the behavior to solve succession expectation issues and hence applied for Covid-19. LSTM is best suited for time series data and hence applied for time series Covid-19 data. GANs have the capability to capture and copy variations on a given dataset and can also generate novel data from previously taken data, and hence due to this behavior, they have been utilized for resolving Covid-19 issues. Auto-encoders can be utilized for pre-training, for instance, when there are a classification task and less distinguished sets. Hence, due to this behavior, they have been successfully utilized for Covid-19-related issues.
Paper publication analysis related to DL for Covid-19
There are several intelligent-based techniques being developed to deal with the novel Covid-19 pandemic. Methods such as statistical, mathematical, machine learning, and deep learning are developed as a solution to Covid-19. However, the publication ratio of DL-based techniques is more as compared to greater allied approaches. Patients’ health condition, heart rate, and blood pressure and different other parameters are considered while using the techniques of both ML as well as DL, respectively. From the study, it is clear that approaches of ML and DL utilized successfully in the analysis of medical images due to some actualities include the capability to differentiate among bacteria as well as other pneumonia, removal of rich characteristics from a multimodal medical dataset, early identification of pandemic patterns, and ability to discover several chest CT imaging characteristics. So, DL methods are issuing new possibilities and permitting physicians, researchers, and clinicians to forecast and realize the disease easily. In this present section, an interesting review is made on the country-wise research data, week-wise and month-wise analysis of research on pandemic Covid-19, performance analysis of various advances, type of used while predicting Covid-19, statistics, different percentages of prediction, detection, and screening.
Month- and week-wise analysis of DL papers related to Covid-19
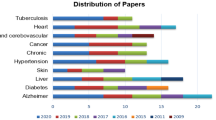
Based on a systematic review, we made a deep analysis on the contribution of articles week-wise as well as month-wise. By considering all the papers from 16 February 2020 to 31 May 2020, we represented its depth analysis in the following Figs. 5 and 6. As per our count, a total of 80 papers of DL related to Covid-19 has been published from February to May 2020. In the starting stage of the outbreak of Covid-19, we found no articles related to our search in the month of January. Later in February, we got published articles of DL related to Covid-19. From our survey, out of 76 papers, we got 5 articles published in February, 19 articles in March, 35 articles in April, and 17 articles in May, respectively. We found most of the articles were available in April. It cannot be overstated to say that researchers have shown their interest in several aspects of the pandemic with an increase in cases throughout the globe. This month-wise analysis is depicted in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6, respectively.
Similarly, based on our gathered articles, we made a weekly analysis of DL papers related to Covid-19 that are published in the months of February to May. We found most of the research articles about DL related to Covid-19 were published in the first and third week of April. This weekly analysis is mentioned in Fig. 7.
Also, weekly analysis has been performed and is mentioned in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8. It is observed that from April 12 to April 18, as the highest number, 15 papers have been published. As the second highest, 5 papers have been published during April 5–11. Moreover, this analysis has been depicted in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8.
Fighting NCOV-19 with DL techniques
People are quarantined, work is declining, and the economy has come to stop. The contagious NCOV-19 is scattering fast. Even though the most superior methods are available in 2020, we are not capable to end this pandemic spread. Over a decade, we have observed a tremendous quality of research and positive consequences in the area of AI as well as computer science (Paperspace, 2020). The actual cause for this explosion includes the accessibility of information, superior computational power, structures, and open-source equipment. DL has changed everything, from energy and manufacturing to education and health fields, respectively. As mentioned earlier, the health government of China has reported a huge number of NCOV-19 in Wuhan at the end of December 2019. This contagious virus can be spread among people who will be in close contact with each other by respiratory droplets formed when a contaminated person speaks, coughs, or sneezes. The symptoms of this virus that are generally reported are tiredness, fever, and dry cough. In the meantime, ML and DL researchers have avidly collaborated extensively throughout the world to discover ways to resolve issues linked to the coronavirus by constructing algorithms or by assembling datasets to be trained from them.
Moreover, specialists are utilizing ML to examine the virus, diagnose individuals, analyze the public health impacts, test potential treatments, and many more. DL has become a significant advance rapidly across clinical research, biomedical detection, precision medicine, and medical diagnostics. Such tools can expose new probabilities for patients, physicians, as well as researchers by letting them build more knowledgeable decisions and attain improved outcomes. Currently, with the growth of the pandemic ensuing from the spread of the NCOV-19, institutions, commercial developers, and medical providers are all considering DL techniques to tackle the risk of this current disaster. Various research groups have proved their model’s efficacy in identifying NCOV-19 by using DL techniques. Methods like CNNs are observed to be the most prominent methods to solve almost all the problems that are mentioned in Section 3. CNNs are used mostly in detecting patterns in various images. Several researchers in China have worked together to enlarge a CNN-based DL model to build the faster procedure of screening and to detect NCOV-19 in its early phases from CT scans. Butt et al. (Butt et al., 2020) have examined various characteristics of Covid-19 that include ground glass form, unusual peripheral allocation, and more than the individual independent focus of viruses. The authors have gathered overall 618 lung CT scans. They have contrasted the proposed method with other subsisted 2D and 3D DL models, combined with the new clinical perceptive, and attained 0.996 of an AUC. Based on the experimentation, the authors have concluded that they assessed 98.2% and 92.2% of sensitivity as well as specificity. Such speed and exact diagnosis of CT datasets that can only be presented by optimized AI techniques are vital for frontline clinicians testing patients in this pandemic. Likewise, some other major ways include detection of Covid-19 with AI-based systems, identification of pandemic using CT scan and image analysis, quantification of lung infection, respiratory pattern classification for screening, drug screening as well as prediction of patient severity and many more.
