Abstract
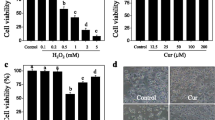
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy in clinic is severely limited by its adverse effect, including neurotoxicity. Oxidative damage contributes to cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity, but the mechanism remains unclearly. Cyanidin, a natural flavonoid compound, exhibits powerful antioxidant activity. Hence, we investigated the protective effects of cyanidin on PC12 cells against cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity and explored the underlying mechanisms. The results showed that cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity was completely reversed by cyanidin through inhibition of PC12 cell apoptosis, as proved by the attenuation of Sub-G1 peak, PARP cleavage, and caspases-3 activation. Mechanistically, cyanidin significantly inhibited reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA damage in cisplatin-treated PC12 cells. Our findings revealed that cyanidin as an apoptotic inhibitor effectively blocked cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity through inhibition of ROS-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis, predicating its therapeutic potential in prevention of chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity.
Graphical Abstract
Cisplatin caused DNA damage, activated p53, and subsequently induced PC12 cells apoptosis by triggering ROS overproduction. However, cyanidin administration effectively inhibited DNA damage, attenuated p53 phosphorylation, and eventually reversed cisplatin-induced PC12 cell apoptosis through inhibition ROS accumulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquaviva R, Russo A, Galvano F, Galvano G, Barcellona ML, Li Volti G, Vanella A (2003) Cyanidin and cyanidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside as DNA cleavage protectors and antioxidants. Cell Biol Toxicol 19:243–252
Campbell KC, Meech RP, Rybak LP, Hughes LF (2003) The effect of D-methionine on cochlear oxidative state with and without cisplatin administration: mechanisms of otoprotection. J Am Acad Audiol 14:144–156
Cepeda V, Fuertes MA, Castilla J, Alonso C, Quevedo C, Perez JM (2007) Biochemical mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 7:3–18
Chen Y, Jungsuwadee P, Vore M, Butterfield DA, St Clair DK (2007) Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy: oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Mol Interv 7:147–156
Chun OK, Kim DO, Lee CY (2003) Superoxide radical scavenging activity of the major polyphenols in fresh plums. J Agric Food Chem 51:8067–8072
Czarna M, Jarmuszkiewicz W (2006) Role of mitochondria in reactive oxygen species generation and removal; relevance to signaling and programmed cell death. Postepy Biochem 52:145–156
Dietrich J, Han R, Yang Y, Mayer-Proschel M, Noble M (2006) CNS progenitor cells and oligodendrocytes are targets of chemotherapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo. J Biol 5:22
Duffner PK (2006) The long term effects of chemotherapy on the central nervous system. J Biol 5:21
Galvano F, La Fauci L, Lazzarino G, Fogliano V, Ritieni A, Ciappellano S, Battistini NC, Tavazzi B, Galvano G (2004) Cyanidins: metabolism and biological properties. J Nutr Biochem 15:2–11
Guerra MC, Galvano F, Bonsi L, Speroni E, Costa S, Renzulli C, Cervellati R (2005) Cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucopyranoside, a natural free-radical scavenger against aflatoxin B1- and ochratoxin A-induced cell damage in a human hepatoma cell line (Hep G2) and a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line (CaCo-2). Br J Nutr 94:211–220
Gulec M, Oral E, Dursun OB, Yucel A, Hacimuftuoglu A, Akcay F, Suleyman H (2013) Mirtazapine protects against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in the rat brain. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 67:50–58
James SE, