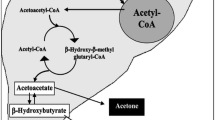
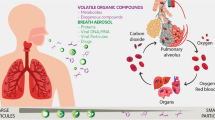
Abstract
In this article, technical developments in breath analysis and its applications in the field of clinical diagnosis and the monitoring of various symptoms, particularly molecular hydrogen in breath, are introduced. First, a brief overview of the current uses of the hydrogen breath test is provided. The principles of the test and how hydrogen can be used as a biomarker for various symptoms, and monitoring microbial metabolism, are introduced. Ten case-study applications of breath hydrogen measurements for which hydrogen exhibits beneficial effects for diagnosis, including the contexts of oxidative stress, gastrointestinal disease, and metabolic disorders, are discussed. The technologies and problems involved in breath hydrogen testing, sampling, pretreatment, and detection in exhaled breath are discussed, and research including current analytical systems and new sensors is focused on in the context of hydrogen detection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Risby TH (2005) Current status of clinical breath analysis. In: Amann A, Smith D (eds) Breath analysis for clinical diagnostics and therapeutic monitoring. World Scientific, London, pp 251–267
Phillips M, Herrera J, Krishnan S, Zain M, Greenberg J, Cataneo RN (1999) Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J Chromatogr B 729:75–88
Martin AN, Farquar GR, Jones AD, Frank M (2010) Human breath analysis: methods for sample collection and reduction of localized background effects. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:739–750
Kamm MA, Leonnard-Jones JE (eds) (1991) Gastrointestinal transit. Pathophysiology and pharmacology. Wrightson Biomedical Publishing, Petersfield
Swagerty DL Jr, Walling AD, Klein RM (2002) Lactose intolerance. Am Fam Physician 65:1845–1850
Simrén M, Stotzer PO (2006) Use and abuse of hydrogen breath tests. Gut 55:297–303
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S, Ohta S (2007) Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 13:688–694
Di Stefano M, Corazza GR (2009) Role of hydrogen and methane breath testing in gastrointestinal diseases. Dig Liver Dis Suppl 3:40–43
Cloarec D, Bornet F, Gouilloud S, Barry JL, Salim B, Galmiche JP (1990) Breath hydrogen response to lactulose in healthy subjects: relationship to methane producing status. Gut 31:300–304
Rumessen JJ, Hamberg O, Gudmand-Høyer E (1989) Influence of orocaecal transit time on hydrogen excretion after carbohydrate malabsorption. Gut 30:811–814
Urita Y, Watanabe T, Ishihara S, Maeda T, Sasaki Y, Hike K, Miura Y, Nanami T, Arai K, Koshino H, Saito Y, Shimada N, Sugimoto M, Miki K (2008) Breath hydrogen and methane levels in a patient with volvulus of the sigmoid colon. J Breath Res 2:037025. doi:10.1088/1752-7155/2/3/037025
Liu F, Kondo T, Toda F (1992) Measurement of breath hydrogen. Nagoya J Health Phys Fit Sports 15(1):33–37
Kagaya M, Iwata N, Toda Y, Nakae Y, Kondo T (1997) Small bowel transit time and colonic fermentation in young and elderly women. J Gastroenterol 32:453–456
Chiloiro M, Darconza G, Piccioli E, De Carne M, Clemente C, Riezzo G (2001) Gastric emptying and orocecal transit time in pregnancy. J Gastroenterol 36(8):538–543
Kagaya M, Iwata M, Toda Y, Nakae Y, Kondo T (1998) Circadian rhythm of breath hydrogen in young women. J Gastroenterol 33(4):472–476
Urita Y, Hike K, Torii N, Kikuchi Y, Sasajima M, Miki K (2002) Efficacy of lactulose plus 13C-acetate breath test in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal motility disorders. J Gastroenterol 37(6):442–448
Kudlacek S, Freudenthaler O, Weissböeck H, Schneider B, Willvonseder R (2002) Lactose intolerance: a risk factor for reduced bone mineral density and vertebral fractures? J Gastroenterol 37(12):1014–1019
Mitsui T, Kagami H, Kinomoto H, Ito A, Kondo T, Shimaoka K (2003) Small bowel bacterial overgrowth and rice malabsorption in healthy and physically disabled older adults. J Hum Nutr Diet 16(2):119–122
Sato Y, Kajiyama S, Amano A, Kondo Y, Sasaki T, Handa S, Takahashi R, Fukui M, Hasegawa G, Nakamura N et al (2008) Hydrogen-rich pure water prevents superoxide formation in brain slices of vitamin C-depleted SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 375:346–350
Li J, Wang C, Zhang JH, Cai JM, Cao YP, Sun XJ (2010) Hydrogen-rich saline improves memory function in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer’s disease by reduction of oxidative stress. Brain Res 1328:152–161
Fu Y, Ito M, Fujita Y, Ito M, Ichihara M, Masuda A, Suzuki Y, Maesawa S, Kajita Y, Hirayama M et al (2009) Molecular hydrogen is protective against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nigrostriatal degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 453:81–85
Fujita K, Seike T, Yutsudo N, Ohno M, Yamada H, Yamaguchi H, Sakumi K, Yamakawa Y, Kido MA, Takaki A et al (2009) Hydrogen in drinking water reduces dopaminergic neuronal loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 4:e7247
Ohta S, Nakao A, Ohno K (2011) The 2011 Medical Molecular Hydrogen Symposium: an inaugural symposium of the journal Medical Gas Research. Med Gas Res 1:10–16
Kajiyama S, Hasegawa G, Asano M et al (2008) Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutr Res 28:137–143
Shimouchi A, Nose K, Yamaguchi M, Ishiguro H, Kondo T (2009) Breath hydrogen produced by ingestion of commercial hydrogen-enriched water and milk. Biomark Insights 4:27–33
Itoh T, Hirayama M, Yamai K, Goto S, Masafumi Ito M, Ichihara M, Ohno K (2012) Drinking hydrogen-enriched water and intermittent hydrogen gas exposure, but not lactulose or continuous hydrogen gas exposure, prevent 6-hydorxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Med Gas Res 2:15–18
La Brooy SJ, Male P-J, Beavis AK et al (1983) Assessment of the reproducibility of the lactulose H 2 breath test as a measure of mouth to caecum transit time. Gut 24:893–896
American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (2005) ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:912–930
Cao W, Duan Y (2007) Current status of methods and techniques for breath analysis. Crit Rev Anal Chem 37(1):3–13
Bunkowski A, Bödeker B, Bader S, Westhoff M, Litterst P, Baumbach JI (2009) MCC/IMS signals in human breath related to sarcoidosis-results of a feasibility study using an automated peak finding procedure. J Breath Res 3(4):046001
Fleischer M, Simon E, Rumpel E, Ulmer H, Harbeck M, Wandel M, Fietzek C, Weimar U, Meixner H (2002) Detection of volatile compounds correlated to human diseases through breath analysis with chemical sensors. Sensors Actuators B 83:245–249
Shin W, Nishibori M, Izu N, Itoh T, Matsubara I, Nose K, Shimouchi A (2011) Monitoring breath hydrogen using thermoelectric sensor. Sens Lett 9:684–687
Peng G, Tisch U, Adams O, Hakim M, Shehada N, Broza YY, Billan S, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Haick H (2009) Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 4:669–673
Kim K-H, Jahan S, Kabir E (2012) A review of breath analysis for diagnosis of human health. Trends Anal Chem 33:1–8
Byun HG, Persaud C, Pisanelli A (2010) Wound-state monitoring for burn patients using e-nose/SPME system. ETRI J 32:440–446
Lee JH (2009) Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: overview. Sensors Actuators B 140:319–336
Shin J, Choi S, Lee I, Youn D, Park CO, Lee JH, Tuller HL, Il-Doo Kim ID (2013) Thin-wall assembled SnO2 fibers functionalized by catalytic Pt nanoparticles and their superior exhaled-breath-sensing properties for the diagnosis of diabetes. Adv Funct Mater 23:2357–2367
Acknowledgment
This work was partially supported by the “Development Project for Extremely Early Diagnostics Technologies for Human Diseases” of Aichi prefecture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Chemosensors and Chemoreception with guest editors Jong-Heun Lee and Hyung-Gi Byun.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, W. Medical applications of breath hydrogen measurements. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 3931–3939 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7606-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7606-6