Abstract
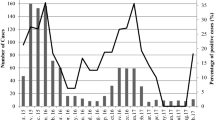
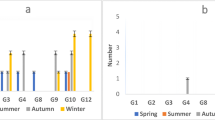
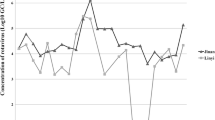
The objective of this study is to compare the prevalence of rotaviruses groups A and C in Egyptian children and aquatic environment. From 110 stool specimens of children with acute diarrhea and using RT-PCR, 35 samples (31.8 %) were positive for human rotavirus group A and 15 samples (13.6 %) were positive for human rotavirus group C. From 96 samples collected from Zenin wastewater treatment plant over a 2-year period (November 2009–October 2011) and using RT-PCR, rotavirus group A was detected in (4/24) 16.7 %, (5/24) 20.8 %, (4/24) 16.7 %, and (4/24) 16.7 %, while rotavirus group C was detected in (2/24) 8.3 %, (3/24) 12.5 %, (3/24) 12.5 %, and (0/24) 0 % in raw sewage, after primary sedimentation, after secondary sedimentation, and after final chlorination, respectively. Moreover, from 96 samples collected from El-Giza water treatment plant over a 2-year period (November 2009–October 2011), rotavirus group A was detected in (7/24) 29.2 %, (6/24) 25 %, (5/24) 20.8 %, and (3/24) 12.5 %, while rotavirus group C was detected in (3/24) 12.5 %, (1/24) 4.2 %, (1/24) 4.2 %, and (0/24) 0 % in raw Nile water, after sedimentation, after sand filtration, and after final chlorination, respectively. Using SYBR Green real-time RT-PCR, the number of human rotavirus group A genome or infectious units was higher than rotavirus group C. VP6 sequence analysis of the RT-PCR positive rotavirus group C samples revealed that four clinical specimens and three environmental samples showed similar sequences clustered with Moduganari/Human Nigerian strain AF 325806 with 98 % homology, and two clinical specimens and one environmental sample showed similar sequences clustered with Dhaka CB/Human Bangladesh strain AY 754826 with 97 % homology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, F. X., Pintó, R. M., Villena, C., Gajardo, R., & Bosch, A. (1997). Astrovirus survival in drinking water. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 63, 3119–3122.
Banyai, K., Jiang, B., Bogdán, A., Horváth, B., Jakab, F., Meleg, E., et al. (2006). Prevalence and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Hungary. Journal of Clinical Virology, 37, 317–332.
Blatchley, E. R, I. I. I., Gong, W. L., Alleman, J. E., Rose, J. B., Huffman, D. E., Otaki, M., & Lisle, J. T. (2007). Effects of wastewater disinfection on waterborne bacteria and viruses. Water Environment Research, 79, 81–92.
Bosch, A. (1998). Human enteric viruses in the water environment: A minireview. International Microbiology, 1, 191–196.
Bosch, A. (2007). Human viruses in water (1st ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Cook, N., Bridger, J., Kendall, K., Iturriza-Gómara, M., El-Attar, L., & Gray, J. (2004). The zoonotic potential of rotavirus. Journal of Infection, 48, 289–302.
Cunliffe, N. A., Dove, W., Jiang, B., Thinwda Cert, B. D., Broadhead, R. L., Molyneux, M. E., & Hart, C. A. (2001). Detection of group C rotavirus in children with acute gastroenteritis in Blantyre, Malawi. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 20, 1088–1090.
El-Senousy, W. M., Barakat, A. B., Ghanem, H. E., & Kamel, M. A. (2013a). Molecular epidemiology of human adenoviruses and rotaviruses as candidate viral indicators in the Egyptian sewage and water samples. World Applied Sciences Journal, 27, 1235–1247.
El-Senousy, W. M., Costafreda, M. I., Pintó, R. M., & Bosch, A. (2013b). Method validation for norovirus detection in naturally contaminated irrigation water and fresh produce. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 167, 74–79.
El-Senousy, W. M., & El-Mahdy, E. M. (2009). Detection and genotyping of rotaviruses in water treatment plants of El-Dakahlia Governorate. Egyptian Journal of Biotechnology, 31, 25–34.
El-Senousy, W. M., Guix, S., Abid, I., Pintó, R. M., & Bosch, A. (2007). Removal of astrovirus from water and sewage treatment plants, evaluated by a competitive reverse transcription-PCR. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 73, 164–167.
El-Senousy, W.M., Pintó, R.M., & Bosch, A. (2004). Epidemiology of human enteric viruses in the Cairo water environment. (Paper presented at the 1st International Conference of Environmental Research Division on Sustainable Development Environmental Challenges Facing Egypt. National Research Centre, Cairo, Egypt).
El-Senousy, W. M., Shahein, Y. E., Barakat, A. B., Ghanem, H. E., El-Hakim, A. E., & Ameen, S. M. (2013c). Molecular cloning and immunogenicity evaluation of rotavirus structural proteins as candidate vaccine. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 59, 67–71.
Estes, M. K. (2001). Rotaviruses and their replication. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, D. E. Griffin, R. A. Lamb, M. A. Martin, B. Roizman, & S. E. Straus (Eds.), Fields virology (4th ed., Vol. 2, pp. 1747–1785). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Gabbay, Y. B., Jiang, B., Oliveira, C. S., Mascarenhas, J. D., Leite, J. P., Glass, R. I., & Linhares, A. C. (1999). An outbreak of group C rotavirus gastroenteritis among children attending a day-care center in Belem, Brazil. Journal of Diarrhoeal Diseases Research, 2, 69–74.
Gallimore, C. I., Taylor, C., Genney, A. R., Cant, A. J., Galloway, A., Iturriza-Gomara, M., & Gray, J. J. (2006). Environmental monitoring for gastroenteric viruses in a pediatric primary immunodeficiency unit. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 44, 395–399.
Gentsch, J. R., Laird, A. R., Bielfelt, B., Griffin, D. D., Bányai, K., Ramachandran, M., et al. (2005). Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: Implications for rotavirus vaccine programs. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 192, 146–159.
Ghazy, M. M. E., El-Senousy, W. M., Abdel-Aatty, A. M., Hegazy, B., & Kamel, M. (2008). Performance evaluation of a waste stabilization pond in a rural area in Egypt. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 4, 316–326.
http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/estimates/rotavirus/en/. Accessed Oct 2014.
http://www.who.int/vaccine_safety/committee/topics/rotavirus/rotashield/en/. Accessed 30 Nov 2010.
Iturriza Gomara, M., Wong, C., Blome, S., Desselberger, U., & Gray, J. (2002). Molecular characterization of VP6 genes of human rotavirus isolates: Correlation of genogroups with subgroups and evidence of independent segregation. Journal of Virology, 76, 6596–6601.
James, V. L. A., Lambden, P. R., Caul, E. O., Cooke, S. J., & Clarke, I. N. (1997). Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in the UK. Journal of Medical Virology, 52, 86–91.
Jiang, B., Dennehy, P. H., Spangenberger, S., Gentsch, J. R., & Glass, R. I. (1995). First detection of group C rotavirus in fecal specimens of children with diarrhea in the United States. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 172, 45–50.
Kang, G., Iturriza-Gomara, M., Wheeler, J. G., Crystal, P., Monica, B., Ramani, S., et al. (2004). Quantitation of group A rotavirus by real-time reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Medical Virology, 73, 118–122.
Kapikian, A. Z., & Chanock, R. M. (1996). Rotaviruses. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, & P. M. Howley (Eds.), Fields virology (3rd ed., pp. 1657–1708). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers.
Katzenelson, E., Fattal, B., & Hostovesky, T. (1976). Organic flocculation: An efficient second-step concentration method for the detection of viruses in tap water. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 32, 838–839.
Kuzuya, M., Fujii, R., Hamano, M., Ohata, R., Ogura, H., & Yamada, M. (2001). Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in Japan based on blocking enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology, 8, 161–165.
Kuzuya, M., Hamano, M., Nishijima, M., Fujii, R., Ogura, H., Tanaka, M., et al. (2005). An outbreak of acute gastroenteritis caused by human group C rotavirus in a welfare institution in Okayama prefecture. Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, 58, 255–257.
Laine, J., Huovinen, E., Virtanen, M. J., Snellman, M., Lumio, J., Ruutu, P., et al. (2011). An extensive gastroenteritis outbreak after drinking-water contamination by sewage effluent. Finland. Epidemiology and Infection, 139, 1105–1113.
Leclerc, H., Schwartzbrod, L., & Dei-Cas, E. (2002). Microbial agents associated with waterborne. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 28, 371–409.
Logan, C., O’Leary, J. J., & O’Sullivan, N. (2006). Real-time reverse transcription-PCR for detection of rotavirus and adenovirus as causative agents of acute viral gastroenteritis in children. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 44, 3189–3195.
Maunula, L. (2007). Waterborne norovirus outbreaks. Future Virology, 2, 101–112.
Meleg, E., Ba´nyai, K., Martella, V., Jiang, B., Kocsis, B., Kisfali, P., et al. (2008). Detection and quantification of group C rotaviruses in communal sewage. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 74, 3394–3399.
Nilsson, M., Svenungsson, B., Hedlund, K. O., Uhnoo, I., Lagergren, A., Akre, T., & Svensson, L. (2000). Incidence and genetic diversity of group C rotavirus among adults. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 182, 678–684.
Offit, P. A., & Clark, H. F. (2000). Rotavirus. In G. L. Mandel, J. E.439 Bennet, & R. Dolin (Eds.), Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (5th ed., pp. 1696–1703) NewYork: Churchill Livingstone.
Parashar, U. D., Burton, A., Lanata, C., Boschi-Pinto, C., Shibuya, K., Steele, D., et al. (2009). Global mortality associated with rotavirus disease among children in 2004. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 200, 9–15.
Phan, T. G., Nishimura, S., Okame, M., Nguyen, T. A., Khamrin, P., Okitsu, S., et al. (2004). Virus diversity and an outbreak of group C rotavirus among infants and children with diarrhoea in Maizuru city, Japan during 2002-2003. Journal of Medical Virology, 74, 173–179.
Ramani, S., & Kang, G. (2009). Viruses causing childhood diarrhea in the developing world. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases, 22, 477–482.
Rodger, S. M., Bishop, R. F., & Holmes, I. H. (1982). Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 16, 724–726.
Rose, J. B., Singh, S. N., Gerba, C. P., & Kelley, L. M. (1984). Comparison of microporous filters for concentration of viruses from waste water. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 47, 989–992.
Saif, L. J., & Jiang, B. (1994). Nongroup A rotaviruses of humans and animals. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 185, 339–371.
Sánchez-Fauquier, A., Roman, E., Colomina, J., Wilhelmi, I., Glass, R. I., & Jiang, B. (2003). First detection of group C rotavirus in children with acute diarrhea in Spain. Archives of Virology, 148, 399–404.
Santosham, M., Chandran, A., Fitzwater, S., Fischer-Walker, C., Baqui, A. H., & Black, R. (2010). Progress and barriers for the control of diarrhoeal disease. Lancet, 376, 63–67.
Schnagl, R. D., Boniface, K., Cardwell, P., McCarthy, D., Ondracek, C., Coulson, B., et al. (2004). Incidence of group C human rotavirus in central Australia and sequence variation of the VP7 and VP4 genes. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42, 2127–2133.
Smith, E. M., & Gerba, C. P. (1982). Development of a method for detection of human rotavirus in water and sewage. Journal of Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 1440–1450.
Steele, A. D., & James, V. L. A. (1999). Seroepidemiology 463 of human group Crotavirus in South Africa. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 37, 4142–4144.
Szucs, G., Kende, M., & Uj, M. (1987). Atypical human rotaviruses in Hungary. Annales de l’Institut Pasteur. Virology., 138, 391–395.
Velazquez, F. R., Matson, D. O., Calva, J. J., Guerrero, L., Morrow, A. L., Carter-Campbell, S., et al. (1996). Rotavirus infection in infants as a protection against subsequent infections. The New England Journal of Medicine, 335, 1022–1028.
Wilhelmi, I., Roman, E., & Sánchez-Fauquier, A. (2003). Viruses causing gastroenteritis. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 9, 247–262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Senousy, W.M., Ragab, A.M.ES. & Handak, E.M.A.E.H. Prevalence of Rotaviruses Groups A and C in Egyptian Children and Aquatic Environment. Food Environ Virol 7, 132–141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9184-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-015-9184-6