Type of data sources used for Covid-19 with DL
Prediction plays a vital role in the outbreak of a pandemic. The success of worldwide effort to utilize the methods of artificial intelligence to tackle the Covid-19 hinges on enough access to information. DL techniques need computing power as well as a huge amount of data disreputably to enhance and learn novel algorithms and architectures of NN, respectively. One cannot understand deadly diseases unless we predict who is distressed by the virus. Various physicians and researchers are using huge information from several domains to predict Covid-19 such as online data, clinical data, biomedical data, molecular data, case data, and text data, respectively. We illustrated a collection of data and a few datasets that subsist at the current time (Bullock et al., 2020). Various types of data used for Covid-19 research are mentioned in Fig. 9.
Biomedical data
The majority of the analysis for prediction, identification, and classification of pandemic has been conceded on the medial image dataset. The current investigation of the medical image offers an accurate prediction of the novel pandemic. Although the information related to Covid-19 has been deemed from biomedical data, the organization of medical images became the major confront in the diagnosis of health due to its incomplete medial images. The automatic division process becomes difficult in CT images due to the regular imagery uniqueness among Covid-19 and other types of pneumonia. Biomedical data consists of both clinical and molecular data.
Clinical data
Currently, there are no massive models and datasets for diagnostic purposes. However, we can study a huge amount of data from several regions of the world to identify the pandemic spread and utilize DL techniques to anticipate the upcoming future. The major reason behind the gathering of data from clinical data is for rapid analysis. The data on the number of cases predicts the infection. Several proposals subsist to mass and open-source related data, for example, the pandemic risk calculator for symptoms and the dataset of Covid-19 chest X-ray (Cohen et al., 2020) for medical imagery. Similarly, the collection of data and training models of DL can be done by scientists; selection, classification, and explanation often require to be carried out by health professionals like clinicians or radiologists.
To address the deficiency of required information, there is a rising number of repositories that intend to allocate techniques and data. Some examples include the clearinghouse dataset of Covid-19 (Clearinghouse dataset, 2020) and Data4COVID Living Data Repository (data repository, 2020) that consists of various links for accessing many open-source data repositories. Also, some ideas combined against pandemic are especially significant, as they become online podium, where DL/ML researchers and data scientist can use their abilities to concentrate needs for aid from the explore community. For example, to clear out the clinical data, remove actionable data about Covid-19-specific research queries, and work together to expand equipment for exploitation in hospitals. Such schemes are capable of specifying their potential to link the gap among those with biological or medical experience, data, and computational skills.
Molecular data
Apart from drug discovery and genomic sequencing, many other datasets are accessible from pre-existing proposals. Following the genome series of Covid-19 is critical for assessing as well as designing analytical tests, mapping, and recognizing the pandemic. Some projects like Nextstrain (Nextstrain, 2020) are searching at the genetic assortment of coronaviruses, to distinguish the worldwide outbreak of Covid-19 by assuming the family tree of hundreds of openly collective genomes of Covid-19. Similarly, there is entrenched inventiveness like global drug discovery institutes (global drug discovery, 2020) and RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB Protein Data Bank, 2020) that have formed national portals with existed information and sources for superior perceptive of Covid-19.
Online data
In the existing online period, the majority of the data has been accessible online that involved nature, outbreak, as well as the growth of Covid-19. The data has already existed online through public medical organizations, population, and travel evidence. Based on the investigational queries, information from systematic articles can also be accomplished with data from an additional basis, such as social media and newspapers. Various kinds of datasets that include Covid-19 Tweets and the Covid-19 twitter dataset (Banda et al., 2020) that are handled with normal tweets related to the pandemic, can help to follow the spread of misinformation and unconfirmed reports on Twitter, and supervise the responses of several individuals to the Covid-19 pandemic (Chen et al., 2020). One special dataset named Covid-19 Real World Worry Dataset involves tagged contents of a person’s emotional replies towards Covid-19 and can hold vital data about public reaction and the effects of the pandemic on mental health in various areas of the world (Kleinberg et al., 2020). Similarly, some repositories like the Covid-19 news article database and television coverage database can also help to survey the queries of how both televisions and print media are covering the pandemic (Covid-19 news article database, 2020 & Television coverage database, 2020). Also, some forecasters would require information from medical experts that discriminates among fatalities that may occur due to pandemic or some other unknown illness. This information may not be accessible in most of the investigations. Hence, identification of the exact level to which individuals need to follow the rules of government is difficult. The occurrence of missing values is one of the disadvantages of online data that needs to figure out for accurate results.
Case data
Case data consists of entire information associated with the case, which may require while functioning on the case. Case data can be preceded as a central repository. The present number and position of cases are necessary for tracking the growth of pandemic, assessing the intensification rate of novel diseases, and examining the contact of protective measures. The associations such as the national Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and WHO have existed to utilize several datasets that include Kaggle (Kaggle, 2020) dataset, GitHub, as well as John Hopkins University dataset, respectively. Here, the dataset of John Hopkins University comprises of positive rate (PR), recovered rate (RR), and death rates (DR), whereas the data set of Kaggle includes the date, demographics, and reporting locality. There is also a rise in the number of equipment and sources urbanized especially for medical experts and organizations, for supervising the pandemic.
Text data
Generally, text data comprises documents that can signify, sentences, words, or paragraphs of free-running text. The intrinsic free and noisy text data makes it difficult for ML and DL to operate directly on unrefined text data. ML and DL techniques can be utilized to assess and parse the huge amount of written data on Covid-19 and additional coronaviruses to make it simpler for clinicians as well as researchers to utilize this data. Some other technical explore datasets that can be oppressed includes the Dimensions AI COVID-19 and LitCOVID dataset, which can contain significant additional data like available scientific trial data (Dimensions AI COVID-19, 2020 & LitCOVID dataset, 2020). By using these resources, natural language processing (NLP) methods can be employed to improve text mining equipment and sources that can assist the health community to progress the analysis of Covid-19.
