Abstract
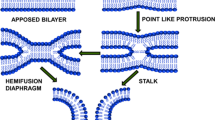
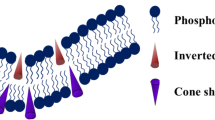
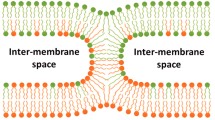
We have reviewed studies on calcium-induced fusion of lipid bilayer membranes and the role of synexin and other calcium-binding proteins (annexins) in membrane fusion. We have also discussed the roles of other cations, lipid phase transitions, long chain fatty acids and other fusogenic molecules. Finally, we have presented a simple molecular model for the mechanism of lipid membrane fusion, consistent with the experimental evidence and incorporating various elements proposed previously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahkong, Q. F., Fisher, D., Tampion, W., and Lucy, J. A. (1973). “The fusion of erythrocytes by fatty acids, esters, retinol and α-tocopherol,”Biochem. J. 136, 147–155.
Akabas, M. H., Cohen, F. S., and Finkelstein, A. (1984). “Separation of the osmotically driven fusion event from vesicle-planar membrane attachment in a model system for exocytosis,”Cell Biol. 98, 1063.
Allen, T. M., Hong, K., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1990). “Membrane contact, fusion, and hexagonal (HII) transitions in phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes,”Biochemistry, in press.
Baker, P. F. (1988). “Exocytosis in electropermeabilized cells: clues to mechanism and physiological control,” inMembrane Fusion in Fertilization, Cellular Transport, and Viral Infection (Düzgünes, N., and Bronner, F., eds), Academic Press, New York, pp. 115–138.
Baker, P. F., and Knight, D. E. (1984). “Calcium control of exocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells,”Trends. Neurosci.,7, 120.
Baker, P. F., Knight, D. E., and Whitaker, M. G. (1980). “Calcium and the control of exocytosis, inCalcium-Binding Proteins: Structure and Function” (Siegel, F. L., Carafoli, E., Kretsinger, R. H., MacLennan, D. H., and Wasserman, R. H., eds), Elsevier/North Holland, New York, pp. 47–55.
Bangham, A. D., Standish, M. M., and Watkins, J. C. (1965). “Diffusion of univalent ions across lamellae of swollen phospholipids,”J. Mol. Biol. 13, 238.
Bearer, E. L., Düzgünes, N., Friend, D. S., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1982). “Fusion of phospholipid vesicles arrested by quick freezing. The question of lipidic particles as intermediates in membrane fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 693, 93.
Bental, M., Wilschut, J., Scholma, J., and Nir, S. (1987). “Ca2+-induced fusion of large unilamellar phosphatidylserine/cholesterol vesicles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 898, 239.
Bentz, J., and Düzgünes, N. (1985). “Fusogenic capacities of divalent cations and the effect of liposome size,”Biochemistry 24, 5436.
Bentz, J., and Ellens, H. (1988). “Membrane fusion: kinetics and mechanisms,”Colloids Surf. 30, 65.
Bentz, J., Nir, S., and Wilschut, J. (1983a). “Mass action kinetics of vesicle aggregation and fusion,”Colloids Surf. 6, 333.
Bentz, J., Düzgünes, N., and Nir, S. (1983b). “Kinetics of divalent cation-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles: correlation between fusogenic capacities and binding affinities,”Biochemistry 22, 3320.
Bentz, J., Düzgünes, N., and Nir, S. (1985). “Temperature dependence of divalent cation-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine liposomes: evaluation of the kinetic rate constants,”Biochemistry 24, 1064.
Bentz, J., Alford, D., Cohen, J., and Düzgünes, N. (1988). “La3+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine liposomes. Close approach, intermembrane intermediates, and the electrostatic membrane potential,”Biophys. J. 53, 593.
Boni, L. T., Hah, J. S., Hui, S. W., Mukherjee, P., Ho, J. T., and Jung, C. Y. (1984).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 775, 409.
