Abstract
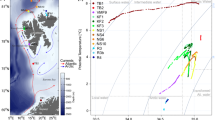
The distribution, behavior and metabolism of the mesopelagic jellyfish, Periphylla periphylla (Péron & Lesueur), were investigated in Lurefjorden, Norway. Field studies, conducted in 1998–1999 with plankton nets and a remotely operated vehicle, indicated that 80-90% of the dense (up to 2.5 m−3) population migrated 200–400 m vertically each day throughout the year. In situ observations with red light revealed that swimming rates and feeding activity varied with age and time of day. Detection of turbulence and contact with surfaces caused this medusa to conceal one or all of its tentacles in the stomach or to shed nematocyst-laden tissue from the tentacles. Stomachs of medusae collected with nets were often full of prey entangled with the sloughed tissue. Stomachs of medusae captured individually with ROV samplers were empty or contained only a few prey in their stomachs (typically, 1–4 copepods Calanus spp. or chaetognaths Eukrohnia hamata Möbius per medusa). Low rates (0.4–5.6 μl O2 mg C−1 h−1) of oxygen consumption of P. periphylla suggested that this species was sustained by relatively few (1–34) prey d−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alldredge, A. L., 1984. The quantitative significance of gelatinous zooplankton as pelagic consumers. In Fasham, M. J. R. (ed.), Flows of Energy and Materials in Marine Ecosystems: Theory and Practice. Plenum New York: 407–433.
Aksnes, D. L. & T. Magnesen, 1983. Distribution, development and production of Calanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus) in Lindåspollene, western Norway, 1979. Sarsia 68: 195–208.
Aure, J. & R. Sætre, 1981. Wind effects on the Skagerrak outflow. In Sætre, R. & M. Mork (eds), The Norwegian Coastal Current. University of Bergen: 263–293.
Bailey, T. G., J. J. Torres, M. J. Youngbluth & G. P. Owen, 1994. Effect of decompression on mesopelagic gelatinous zooplankton: A comparison of in situ and shipboard measurements of metabolism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 113: 13–27.
Båmstedt, U., M. B. Martinussen & S. Matsakis, 1994. Trophodynamics of the two scyphozoan jellyfishes, Aurelia aurita and Cyanea capillata, in western Norway. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 51: 369–382.
Båmstedt, U., J. H. Fosså, M. B. Martinussen & A. Fosshagen, 1998. Mass occurrence of the physonect siphonophore Apolemia uvaria (Lesueur) in Norwegian waters. Sarsia 83: 79–85.
Barham, E. G., 1966. Deep scattering layer migration and composition: observations from a diving saucer. Science 151: 1399–1403.
Berstad, V., U. Båmstedt & M. B. Martinussen, 1995. Distribution and swimming of the jellyfishes Aurelia aurita and Cyanea capillata. In Skjoldal, H. R., C. Hopkins, K. E. Erikstad & H. P. Leinaas (eds), Ecology of Fjords and Coastal Waters. Elsevier Science, London: 257–271.
Child, C. A. & G. R. Harbison, 1986. A parasitic association between a pycnogonid and a scyphomedusa in midwater. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 66: 113–117.
Conover, R. J., 1978. Transformation of organic matter. In Kinne, O. (ed.), Marine Ecology IV, Dynamics. Wiley, Chichester: 221–499.
Dalpadado, P., B. Ellertsen, W. Melle & H. R. Skjoldal, 1998. Summer distribution patterns and biomass estimates of macrozooplankton and micronekton in the Nordic seas. Sarsia 83: 103–116.
Eiane, K., D. L. Aksnes & M. D. Ohman, 1998. Advection and zooplankton fitness. Sarsia 83: 87–93.
Eiane, K., D. L. Aksnes, E. Bagoeien & S. Kaartvedt, 1999. Fish or jellies – a question of visibility? Limnol. Oceanogr. 44: 1352–1357.
Fosså, J. H., 1992. Mass occurrence of Periphylla periphylla (Scyphozoa, Coronatae) in a Norwegian fjord. Sarsia 77: 237–251.
Golmen, L., H. Svendsen, A. Bakke & J. Molvaer, 1998. Strong tide-induced vertical mixing in a deep fjord with a shallow sill. Oceanography 11: 1–5.
Hansson, L. J., 1997. Effect of temperature on growth rate of Aurelia aurita (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) from Gullmarsfjorden, Sweden. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 161: 145–153.
Hay, S. J., J. R. G. Hislop & A. M. Shanks, 1990. North Sea scyphomedusae: summer distribution, estimated biomass and significance particularly for 0-group gadoid fish. Neth. J. Sea Res. 25: 113–130.
Hernroth, L. & F. Grøndal, 1983. On the biology of Aurelia aurita. I. Release and growth of Aurelia aurita (L.) ephyrae in the Gullmar Fjord, western Sweden, 1982–83. Ophelia 22: 189–199.
Ikeda, T., J. J. Torres, S. Hernández-León & S. P. Geiger, 2000. Metabolism. In Harris, R., P. Wiebe, J. Lenz, H. R. Skjoldal & M. Huntley (eds), ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual. Academic Press, New York: 455–532.
Jarms, G., U. Båmstedt, H. Tiemann, M. B. Martinussen & J. H. Fosså, 1999. The holopelagic life cycle of the deep-sea medusa Periphylla periphylla (Scyphozoa, Coronata). Sarsia 84: 55–65.
Johannessen, P., 1980. Resipientundersøkelse av enkelte fjordavsnitt I Lindås kommune med hovedvekt lagt på bunnforhold og bunndyr. Institutt for Marin-biologi, Universitetet I Bergen: 39 pp.
Larson, R. J., 1979. Feeding in coronate medusae (Class Scyphozoa, Order Coronatae). Mar. Behav. Physiol. 6: 123–129.
Larson, R. J., 1986. Pelagic scyphomedusae (Scyphozoa: Coronatae and Semaeostomeae) of the southern Ocean. In Kornicker, L. (ed.), Biology of the Antarctic Seas. XVI. Ant. Res. Ser. 41: 59–165.
Larson, R. J., 1987. Respiration and carbon turnover rates of medusae from the NE Pacific. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 87A: 93–100.
Larson, R. J., 1990. Scyphomedusae and cubomedusae from the Eastern Pacific. Bull. mar. Sci. 47: 546–556.
Larson, R. J., C. E. Mills & G. R. Harbison, 1991. Western Atlantic midwater hydrozoan and scyphozoan medusae: in situ studies using manned submersibles. Hydrobiologia. 216/217: 311–317.
Lucas, C. H., 2001. Reproduction and life history strategies of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita, in relation to its ambient environment. Hydrobiologia 451 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 155): 229–246.
Maas, O., 1897. Reports on an exploration off the west coasts of Mexico, Central and South America, and off the Galapagos Islands. XXXI. Die Medusen. Mem. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. 23: 9–92.
Mauchline, J., 1998. The biology of calanoid copepods. Adv. mar. Biol. 33: 1–710.
Mills, C. E., 1995. Medusae, siphonophores and ctenophores as planktivorous predators in changing global ecosystems. ICES J. mar. Sci. 52: 575–581.
Möller, H., 1980. Population dynamics of Aurelia aurita medusae in Kiel Bight, Germany (FRG). Mar. Biol. 60: 123–128.
Pagès, F. & J. –M. Gili, 1992. Influence of the thermocline on the vertical migration of medusae during a 48 h sampling period. S. –Afr. Tydskr. Dierk. 27: 50–59.
Pagès, F. & F. Kurbjeweit, 1994. Vertical distribution and abundance of mesoplanktonic medusae and siphonophores from theWeddell Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 14: 243–251.
Pagès, F., M. G. White & P. G. Rodhouse, 1996. Abundance of gelatinous carnivores in the nekton community of the Antarctic polar frontal zone in summer 1994. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 141: 139–147.
Parsons, T. R., Y. Maita & C.M. Lalli, 1985. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. Pergamon Press, New York.
Purcell, J. E., 1983. Digestion rates and assimilation efficiencies of siphonophores fed zooplankton prey. Mar. Biol. 73: 257–261.
Purcell, J. E. & C. E. Mills, 1988. The correlation between nematocyst types and diets in pelagic Hydrozoa. In Hessinger, D. & H. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, New York: 463–485.
Purcell, J. E. & M. N. Arai, 2001. Interactions of pelagic cnidarians and ctenophores with fish: a review. Hydrobiologia 451 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 155): 27–44.
Purcell, J. E., T. A. Shiganova, M. B. Decker & E. D. Houde, 2001. The ctenophore Mnemiopsis in native and exotic habitats: U.S. estuaries versus the Black Sea basin. Hydrobiologia, this volume.
Robison, B. H., 1999. Shape change behavior by mesopelagic animals. Mar. Fresh. Behav. Physiol. 32: 17–25.
Robison, B. H., K. R. Reisenbichler, R. Sherlock, J. M. B. Silguero & F. P. Chavez, 1998. Seasonal abundance of Nanomia bijuga in Monterey Bay. Deep-Sea Res. II, 45: 1741–1751.
Rogers, C. A., D. C. Biggs & R. A. Cooper, 1978. Aggregation of the siphonophore Nanomia cara in the Gulf of Maine. Fish. Bull. 76: 281–284.
Thuesen, E. V. & J. J. Childress, 1994. Oxygen consumption rates and metabolic enzyme activities of oceanic California medusae in relation to body size and habitat depth. Biol Bull. 187: 84–98.
Tietze, R. C. & A. M. Clark, 1986. Remotely operated tools for undersea vehicles. In McGuiness, T. (ed.), Current Practices and New Technology in Ocean Engineering, Am. Soc. Mech. Engin. 11: 219–223.
Tusting, R. F. & D. L. Davis, 1993. Laser systems and structured illumination for quantitative undersea imaging. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 26: 5–12.
Van Der Veer, H. M. & W. Oorthuysen, 1985. Abundance, growth and food demand of the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita in the western Wedden Sea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 19: 38–44.
Volovik, S. P., Z. A. Myrzoyan & G. S. Volovik, 1993. Mnemiopsis leidyi in the Azov Sea: biology, population dynamics, impact to the ecosystem and fisheries. ICES-CM-1993/L:69: 11 pp.
Youngbluth, M. J., 1984. Manned submersibles and sophisticated instrumentation: Tools for oceanographic research. In Proceedings of SUBTECH 1983 Symposium, Society of underwater technology, London: 335–344.
Youngbluth, M. J., T. G. Bailey & C. A. Jacoby, 1990. Biological explorations in the mid-ocean realm: foods webs, particle flux and technological advancements. In Lin, Y. C. & K. K. Shida (eds), Man in the Sea, Volume II, Best Publishing, San Pedro: 191–208.
Youngbluth, M. J., P. Kremer, T. G. Bailey & C. A. Jacoby, 1988. Chemical composition, metabolic rates and feeding behavior of the midwater ctenophore Bathocyroe fosteri. Mar. Biol. 98: 87–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youngbluth, M.J., Båmstedt, U. Distribution, abundance, behavior and metabolism of Periphylla periphylla, a mesopelagic coronate medusa in a Norwegian fjord. Hydrobiologia 451, 321–333 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011874828960
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011874828960