Abstract
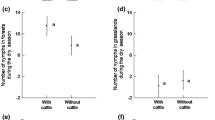
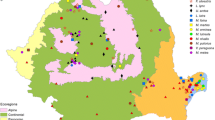
Twenty-four adult ixodid tick species, infesting livestock and some wildlife hosts along the Blue and White Nile in the Sudan, were identified. Three species,Boophilus geigyi, Rhipicephalus camicasi andR. bergeoni, were recorded for the first time from the Sudan. Tick numbers on indigenous breeds of cattle (Bos indicus) were relatively low, ranging between 17.1 and 40.5 per animal. Young cattle grazing with the herd carried significantly fewer ticks than older animals. With the exception ofB. annulatus andR. simus, which have extended their distribution further north into Blue Nile, Gezira and Khartoum Provinces, the distribution patterns of the most important cattle ticks have been relatively unchanged over the past 30 years.
TheRhicicephalus sanguineus group was represented by six species.R. camicasi was the only species present on cattle, sheep and goats in the north in Kassala and Khartoum Provinces, whereas this species occurred sympatrically withR. guilhoni andR. turanicus further south in Gezira and Blue Nile Provinces. In the Southern Region of the Sudan onlyR. turanicus andR. guilhoni were present, the latter being by far the predominant species, with peak activity towards the end of the rains in the Jonglei Canal Area.R. bergeoni was collected once, from cattle near the Ethiopian border in Blue Nile Province, whereasR. sanguineus sensu stricto was collected throughout the study area, from domestic dogs only. Finally,R. sulcatus was found once on a hare.
The distributions of the common tick species are correlated with the occurrence of tick-borne diseases of domestic animals and recommendations for the control of tick-borne diseases and their vectors in the Sudan are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon., 1983. Development Studies in the Jonglei Canal Area. Final Report, Vols. 1–9. Mefit-Babtie Shaw and Morton, Glasgow, 1374 pp.
Hoogstraal, H., 1956. African Ixodidae. 1. Ticks of the Sudan with special reference to Equatoria Province and with preliminary reviews of the generaBoophilus Margaropus andHyalomma. Department of the Navy, Bureau of Medical Surgery, Washington, DC, 1101 pp.
Jongejan, F., Morzaria, S.P., Mustafa, U.E.H., and Latif, A.A., 1983. Infection rates ofTheileria annulata in the salivary glands of the tickHyalomma marginatum rufipes. Veterinary Parasitol., 13: 121–126.
Jongejan, F., Morzaria, S.P., Shariff, O.A. and Abdalla H.M., 1984. Isolation and transmission ofCowdria ruminantium in Blue Nile Province. Sudan. Vet. Res. Commun., 8: 141–145.
Karrar, G., 1960. Rickettsial infection (heartwater) in sheep and goats in the Sudan. Br. Vet. J., 116: 105–114.
Karrar, G., 1968. Ovine rickettsiosis in the Sudan. Bull. Epiz. Dis. Afr., 70: 325–327.
Karrar, G., Kaiser, M.N. and Hoogstraal, H., 1963. Ecology and host-relationships of ticks infesting domestic animals in Kassala Province, Sudan, with special reference toAmblyomma lepidum. Bull. Entomol. Res., 54: 509–522.
Latif, A.A., 1984. Resistance toHyalomma anatolicum anatolicum andRhipicephalus evertsi by cattle in the Sudan. Insect Sci. Applic., 5: 509.
MacLeod, J. and Mwanaumo, B., 1978. Ecological studies of Ixodid ticks in Zambia. IV. Some anomalous infestation patterns in the northern and eastern regions. Bull. Entomol. Res., 68: 409–429.
Matthysse, G. and Colbo (in press). The ixodid ticks of Uganda. Misc. Publ. Entomol. Soc. Am.
Morzaria, S.P., 1983. Studies on important tick-borne diseases of cattle in the Sudan. FAO, Rome, Technical Report no. 2, AG/GCP/SUD/024/DEN, 52 pp.
Morzaria, S.P., Mustafa, U.E.H., Shawgi, M.H., Pedersen, V. and Osman, A.M., 1981a. Isolation, identification and transmission ofTheileria mutans in northern Sudan. In: A.D. Irvin, M.P. Cunningham and A.S. Young (Editors), Advances in the Control of Theileriosis. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, The Hague, pp. 166–169.
Morzaria, S.P., Tatchell, R.J., Minor, R., Pedersen, V., Julia, I., Rahim, A., Dyson, D. and Van Aarle, P.A.M., 1981b. Preliminary studies on the epidemiology of theileriosis in Eastern Equatoria Province of the Sudan. In: A.D. Irvin, M.P. Cunningham and A.S. Young (Editors), Advances in the Control of Theileriosis. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, The Hague, pp. 83–85.
Mustafa, U.E.H., Jongejan, F. and Morzaria, S.P., 1983. Note on the transmission ofTheileria annulata byHyalomma ticks in the Sudan, Vet. Quart., 5: 112–113.
Osman, O.M., 1978. Preliminary notes on the distribution of ticks in Darfur Province Sudan. Bull. Anim. Health Prod. Afr., 26: 329–333.
Osman, O, M., Husein, A.M. El, Ahmed, N. and Abdulla, H.S., 1982. Ecological studies on ticks of Kordofan Region, Sudan. Bull. Anim. Health Prod. Afr., 30: 45–53.
Pegram, R.G., 1979. Ticks of Ethiopia with special reference to cattle and a critical review of the taxonomic status of species within theRhipicephalus sanguineus group. M. Phil. Thesis, Brunel University, Uxbridge, 169 pp.
Pegram, R.G., 1984. Biosystematic studies on the genusRhipicephalus: TheR. sanguineus andR. simus groups. Ph.D., Thesis, Brunel University, Uxbridge, 160 pp.
Pegram, R.G., Walker, J.B., Clifford, C.M. and Keirans, J.E. (in press). Comparison of populations of theRhipicephalus simus group:R. simus, R. praetextatus, andR. muhsamae. J. Med. Entomol.
Tatchell, R.G., 1983. Tick ecology and tick control. FAO, Rome, Technical Report no. 1, AG:GCP/SUD/024/DEN, 33 pp.
Uilenberg, G. and Schreuder, B.E.C., 1976. Studies on Theileriidae (Sporozoa) in Tanzania. I. Tick transmission ofHaematoxenus veliferus. Tropenmed. Parasitol., 27: 106–111.
Uilenberg, G., Robson, J. and Pederson, V., 1974. Some experiments on the transmission ofTheileria mutans andTheileria parva by the ticksAmblyomma variegatum andRhipicephalus appendiculatus in Uganda. Tropenmed. Parasitol., 25: 207–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jongejan, F., Zivkovic, D., Pegram, R.G. et al. Ticks (Acari:Ixodidae) of the Blue and White Nile ecosystems in the Sudan with particular reference to theRhipicephalus sanguineus group. Exp Appl Acarol 3, 331–346 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193169
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193169