The Hospital Industry’s
10 Most Critical Metrics
Share this Post
The article does not include metrics such as Profits and Sales that are critical to companies in all industries; rather the focus is on metrics more specific to the Cloud Service Industry.
By tracking your metrics, you will dramatically improve your business results and be able to achieve the goals set forth in your business plan.
Why? Because not only is the old saying “If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it” true, but visibility into your metrics allows you to identify WHERE you can make the easiest and most impactful improvements.
For each metric, we will answer the following questions:
– What is the metric?
– What is the average value of this metric?
– Why is this metric important?
Let’s get started…
1. Average Length of Stay
What is this metric?
This metric tracks how long a patient stays at a hospital, from time admitted through discharge, and is tracked by quarter, month, weeks, days or even by hours. This metric may be used for the hospital as a whole or may segment out each diagnosis group within a facility.
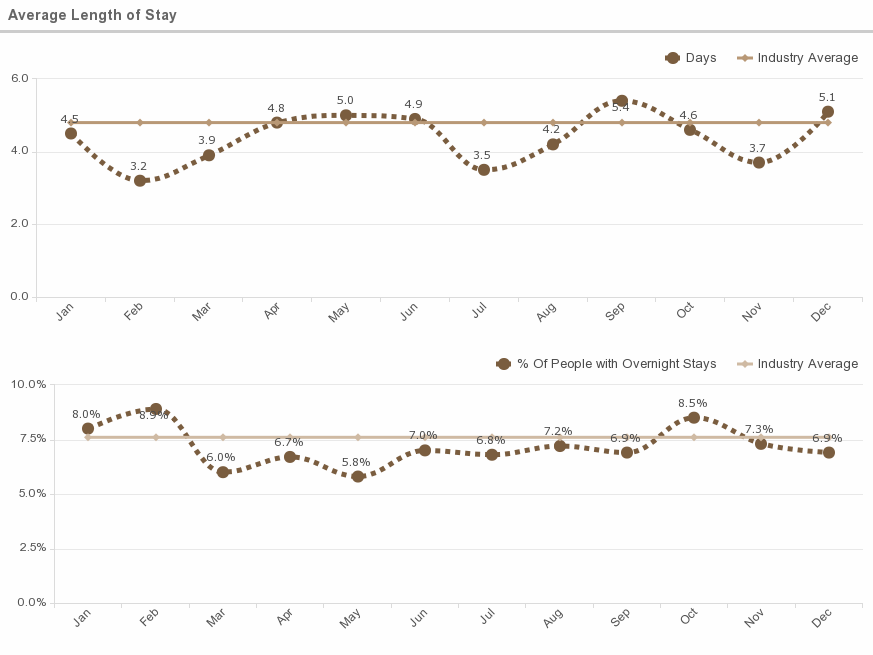
Average Availability: : According to the CDC, it is 4.8 days; Percent of people with overnight stays: 7.6%
Why is this metric important?
Average length of stay is important because it can provide a measure of efficiency within each hospital.
2. Time to service
What is this metric?
This metric measures the time it takes from when the patient arrives at the hospital to when the patient receive healthcare services, including the amount of time it takes to see either a nurse or a doctor. This metric may be measured specifically for the ER or other specific departments within the hospital.
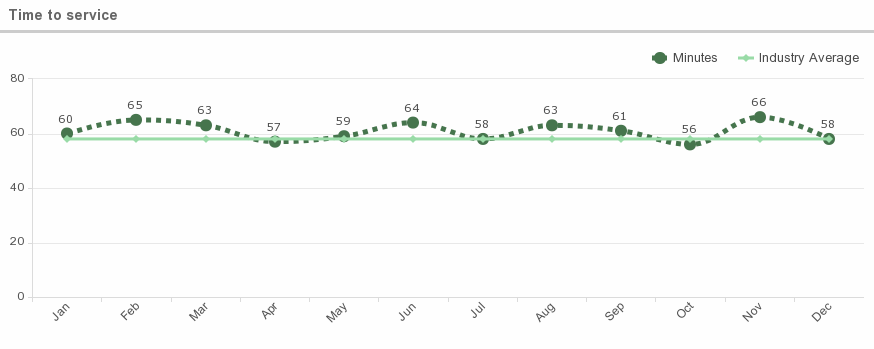
Average wait time in an ER/ED:
According to the CDC, it is 58 minutes. Longer wait times were associated with EDs in urban areas (62.4 minutes), compared with nonurban areas (40.0 minutes)
Why is this metric important?
Time to service is important because it provides useful information on a hospital’s ability to provide prompt services to its patients. This metric ties into patient satisfaction as shorter wait times lead to more satisfied patients.
3. Hospital Incidents
What is this metric?
This metric measures the ability of a hospital to provide quality care for its patients, without patients developing infections, developing bed sores, reacting to transfusions, postoperative respiratory failure, postoperative hemorrhages, postoperative sepsis, or postoperative pulmonary embolisms.
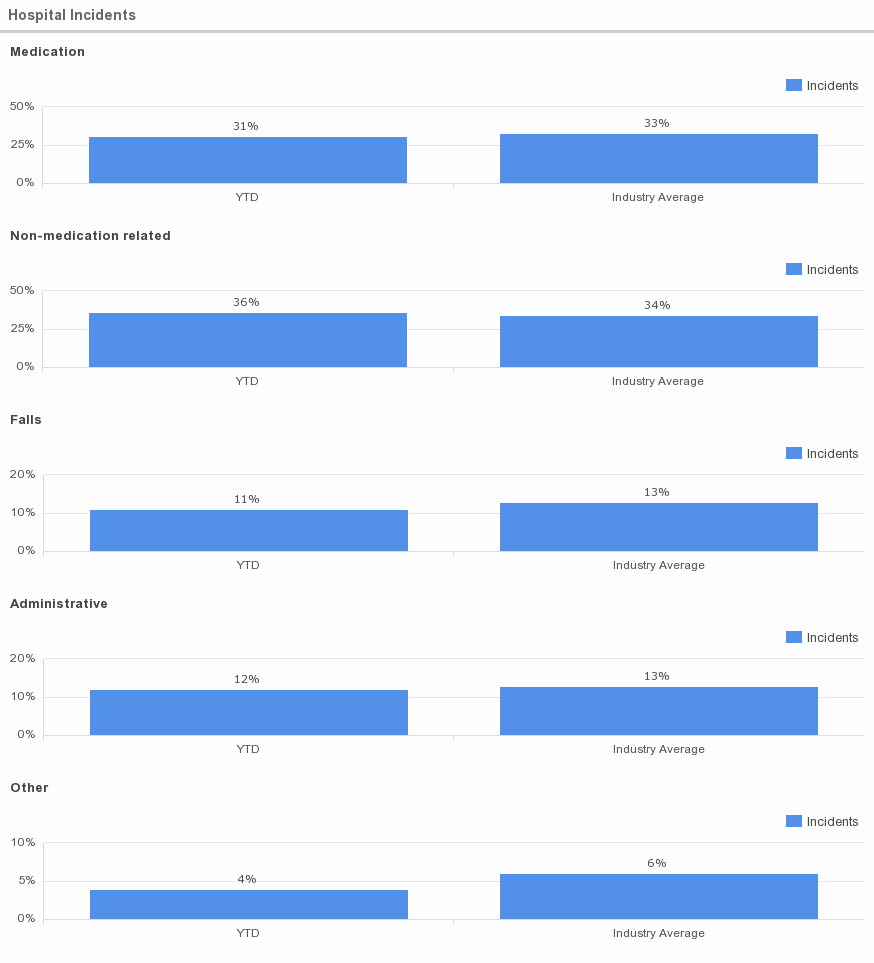
Average Value
Incident Reports, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality:
- Medication- 33%
- Non-medication related: 34%
- Falls: 13%
- Administrative: 13%
- Other 6%
Why is this metric important?
Tracking hospital incidents is important because it provides data on the quality of care patients are receiving via a specific hospital. This metric may provide information on what the hospital must do to improve its healthcare services.
4. Patient Satisfaction
What is this metric?
This metric measures the satisfaction level of a patient’s hospital stay and care provided. Patient satisfaction may specifically dive into questions regarding quality of physician care, quality of nursing care, cleanliness of hospital, and quality of hospital food.

Average Patient Satisfaction Rate:
3.25 stars.
Only 251 hospitals in the U.S. received a 5 out of 5 stars patient satisfaction rating. According to a Modern Healthcare review of the data, a total of 101 hospitals received the lowest ranking of one star; 582 received two stars; 1,414 received three stars; 1,205 received four stars; and 251 received the highest ranking of five stars.
Why is this metric important?
Patient satisfaction is important because it provides actionable data on how hospitals can improve their care and service as well as provides feedback to hospitals and their staff as to how they are doing well. If patient satisfaction is high, patients may recommend the hospital to family and friends. This metric may also have an impact on how hospitals market themselves.
5. Physician performance
What is this metric?
This metric measures performances of physicians, which may be determined by revenue per case, number of cases, and utilization cost per case.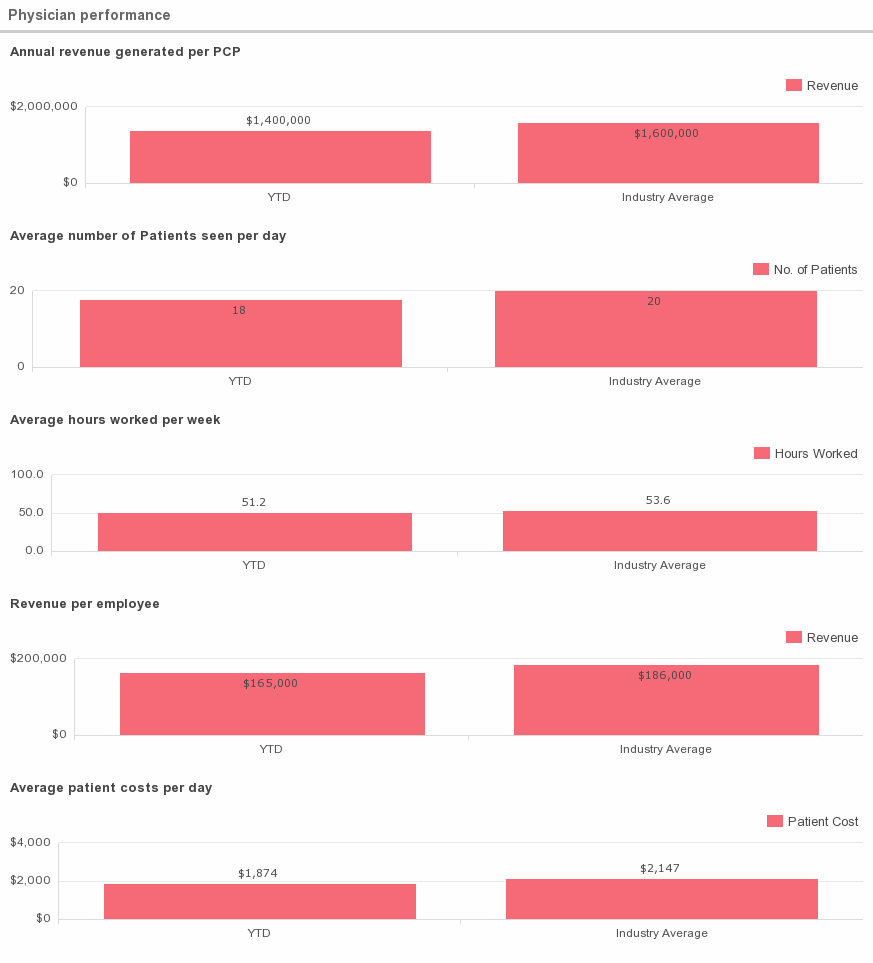
Average Value
Performance indicators, according to a study by Merrit Hawkins:
- Annual revenue generated per PCP: $1.6 m; per SCP= $1.4m
- Average number of Patients seen per day: 20
- Average hours worked per week: 53.6
- Revenue per employee: $186k
- Average patient costs per day: $2,147
Why is this metric important?
Physician performance is important because it details how a physician is performing and this metric impacts a hospital’s bottom line.
6. Patient readmission rate
What is this metric?
This metric provides data on the number of patients that must return to the hospital after a short period of being discharged.
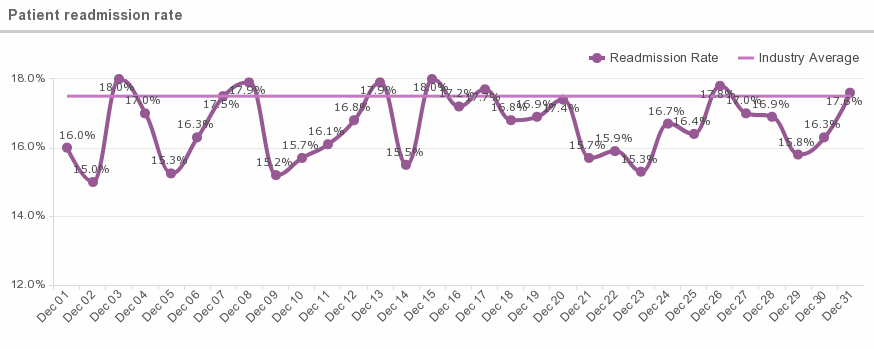
Average readmission rate
According to the US Department of Health and Human Services’ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), the 30-day hospital readmission rate is 17.5%.
Why is this metric important?
This metric is important because it provides information on the quality of care the hospital has provided to its patients. A lower readmission rate speaks to a higher quality of care. A high rate of readmission indicates a hospital may have been able to take additional steps during the first admission to prevent the readmission from occurring. In addition, hospitals that have high patient readmission rates may not receive full Medicare payments as a penalty for high readmissions.
7. Inpatient mortality rate
What is this metric?
This metric provides data on how many inpatients have died while in a hospital’s care prior to being discharged.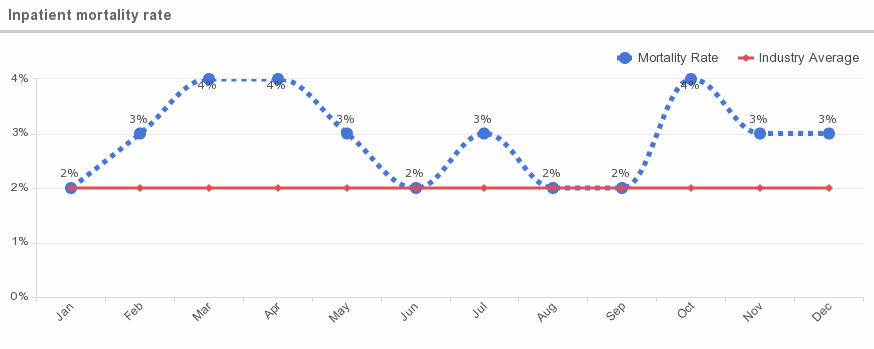
Mortality Rates:
According to the CDC, 2% of all hospitals patients die, equaling 715,000 total deaths annually. 25% of inpatient hospital deaths were for patients aged 85 and over. Below is an overview of mortality rates over the past ten years and by diagnosis.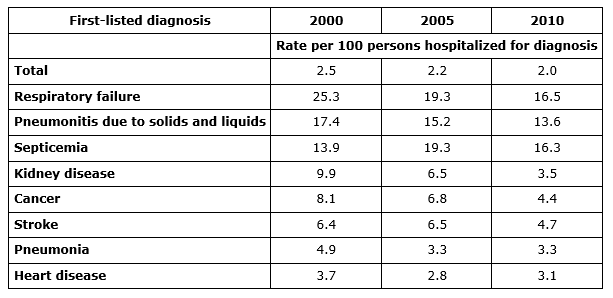
Why is this metric important?
Patient mortality rates are important because they indicate a hospital’s ability to stabilize patients following operations or procedures versus having a patient pass away while in the hospital’s care.
8. Operating Margin
What is this metric?
This metric provides data on the how much revenue a hospital has after operating costs are paid including wages, material and equipment purchases, rent, and marketing.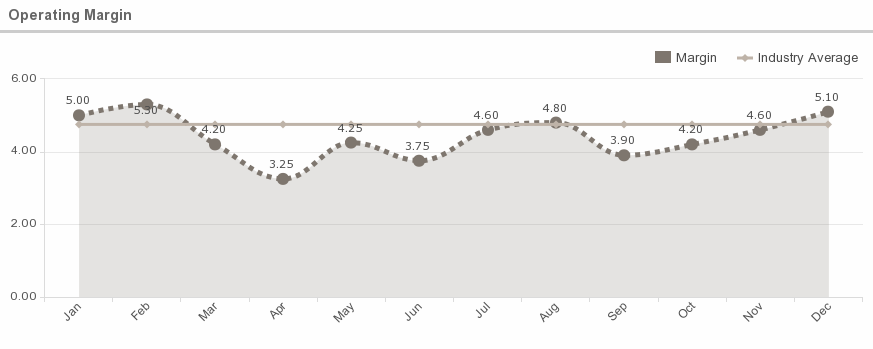
Average Operating Margin:
According to a recent Hospital Council Survey:
- The average hospital operating margin is 4.75 percent, up 137.5 percent YoY.
- Just over 30% of hospitals operate on a negative operating margin
Why is this metric important?
A strong operating margin is important to hospitals because they must be able to pay for fixed costs such as interest on debt. This metric also provides analysts with data on how much a hospital makes on each dollar of sales they bring in.
9. Bed Occupancy Rate
What is this metric?
This metric provides data on the number of beds in a hospital that are occupied.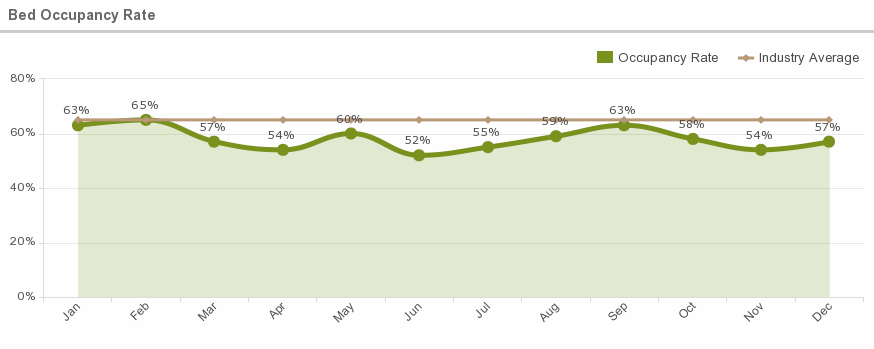
Average Occupancy Rate
Occupancy Rates, according to Becker Hospital Review
- 61% or 35.4 million people annually
- Number of beds available (per 1,000 people) 2.6 beds
- Occupancy rate for urban hospitals: 64 percent
- Occupancy rate for rural hospitals: 43 percent
Why is this metric important?
The hospital bed occupancy rate is used to measure hospital bed demand to assess the number of inpatients needing health care compared to the number of beds in a hospital. If a bed occupancy rate is too high, quality of care may decline.
10. Asset Utilization Rate
What is this metric?
This metric measures how often medical equipment is used within a hospital.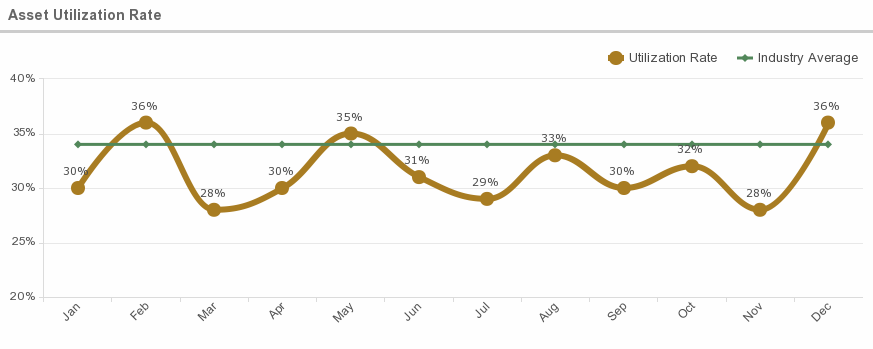
Average Asset Utilization Rate:
According to GE Healthcare, hospitals own 35,000 inventory SKUs and utilization hovers around 32-38%. Nationwide, hospitals are overspending billions each year — usually unknowingly— on mobile assets that are not utilized effectively. Nurses spent, on average, 21 minutes per shift looking for equipment- a loss of $500k in non-productive work time.
Why is this metric important?
The asset utilization rate is important because if a hospital’s medical equipment is being used frequently, the hospital is generating money from that equipment. However, a low utilization rate for medical equipment may lead to a drop in revenue.
Share this Post
