Developing lactose-free milk with graphene oxide based nano filtration membranes
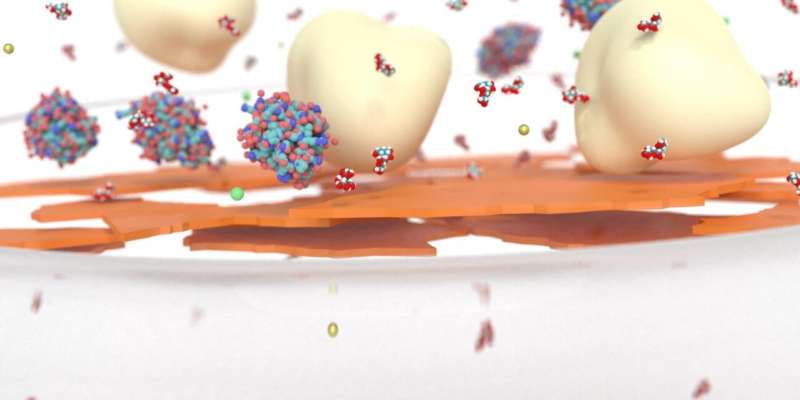
Over the past years, graphene oxide membranes have been mainly studied for water desalination and dye separation. However, membranes have a wide range of applications, such as within the food industry. A research group led by Aaron Morelos-Gomez of Shinshu University's Global Aqua Innovation Center investigated the application of graphene oxide membranes for milk, which typically creates dense foulant layers on polymeric membranes.
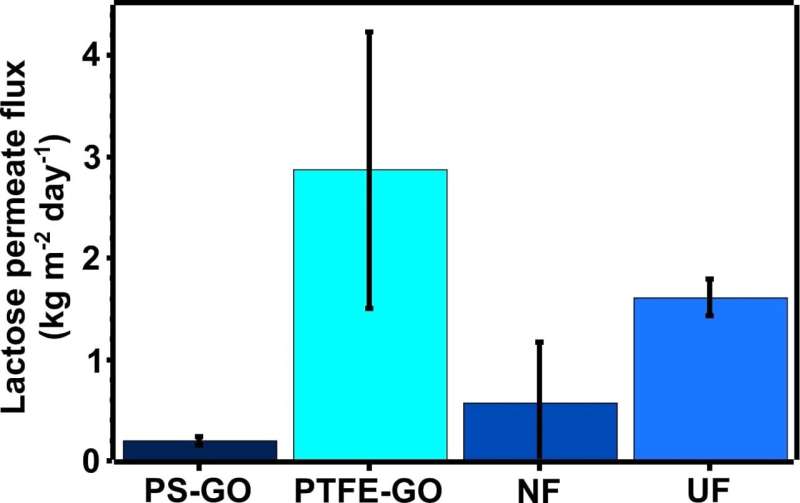
Graphene oxide membranes have the advantage to create a porous foulant layer. Therefore, their filtration performance can be maintained better than commercial polymeric membranes. The unique chemical and laminar structure of the graphene oxide membrane allowed an enhanced permeation of lactose and water while rejecting fat, proteins, and some minerals. Thus the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of milk were preserved better than with commercial polymer membranes.
The concentration of lactose and lactose permeate flux was much higher than commercial nanofiltration membranes, due to the porous foulant layer and the unique laminar structure of the graphene oxide membrane. The irreversible fouling was improved by using a support membrane with 1 μm pore size for the graphene oxide membrane. This caused the formation of a porous fouling layer that allowed a higher recovery of water flux after milk filtration.
Highlighting its excellent antifouling property and high selectivity for lactose, this pioneering work demonstrates the application of graphene oxide membranes for the food industry, particularly the dairy industry. This method retains a high potential for removing sugars from beverages while preserving other ingredients, therefore increasing their nutritional value. The high antifouling property against a solution rich in organic matter, such as milk, makes it also an ideal candidate for other applications such as wastewater treatment and medical applications. The group plans to keep exploring applications of graphene oxide membranes.
This work was based on the group's previous findings to create spray-coated graphene oxide membranes for water desalination in Nature Nanotechnology 12 (2017), 1083-1088. The membranes showed enhanced chemical stability by adding few-layered graphene while demonstrating stable filtration performance after five days of operation. In addition, The deposition method by spray-coating is promising for scalability.
More information: Aaron Morelos-Gomez et al, Graphene oxide membranes for lactose-free milk, Carbon (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.05.005
Journal information: Nature Nanotechnology , Carbon
Provided by Shinshu University