Abstract
Objective
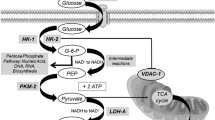
The abnormal expression of the key enzymes in glycolytic pathways, including glucose transporter-1, glucose transporter-3, hexokinase-II, lactate dehydrogenase 5, pyruvate kinase M2, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase-like protein 1 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-1 was reported to be associated with poor prognosis of various cancers. However, the association remains controversial. The objective of this study was to investigate the prognostic significance of glycolysis-related proteins.
Materials and methods
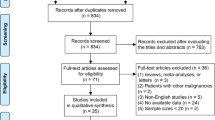
We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, using Pubmed and Ovid as search engines and Google Scholar from inception to April 2017. Eighty-six studies with 12,002 patients were included in the study.
Results
Our pooled results identified that glycolysis-related proteins in cancers were associated with shorter overall survival of colorectal cancer (HR 2.33, 95% CI 1.38–3.93, P = 0.002), gastric cancer (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.31–1.82, P < 0.001), cancer of gallbladder or bile duct (HR 2.16, 95% CI 1.70–2.75, P < 0.001), oral cancer (HR 2.07, 95% CI 1.32–3.25, P < 0.001), esophageal cancer (HR 1.66, 95% CI 1.25–2.21, P = 0.01), hepatocellular carcinoma (HR 2.04, 95% CI 1.64–2.54, P < 0.001), pancreatic cancer (HR 1.72, 95% CI 1.39–2.13, P < 0.001), breast cancer(HR 1.67, 95% CI 1.34–2.08, P < 0.001), and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (HR 3.59, 95% CI 1.75–7.36, P < 0.001). No association was found for lung cancer, ovarian cancer or melanoma. The key glycolytic transcriptional regulators (HIF-1α, p53) were analyzed in parallel to the glycolysis-related proteins, and the pooled results identified that high-level expression of HIF-1α was significantly associated with shorter overall survival (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.42–0.79, P < 0.001) Furthermore, glycolysis-related proteins linked with poor differentiated tumors (OR 1.81, 95% CI 1.46–2.25, P < 0.001), positive lymph node metastasis (OR 2.73, 95% CI 2.16–3.46, P < 0.001), positive vascular invasion (OR 2.05, 95% CI 1.37–3.07, P < 0.001), large tumor size (OR 2.06, 95% CI 1.80–2.37, P < 0.001), advanced tumor stage (OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.19–2.09, P < 0.001), and deeper invasion (OR 2.37, 95% CI 1.93–2.91, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Glycolytic transcriptional regulators and glycolysis-related proteins in cancers were significantly associated with poor prognosis, suggesting glycolytic status may be potentially valuable prognostic biomarkers for various cancers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen S, Eilertsen M, Donnem T, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S et al (2011) Diverging prognostic impacts of hypoxic markers according to NSCLC histology. Lung Cancer 72:294–302
Ashrafian H (2006) Cancer’s sweet tooth: the Janus effect of glucose metabolism in tumorigenesis. Lancet 367:618–621
Ayala FR, Rocha RM, Carvalho KC, Carvalho AL, da Cunha IW et al (2010) GLUT1 and GLUT3 as potential prognostic markers for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Molecules 15:2374–2387
Baer S, Casaubon L, Schwartz MR, Marcogliese A, Younes M (2002) Glut3 expression in biopsy specimens of laryngeal carcinoma is associated with poor survival. Laryngoscope 112:393–396
Benesch C, Schneider C, Voelker HU, Kapp M, Caffier H et al (2010) The clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of pyruvate kinase M2 and pAkt expression in breast cancer. Anticancer Res 30:1689–1694
Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA, Vidal MN, Nakano K et al (2006) TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 126:107–120
Bensinger SJ, Christofk HR (2012) New aspects of the Warburg effect in cancer cell biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:352–361
Bentz S, Cee A, Endlicher E, Wojtal KA, Naami A et al (2013) Hypoxia induces the expression of transketolase-like 1 in human colorectal cancer. Digestion 88:182–192
Berlth F, Monig S, Pinther B, Grimminger P, Maus M et al (2015) Both GLUT-1 and GLUT-14 are independent prognostic factors in gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 22(Suppl 3):S822–S831
Bostrom PJ, Thoms J, Sykes J, Ahmed O, Evans A et al (2016) Hypoxia marker GLUT-1 (glucose transporter 1) is an independent prognostic factor for survival in bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy. Bladder Cancer 2:101–109
Brito AF, Abrantes AM, Ribeiro M, Oliveira R, Casalta-Lopes J et al (2015) Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with glucose transporters and p53 expression. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5:183–189
