The costs of a CRM project are not limited to the cost of licensing the CRM software. Selection, integration, training, maintenance and hidden costs can quickly add up if they’re poorly anticipated.
To help you find your way around, this article details the different cost items of a commercial CRM, with detailed estimates and cost drivers for each item.
Check out our recommendation engine to shortlist the 3 CRM apps that best fit your requirements
Sommaire
How much does CRM software cost?
On average, setting up a CRM costs about as much as the CRM software itself over the course of a year.
For light requirements with around ten users, you should expect to pay between €15,000 and €20,000 in the first year, and around €5,000 in subsequent years.
For more advanced requirements, with around 50 users, you’re looking at between €60,000 and €80,000 for the first year, then around €40,000 per year.
Finally, for more complex organizations, with more than 150 users, expect to pay between €350,000 & €500,000 in the first year, then at least €200,000 / year.
Note that licensing costs are highly degressive according to volume. Catalog prices are never used for large CRM projects.
We have summarized the detailed costs of a CRM project for 3 company profiles below
| Simple needs | Intermediate requirements | Advanced needs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | For small & medium-sized businesses looking for an easy-to-use CRM solution to ensure better lead follow-up. We estimate 10 users here. | For more advanced SMEs looking for a true lead management solution, with advanced reporting. Here we estimate 50 users | For the most advanced SMBs & SMEs looking to homogenize the customer experience across multiple channels, teams and sometimes franchises. We estimate 150 users here |
| CRM software selection | 6500 | 15000 | 50000 |
| CRM software prices | 1,800 € / year | 30,000 € / year | 180,000 € / year |
| CRM software implementation | 5000 | 15 000 € | 65 000 € |
| Training | 2500 | 6000 | 30000 |
| Maintenance | 2500 | 10000 | 35000 |
| Total cost year 1 | 18 300 € | 76 000 € | 360 000 € |
| Total cost year 2 | 4 300 € | 40 000 € | 215 000 € |
Let’s go into more detail about the cost categories mentioned:
- CRM selection
- CRM software costs
- Setting up a sales CRM
- Training
- Maintenance
Check out our recommendation engine to shortlist the 3 CRM apps that best fit your requirements
#1. The cost of CRM software selection
Why invest in a structured selection process?
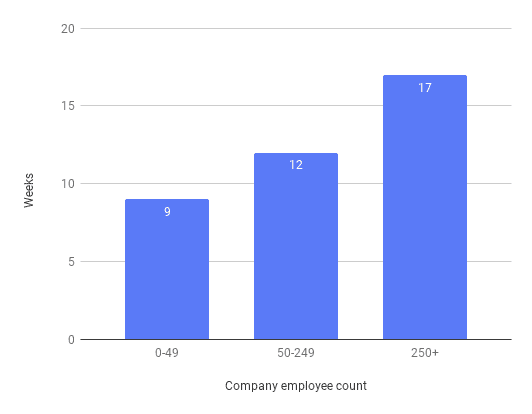
On average, companies spend 11 weeks selecting a CRM.
But this is only an average: it depends on the size of the company. Companies with over 250 employees take almost 2x as long to select a system as those with fewer than 50 employees.
Selecting your sales CRM won’t cost you anything “directly” from a publisher, but it will cost your teams time: it’s an expense you need to anticipate.
Choosing a commercial CRM is obviously an essential step, as it enables you to qualify your company’s CRM needs, expectations and objectives: you’ll need to define the main use cases, deduce the target functionalities that the software should offer, draw up a set of specifications, benchmark several CRM vendors, and so on.
Something to keep in mind
You really need to be able to distinguish “must-haves” from “nice-to-haves”. Too many CRM projects fail, and too much software is not adopted internally because the commercial CRM chosen is too complex. The success of your CRM project lies in the effective adoption of the chosen software by your employees.
How do you choose your CRM?
“The more thoroughly your team defines its needs before choosing a CRM system, the more successful your CRM implementation will be.” – Steve Chipman
The scope of CRM features can be summarized in 4 areas:
- The functional scope of CRM software
- Business needs
- Access to commercial data
- Solution scalability
#1 Essential features
Create a list of “must have” and “nice to have” features. What do you need for each of these areas?
- Contact management
- E-mail marketing and automation
- Opportunity management
- Sales analysis and reports
- Workflow automation
- Account management
#2 Business needs
What specific tasks does the system need to perform for your business processes?
What are your specific uses?
What are the stages in the sales process? When does account ownership change? What does your sales process look like?
What problems do you encounter? What processes seem chaotic and disorganized? Where do you start losing prospects? Who needs to communicate? What information do you lose?
We need to go beyond functionality.
#3 Access to commercial data
The idea is to think about this question from the point of view of each team that will be using the tool: each team needs to take part in this discussion about its needs in terms of CRM.
- Sales team
- Marketing team
- General Management
- Support team
- Operations team
- Finance team
Will different teams need different dashboards? What information will be displayed on each dashboard? How will this information be displayed? How will users use it?
#4 Solution scalability
How fast are you developing? How much information do you add? What would happen if the system failed? How important is the information you store on your customers? The elements to be taken into account here are :
- Operating time
- CRM scalability
- Backup and disaster recovery
- Cost (of course)
My advice
Investing the necessary time will make the task easier: the clearer the objective, the easier the process.
How to buy CRM software
Here are a few tips:
- Identify between 1 and 3 people in your organization who will be in charge of dialog with CRM editors, to avoid all employees investing time with different editors. Having a clear set of specifications, or failing that, a precise knowledge of what you want, will also save time in discussions.
- At the end of your search, select between 3 and 4 CRM editors, no more. Ask everyone for a demo and test each software. Check whether or not all your teams’ needs are covered. Build an analysis grid, listing all your criteria, so you can compare each solution and identify the best one.
- Organize internal meetings. CRM selection is not just a matter for management. All commercial CRM end-users (marketing, sales, customer service, etc.) must be consulted and have their say. This is the best way to optimize CRM adoption after implementation.
Something to keep in mind
Negotiations with CRM publishers take time. Don’t forget to anticipate it.
#2. Evaluate the real cost of your CRM software

There are 2 types of CRM software: SaaS and “on-premise” CRM, i.e. in license mode. Here, we’ll focus on the SaaS business model.
- Saas (Software as a Service) are online systems: you pay a subscription fee to obtain a license for your company. They offer greater flexibility in terms of personalization and payment options, are easier to expand, and provide remote access for all your devices.
- In contrast, an “on-premise” CRM is a system that you buy outright (usually for a large sum), and which you are responsible for hosting, maintaining and updating.
Saas is popular because of its scalability and plug-and-play nature. They’re also easily accessible from a distance, a major advantage in today’s (tele)working world.
My advice
On the whole, anon-premise CRM is only a good option if you really need to control access to your sales data. If you manage sensitive data or need total control over the system (often for regulatory compliance reasons). Still, note that since the RGPD, most SaaS CRM solutions (which manage the commercial data of hundreds of thousands of customers) will very often be rather better at managing personal data than you or your IT team.
Saas generally offer the following options:
- Monthly subscriptions (most common).
- Annual subscriptions (often with discounts)
- Quarterly subscriptions (rare, but sometimes possible)
CRM software pricing structure
To understand the price of CRM software, it’s important to remember the business model used by CRM software publishers.
First, you need to calculate the cost of your service level. It is determined by 3 factors:
- Plan level: this is the set of services you purchase from the supplier.
- Volume: the number of records, contacts or data points you can store for a given price.
- Add-on modules: additional functions, integrations or capabilities that you can add later.
In the SaaS model, CRM vendors offer different “levels” or “tiers” of a CRM platform. Each plan level contains a specific set of features and capabilities.
For example, Pipedrive CRM limits the use of functions according to the number of :
- current bids (opportunities in a pipe)
- custom fields (set of data fields added to a prospect, offer, person, organization or product)
- reports (combined reports on activities, offers, forecasts, etc.)
Something to keep in mind
When you’re limited by the volume of contacts or opportunities, or when you’re expanding, some CRMs will automatically switch you to a … more expensive formula!
#3. How much does it cost to implement a CRM solution?
Whatever CRM solution you choose, and however complex it may be, remember that you’ll be implementing a tool in your organization on which all customer-facing staff will depend in one way or another.
It’s a real challenge. The biggest risk is low adoption. The teams have their own habits. Implementing a CRM system can mean profound changes to the way they work. Poorly implemented, a commercial CRM can have a very negative impact on team productivity, customer service quality and even company profits.
My advice
There’s a rule of thumb that recommends investing as much in implementation support as in the annual cost of the commercial CRM subscription. If the cost of your subscription is 1,500 euros per year, you need to invest that much in implementation support – by hiring an expert CRM consultant.
The costs involved in implementing commercial CRM software correspond more or less to these elements:
- Data cleansing
- Data migration
- Software configuration and settings
- Creating detailed documentation
- Integration into your enterprise software environment
#1 Data cleansing
You’ll probably need to gather data from several sources: files managed by sales staff, databases used by marketing, data from accounting, e-commerce, etc.
There is inevitably some data cleansing to be done, and deduplication in particular.
To successfully bring all this data together in a single file, you first need to identify the important data and their sources, and then call in a database management expert to centralize all this data in the file.
#2 Data migration
Once all your data has been put together in a single database, you need to load it into your new sales CRM software.
If the file is in .xls format, this step is fairly straightforward. But chances are you’ll have to load the data into the system using different formats.
To find out what data to load, where to load it and how to do it successfully, you’ll certainly need advice from the editor or a CRM consultant.
#3 Software configuration and settings
This is surely one of the most important pieces of the puzzle.
At first glance, CRM software may seem like the right choice for your business. But you’ll soon realize that the dashboards, for example, which you find very well designed, don’t include all the information you need. You’ll see that some fine-tuning and adjustments are required to operate your own customer dialog.
You need to implement the specifics of your customer relationship management in the software. For this, it may be advisable to call in an external consultant, who can advise you on which functionalities to activate, which data fields to use, which processes to set up to manage and automate your reporting, etc.
The right balance needs to be struck between simplicity and completeness. Too many data fields and too many new procedures to store will discourage software users.
My advice
We recommend a pragmatic, step-by-step approach: start by implementing priority features and specifications, and roll out the rest as you go along.
#4 Creating documentation
If you customize your CRM software, the documentation provided by the publisher will no longer be sufficient.
The idea is to create a document, a “user guide”, enabling CRM users to easily understand procedures and the distribution of roles, tasks and responsibilities between different users. This accelerates the adoption of CRM by teams.
Something to keep in mind
This documentation needs to be updated regularly, to incorporate any changes in functionality or processes that occur along the way. This document must be easily accessible to employees.
#5 Integrating CRM with your software environment
You also need to use connectors or APIs to connect your CRM to your other systems (ERP, CMS, marketing tools, customer service tools, etc.).
This requires quite advanced technical skills that even some consultants don’t possess. Here again, you can opt for a gradual integration, for example, by initially focusing on integration with the CMS.
My advice
If you take too long to clean up your data and migrate it into CRM, it’s possible that half your customer data will be out of date by the end of the process. This can be very costly for the company. The ideal process: gather the most recent data from the most important sources and merge them together before loading them into the CRM as quickly as possible.
#4 The cost of CRM training for your teams
Why train your teams?
As already mentioned, the biggest risk of this deployment process is that it results in low adoption, as teams have their own habits and may find it difficult to change the way they work.
If you don’t want to jeopardize the substantial investment you’ve made in deploying this tool, training is an essential dimension.
This also ensures that the main procedures are correctly assimilated, and avoids the drop in productivity that often initially accompanies the introduction of a new tool.
Which teams to train?
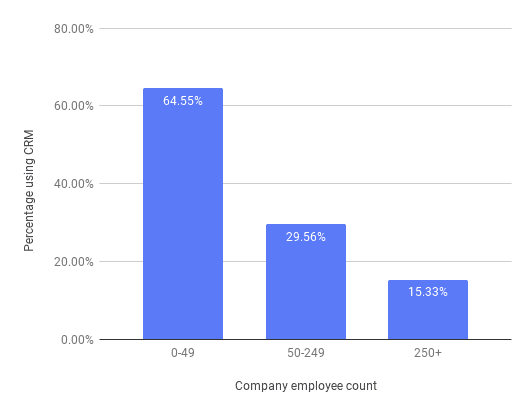
On average, almost half of a company’s employees use their CRM system.
Once again, this figure varies enormously according to company size: the results show that companies with fewer than 50 employees have a much higher percentage of employees using their CRM system. Conversely, companies with more than 250 employees have only 15.33% of their employees using their CRM.
According to this data, a company with 40 employees should have around 26 CRM users in its organization. According to our CRM pricing data, she can expect to spend $780 per month or $9,360 per year on her system.
By way of comparison, a company with 400 employees would have around 61 CRM users. The monthly cost of their CRM would be $1,830 per month or $21,960 per year for their system.
Something to keep in mind
CRM software is designed for all company teams, not just the sales team. So it’s important to provide training tailored to the needs of different teams. For example:
- Training to help salespeople manage the pipeline
- Another training course, aimed at marketers, explains how to manage leads.
How do you train them?
Some publishers offer training courses, as in the case of Pipedrive CRM, which offers an “Academy”:
You can also call on the services of a CRM consultant with expertise in your software, or an approved training organization. For example, Zohosphere, Zoho’s specialized integrator: this team of specialized consultants offers to guide companies through the integration of Zoho CRM.
Something to keep in mind
Once again, whatever option you choose, don’t overlook the cost of training your teams and the time spent organizing it: finding service providers, discussions, recruitment, organizing training days and, of course, the training itself!
#5. CRM maintenance costs
Faults & bugs
CRM crashes are undoubtedly the biggest cost item, if they occur at all. You need to ensure that the risks of crashes, bugs, data loss, etc. are kept to a minimum by implementing an effective maintenance system.
If you choose a SaaS commercial CRM solution, your system will be maintained in part by the publisher.
In this case, check the system backup guarantees offered by the publisher:
- How often is your data backed up automatically?
- What are the options for manual backup?
- Has the publisher you’ve chosen suffered any breakdowns?
- If so, how long do breakdowns last on average?
- If you choose licensed software, ask some of the platform’s customers about their experience of the software and its “stability”?
My advice
These costs correspond both to the time spent by your teams on maintenance and to the money lost due to breakdowns and other bugs when they occur. In the event of a serious problem, an external service provider may be required.
Developments
A high-performance CRM tool needs to be flexible and scalable. Over time (we hope), you’ll develop, your business will grow and with it the will :
- Add new data sources
- Access more advanced functions
- Integrate new tools
These changes should be anticipated in the years following the deployment of your tool.
The hidden costs of CRM software

There can be hidden costs at every stage of a commercial CRM project. They must be identified at the time of purchase.
Sometimes, the “cost per user” is indicated directly, or the plan includes a specific number of users. If you can’t find either, ask the supplier.
Customize your CRM software
- Customized dashboards: How many dashboards can you create before being invoiced? Are there any limits to what you can include? Do you receive training or assistance?
- Customized pipelines: How many pipelines can you create? Is there a limit to the size of a pipeline?
- Custom fields: Is there a limit to the number of custom fields you can add?
- Customized user permissions: To what extent can you manage your team’s access?
Minimum contractual conditions
they are almost never mentioned during pricing or negotiations, unless you expressly request it.
- Named user or simultaneous user: is the rate based on the number of CRM users or on the total number of employees?
- Renewal cycle: Is there a minimum number of renewals? Does your contract provide for automatic renewal or upgrade?
- Security: Who is responsible in the event of a breach? Are there any minimum security measures you need to provide?
CRM add-on module prices
Integrations, analyses, reports or intelligence functions, they’re usually advertised in the purchase process, but hidden behind paywalls once you’ve paid.
Some CRM providers offer add-on modules to give you this option, which can be free or paid for.
| Examples of free modules | Pay-per-use add-on modules |
|---|---|
| Native integrations with other tools | Third-party integrations |
| Basic reports and analyses | Advanced reporting and analysis |
| Basic dashboard customization | Advanced dashboard customization |
| Artificial intelligence or machine learning capabilities |
My advice
There are 2 reasons for the hidden costs of CRM software: vendors aren’t totally honest about their prices, and customers don’t ask enough questions. Don’t hesitate to ask many questions beforehand to clarify the above points.
Check out our recommendation engine to shortlist the 3 CRM apps that best fit your requirements
Who’s in charge of implementation?
Depending on the maturity of your sales organization, you’ll opt for a solution that’s more or less advanced, and therefore more or less “heavy” in terms of deployment.
For small projects: the publisher itself
For a “light” solution: Vendors often offer all or part of the integration. Software such as Pipedrive or Active campaign can help you (at the very least) with data migration, and can even go so far as to offer you migration services free of charge or at very attractive rates.
For larger projects: A CRM integrator
For more advanced business organizations (more users, more features, more data sources, etc.). In this case, whatever CRM software you choose, it takes time to set up, and doesn’t just rely on technical integration.
Going further
Discover our comparison of French CRM integrators, with a complete guide on the subject.
For larger projects, a CRM consultant is also invaluable. He is involved in :
- Support your team in structuring business needs
- Support the software publisher in implementing the tool
- Define the right data models for your organization
- Optimize software integration with your existing stack
The cost of this support depends on the complexity of your system, the CRM software you choose and your existing tools. Note that it’s quite valuable to involve a consultant early on in the selection process to frame the project properly.
Something to keep in mind
In both cases, it’s essential to bear in mind that your teams will inevitably be involved, and that this cost needs to be anticipated. It is therefore impossible to envisage a totally free deployment.
Going further
Read all our articles on commercial CRM: