Abstract.
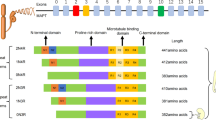
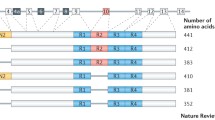
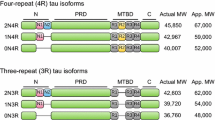
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein predominantly expressed in nerve cells that promote microtubule assembly and microtubule stabilization. Tau is a cytosolic protein mainly present in axons and involved in anterograde axonal transport. In several neurodegenerative diseases, as for example Alzheimer’s disease, tau metabolism is altered. Thus, alterations in the amount of the tau protein, missense mutations, posttranscriptional modifications like phosphorylation, aberrant tau aggregation or a different expression of some of its isoforms could provoke pathological effects resulting in the appearance of neuronal disorders known as tauopathies. The purpose of this work is to review the possible mechanisms for tau alterations that could lead to the onset of tau pathology. First we will focus on tau turnover, then on tau phosphorylation and, finally, on tau aggregation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, F., Avila, J. Tauopathies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 2219–2233 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7220-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7220-x