Cavalcante IP, Zerbini MC, Alencar GA, Mariani Bde P, Buchpiguel CA et al (2016) High 18F-FDG uptake in PMAH correlated with normal expression of Glut1, HK1, HK2, and HK3. Acta Radiol 57:370–377
Chen Z, Lu X, Wang Z, Jin G, Wang Q et al (2015) Co-expression of PKM2 and TRIM35 predicts survival and recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:2538–2548
Cho H, Lee YS, Kim J, Chung JY, Kim JH (2013) Overexpression of glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1) predicts poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Invest 31:607–615
Cho MH, Park CK, Park M, Kim WK, Cho A et al (2015) Clinicopathologic features and molecular characteristics of glucose metabolism contributing to (1)(8)F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. PLoS One 10:e0141413
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE et al (2008a) The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 452:230–233
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Wu N, Asara JM, Cantley LC (2008b) Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature 452:181–186
Contractor T, Harris CR (2012) p53 negatively regulates transcription of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase Pdk2. Cancer Res 72:560–567
Dai Z, Pan S, Chen C, Cao L, Li X et al (2016) Down-regulation of succinate dehydrogenase subunit B and up-regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 predicts poor prognosis in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol 37:5145–5152
Danner BC, Didilis VN, Wiemeyer S, Stojanovic T, Kitz J et al (2010) Long-term survival is linked to serum LDH and partly to tumour LDH-5 in NSCLC. Anticancer Res 30:1347–1351
Dong T, Kang X, Liu Z, Zhao S, Ma W et al (2016) Altered glycometabolism affects both clinical features and prognosis of triple-negative and neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated breast cancer. Tumour Biol 37:8159–8168
Elson DA, Ryan HE, Snow JW, Johnson R, Arbeit JM (2000) Coordinate up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-1 target genes during multi-stage epidermal carcinogenesis and wound healing. Cancer Res 60:6189–6195
Fenske W, Volker HU, Adam P, Hahner S, Johanssen S et al (2009) Glucose transporter GLUT1 expression is an stage-independent predictor of clinical outcome in adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer 16:919–928
Foldi M, Stickeler E, Bau L, Kretz O, Watermann D et al (2007) Transketolase protein TKTL1 overexpression: a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 17:841–845
Fong Y, Saldinger PF, Akhurst T, Macapinlac H, Yeung H et al (1999) Utility of 18F-FDG positron emission tomography scanning on selection of patients for resection of hepatic colorectal metastases. Am J Surg 178:282–287
Fritz P, Coy JF, Murdter TE, Ott G, Alscher MD et al (2012) TKTL-1 expression in lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract 208:203–209
Furudoi A, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Yoshihara M, Sumii K et al (2001) Clinical significance of human erythrocyte glucose transporter 1 expression at the deepest invasive site of advanced colorectal carcinoma. Oncology 60:162–169
Furuta E, Okuda H, Kobayashi A, Watabe K (2010) Metabolic genes in cancer: their roles in tumor progression and clinical implications. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805:141–152
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Vander Heiden MG, Kroemer G (2013) Metabolic targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:829–846
Gao Y, Xu D, Yu G, Liang J (2015) Overexpression of metabolic markers HK1 and PKM2 contributes to lymphatic metastasis and adverse prognosis in Chinese gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:9264–9271
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Turley H, Harris AL et al (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 (LDH-5) expression in endometrial cancer relates to the activated VEGF/VEGFR2(KDR) pathway and prognosis. Gynecol Oncol 103:912–918
Gong L, Cui Z, Chen P, Han H, Peng J et al (2012) Reduced survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma expressing hexokinase II. Med Oncol 29:909–914
Goos JA, de Cuba EM, Coupe VM, Diosdado B, Delis-Van Diemen PM et al (2016) Glucose transporter 1 (SLC2A1) and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) predict survival after resection of colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Ann Surg 263:138–145
Gottlieb E (2011) p53 guards the metabolic pathway less travelled. Nat Cell Biol 13:195–197
Grimm M, Alexander D, Munz A, Hoffmann J, Reinert S (2013a) Increased LDH5 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 30:529–540
Grimm M, Schmitt S, Teriete P, Biegner T, Stenzl A et al (2013b) A biomarker based detection and characterization of carcinomas exploiting two fundamental biophysical mechanisms in mammalian cells. BMC Cancer 13:569
Hamanaka RB, Chandel NS (2012) Targeting glucose metabolism for cancer therapy. J Exp Med 209:211–215
Hjerpe E, Egyhazi Brage S, Carlson J, Frostvik Stolt M, Schedvins K et al (2013) Metabolic markers GAPDH, PKM2, ATP5B and BEC-index in advanced serous ovarian cancer. BMC Clin Pathol 13:30
Ho HY, Cheng ML, Chiu DT (2007) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase—from oxidative stress to cellular functions and degenerative diseases. Redox Rep 12:109–118
Hoskin PJ, Sibtain A, Daley FM, Wilson GD (2003) GLUT1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in bladder cancer: relationship with vascularity and proliferation as predictors of outcome of ARCON. Br J Cancer 89:1290–1297
Hu W, Lu SX, Li M, Zhang C, Liu LL et al (2015) Pyruvate kinase M2 prevents apoptosis via modulating Bim stability and associates with poor outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:6570–6583
Huang X, Liu M, Sun H, Wang F, Xie X et al (2015) HK2 is a radiation resistant and independent negative prognostic factor for patients with locally advanced cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:4054–4063
Iwasaki K, Yabushita H, Ueno T, Wakatsuki A (2015) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, carbonic anhydrase-IX, glucose transporter-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor associated with lymph node metastasis and recurrence in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Oncol Lett 10:1970–1978
Jang SM, Han H, Jang KS, Jun YJ, Jang SH et al (2012) The glycolytic phenotype is correlated with aggressiveness and poor prognosis in invasive ductal carcinomas. J Breast Cancer 15:172–180
Kallinowski F, Schlenger KH, Runkel S, Kloes M, Stohrer M et al (1989) Blood flow, metabolism, cellular microenvironment, and growth rate of human tumor xenografts. Cancer Res 49:3759–3764
Kang SS, Chun YK, Hur MH, Lee HK, Kim YJ et al (2002) Clinical significance of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression in human breast carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:1123–1128
Karachaliou N, Papadaki C, Lagoudaki E, Trypaki M, Sfakianaki M et al (2013) Predictive value of BRCA1, ERCC1, ATP7B, PKM2, TOPOI, TOPOmicron-IIA, TOPOIIB and C-MYC genes in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) who received first line therapy with cisplatin and etoposide. PLoS One 8:e74611
Katagiri M, Karasawa H, Takagi K, Nakayama S, Yabuuchi S et al (2016) Hexokinase 2 in colorectal cancer: a potent prognostic factor associated with glycolysis, proliferation and migration. Histol Histopathol 2016:11799
Kawamura T, Kusakabe T, Sugino T, Watanabe K, Fukuda T et al (2001) Expression of glucose transporter-1 in human gastric carcinoma: association with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and patient survival. Cancer 92:634–641
Kayser G, Kassem A, Sienel W, Schulte-Uentrop L, Mattern D et al (2010) Lactate-dehydrogenase 5 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with the expression of the transketolase-like protein 1. Diagn Pathol 5:22
Kim YW, Park YK, Yoon TY, Lee SM (2002) Expression of the GLUT1 glucose transporter in gallbladder carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology 49:907–911
Kim BW, Cho H, Chung JY, Conway C, Ylaya K et al (2013a) Prognostic assessment of hypoxia and metabolic markers in cervical cancer using automated digital image analysis of immunohistochemistry. J Transl Med 11:185
Kim JG, Lee SJ, Chae YS, Kang BW, Lee YJ et al (2013b) Association between phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase and MAPK3/1 expression and prognosis for patients with gastric cancer. Oncology 85:78–85
Kim HS, Lee HE, Yang HK, Kim WH (2014) High lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression correlates with high tumoral and stromal vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric cancer. Pathobiology 81:78–85
Kitamura K, Hatano E, Higashi T, Narita M, Seo S et al (2011) Proliferative activity in hepatocellular carcinoma is closely correlated with glucose metabolism but not angiogenesis. J Hepatol 55:846–857
Kolev Y, Uetake H, Takagi Y, Sugihara K (2008) Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) expression in human gastric cancer: association with hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1alpha) pathway, angiogenic factors production and poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 15:2336–2344
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Bougioukas G, Didilis V et al (2003) Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) overexpression in non-small-cell lung cancer tissues is linked to tumour hypoxia, angiogenic factor production and poor prognosis. Br J Cancer 89:877–885
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Harris AL et al (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in operable colorectal cancer: strong association with survival and activated vascular endothelial growth factor pathway—a report of the Tumour Angiogenesis Research Group. J Clin Oncol 24:4301–4308
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Winter S, Leek R, Sivridis E et al (2009) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in squamous cell head and neck cancer relates to prognosis following radical or postoperative radiotherapy. Oncology 77:285–292
Kuo W, Lin J, Tang TK (2000) Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) gene transforms NIH 3T3 cells and induces tumors in nude mice. Int J Cancer 85:857–864
Kwee SA, Hernandez B, Chan O, Wong L (2012) Choline kinase alpha and hexokinase-2 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with survival. PLoS One 7:e46591
Kwon JE, Jung WH, Koo JS (2013) The expression of metabolism-related proteins in phyllodes tumors. Tumour Biol 34:115–124
Li W, Xu Z, Hong J, Xu Y (2014a) Expression patterns of three regulation enzymes in glycolysis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: association with survival. Med Oncol 31:118
Li J, Yang Z, Zou Q, Yuan Y, Li J et al (2014b) PKM2 and ACVR 1C are prognostic markers for poor prognosis of gallbladder cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 16:200–207
Lim JY, Yoon SO, Seol SY, Hong SW, Kim JW et al (2012) Overexpression of the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is an adverse prognostic factor for signet ring cell gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 18:4037–4043
Liu WR, Tian MX, Yang LX, Lin YL, Jin L et al (2015) PKM2 promotes metastasis by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells and indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:846–861
Lockney NA, Zhang M, Lu Y, Sopha SC, Washington MK et al (2015) Pyruvate kinase muscle isoenzyme 2 (PKM2) expression is associated with overall survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer 46:390–398
Lu R, Jiang M, Chen Z, Xu X, Hu H et al (2013) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with the induced hypoxia regulated protein and poor prognosis. PLoS One 8:e74853
Lu K, Yang J, Li DC, He SB, Zhu DM et al (2016) Expression and clinical significance of glucose transporter-1 in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett 12:243–249
Lubezky N, Metser U, Geva R, Nakache R, Shmueli E et al (2007) The role and limitations of 18-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan and computerized tomography (CT) in restaging patients with hepatic colorectal metastases following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: comparison with operative and pathological findings. J Gastrointest Surg 11:472–478
Lum JJ, Bui T, Gruber M, Gordan JD, DeBerardinis RJ et al (2007) The transcription factor HIF-1alpha plays a critical role in the growth factor-dependent regulation of both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis. Genes Dev 21:1037–1049
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Hara T, Nakamoto Y, Fujimoto K et al (2007) Expression of glucose transporter-1, hexokinase-II, proliferating cell nuclear antigen and survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Invest 25:154–162
Maki Y, Soh J, Ichimura K, Shien K, Furukawa M et al (2013) Impact of GLUT1 and Ki-67 expression on early stage lung adenocarcinoma diagnosed according to a new international multidisciplinary classification. Oncol Rep 29:133–140
Matoba S, Kang JG, Patino WD, Wragg A, Boehm M et al (2006) p53 regulates mitochondrial respiration. Science 312:1650–1653
McArdle S, Fallet R, Jeffries WB, Pettinger WA (1992) DOCA-enhanced sites of vasopressin-stimulated cAMP formation in rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol 263:F1093–F1097
Mineta H, Miura K, Takebayashi S, Misawa K, Araki K et al (2002) Prognostic value of glucose transporter 1 expression in patients with hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 22:3489–3494
Mohammad GH, Olde Damink SW, Malago M, Dhar DK, Pereira SP (2016) Pyruvate kinase M2 and lactate dehydrogenase a are overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and correlate with poor outcome. PLoS One 11:e0151635
Mori Y, Tsukinoki K, Yasuda M, Miyazawa M, Kaneko A et al (2007) Glucose transporter type 1 expression are associated with poor prognosis in patients with salivary gland tumors. Oral Oncol 43:563–569
Ogawa H, Nagano H, Konno M, Eguchi H, Koseki J et al (2015) The combination of the expression of hexokinase 2 and pyruvate kinase M2 is a prognostic marker in patients with pancreatic cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 3:563–571
Osugi J, Yamaura T, Muto S, Okabe N, Matsumura Y et al (2015) Prognostic impact of the combination of glucose transporter 1 and ATP citrate lyase in node-negative patients with non-small lung cancer. Lung Cancer 88:310–318
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Pauwels EK, Sturm EJ, Bombardieri E, Cleton FJ, Stokkel MP (2000) Positron-emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. Part I. Biochemical uptake mechanism and its implication for clinical studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:549–559
Pu H, Zhang Q, Zhao C, Shi L, Wang Y et al (2015) Overexpression of G6PD is associated with high risks of recurrent metastasis and poor progression-free survival in primary breast carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 13:323
Qiu MZ, Han B, Luo HY, Zhou ZW, Wang ZQ et al (2011) Expressions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hexokinase-II in gastric adenocarcinoma: the impact on prognosis and correlation to clinicopathologic features. Tumour Biol 32:159–166
Ramani P, Headford A, May MT (2013) GLUT1 protein expression correlates with unfavourable histologic category and high risk in patients with neuroblastic tumours. Virchows Arch 462:203–209
Rho M, Kim J, Jee CD, Lee YM, Lee HE et al (2007) Expression of type 2 hexokinase and mitochondria-related genes in gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines. Anticancer Res 27:251–258
Sasaki H, Shitara M, Yokota K, Hikosaka Y, Moriyama S et al (2012) Overexpression of GLUT1 correlates with Kras mutations in lung carcinomas. Mol Med Rep 5:599–602
Sato-Tadano A, Suzuki T, Amari M, Takagi K, Miki Y et al (2013) Hexokinase II in breast carcinoma: a potent prognostic factor associated with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and Ki-67. Cancer Sci 104:1380–1388
Sawayama H, Ishimoto T, Watanabe M, Yoshida N, Baba Y et al (2014) High expression of glucose transporter 1 on primary lesions of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with hematogenous recurrence. Ann Surg Oncol 21:1756–1762
Schlosser HA, Drebber U, Urbanski A, Haase S, Baltin C et al (2017) Glucose transporters 1, 3, 6, and 10 are expressed in gastric cancer and glucose transporter 3 is associated with UICC stage and survival. Gastric Cancer 20:83–91
Sebastiani V (2004) Fatty acid synthase is a marker of increased risk of recurrence in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 92:101–105
Son J, Lyssiotis CA, Ying H, Wang X, Hua S et al (2013) Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature 496:101–105
Song Y, Liu D, He G (2015) TKTL1 and p63 are biomarkers for the poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark 15:591–597
Starska K, Forma E, Jozwiak P, Brys M, Lewy-Trenda I et al (2015) Gene and protein expression of glucose transporter 1 and glucose transporter 3 in human laryngeal cancer-the relationship with regulatory hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression, tumor invasiveness, and patient prognosis. Tumour Biol 36:2309–2321
Stubbs M, McSheehy PM, Griffiths JR, Bashford CL (2000) Causes and consequences of tumour acidity and implications for treatment. Mol Med Today 6:15–19
Suh DH, Kim MA, Kim H, Kim MK, Kim HS et al (2014) Association of overexpression of hexokinase II with chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Exp Med 14:345–353
Sung JY, Kim GY, Lim SJ, Park YK, Kim YW (2010) Expression of the GLUT1 glucose transporter and p53 in carcinomas of the pancreatobiliary tract. Pathol Res Pract 206:24–29
Swartz JE, Pothen AJ, van Kempen PM, Stegeman I, Formsma FK et al (2016) Poor prognosis in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas that overexpress hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha. Head Neck 38:1338–1346
Symmans WF, Peintinger F, Hatzis C, Rajan R, Kuerer H et al (2007) Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25:4414–4422
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR (2007) Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 8:16
Wang J, Yuan W, Chen Z, Wu S, Chen J et al (2012) Overexpression of G6PD is associated with poor clinical outcome in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 33:95–101
Wang X, Li X, Zhang X, Fan R, Gu H et al (2015a) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression is correlated with poor clinical prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 41:1293–1299
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Yuan C et al (2015b) Overexpression of pyruvate kinase M2 associates with aggressive clinicopathological features and unfavorable prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 16:839–845
Warburg O (1956a) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–314
Warburg O (1956b) On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 124:269–270
Warburg O, Wind F, Negelein E (1927) The metabolism of tumors in the body. J Gen Physiol 8:519–530
Williamson PR, Smith CT, Hutton JL, Marson AG (2002) Aggregate data meta-analysis with time-to-event outcomes. Stat Med 21:3337–3351
Yan S, Coffing BN, Li Z, Xie H, Brennick JB et al (2016) Diagnostic and prognostic value of ProEx C and GLUT1 in melanocytic lesions. Anticancer Res 36:2871–2880
Yang Z, Wu Z, Liu T, Han L, Wang C et al (2014) Upregulation of PDK1 associates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with facilitating tumorigenicity in vitro. Med Oncol 31:337
Yu ZT, Zhao HF, Shang XB (2008) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vessel endothelial growth factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and clinico-pathological significance thereof. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 88:2465–2469
Yu G, Yu W, Jin G, Xu D, Chen Y et al (2015a) PKM2 regulates neural invasion of and predicts poor prognosis for human hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Cancer 14:193
Yu M, Zhou Q, Zhou Y, Fu Z, Tan L et al (2015b) Metabolic phenotypes in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 10:e0115153
Yuan C, Li Z, Wang Y, Qi B, Zhang W et al (2014) Overexpression of metabolic markers PKM2 and LDH5 correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features and adverse patient prognosis in tongue cancer. Histopathology 65:595–605
Zhan C, Shi Y, Lu C, Wang Q (2013) Pyruvate kinase M2 is highly correlated with the differentiation and the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell cancer. Dis Esophagus 26:746–753
Zhang D, Wang Y, Dong L, Huang Y, Yuan J et al (2013a) Therapeutic role of EF24 targeting glucose transporter 1-mediated metabolism and metastasis in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Sci 104:1690–1696
Zhang X, He C, He C, Chen B, Liu Y et al (2013b) Nuclear PKM2 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 209:510–515
Zhang MX, Hua YJ, Wang HY, Zhou L, Mai HQ et al (2016a) Long-term prognostic implications and therapeutic target role of hexokinase II in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 7:21287–21297
Zhang ZF, Feng XS, Chen H, Duan ZJ, Wang LX et al (2016b) Prognostic significance of synergistic hexokinase-2 and beta2-adrenergic receptor expression in human hepatocelluar carcinoma after curative resection. BMC Gastroenterol 16:57
Zhao Y, Liu H, Riker AI, Fodstad O, Ledoux SP et al (2011) Emerging metabolic targets in cancer therapy. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 16:1844–1860
Zhao Y, Shen L, Chen X, Qian Y, Zhou Q et al (2015) High expression of PKM2 as a poor prognosis indicator is associated with radiation resistance in cervical cancer. Histol Histopathol 30:1313–1320
Zhou S, Wang S, Wu Q, Fan J, Wang Q (2008) Expression of glucose transporter-1 and - 3 in the head and neck carcinoma—the correlation of the expression with the biological behaviors. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 70:189–194
Zhuang L, Scolyer RA, Murali R, McCarthy SW, Zhang XD et al (2010) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in melanoma increases with disease progression and is associated with expression of Bcl-XL and Mcl-1, but not Bcl-2 proteins. Mod Pathol 23:45–53
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (no. 2014A030310073), Guangdong Province Public interest research and capacity—building projects, China (no. 2014A020212448), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province—Doctor Foundation (no. 2014A030310073), and Guangzhou Science and technology plan of scientific research projects, China (no. 201510010286).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was funded by the above institutions and has received research grants from it. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2019_2847_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1A: Forest plot of hazard ratio (HR) for the association between HIF-1α and OS (A), DFS (B) (TIF 5223 KB)
432_2019_2847_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1B: Forest plot of hazard ratio (HR) for the association between HIF-1α and OS (A), DFS (B) (TIF 4388 KB)
432_2019_2847_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 3A: Begg’s funnel plot for the assessment of publication bias in the present study for HIF-1. (A) OS, (B) DFS (TIF 1351 KB)
432_2019_2847_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 3B: Begg’s funnel plot for the assessment of publication bias in the present study for HIF-1. (A) OS, (B) DFS (TIF 1351 KB)
432_2019_2847_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 4: Begg’s funnel plot for the assessment of publication bias in the present study for p53 (TIF 1351 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Chen, S., Hong, W. et al. Prognostic role of glycolysis for cancer outcome: evidence from 86 studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 967–999 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02847-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02847-w