Braun, G., Lelkes, P., and Nir, S. (1985). “Effect of cholesterol on Ca2+-induced aggregation and fusion of sonicated phosphatidylserine/cholesterol vesicles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 812, 688.
Burns, A. L., Magendzo, K., Shirvan, A., Shrivastava, M., Rojas, E., Aligani, M. R., and Pollard, H. B. (1989). “Calcium channel activity of purified human synexin and structure of the human synexin gene.”Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 3798.
Chernomordik, L. V., Kozlov, M. M., Melikyan, G. B., Abidor, I. G., Markin, V. S., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A. (1985). “The shape of lipid molecules and monolayer membrane fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 812, 643.
Chernomordik, L. V., Melikyan, G. B., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A. (1987). “Biomembrane fusion: a new concept derived from model studies using two interacting planar lipid bilayers,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 906, 309.
Creutz, C. E. (1981). “cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin,”J. Cell Biol. 91, 247.
Creutz, C. E., and Sterner, D. C. (1983). “Calcium dependence of the binding of synexin to isolated chromaffin granules,”Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 114, 355.
Creutz, C. E., Pazoles, C. J., and Pollard, H. B. (1978). Identification and purification of an adrenal medullary protein (synexin) that causes calcium-dependent aggregation of isolated chromaffin granules,”J. Biol. Chem. 253, 2858.
Creutz, C. E., Pazoles, C. J., and Pollard, H. B. (1979). “Self-association of synexin in the presence of calcium: correlation with synexin-induced membrane fusion and examination of the structure of synexin aggregates,”J. Biol. Chem. 254, 553.
Creutz, C. E., Dowling, L. G., Sando, J. J., Villar-Palasi, C., Whipple, J. H., and Zaks, W. J. (1983). “Characterization of the chromobindins: soluble proteins that bind to the chromaffin granule membrane in the presence of Ca2+,”J. Biol. Chem. 258, 14664.
Creutz, C. E., Zaks, W. J., Hamman, H. C., and Martin, W. H. (1987). “The roles of Ca2+-dependent membrane-binding proteins in the regulation and mechanism of exocytosis, inCell Fusion (Sowers, A. E., ed.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 45–68.
Crompton, M. R., Moss, S. E., and Crumpton, M. J. (1988). “Diversity in the Lipocortin/calpactin family,”Cell 55, 1.
Cullis, P. R., and Hope, M. J. (1978). “Effects of fusogenic agent on membrane structure of erythrocyte ghosts and the mechanism of membrane fusion,”Nature (London)271, 672.
Cullis, P. R., and de Kruijff, B. (1979). “Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 559, 399.
Cullis, P. R., and Verkleij, A. J. (1979). “Modulation of membrane structure by Ca2+ and dibucaine as detected by31P NMR,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552, 546.
Dahl, G., Ekerdt, R., and Gratzl, M. (1979). “Models for exocytotic membrane fusion,”Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 33, 349.
Das, S., and Rand, R. P. (1986). “Modification by diacylglycerol of the structure and interaction of various phospholipid bilayers,”Biochemistry,25, 2882.
Dewald, B., Bretz, U., and Baggiolini, M. (1982). “Release of gelatinase from a novel secretory compartment of human neutrophils,”J. Clin. Invest. 70, 518.
Drust, D. S., and Creutz, C. E. (1988). “Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium,”Nature (London)331, 88.
Dunn, L. A., and Holz, R. W. (1983). “Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells,”J. Biol. Chem. 248, 4989.
Düzgünes, N. (1985). “Membrane fusion,” inSubcellular Biochemistry, Vol. 11 (Roodyn, D. B., ed.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 195–286.
Düzgünes, N. (1988). “Cholesterol and membrane fusion,” inBiology of Cholesterol (Yeagle, P. L., ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 197–212.
Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1983). “Ionotropic effects on phospholipid membranes: calcium-magnesium specificity in binding, fluidity, and fusion,” inMembrane Fluidity in Biology, Vol. 2 (Aloia, R. C., ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 187–213.
Düzgünes, N., and Hoekstra, D. (1986). “Agglutination and fusion of glycolipid-phospholipid vesicles mediated by lectins and calcium ions,”Stud. Biophys. 111, 5.
Düzgünes, N., and Bentz, J. (1988). “Fluorescence assays for membrane fusion,” inSpectroscopic Membrane Probes,” Vol. 1 (Loew, L. M., ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 117–159.
Düzgünes, N., Hong, K., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1980). “Membrane fusion: the involvement of phospholipids, proteins, and calcium binding,” inCalcium-Binding Proteins: Structure and Function, (Siegel, F. L., Carafoli, E., Kretsinger, R. H., MacLennan, D. H. and Wasserman, R. H., eds), Elsevier/North-Holland, New York, pp. 17–22.
Düzgünes, N., Nir, S., Wilschut, J., Bentz, J., Newton, C., Portis, A. and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981a). “Calcium- and magnesium-induced fusion of mixed phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine vesicles: effect of ion binding,”J. Membr. Biol. 59, 115.
Düzgünes, N., Wilschut, J., Fraley, R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981b). “Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: role of head-group composition in calcium- and magnesium-induced fusion of mixed phospholipid vesicles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 642, 182.
Düzgünes, N., Paiement, J., Freeman, K. B., Lopez, N. G., Wilschut, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1984a). “Modulation of membrane fusion by ionotropic and thermotropic phase transitions,”Biochemistry 23, 3486.
Düzgünes, N., Hoekstra, D., Hong, K., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1984b). “Lectins facilitate calcium-induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles containing glycosphingolipids,”FEBS Lett. 173, 80.
Düzgünes, N., Wilschut, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1985a). “Control of membrane fusion by divalent cations, phospholipid head-groups, and proteins, inPhysical Methods on Biological Membranes and their Model Systems (Conti, F., Blumberg, W. E., DeGier, J. and Pocchiari, F., eds), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 193–218.
Düzgünes, N., Straubinger, R. M., Baldwin, P. A., Friend, D. S., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1985b). “Proton-induced fusion of oleic acid-phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes,”Biochemistry 24, 3091.
Düzgünes, N., Hong, K., Baldwin, P. A., Bentz, J., Nir, S., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1987a). “Fusion of phospholipid vesicles induced by divalent cations and protons. Modulation by phase transitions, free fatty acids, monovalent cations, and polyamines,” inCell Fusion (Sowers, A. E., ed.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 241–267.
Düzgünes, N., Allen, T. M., Fedor, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1987b). “Lipid mixing during membrane aggregation and fusion. Why fusion assays disagree,”Biochemistry 26, 8435.
Düzgünes, N., Allen, T. M., Fedor, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1988). “Why fusion assays disagree,” inMolecular Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion (Ohki, S., Doyle, D., Flanagan, T., Hui, S. W., and Mayhew, E., eds), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 543–555.
Ekerdt, R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1982). “Intermembrane contact effects calcium binding to phospholipid vesicles,”Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2273.
Ekerdt, R., Dahl, G., and Gratzl, M. (1981). “Membrane fusion of secretory vesicles and liposomes. Two different types of fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 646, 10.
Ellens, H., Bentz, J., and Szoka, F. C. (1985). “H+-and Ca2+-induced fusion and destabilization of liposomes,”Biochemistry 24, 3099.
Ellens, H., Bentz, J., and Szoka, F. C. (1986a). “Destabilization of phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes at the hexagonal phase transition temperature,”Biochemistry 25, 285.
Ellens, H., Bentz, J., and Szoka, F. C. (1986b). “Fusion of phosphatidylethanolamine-containing liposomes and the mechanism of the Lα-HII phase transition,”Biochemistry 25, 4141.