Measures taken to cope up with the Covid-19 pandemic
It’s obvious that Covid-19 has been treated as the most dangerous pandemic around the world till date. Many measures have been taken such as lockdowns, social distancing, closing organizations and schools, etc. to deal with it. Initially, to stop the spread of novel coronavirus, measures such as national and international border shutdown, transportation restrictions on international flights followed by domestic flights, and curfews on mass gathering are implemented. The countries like China, Iran, Italy, Spain, France, Belgium, and Portugal announced the shutdown of borders. The countries like the USA, Canada, Brazil, Russia, the Netherlands, Austria, Switzerland, and Israel have halted international flights but did not impose strict restrictions on domestic flights. Countries most affected by the virus have followed different policies on social gathering. For instance, Italy, Spain, Russia, and India announced complete lockdown, while countries like the UK, Ireland, and China preferred lighter lockdown restrictions. But the countries like the USA, Canada, Iran, France, Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Portugal, Brazil, Austria, and Israel have not imposed lockdown restrictions, but they asked the citizens to stay at home to prevent the spread of disease. The novel coronavirus not only affected the health of the public, but it also impacted the economic condition of the countries due to the implementation of lockdown policies. To cope up with the economic crisis, most of the countries except Brazil, Switzerland, and Israel announced the postponement of taxes by the private sector. The countries like Turkey, Spain, France, Germany, China, Iran, Russia, the Netherlands, Switzerland, and India have also provided funding and financial support to the adversely affected companies (steps taken by countries in fighting Covid-19 pandemic, 2020). In developing countries like India, the rapid spread of the virus may devastate the healthcare system. Therefore, to prevent the dissemination of disease, strict lockdown restrictions have been announced by the government of India. After noticing the worst financial crisis due to lockdown, the central government in India has granted permission for reopening of malls from June 8 in non-confinement zones, but some places like Gurgaon, Mumbai, and Delhi are against to it. Public places like malls, cinemas, and entertainment zones are hot spots for individual congregation. Unless strict rules are preserved, the easing of restrictions may take a thrashing on the brand image if they supply harmfully to public health beneath the present circumstances. The government has declared the gradual moderation of limitations all over the state from 31 May 2020 by giving measures to all the sectors including sport and recreation, social events and ceremonies, fitness, cafes and restaurants, culture and entertainment, personal services, travel, and leisure. Some of the measures taken have been mentioned in Table 6.
Discussions
It has been obvious from most of the studies that ML approaches have also been effectively utilized in the forecast and analysis of Covid-19. Both ML and DL are the two popular concepts that have been used in the detection and prediction of the pandemic. Though ML techniques have been majorly used in the analysis of the Covid-19 pandemic, still some challenges such as temporal dependency, scarcity, irregularity, and complete usage of biomedical information, etc. have made it lacking. On the other hand, DL is attaining more popularity due to its superiority in terms of correctness when trained with an enormous quantity of data. Generally, DL is a subset of ML that acquires flexibility and power through the process of learning. Techniques of DL are the top most exact methods for managing medicinal datasets which include categorization of various cancers, pathogenic bacteria, brain abnormalities, and biomedical image segmentation, respectively. DL models offer novel prospects in the biomedical field due to the wide growth of practical developments. Some additional features of DL such as accurate performance, the capability of handling difficulty, end-to-end training method with mutual feature learning, and many more made it the best appropriate model for the healthcare field. So, the majority of the researchers have made their research in the Covid-19 diagnosis by using DL advances. Based on the deep review, it is evident that CNN, GAN, RNN, LSTM, GRU, and auto-encoder are the most used DL methods for the diagnosis of the pandemic. All these DL methods have been successfully used by various researchers for the prediction of Covid-19. The characteristics such as deficiency of human involvement in the procedure of quality extraction and recognition, high performance, and no usage of engineering benefits in the learning phase made the DL methods more popular over ML methods.
Many researchers and doctors globally have enhanced various amount of prediction techniques to forecast the pandemic, since the outbreak of Covid-19. But most of the prediction models are failing, because there is no such model that can have exact predictions, due to the involvement of several factors. None of the forecasting techniques are perfect. Every model utilizes various techniques, makes several assumptions, fights with ambiguity in several ways, and produces various outcomes. The predicted data regarding trends in the pandemic throughout the world include unhygienic cases, improved cases, upcoming fatalities, hospital requirements, travel restrictions, the influence of social distancing, and many more. Also, there was no formal liability at a period when the correctness of methods is significant. Most of the statisticians mention that the prediction models that are predicting the number of Covid-19 fatalities corresponding with actuality were not consistent. All the forecasted techniques have exposed a huge range of differences in calculation because of the lack of exact data. The deficiency of reliable data is one of the major reasons for the variations of predictions. Similarly, forecasting of upcoming consequences based on information of confirmed cases is another reason behind the variations of prediction. Apart from spreading disease, demographics, basic health conditions, environmental variables, and social distancing, many other factors need to be considered such as low immunity, chronic disease, hypertension, disabilities, and many more. The intention behind the forecasting models by various researchers was failed to show exact accurate results. So, to make more exact predictions in the upcoming future, more investigation has to be conceded on developing techniques as well as equipment for prediction on the majority of biological data.
Irrespective of several methods, several numbers of research articles, and various precautions taken by the individuals, the cases of Covid-19 are still increasing day by day. The total pandemic confirmed cases have reached 8,028,253, along with 4,148,128 recoveries as well as 436,276 deaths globally as of 15 June 2020. The USA, Brazil, and Russia are placed as the three topmost affected countries till the day. Cases in India are predicted to persist to rise as measures of social distancing are being tranquil before considering a reliable decline in new daily cases. The solutions, precautions, and various prediction methods taken to date can stop the spread of Covid-19 temporarily only and hence assists in the suppression of Covid-19. None has the clarity about the ending of this pandemic. This Covid-19 is exceptional in the grouping of its simple transmissibility, a variety of symptoms leaving from one to another in a deadly manner, and the level of the pandemic has disturbed the world. The disease may come into an ending stage for not being its low growth, but due to the people grow exhausted of fright manner and be taught to stay with a disease, because the past pandemics do present suggestions of future. Projections on how the Covid-19 pandemic will continue to be are provisional, but the end of it will involve a unity of the whole thing that ensured past pandemics such as social preventive guidelines, new medicines to alleviate symptoms, and a vaccine. On the other hand, most of the researchers have to work together on several fronts to enhance medications. So, the permanent solution for stopping this pandemic is vaccines that require months and even years to be complete. Unless the vaccine is released to the entire world, Covid-19 is probable to become widespread to the people who are not sick or recovered presently. The mixture of natural immunities and vaccinations will secure most of the population. So, as per our analysis, it can be ensured that this gap can be effortlessly filled by identifying vaccines using a grouping of existing virus vaccines such as Spanish flu, SARS-1, etc. Also, several intelligent AI-based techniques are to be developed for further impactful analysis on Covid-19 for stopping the chain. Countries like India and some others require the proper healthcare resources such as ventilators or beds to a minimum of 30 to 40% of the population.
From the critical analysis, it has been noticed that DL approaches have been efficiently utilized in the advancement of efficient models for the forecasting and diagnosis of the Covid-19 pandemic since the surge of the outbreak. These models have exhibited wide variations in the predictions because of the presence of some challenges such as uncertainty of data that needs to be resolved for developing more accurate models. Only limited data sets for medical images and textual analysis are available due to the segregation of data in different regions of the world. Generally, deep learning approaches require large datasets to yield more accurate results. Therefore, regulation of data sources is one of the key challenges that need to be addressed to develop accurate models. As the forecasting models use online datasets, it results in poor outcomes. Therefore, it is necessary to produce real-world datasets to improve the performance of the models. Another important issue is the less involvement of clinical experts while performing the classification of Covid-19 images. This needs to be addressed to generate accurate predictions.
Conclusion
The emerging confront that occurs in several functional fields is always actively addressed by the researchers. Covid-19 is the latest growing research domain in recent days. According to Worldometer, the effect of Covid-19 has contaminated about 8.1 million citizens and made 436,276 deaths across the world as of 15 June 2020. As the registered cases of Covid-19 have crossed all the earlier accounts of transmittable disease, it is measured to be the deadliest disease. The spread of this pandemic has distressed the social, economic, political, financial, and religious growth of the overall world. So, to authorize the health and government region, it is essential to analyze different prediction as well as forecasting tools. From the deep analytical study in this paper, it is surveyed that most DL methods have been used majorly for classifying, forecasting, and diagnosing Covid-19. The main contribution of this analysis is the study of several forecasting as well as prediction models of DL approaches along with their applications in pandemic control. It is worth capable to mention that every practitioner and researcher and others over the world are facing a challenge of data deficiency. More current existing data sets with updated Covid-19 information need to be generated, so it may complete the deficiency issue. The topmost economies of the globe include China, the USA, Japan, Germany, India, etc. which are at the border of collapse. Due to lockdown, the business over the globe is functioning within fright of an approaching collapse of worldwide financial markets. The shutting of malls and shops has mostly impacted the organized dealers. Aviation is the worst-hit sector due to the cancelation of domestic and international flights on the lockdown report. Overall trades, supply chains, tourism, and transport have been distressed brutally due to the pandemic. Some other buildings, construction, textile, and apparel fields have been affected badly because of both the labors and raw material deficiencies. The effect of lockdown on education caused a stoppage in students’ study, cancelation of public and internal assessments for substitutions, or qualifications by a substandard alternative. Though various sectors had a major effect due to Covid-19, there are a few sectors that have noticed the rise at the time of lockdowns such as pharma, chemicals, food-based retail, digital, and Internet economies. Despite examining apparent risks in both the Indian and global economies, there is still anticipation that this terrible situation can be avoided. Governments have attained from the previous adversities that the consequences of a demand-possessed decline can be contrasting to the expenditure of the government. So, most of the governments are lifting their provision of financial interests to society and assuring businesses can access the funds desired to retain their workers employed in the pandemic. Likewise, various areas have been affected due to this pandemic.
This study presents a brief review of the usage of DL for Covid-19. The DL method is appropriate in predicting the effect of Covid-19 on several domains which may assist the government in executing appropriate strategies to defeat the financial crisis. Although computing advances have been effectively used in the forecasting and prediction of the Covid-19 pandemic, still some limitations exist which include inadequate accessibility of interpreted medical images, inconsiderate radiological features (like GGO and bilateral involvement in diagnosing Covid-19), predictive end events, etc. These limitations are required to be the focus to implement more accurate methods. We mentioned various DL models along with effective incentives. Based on our study, we strongly recommend that there is a requirement of addressing the challenges of data deficiency of Covid-19 to perform further higher researches. Usage of artificial neural networks (ANNs) as well as higher-order neural networks (HONN) in the prediction as well as forecasting of this pandemic is measured as the upcoming extent of the research. However, DL techniques are still promising, attractive, and more and more becoming mature which makes them more attractive and faithful to assist in holding the Covid-19 pandemic.
References
Abbas, A., Abdelsamea, M. M., & Gaber, M. M. (2020). Classification of COVID-19 in chest x-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.13815.
Alibaba. (2020) https://www.alibabacloud.com/blog/fighting-coronavirus-with-technology-another-breakthrough-for-alibaba-in-nlp-research_595973
Amyar, A., Modzelewski, R., & Ruan, S. (2020). Multi-task deep learning based CT imaging analysis for COVID-19: classification and segmentation. medRxiv.
Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Holmes EC, Garry RF. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med. 2020;26(4):450–2.
Apostolopoulos ID, Mpesiana TA. Covid-19: automatic detection from x-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine. 2020;1.
Apostolopoulos ID, Aznaouridis SI, Tzani MA. Extracting possibly representative COVID-19 biomarkers from x-ray images with deep learning approach and image data related to pulmonary diseases. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2020:1.
Ardakani AA, Kanafi AR, Acharya UR, Khadem N, Mohammadi A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput Biol Med. 2020;103795.
Ayyoubzadeh SM, Ayyoubzadeh SM, Zahedi H, Ahmadi M, Kalhori SRN. Predicting COVID-19 incidence through analysis of Google trends data in Iran: data mining and deep learning pilot study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6(2):e18828.
Banda, J. M., Tekumalla, R., Wang, G., Yu, J., Liu, T., Ding, Y., & Chowell, G. (2020). A large-scale COVID-19 twitter chatter dataset for open scientific research--an international collaboration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03688.
Bandyopadhyay, S. K., & Dutta, S. (2020). Machine learning approach for confirmation of COVID-19 cases: positive, negative, Death and Release. medRxiv.
Bernheim A, Mei X, Huang M, Yang Y, Fayad ZA, Zhang N, et al. Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection. Radiology. 2020;200463.
Bhardwaj R, Nambiar AR, Dutta D. A study of machine learning in healthcare. In: 2017 IEEE 41st annual computer software and applications conference (COMPSAC) (Vol. 2, pp. 236-241). IEEE; 2017, July.
Bukhari, S. U. K., Bukhari, S. S. K., Syed, A., & SHAH, S. S. H. (2020). The diagnostic evaluation of convolutional neural network (CNN) for the assessment of chest X-ray of patients infected with COVID-19. medRxiv.
Bullock, J., Pham, K. H., Lam, C. S. N., & Luengo-Oroz, M. (2020). Mapping the landscape of artificial intelligence applications against COVID-19. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.11336.
Butt C, Gill J, Chun D, Babu BA. Deep learning system to screen coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Applied Intelligence. 2020:1.
Cafes and restaurant guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/restaurants-and-cafes-covid19
Cao Y, Xu Z, Feng J, Jin C, Han X, Wu H, et al. Longitudinal assessment of covid-19 using a deep learning–based quantitative ct pipeline: illustration of two cases. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 2020;2(2):e200082.
Celik Y, Talo M, Yildirim O, Karabatak M, Acharya UR. Automated invasive ductal carcinoma detection based using deep transfer learning with whole-slide images. Pattern Recogn Lett. 2020;133:232–9.
Chen, E., Lerman, K., & Ferrara, E. (2020). Covid-19: the first public coronavirus twitter dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07372.
Chen, J., Wu, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Gong, D., Zhao, Y., ... & Zhang, K. (2020a). Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel corona virus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography: a prospective study. medRxiv.
Cho Y, Bianchi-Berthouze N, Julier SJ. DeepBreath: deep learning of breathing patterns for automatic stress recognition using low-cost thermal imaging in unconstrained settings. In: 2017 Seventh International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII) (pp. 456-463). IEEE; 2017.
Clearinghouse dataset (2020) https://asone.ai/polymath/index.php?title=COVID-19_dataset_clearinghouse
Codella NC, Nguyen QB, Pankanti S, Gutman DA, Helba B, Halpern AC, et al. Deep learning ensembles for melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images. IBM J Res Dev. 2017;61(4/5):5–1.
Cohen, J. P., Morrison, P., & Dao, L. (2020). COVID-19 image data collection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.11597.
COVID-19 news article database (2020) https://www.covid19-archive.com/
Data repository (2020) https:// docs.google.com/ document/d/ 1JWeD1AaIGKMPry _EN8GjIqwX4J4KLQIAqP09exZ-ENI.
Dimensions AI COVID-19 (2020) https://covid-19.dimensions.ai/
Dong L, Hu S, Gao J. Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Drug discoveries & therapeutics. 2020;14(1):58–60.
Elasnaoui K, Chawki Y. Using x-ray images and deep learning for automated detection of coronavirus disease. Journal of biomolecular structure and dynamics, (just-accepted). 2020:1–22.
El-Din Hemdan, E., Shouman, M. A., & Karar, M. E. (2020). COVIDX-net: a framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose COVID-19 in x-ray images. arXiv, arXiv-2003.
Entertainment and culture guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/entertainment-and-culture-restrictions-covid-19
Estola T. Corona viruses, a new group of animal RNA viruses. Avian Dis. 1970;14:330–6.
Ezzat, D., & Ella, H. A. (2020). GSA-DenseNet121-COVID-19: a hybrid deep learning architecture for the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease based on gravitational search optimization algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.05084.
Fan DP, Zhou T, Ji GP, Zhou Y, Chen G, Fu H, et al. Inf-Net: automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020;39:2626–37.
Farooq, M., & Hafeez, A. (2020). Covid-ResNet: a deep learning framework for screening of covid19 from radiographs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.14395.
Fu, M., Yi, S. L., Zeng, Y., Ye, F., Li, Y., Dong, X., ... & Zhang, Q. (2020). Deep learning-based recognizing COVID-19 and other common infectious diseases of the lung by chest CT scan images. medRxiv.
Ghoshal, B., & Tucker, A. (2020). Estimating uncertainty and interpretability in deep learning for corona virus (COVID-19) detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10769.
Global drug discovery (2020) https://ghddi-ailab.github.io/Targeting2019-nCoV/
Goodfellow, I. J. (2014). On distinguishability criteria for estimating generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6515.
Gozes, O., Frid-Adar, M., Greenspan, H., Browning, P. D., Zhang, H., Ji, W., ... & Siegel, E. (2020). Rapid ai development cycle for the corona virus (covid-19) pandemic: initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning ct image analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.05037.
Gozes, O., Frid-Adar, M., Sagie, N., Zhang, H., Ji, W., & Greenspan, H. (2020a). Corona virus detection and analysis on chest ct with deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.02640.
Hall, L. O., Paul, R., Goldgof, D. B., & Goldgof, G. M. (2020). Finding COVID-19 from chest x-rays using deep learning on a small dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.02060.
Haller S, Badoud S, Nguyen D, Garibotto V, Lovblad KO, Burkhard PR. Individual detection of patients with Parkinson disease using support vector machine analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data: initial results. Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(11):2123–8.
Hamilton D, List A, Butler T, Hogg S, Cawley M. Discrimination between parkinsonian syndrome and essential tremor using artificial neural network classification of quantified DaTSCAN data. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27(12):939–44.
Hammoudi, K., Benhabiles, H., Melkemi, M., Dornaika, F., Arganda-Carreras, I., Collard, D., & Scherpereel, A. (2020). Deep learning on chest x-ray images to detect and evaluate pneumonia cases at the era of COVID-19. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03399.
Haque, A. B., & Rahman, M. (2020). Augmented COVID-19 X-ray images dataset (Mendely) analysis using convolutional neural network and transfer learning.
He, X., Yang, X., Zhang, S., Zhao, J., Zhang, Y., Xing, E., & Xie, P. (2020). Sample-efficient deep learning for COVID-19 diagnosis based on CT scans. medRxiv.
Heidari M, et al. Improving the performance of CNN to predict the likelihood of COVID-19 using chest x-ray images with preprocessing algorithms. International journal of medical informatics. 2020;144:104284.
Henderson DA. Smallpox: the death of a disease, vol. 237. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books; 2009.
Horry, M. J., Paul, M., Ulhaq, A., Pradhan, B., Saha, M., & Shukla, N.(2020) X-ray image based COVID-19 detection using pre-trained deep learning models.
Hospitals and industry guidelines (2020) https://www.business.vic.gov.au/disputes-disasters-and-succession-planning/coronavirus-covid-19/hospitality-industry-guidelines-for-coronavirus-covid-19
Hu S, Gao Y, Niu Z, Jiang Y, Li L, Xiao X, et al. Weakly supervised deep learning for covid-19 infection detection and classification from ct images. IEEE Access. 2020;8:118869–83.
Huang, C. J., Chen, Y. H., Ma, Y., & Kuo, P. H. (2020). Multiple-input deep convolutional neural network model for covid-19 forecasting in China. medRxiv.
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020a;395(10223):497–506.
Huang L, Han R, Ai T, Yu P, Kang H, Tao Q, et al. Serial quantitative chest ct assessment of covid-19: deep-learning approach. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 2020b;2(2):e200075.
Huertas-Fernandez I, Garcia-Gomez FJ, Garcia-Solis D, Benitez-Rivero S, Marin-Oyaga VA, Jesus S, et al. Machine learning models for the differential diagnosis of vascular parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease using [123 I] FP-CIT SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(1):112–9.
Kaggle. (2020) https: //www.kaggle.com/andre wmvd/convi d19-X-rays.
Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell. 2018;172:1122–1131.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010).
Khalifa, N. E. M., Taha, M. H. N., Hassanien, A. E., & Elghamrawy, S. (2020). Detection of Corona virus (COVID-19) associated pneumonia based on generative adversarial networks and a fine-tuned deep transfer learning model using chest X-ray dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.01184.
Khobahi, S., Agarwal, C., & Soltanalian, M. (2020). CoroNet: a deep network architecture for semi-supervised task-based identification of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. medRxiv.
Kim SH, Han GT. 1D CNN based human respiration pattern recognition using ultra wideband radar. In: 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC) (pp. 411-414). IEEE; 2019.
Kleinberg, B., van der Vegt, I., & Mozes, M. (2020). Measuring emotions in the covid-19 real world worry dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.04225.
Kramer MA. "Nonlinear principal component analysis using autoassociative neural networks" (PDF). AICHE J. 1991;37(2):233–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690370209.
Kuo, M. D., Chiu, W. H. K., Vardhanabhuti, V., Poplavskiy, D., Yu, P. L., Du, R., ... & Lee, J. C. Y. (2020). Nowcast deep learning models for constraining zero-day pathogen attacks–application on chest radiographs to Covid-19.
Lai CC, Shih TP, Ko WC, Tang HJ, Hsueh PR. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and corona virus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges. International journal of antimicrobial agents. 2020:105924.
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning nature. 2015:521.
LitCOVID dataset (2020) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/coronavirus/
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal. 2017;42:60–88.
Loey, M., Smarandache, F., & Khalifa, N. E. M. (2020). Within the lack of COVID-19 benchmark dataset: a novel GAN with deep transfer learning for corona-virus detection in chest X-ray images.
Loey, M., Smarandache, F., & Khalifa, N. E. M. (2020a). A deep transfer learning model with classical data augmentation and CGAN to detect COVID-19 from chest CT radiography digital images.
Lundervold AS, Lundervold A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z Med Phys. 2019;29(2):102–27.
Luz, E., Silva, P. L., Silva, R., & Moreira, G. (2020). Towards an efficient deep learning model for COVID-19 patterns detection in X-ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.05717.
Maghdid, H. S., Asaad, A. T., Ghafoor, K. Z., Sadiq, A. S., & Khan, M. K. (2020). Diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia from X-ray and CT images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00038.
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA. V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV) (pp. 565-571). IEEE; 2016.
Minaee, S., Kafieh, R., Sonka, M., Yazdani, S., & Soufi, G. J. (2020). Deep-COVID: predicting COVID-19 from chest x-ray images using deep transfer learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.09363.
Mooney. Kaggle chest x-ray images (pneumonia) dataset. https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestX-ray-dataset, 2020. 2, 3.
Mor, N. S (2020). Corona virus disease (COVID-19) screening with deep learning using CT images.
Mukherjee, H., Ghosh, S., Dhar, A., Obaidullah, S., Santosh, K. C., & Roy, K. (2020). Shallow convolutional neural network for COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest x-rays.
Narin, A., Kaya, C., & Pamuk, Z. (2020). Automatic detection of corona virus disease (covid-19) using x-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10849.
Nextstrain (2020) https://nextstrain.org/
Oh Y, Park S, Ye JC. Deep learning covid-19 features on cxr using limited training data sets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020;39:2688–700.
Ozkaya, U., Ozturk, S., & Barstugan, M. (2020). Corona virus (COVID-19) classification using deep features fusion and ranking technique. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03698.
Ozturk T, Talo M, Yildirim EA, Baloglu UB, Yildirim O, Acharya UR. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with x-ray images. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2020:103792.
Pal, R., Sekh, A. A., Kar, S., & Prasad, D. K. (2020). Neural network based country wise risk prediction of COVID-19. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00959.
Pandemic H1N1 (2009).https://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/en/.
Pandemic MER's-Cov (2012). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/middle-east-respiratory-syndrome-coronavirus-(mers-cov).
Pandemic SARS (2003). https://www.who.int/health-topics/severe-acute-respiratory-syndrome#tab=tab_1
Panwar H, Gupta PK, Siddiqui MK, Morales-Menendez R, Singh V. Application of deep learning for fast detection of COVID-19 in x-rays using nCOVnet. Chaos, Solitons Fractals. 2020;109944.
Paperspace. (2020) https://blog.paperspace.com/fighting-covid-19-using-artificial-intelligence-and-data/
Patankar, S. (2020). Deep learning-based computational drug discovery to inhibit the RNA dependent RNA polymerase: application to SARS-CoV and COVID-19.
Pathak Y, Shukla PK, Tiwari A, Stalin S, Singh S, Shukla PK. Deep transfer learning based classification model for COVID-19 disease. IRBM. 2020.
Pathari, S., & Rahul, U. (2020). Automatic detection of COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray using transfer learning. medRxiv.
Paules CI, Marston HD, Fauci AS. Corona virus infections—more than just the common cold. Jama. 2020;323(8):707–8.
Pereira, R. M., Bertolini, D., Teixeira, L. O., Silla Jr, C. N., & Costa, Y. M. (2020). COVID-19 identification in chest x-ray images on flat and hierarchical classification scenarios. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.05835.
Punn, N. S., Sonbhadra, S. K., & Agarwal, S. (2020). COVID-19 epidemic analysis using machine learning and deep learning algorithms. medRxiv.
Rahimzadeh, M., & Attar, A. (2020). A new modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 from x-ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.08052.
Rahimzadeh M, Attar A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest x-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. 2020a:100360.
Rajaraman S, Antani S. Weakly labeled data augmentation for deep learning: a study on COVID-19 detection in chest x-rays. Diagnostics. 2020;10(6):358.
Rajaraman, S., Siegelman, J., Alderson, P. O., Folio, L. S., Folio, L. R., & Antani, S. K. (2020). Iteratively pruned deep learning ensembles for COVID-19 detection in chest x-rays. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.08379.
Razzak, I., Naz, S., Rehman, A., Khan, A., & Zaib, A. (2020). Improving corona virus (COVID-19) diagnosis using deep transfer learning. medRxiv.
RCSB Protein Data Bank (2020) http://www.rcsb.org/news?year=2020&article=5e3c4bcba5007a04a313edcc
Rekha Hanumanthu S. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: a state-of-the-art review. Chaos, Solitons Fractals. 2020;109947.
Religion and ceremony guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/religion-and-ceremony-restrictions-covid-19.
Roy S, Menapace W, Oei S, Luijten B, Fini E, Saltori C, et al. Deep learning for classification and localization of COVID-19 markers in point-of-care lung ultrasound. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020;39:2676–87.
Santosh, K., Das, D., & Pal, U. (2020). Truncated inception net: COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest x-rays.
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997;9(8):1735–80. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735.S2CID1915014.
Sethy PK, Behera SK. Detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) based on deep features. Preprints. 2020;2020030300:2020.
Shan, F., Gao, Y., Wang, J., Shi, W., Shi, N., Han, M., ... & Shi, Y. (2020). Lung infection quantification of covid-19 in ct images with deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04655.
Sharma K, Kaur A, Gujral S. Brain tumor detection based on machine learning algorithms. International Journal of Computer Applications. 2014;103(1):7–11.
Sherstinsky, A. (2018). Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (rnn) and long short-term memory (lstm) network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.03314.
Shopping and retail restriction guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/shopping-and-retail-restrictions-covid-19
Singh R, Singh R, Bhatia A. Sentiment analysis using machine learning technique to predict outbreaks and epidemics. Int J Adv Sci Res. 2018;3(2):19–24.
Social gathering guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/social-gatherings-covid-19
Song, Y., Zheng, S., Li, L., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Huang, Z., ... & Chong, Y. (2020). Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel corona virus (COVID-19) with CT images. medRxiv.
Souza JC, Diniz JOB, Ferreira JL, da Silva GLF, Silva AC, de Paiva AC. An automatic method for lung segmentation and reconstruction in chest X-ray using deep neural networks. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 2019;177:285–96.
Sports and exercise guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/sport-and-exercise-restrictions-covid-19#changes-to-restrictions-from-1159pm-on-21-june
Spreeuwenberg P, Kroneman M, Paget J. Reassessing the global mortality burden of the 1918 influenza pandemic. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(12):2561–7.
steps-taken-by-countries-in-fighting-covid-19-pandemic (2020), https://www.aa.com.tr/en/health/steps-taken-by-countries-in-fighting-covid-19-pandemic/1812009
Talo M, Yildirim O, Baloglu UB, Aydin G, Acharya UR. Convolutional neural networks for multi-class brain disease detection using MRI images. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2019;78:101673.
Tan JH, Fujita H, Sivaprasad S, Bhandary SV, Rao AK, Chua KC, et al. Automated segmentation of exudates, haemorrhages, microaneurysms using single convolutional neural network. Inf Sci. 2017;420:66–76.
Tartaglione, E., Barbano, C. A., Berzovini, C., Calandri, M., & Grangetto, M. (2020). Unveiling COVID-19 from chest x-ray with deep learning: a hurdles race with small data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.05405.
Television coverage database (2020) https://blog.gdeltproject.org/a-new-dataset-for-exploring-the-coronavirus-narrative-on-television-news/
Toğaçar M, Ergen B, Cömert Z. COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit social mimic optimization and structured chest x-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2020:103805.
Travel guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/travel-restrictions-covid-19
Ucar F, Korkmaz D. COVIDiagnosis-net: deep Bayes-SqueezeNet based diagnostic of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from x-ray images. Medical hypotheses. 2020:109761.
Vaid S, Kalantar R, Bhandari M. Deep learning COVID-19 detection bias: accuracy through artificial intelligence. International Orthopaedics. 2020:1.
van der Schaar, M., & Alaa, A. (2020). How artificial intelligence and machine learning can help healthcare systems respond to COVID-19.
Visiting care facilities guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/visiting-care-facilities-covid-19
Waheed A, Goyal M, Gupta D, Khanna A, Al-Turjman F, Pinheiro PR. Covidgan: data augmentation using auxiliary classifier gan for improved covid-19 detection. IEEE Access. 2020;8:91916–23.
Wang, S., Kang, B., Ma, J., Zeng, X., Xiao, M., Guo, J., ... & Xu, B. (2020a). A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for corona virus disease (COVID-19). MedRxiv.
Wang X, Deng X, Fu Q, Zhou Q, Feng J, Ma H, et al. A weakly-supervised framework for COVID-19 classification and lesion localization from chest CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020b.
Wang, Y., Hu, M., Li, Q., Zhang, X. P., Zhai, G., & Yao, N. (2020c). Abnormal respiratory patterns classifier may contribute to large-scale screening of people infected with COVID-19 in an accurate and unobtrusive manner. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05534.
Williams, Ronald J.; Hinton, Geoffrey E.; Rumelhart, David E. (October 1986). Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature. 323 (6088): 533–536. Bibcode:1986Natur.323..533R. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0. ISSN 1476-4687. S2CID 205001834.
Work and study guidelines (2020) https://www.dhhs.vic.gov.au/work-and-study-restrictions-covid-19
World Health Organization. (2020). WHO Novel Corona virus-Thailand (ex-China). Geneva, Swiss. Accessed: Jan. 14, 2020. [Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/csr/don/14-january-2020-novel-coronavirusthailand/en/.
World Health Organization. (2020a). Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, 2 March 2020 (No. WHO/COVID-19/laboratory/2020.4). World Health Organization.
Wu X, Hui H, Niu M, Li L, Wang L, He B, et al. Deep learning-based multi-view fusion model for screening 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia: a multicentre study. European Journal of Radiology. 2020:109041.
Xu, X., Jiang, X., Ma, C., Du, P., Li, X., Lv, S., ... & Li, Y. (2020). Deep learning system to screen corona virus disease 2019 pneumonia. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.09334.
Yan, L., Zhang, H. T., Goncalves, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Guo, Y., ... & Huang, X. (2020). A machine learning-based model for survival prediction in patients with severe COVID-19 infection. medRxiv.
Yan, L., Zhang, H. T., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Sun, C., Liang, J., ... & Tang, X. (2020a). Prediction of criticality in patients with severe Covid-19 infection using three clinical features: a machine learning-based prognostic model with clinical data in Wuhan. MedRxiv.
Yıldırım Ö, Pławiak P, Tan RS, Acharya UR. Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals. Comput Biol Med. 2018;102:411–20.
Zahangir Alom, M., Shaifur Rahman, M. M., Shamima Nasrin, M., Taha, T. M., & Asari, V. K. (2020). COVID_MTNet: COVID-19 detection with multi-task deep learning approaches. arXiv, arXiv-2004.
Zhang H, Saravanan KM, Yang Y, Hossain MT, Li J, Ren X, et al. Deep learning based drug screening for novel coronavirus 2019-nCov. Interdisciplinary Sciences, Computational Life Sciences. 2020a:1.
Zhang J, Xie Y, Li Y, Shen C, Xia Y. Covid-19 screening on chest x-ray images using deep learning based anomaly detection. arXiv preprint arXiv. 2020, 2003:12338.
Zhavoronkov A, Aladinskiy V, Zhebrak A, Zagribelnyy B, Terentiev V, Bezrukov DS, et al. Potential COVID-2019 3C-like protease inhibitors designed using generative deep learning approaches. In silico Medicine Hong Kong Ltd A. 2020;307:E1.
Zheng C, Deng X, Fu Q, Zhou Q, Feng J, Ma H, et al. Deep learning-based detection for COVID-19 from chest CT using weak label. medRxiv. 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
I on behalf of the authors would like to state that the above manuscript is our original research work and it has not been published elsewhere. Also, it has not been submitted to any journal for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, J., Naik, B., Dinesh, P. et al. Significance of deep learning for Covid-19: state-of-the-art review. Res. Biomed. Eng. 38, 243–266 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-021-00135-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-021-00135-6