Abstract
Aim
To date, few studies have analyzed the effects of exercise on cardiac adipose tissue. Overall, exercise programs did not meet the recommendations for significant weight loss, the utilization of resistance training was minimal, and the conclusions derived from these studies have diminished exercise as a strategy for cardiac fat loss.
Purpose
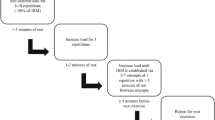
The objective of this pilot study was to analyze the effects of 3-week high-intensity, moderate-volume muscular endurance resistance training (RT) on cardiac fat and arterial stiffness.
Methods
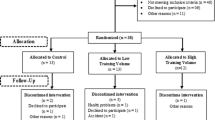
A total of 11 young females with obesity, BMI = 34.13 (± 3.16) kg/m2 (n = 5 control, n = 6 intervention) completed the study. Absolute strength was assessed using one repetition maximum test (1RM) for bench press (BP) and leg press (LP), and relative strength was calculated using body weight (BW) as BP-to-BW and LP-to-BW ratio. Magnetic resonance was used to quantify epicardial and paracardial adipose tissue (EAT and PAT) volume, and applanation tonometry was used to assess arterial stiffness by estimating pulse wave velocity (PWV).
Results
EAT and PAT volumes (ml) showed significant interaction effects (p = 0.037 and p = 0.031), and very large changes (d > 1) of EAT (p = 0.006) and PAT (p = 0.036) in the intervention group. In addition, strength was significantly improved, including BP (p = 0.003), LP (p = 0.001), BP-to-BW ratio (p = 0.001), and LP-to-BW ratio (p = 0.002), while no changes were found in PWV.
Conclusions
High-intensity, moderate-volume RT, designed to enhance muscular endurance following the recommendations reduces EAT and PAT volumes, improves physical fitness in females with obesity, and has no negative effects on arterial stiffness.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A-DBP:
-
Aortic diastolic blood pressure
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- A-SBP:
-
Aortic systolic blood pressure
- aVO2 :
-
Absolute oxygen consumption
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Bench press
- BP-to-BW:
-
Bench press to body weight
- BW:
-
Body weight
- CI:
-
Cardiac index
- EAT:
-
Epicardial adipose tissue
- FFM:
-
Fat free mass
- FM:
-
Fat mass
- HR max:
-
Maximal heart rate
- LBM:
-
Lean body mass
- LP:
-
Leg press
- LP-to-BW:
-
Leg press to body weight
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OMNI-RES:
-
OMNI-Resistance Exercise Scale
- PAT:
-
Paracardial adipose tissue
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- Q :
-
Cardiac output
- rVO2 :
-
Relative oxygen consumption
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- 1RM:
-
1 repetition maximum
- %BF:
-
Percentage of body fat
References
Alam MS, Green R, de Kemp R et al (2013) Epicardial adipose tissue thickness as a predictor of impaired microvascular function in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease. J Nucl Cardiol 20:804–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-013-9739-6
Bechle TR, Earle RWNS, CA (2008) Essentials of strength training and conditioning. Human Kinetics, USA
Bruce RA, Kusumi F, Hosmer D (1973) Maximal oxygen intake and nomographic assessment of functional aerobic impairment in cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J 85:546–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-8703(73)90502-4
Casey DP, Beck DT, Braith RW (2007) Progressive resistance training without volume increases does not alter arterial stiffness and aortic wave reflection. Exp Biol Med 232:1228–1235. https://doi.org/10.3181/0703-RM-65
Collier SR, Frechette V, Sandberg K et al (2011) Sex differences in resting hemodynamics and arterial stiffness following 4 weeks of resistance versus aerobic exercise training in individuals with pre-hypertension to stage 1 hypertension. Biol Sex Differ 2(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2042-6410-2-9
Cortez-Cooper M, Devan A, Anton M et al (2005) Effects of high intensity resistance training on arterial stiffness and wave reflection in women. Am J Hypertens 18:930–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.01.008
Croymans DM, Krell SL, Oh CS et al (2014) Effects of resistance training on central blood pressure in obese young men. J Hum Hypertens 28:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.81
DeVallance E, Fournier S, Lemaster K et al (2016) The effects of resistance exercise training on arterial stiffness in metabolic syndrome. Eur J Appl Physiol 116:899–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3348-4
Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM et al (2009) American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:459–471. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181949333
Fornieles González G, Ángel Rosety Rodríguez M, Antonia Rodríguez Pareja M et al (2014) A home-based treadmill training reduced epicardial and abdominal fat in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Hosp. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2014.30.3.7129
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR et al (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1334–1359. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb
Heil DP (2006) Predicting activity energy expenditure using the Actical activity monitor. Res Q Exerc Sport 77:64–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.2006.10599333
Hill JE, Fernandez-Del-Valle M, Hayden R, Mitra S (2017) An automated segmentation for direct assessment of adipose tissue distribution from thoracic and abdominal Dixon-technique MR images. In: Styner MA, Angelini ED (eds) International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 1013315
Ho et al (2012) J Clin Hypertens 14:848–854
Iacobellis G (2015) Local and systemic effects of the multifaceted epicardial adipose tissue depot. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 11(6):363–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.58
Iacobellis G (2016) Epicardial fat: a new cardiovascular therapeutic target. Curr Opin Pharmacol 27:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2016.01.004
Iacobellis G, Assael F, Ribaudo MC et al (2003) Epicardial fat from echocardiography: a new method for visceral adipose tissue prediction. Obes Res 11:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2003.45
Iozzo P (2011) Myocardial, perivascular, and epicardial fat. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 2):S371-9. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-s250
Jonker JT, de Mol P, de Vries ST et al (2013) Exercise and type 2 diabetes mellitus: changes in tissue-specific fat distribution and cardiac function. Radiology 269:434–442. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121631
Kawano H, Tanaka H, Miyachi M (2006) Resistance training and arterial compliance: keeping the benefits while minimizing the stiffening. J Hypertens 24:1753–1759. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hjh.0000242399.60838.14
Kim M-K, Tomita T, Kim M-J et al (2009) Aerobic exercise training reduces epicardial fat in obese men. J Appl Physiol 106:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.90756.2008
Mazurek T, Zhang L, Zalewski A et al (2003) Human epicardial adipose tissue is a source of inflammatory mediators. Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000099542.57313.C5
Miyachi M, Kawano H, Sugawara J et al (2004) Unfavorable effects of resistance training on central arterial compliance. Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000146380.08401.99
Naclerio F, Rodríguez-Romo G, Barriopedro-Moro MI et al (2011) Control of resistance training intensity by the OMNI perceived exertion scale. J Strength Cond Res 25:1879–1888. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181e501e9
Okamoto T, Masuhara M, Ikuta K (2009) Upper but not lower limb resistance training increases arterial stiffness in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 107:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1110-x
Pescatello LS (2014) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia
Rakobowchuk M, McGowan CL, de Groot PC et al (2005) Effect of whole body resistance training on arterial compliance in young men. Exp Physiol 90:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2004.029504
Ralston GW, Kilgore L, Wyatt FB, Baker JS (2017) The effect of weekly set volume on strength gain: a meta-analysis. Sports Med 47:2585–2601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-017-0762-7
Ratamess N, Alvar BA, Evetoch TK et al (2009) Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med Sci Sport Exerc 41:687–708. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181915670
Rognmo Ø, Moholdt T, Bakken H et al (2012) Cardiovascular risk of high- versus moderate-intensity aerobic exercise in coronary heart disease patients clinical perspective. Circulation 126:1436–1440. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.123117
Rosety MA, Pery MT, Rodriguez-Pareja MA et al (2015) A short-term circuit resistance program reduced epicardial fat in obese aged women. Nutr Hosp 32:2193–2197. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2015.32.5.9696
Schulz KF, Altman DGMD, CONSORT Group (2010) Consort 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMC Med 8
Sicari R, Sironi AM, Petz R et al (2011) Pericardial rather than epicardial fat is a cardiometabolic risk marker: an MRI vs echo study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24:1156–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2011.06.013
Srikanthan P, Horwich TB, Tseng CH (2016) Relation of muscle mass and fat mass to cardiovascular disease mortality. Am J Cardiol 117:1355–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.01.033
Swain DP, Franklin BA (2006) Comparison of cardioprotective benefits of vigorous versus moderate intensity aerobic exercise. Am J Cardiol 97:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.07.130
Wilund KR, Tomayko EJ, Wu P-T et al (2010) Intradialytic exercise training reduces oxidative stress and epicardial fat: a pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transpl 25:2695–2701. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq106
Wisløff U, Støylen A, Loennechen JP et al (2007) Superior cardiovascular effect of aerobic interval training versus moderate continuous training in heart failure patients. Circulation 115:3086–3094. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.675041
Acknowledgements
This study was partially funded by the Office of the Vicepresident for Research Seed Funds Program Texas Tech University. This project registered at http://www.clinicaltrial.gov (NCT02589327). The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose. The results of this study are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: MF, EL. Acquisition of data: MF, JG, SK, JK, SM. Analysis and interpretation of data: MF, EL, JG. Drafting of the manuscript: MF, SK. Critical revision: MF, EL, JG, JK, SM. Statistical Analysis: MF, EL. Technical and material support: SK, JG, JK. Study supervision: MF, SK, SM. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Pagani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandez-del-Valle, M., Gonzales, J.U., Kloiber, S. et al. Effects of resistance training on MRI-derived epicardial fat volume and arterial stiffness in women with obesity: a randomized pilot study. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 1231–1240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3852-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3852-9