Ellens, H., Siegel, D. P., Alford, D., Yeagle, P. L., Boni, L., Lis, L. J., Quinn, P. J., and Bentz, J. (1989). “Membrane fusion and inverted phases,”Biochemistry 28, 3692.
Ernst, J. D., Meers, P., Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., Papahadjopoulos, D., and Goldstein, I. M. (1986). “Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes contain synexin, a calcium-binding protein that mediates membrane fusion,”Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 49, 58.
Feigenson, G. W. (1986). “On the nature of calcium ion binding between phosphatidylserine lamellae,”Biochemistry 25, 5819.
Fraley, R., Wilschut, J., Düzgünes, N., Smith, C., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1980). “Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: the role of phosphate in promoting calcium-induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles,”Biochemistry 19, 6021.
Geisow, M. J. (1986). “Common domain structure of Ca2+ and lipid-binding proteinsFEBS Lett. 203, 99.
Geisow, M. J., Walker, J. H., Boustead, C., and Taylor, W. (1987).Biosci. Rep. 7, 289.
Gratzl, M., Schudt, C., Ekerdt, R., and Dahl, G. (1980). “Fusion of isolated biological membranes: a tool to investigate basic processes of exocytosis and cell-cell fusion,” inMembrane Structure and Function, Vol. 3 (Bittar, E. E., ed.), Wiley, New York, pp. 59–92.
Gruner, S. M., Cullis, P. R., Hope, M. J., and Tilcock, C. P. S. (1985). “Lipid polymorphism. The molecular basis of nonbilayer phases,”Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 14, 211.
Gruner, S. M., Tate, M. W., Kirk, G. L., So, P. T. C., Turner, D. C., Keane, D. T., Tilcock, C. P. S., and Cullis, P. R. (1988). “X-ray diffraction study of the polymorphic behavior of N-methylated dioleylphosphatidy ethanolamine,”Biochemistry 27, 2853.
Hauser, H., Pascher, I., Pearson, R. H., and Sundell, S. (1981). “Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 650, 21.
Helm, C. A., Israelachvilli, J. N., and McGuiggan, P. M. (1989). “Molecular mechanisms and forces involved in adhesion and fusion of bilayers,”Science 246, 919.
Hoekstra, D. and Düzgünes, N. (1986). “Ricinus communis agglutinin-mediated agglutination and fusion of glycolipid-containing phospholipid vesicles. Effect of carbohydrate head-group size, calcium ions, and spermine,”Biochemistry 25, 1321.
Hoekstra, D., and Wilschut, J. (1989). “Membrane fusion of artificial and biological membranes: Role of local membrane dehydration,” inWater Transport in Biological Membranes, Vol. 1 (Benga, G., ed.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 143–176.
Hoekstra, D., de Boer, T., Klappe, K., and Wilschut, J. (1984). “Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes,”Biochemistry 23, 5675.
Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981). “Role of synexin in membrane fusion,”J. Biol. Chem. 256, 3651.
Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1982a). “Modulation of membrane fusion by calcium-binding proteins,”Biophys. J. 37, 296.
Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., Ekerdt, R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1982b). “Synexin facilitates fusion of specific phospholipid vesicles at divalent cation concentrations found intracellularly,”Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 4942.
Hong, K., Schuber, F., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1983). “Polyamines. Biological modulators of membrane fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 732, 469.
Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., Meers, P. R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1987). “Protein modulation of liposome fusion,” inCell Fusion (Sowers, A. E., ed.), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 269–284.
Hope, M. J., Walker, D. C., and Cullis, P. R. (1983). “Calcium and pH-induced fusion of small unilamellar vesicles consisting of phosphatidylethanolamine and negatively charged phospholipids: a freeze-fracture study,”Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 110, 15.
Horn, R. G. (1984). “Direct measurement of the forces between two lipid bilayers and observation of their fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 778, 224.
Hui, S. W., Stewart, T. P., Boni, L. T., and Yeagle, P. L. (1981). “Membrane fusion through point defects in bilayers,”Science 212, 921.
Hui, S. S., Nir, S., Stewart, T. P., Boni, L. T., and Huang, S. K. (1988). “Kinetic measurements of fusion of phosphatidylserine-containing vesicles by electron microscopy and fluorometry,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 941, 130.
Jendrasiak, G. L., and Hasty, J. H. (1974). “The hydration of phospholipids,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 337, 79–91.
Kachar, B., Fuller, N., and Rand, P. R. (1986). “Morphological responses to calcium-induced interaction of phosphatidylserine-containing vesicles,”Biophys. J. 50, 779.
Klee, C. B. (1988). “Ca2+-Dependent phospholipid- (and membrane-) binding proteins,”Biochemistry 27, 6645.
Leikin, S. L., Kozlov, M. M., Chernomordik, L. V., Markin, V. S., and Chizmadzhev, Y. A. (1987). “Membrane fusion: overcoming the hydration barrier and local restructuring,”J. Theor. Biol. 129, 411.
Luzzati, V., and Tardieu, A. (1974). “Lipid phases: structure and structural transitions,”Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 25, 79.
MacDonald, R. I. (1985). “Membrane fusion due to dehydration by polyethylene glycol, dextran, or sucrose,”Biochemistry 24, 4058–4066.
MacDonald, R. I., and MacDonald, R. C. (1983). “Lipid mixing during freeze-thawing of liposome membranes as monitored by fluorescence energy transfer,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 735, 243.
Markin, V. S., Kozlov, M. M., and Borovjagin, V. L. (1984). “On the theory of membrane fusion. The stalk mechanism,”Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 5, 361.
Marra, J., and Israelachvili, J. (1985). “Direct measurements of forces between phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers in aqueous electrolyte solutions,”Biochemistry 24, 4608.
McIntosh, T. J., Magid, A. D. and Simon, S. A. (1987). “Steric repulsion between phosphatidylcholine bilayers,”Biochemistry 26, 7325.
Meers, P., Hong, K., Bentz, J., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1986). “Spermine as a modulator of membrane fusion: interactions with acidic phospholipids,”Biochemistry 25, 3109.
Meers, P., Ernst, J. D., Düzgünes, N., Hong, K., Fedor, J., Goldstein, I. M., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1987a). “Synexin-like proteins from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Identification and characterization of granule-aggregating and membrane-fusing activities,”J. Biol. Chem. 262, 7850.
Meers, P., Hong K., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1987b). “Studies on the binding of synexin to phospholipid vesicles,” inProceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Calcium Binding Proteins in Health and Disease (Norman, A. W., Vanaman, T. C., and Means, A. R., eds), Academic Press, Orlando, Florida, pp. 338–390.
Meers, P., Bentz, J., Alford, D., Nir, S., Papahadjopoulos, D., and Hong, K. (1988a). “Synexin enhances the aggregation rate but not the fusion rate of liposomes,”Biochemistry 27, 4430.
Meers, P., Hong, K., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1988b). “Free fatty acid enhancement of cation-induced fusion of liposomes: synergism with synexin and other promoters of vesicle aggregation,”Biochemistry 27, 6784.
Michell, R. H. (1975). “Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 415, 81.
Michell, R. H., Kirk, C. J., Jones, L. M., Downes, C. P., and Creba, J. A. (1981). “The stimulation action of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions,”Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B. 296, 123.
Miller, D. C., and Dahl, G. P. (1982). “Early events in calcium-induced liposome fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 689, 165.
Morris, S. J., Hughes, J. M. X., and Whittaker, V. P. (1982). “Purification and mode of action of synexin: a protein enhancing calcium-induced membrane aggregation,”J. Neurochem. 39, 529.
Nir, S. (1984). “A model for cation adsorption in closed systems: application to calcium binding to phospholipid vesicles,”J. Colloid Interface Sci. 102, 313.
Nir, S., Bentz, J., and Portis, A. R., Jr. (1980a). “Effect of cation concentrations and temperature on the rates of aggregation of acidic phospholipid vesicles. Application to fusion,”Adv. Chem. Ser. 188, 75.
Nir, S., Bentz, J., and Wilschut, J. (1980b). “Mass action kinetics of phosphatidylserine vesicle fusion as monitored by coalescence of internal vesicle volumes,”Biochemistry 19, 6030.
Nir, S., Bentz, J., and Düzgünes, N. (1981). “Two modes of reversible vesicle aggregation: particle size and the DLVO theory,”J. Colloid Interface Sci. 84, 266.
Nir, S., Wilschut, J., and Bentz, J. (1982). “The rate of fusion of phospholipid vesicles and the role of bilayer curvature.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 688, 275.
Nir, S., Bentz, J., Wilschut, J., and Düzgünes, N. (1983a). “Aggregation and fusion of phospholipid vesicles,”Prog. Surf. Sci. 13, 1.
Nir, S., Düzgünes, N., and Bentz, J. (1983b). “Binding of monovalent cations to phosphatidylserine and modulation of Ca2+-and Mg2+-induced vesicle fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 735, 160.
Nir, S., Stutzin, A., and Pollard, H. B. (1987). “Effect of synexin on aggregation and fusion of chromaffin granule ghosts at pH 6,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 903, 309.
Ohki, S. (1982). “A mechanism of divalent ion-induced phosphatidylserine membrane fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 689, 1.
Ohki, S. (1984). “Effects of divalent cations, temperature, osmotic pressure gradient, and vesicle curvature on phosphatidylserine vesicle fusion,”J. Membr. Biol. 77, 265.
Ohki, S., and Düzgünes, N. (1979). “Divalent cation-induced interaction of phospholipid vesicle and monolayer membranes,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552, 438.
Ohki, S., and Ohshima, H. (1984). “Divalent cation-induced surface tension increase in acidic phospholipid membranes. Ion binding and membrane fusion,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 776, 177.
Ohki, S., Düzgünes, N., and Leonards, K. (1982). “Phospholipid vesicle aggregation: Effect of monovalent and divalent ions,”Biochemistry,21, 2127.
Ohnishi, S.-I. (1988). “Fusion of viral envelopes with cellular membranes,” inMembrane Fusion in Fertilization, Cellular Transport, and Viral Infection (Düzgünes, N., and Bronner, F., eds.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 257–296.
Papahadjopoulos, D., and Bangham, A. D. (1966). “Biophysical properties of phospholipids. II. Permeability of phosphatidylserine liquid crystals to univalent ions,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 126, 185.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Poste, G., Schaeffer, B. E., and Vail, W. J. (1974). “Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles.”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 352, 10.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Vail, W. J., Pangborn, W. A., and Poste, G. (1976). “Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium and other divalent metals,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 448, 265.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Vail, W. J., Newton, C., Nir, S., Jacobson, K., Poste, G., and Lazo, R. (1977). “Studies on membrane fusion. III. The role of calcium-induced phase changes,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 465, 579.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Poste, G., and Vail, W. J. (1979). “Studies on membrane fusion with natural and model membranes,”Methods Membr. Biol. 10, 1.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Meers, P. R., Hong, K., Ernst, J. D., Goldstein, I. M., and Düzgünes, N. (1988). “Calcium-induced membrane fusion: from liposomes to cellular membranes,” inMolecular Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion (Ohki, S., Doyle, D., Flanagan, T., Hui, S. W., and Mayhew, E., eds), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 1–16.
Parente, R. A., and Lentz, B. (1986). “Rate and extent of PEG-induced large vesicle fusion, monitored by bilayer and internal contents mixing,”Biochemistry 25, 6678.
Pohl, H. A. (1978).Dielectrophoresis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Pollard, H. B., and Scott, J. H. (1982). “Synhibin: a new calcium-dependent membrane-binding protein that inhibits synexin-induced chromaffin granule aggregation and fusion,”FEBS Lett. 150, 201.
Portis, A., Newton, C., Pangborn, W. and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1979). “Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: evidence for an intermembrane Ca2+-phospholipid complex, synergism with Mg2+ and inhibition by spectrin,”Biochemistry 18, 780.
Prestegard, J. H., and O'Brien, M. P. (1987). Membrane and vesicle fusion,”Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 38, 383.
Rand, R. P. (1981). “Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes,”Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 10, 277.
Rand, R. P., Kachar, B., and Reese, T. S. (1985). “Dynamic morphology of calcium-induced interactions between phosphatidylserine vesicles,”Biophys. J. 47, 483.
Rehfeld, S. J., Düzgünes, N., Newton, C., Papahadjopoulos, D., and Eatough, D. J. (1981). “The exothermic reaction of calcium with unilamellar phosphatidylserine vesicles: titration microcalorimetry,”FEBS Lett. 123, 249.
Rosenberg, J., Düzgünes, N., and Kayalar, C. (1983). “Comparison of two liposome fusion assays monitoring the intermixing of aqueous contents and of membrane components.”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 735, 173.
Rupert, L. A. M., van Breemen, J. F. L., van Bruggen, E. F. J., Engberts, J. B. F. N. and Hoekstra, D. (1987). “Calcium-induced fusion of didodecylphosphate vesicles: the lamellar to hexagonal II (HH) phase transition,”J. Membr. Biol. 95, 255.
Schuber, F., Hong, K., Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1983). “Polyamines as modulators of membrane fusion: aggregation and fusion of liposomes,”Biochemistry 22, 6134.
Shavnin, S. A., Pedroso de Lima, M. C., Fedor, J., Wood, P., Bentz, J., and Düzgünes, N. (1988). “Cholesterol affects divalent cation-induced fusion and isothermal phase transitions of phospholipid membranes,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 946, 405.
Siegel, D. P. (1984). “Inverted micellar structures in bilayer membranes: Formation rates and half-lives,”Biophys. J. 45, 399.
Siegel, D. P., Ellens, H., and Bentz, J. (1988). “Membrane fusion via intermediates in Lx/HH phase transitions,” inMolecular Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion (Ohki, S., Doyle, D., Flanagan, T., Hui, S. W., and Mayhew, E., eds), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 53–71.
Siegel, D. P., Banschbach, J., Alford, D., Ellens, H., Lis, L. J., Quinn, P. J., Yeagle, P. L., and Bentz, J. (1989). “Physiological levels of diacylglycerols in phospholipid membranes induce membrane fusion and stabilize inverted phases,”Biochemistry 28, 3703.
Stenson, W. F., and Parker, C. W. (1979). “Metabolism of arachidonic acid in ionophorestimulated neutrophils,”J. Clin. Invest. 64, 1457.
Stollery, J. G., and Vail, W. J. (1977). “Interaction of divalent cations or basic proteins with phosphatidylethanolamine vesicles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 471, 372.
Struck, D. K., Hoekstra, D., and Pagano, R. E. (1981). “Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion,”Biochemistry 20, 4093.
Südhof, T. C., Walker, J. H., and Obrocki, J. (1982). “Calelectrin self-aggregates and promotes membrane aggregation in the presence of calcium,”EMBO J. 1, 1167.
Südhof, T. C., Ebbecke, M., Walker, J. H., Fritsche, U., and Boustead, C. (1984). “Isolation of mammalian calelectrins: a new class of ubiquitous Ca2+-regulated proteins,”Biochemistry 23, 1103.
Südhof, T. C., Slaughter, C. A., Leznicki, I., Barjon, P., and Reynolds, G. A. (1988). “Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins,”Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 664.
Sundler, R. (1984). “Role of phospholipid head group structure and polarity in the control of membrane fusion,”Biomembranes 12, 563.
Sundler, R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981). “Control of membrane fusion by phospholipid head groups. I. Phosphatidate/phosphatidylinositol specificity,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 649, 743.
Sundler, R., and Wijkander, J. (1983). “Protein-mediated intermembrane contact specifically enhances Ca2+-induced fusion of phosphatidate-containing membranes,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 730, 391.
Sundler, R., Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981). “Control of membrane fusion by phospholipid head groups. II. The role of phosphatidylethanolamine in mixtures with phosphatidate and phosphatidylinositol,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 649, 751.
Uster, P. S. and Deamer, D. W. (1981). “Fusion competence of phosphatidylserine-containing liposomes quantitatively measured by a fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay,”Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 209, 385.
Verkleij, A. J. (1984). “Lipidic intramembranous particles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 779, 43.
Verkleij, A. J., Mombers, C., Gerritsen, W. J., Leunissen-Bijvelt, L., and Cullis, P. R. (1979). “Fusion of phospholipid vesicles in association with the appearance of lipidic particles as visualized by freeze-fracturing,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 555, 358.
Verkleij, A. J., van Echteld, C. J. A., Gerritsen, W. J., Cullis, P. R., and de Kruijff, B. (1980). “The lipidic particle as an intermediate structure in membrane fusion processes and bilayer to hexagonal HII transitions,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600, 620.
Verkleij, A. J., Leunissen-Bijvelt, J., de Kruijff, B., Hope, M., and Cullis, P. R. (1984). “Non-bilayer structures in membrane fusion,” inCell Fusion, Ciba Foundation Symposium 103, Pitman Books, London, pp. 45–59.
Waite, M., DeChatelet, L. R., King, L., and Shirley, P. S. (1979). “Phagocytosis-induced release of arachidonic acid from human neutrophils,”Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 90, 984.
Walsh, C. E., Waite, B. M., Thomas, M. J., and DeChatelet, L. R. (1981). Release and metabolism of arachidonic acid in human neutrophils,J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7228.
Wilschut, J. (1988). “Membrane interactions and fusion,” inEnergetics of Secretion Responses, Vol. II (Akkerman, J. W. N., ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 63–80.
Wilschut, J., and Hoekstra, D. (1984). “Membrane fusion: from liposomes to biological membranes,”Trends Biochem. Sci. 9, 479.
Wilschut, J., Düzgünes, N., Fraley, R., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1980). “Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: kinetics of Ca2+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles followed by a new assay for mixing of aqueous vesicle contents,”Biochemistry 19, 6011.
Wilschut, J., Düzgünes, N., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1981). “Calcium/magnesium specificity in membrane fusion: kinetics of aggregation and fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles and the role of bilayer curvature,”Biochemistry 20, 3126.
Wilschut, J., Düzgünes, N., Hong, K., Hoekstra, D., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1983). “Retention of aqueous contents during divalent cation-induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 734, 309.
Wilschut, J., Nir, S., Scholma, J., and Hoekstra, D. (1985a). “Kinetics of Ca2+-induced fusion of cardiolipin-phosphatidylcholine vesicles: correlation between vesicle aggregation, bilayer destabilization, and fusion,”Biochemistry 24, 4630.
Wilschut, J., Scholma, J., Bental, M., Hoekstra, D., and Nir, S. (1985b). “Ca2+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles: mass action kinetic analysis of membrane lipid mixing and aqueous contents mixing,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 821, 45.
Wilschut, J., Düzgünes, N., Hoekstra, D., and Papahadjopoulos, D. (1985c). “Modulation of membrane fusion by membrane fluidity: temperature dependence of divalent cation-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles,”Biochemistry 24, 8.
Wilson, S. P., and Kirshner, N. (1983). “Calcium-evoked secretion from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal medullary chromaffin cells,”J. Biol. Chem. 258, 4994.
Zimmermann, U. (1982). “Electric field-mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena,”Biochim. Biophys. Acta 694, 227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papahadjopoulos, D., Nir, S. & Düzgünes, N. Molecular mechanisms of calcium-induced membrane fusion. J Bioenerg Biomembr 22, 157–179 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762944
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00762944