Markets
Four Maps Showing China’s Rising Dominance in Trade
We often use big, overarching ideas to help us understand the world and the opportunities contained within. These narratives, which can change over time, are used to create context. They give us a frame of reference for comprehending the news and events that affect our outlook on things.
China’s economic prowess is one of these new paradigms that has emerged, but many people still can’t really wrap their heads around the scale or scope of it.
It’s happened suddenly, and the ramifications are extremely relevant to our investments and understanding. Here’s four maps on China’s trade dominance that will help you think differently about the world:
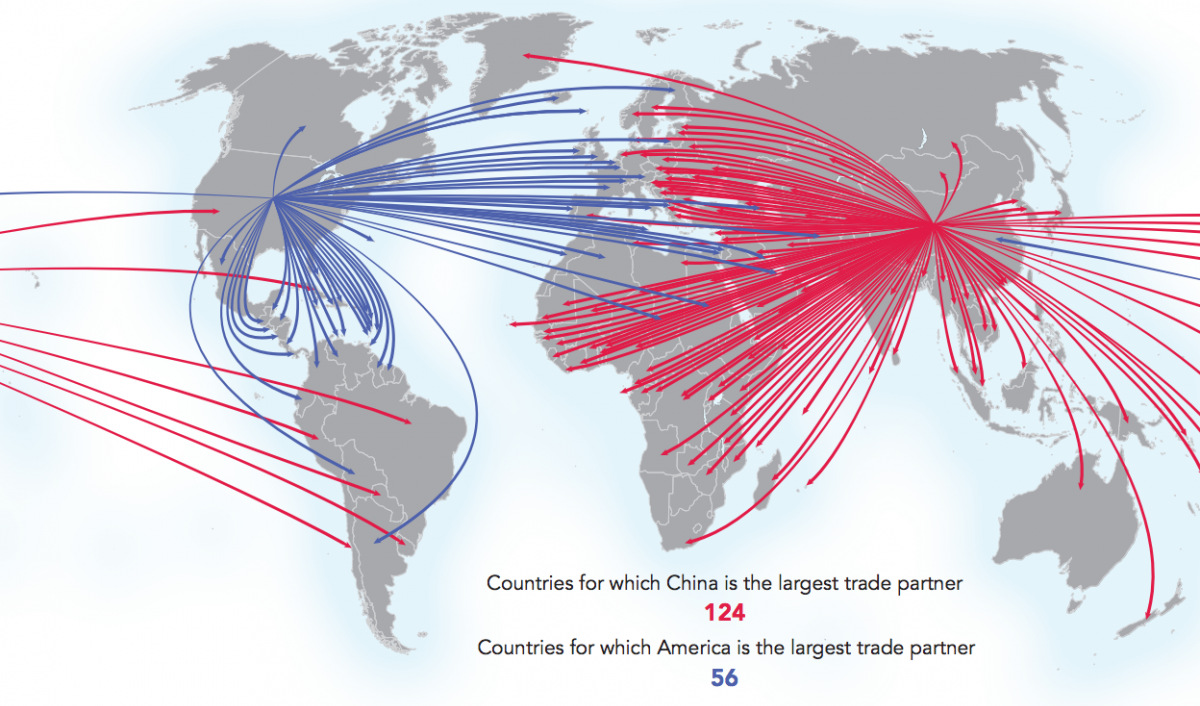
China is the world’s #1 trade partner
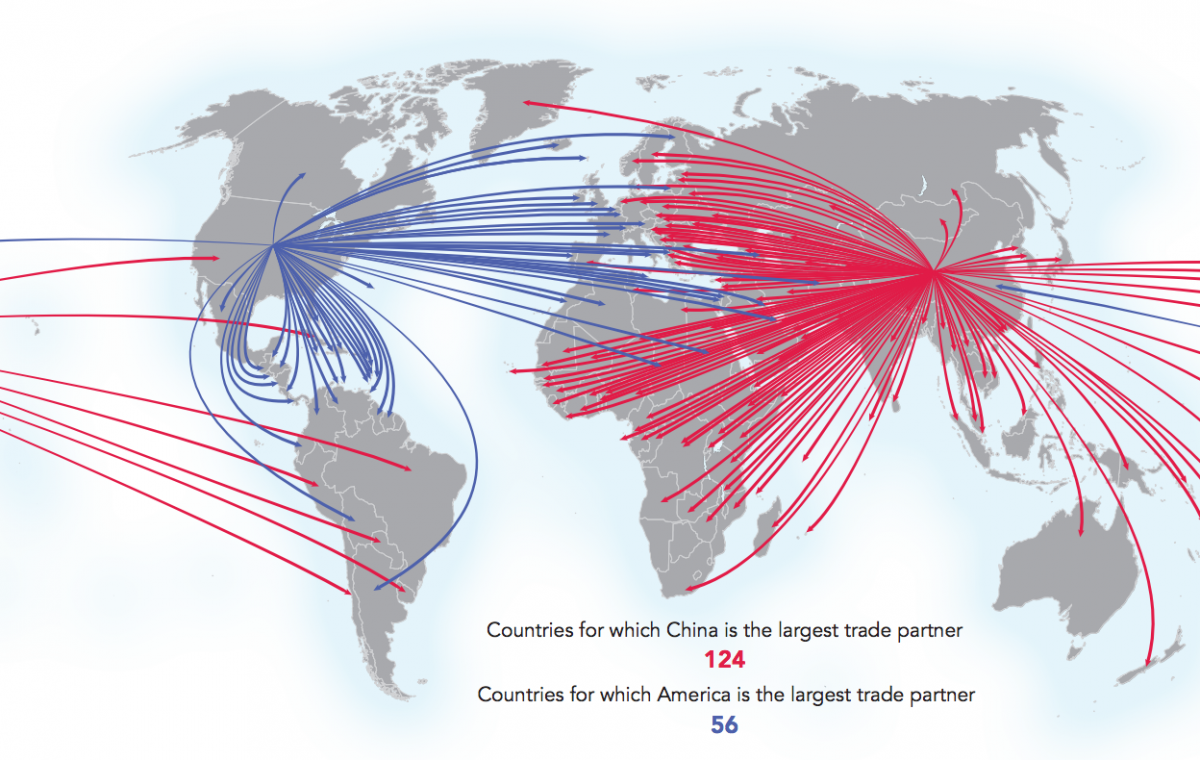
Image courtesy of: Connectography
The United States is the number one trading partner for 56 countries, with important relationships throughout North America, South America, and Western Europe.
Meanwhile, China is the top partner for 124 countries, dominating trade in Asia, Eastern Europe, Africa, and Australia.
China’s Sphere of Influence
This map shows the portion of trade conducted by each country with China in Southeast Asia.
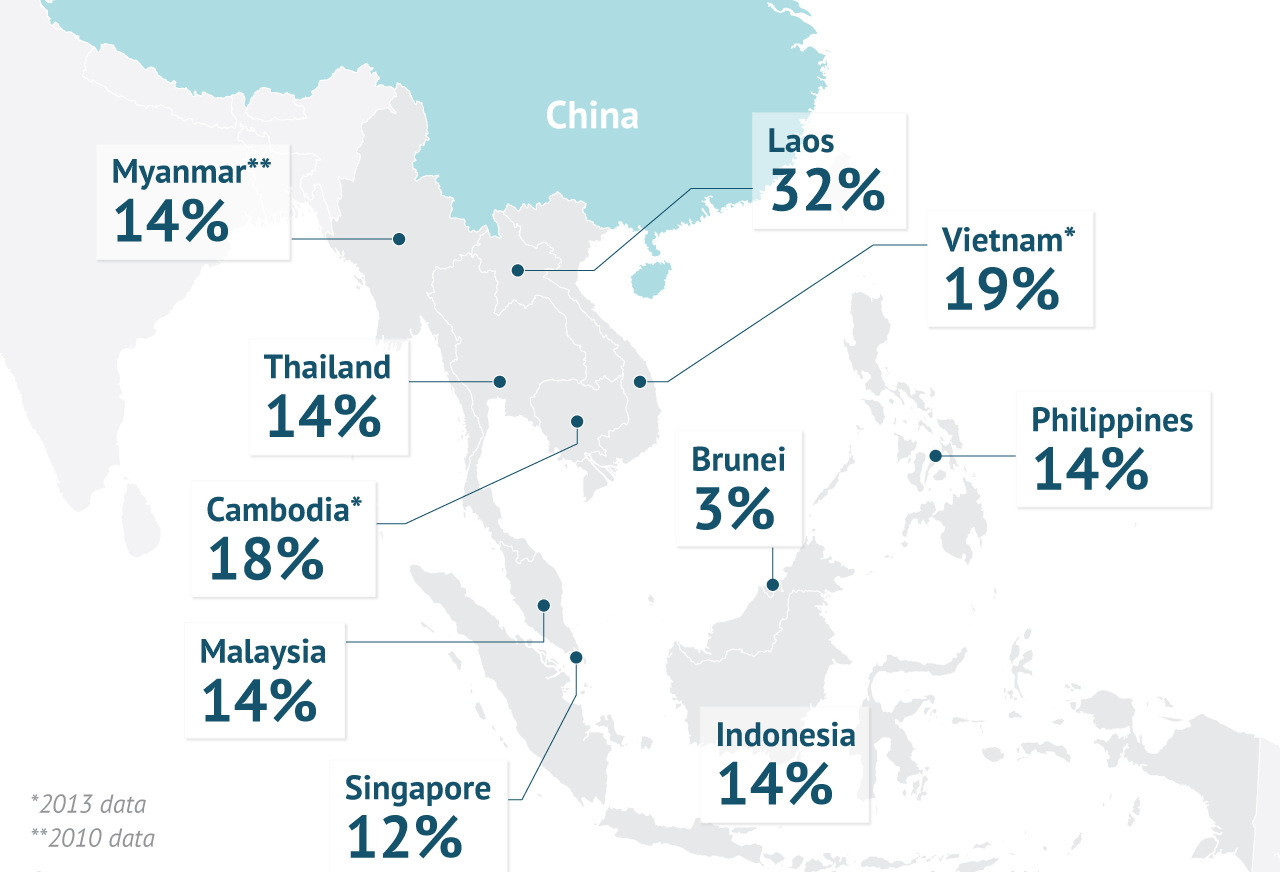
Image courtesy of: Stratfor
The influence that China has with nations in Southeast Asia is significant. Most trade is in double-digit percentages, and China views this as its immediate sphere of influence. Throughout history, territories in this region would even pay tribute to China to gain access to trade.
“In East Asia’s tribute system, China was the superior state, and many of its neighboring states were vassal states, and they maintained a relationship of tribute and rewards,” writes Liu Mingfu in The China Dream, a popular book about China’s plans to return to power.
Maintaining influence in Southeast Asia is part of the reason that Beijing is posturing in the South China Sea. In fact, China’s coastguard is growing so fast that in 10 years it will have more tonnage than all of the coastguards in Southeast Asia, the United States, and Japan combined.
Building a New Silk Road for Chinese Trade
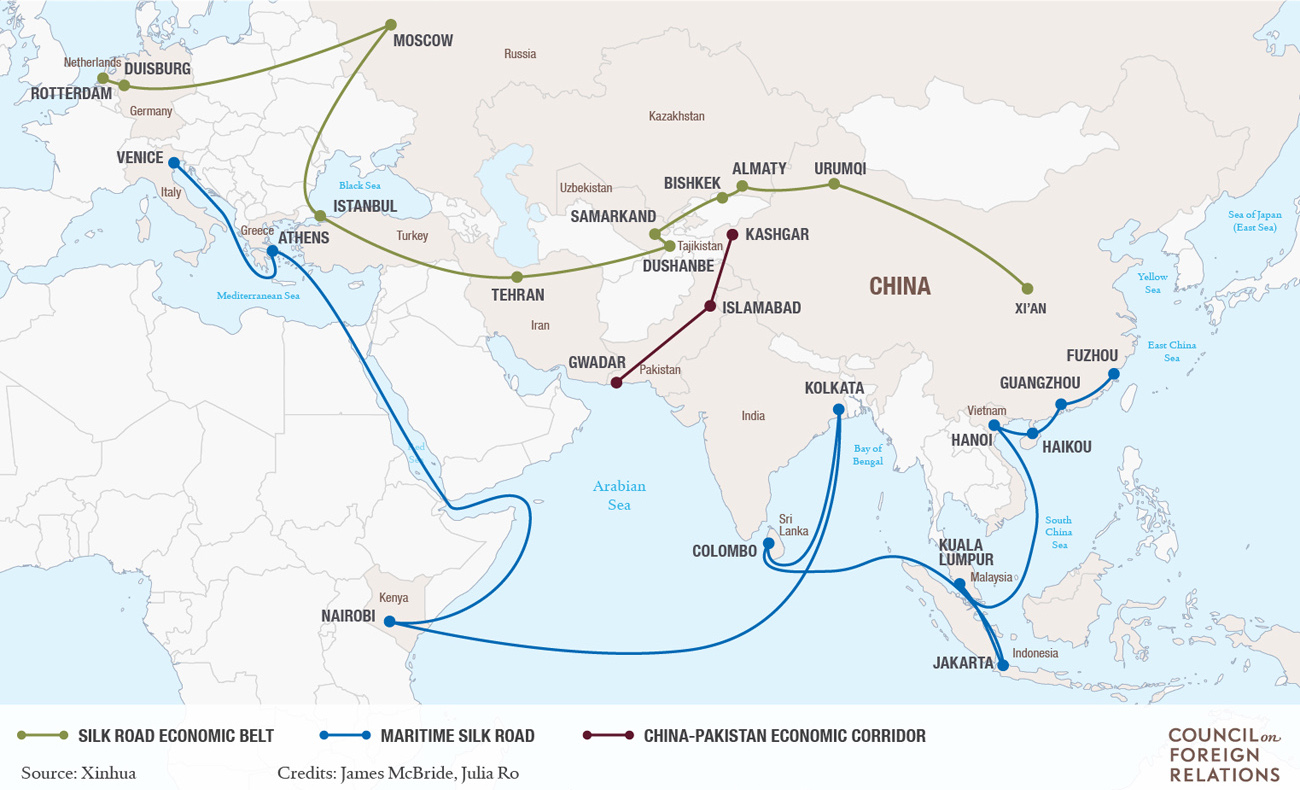
Image courtesy of: Council of Foreign Relations
China seeks to increase trade ties with Asia and Europe even further by building a new Silk Road that puts even Marco Polo’s route to shame.
The Chinese transcontinental network, a massive infrastructure project pegged for completion by 2025, is expected to bring down overland travel time from Beijing to London to just two days. Currently, it takes 15 days for the journey.
The project’s aim is to shorten the time of bulk consumer-goods transport to Europe, while unlocking the economic potential behind Eurasian cities from Almaty to Tehran. The new Silk Road will include at least one high-speed line that goes 320 km/h, and the network will help to link up 70% of the world’s population in roughly 40 countries.
Infrastructure Override
You may have heard of the AIIB (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank), which was officially launched at the end of last year. Initially proposed by China, the bank now has over a $100 billion of capitalization and 57 founding member states.
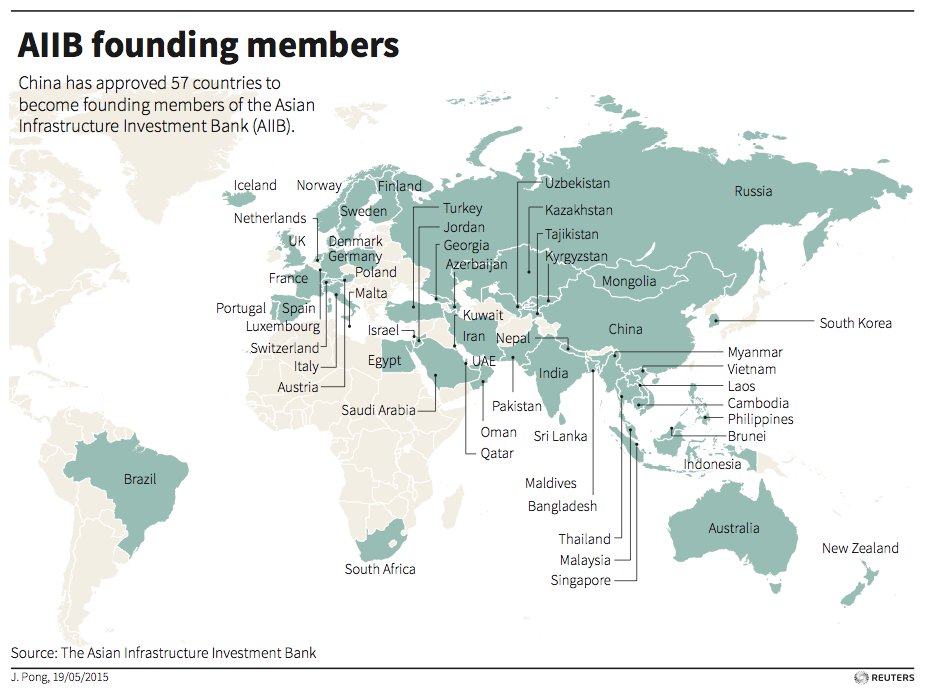
Image courtesy of: Reuters
While this shows China’s push for infrastructure especially to coincide with its new Silk Road, there is another very interesting detail: Beijing controls 26.06% of the votes, essentially giving it veto power as most bank decisions need 75% of the votes to pass.
In other words, only infrastructure projects that benefit Chinese trade will likely get the nod from Beijing.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries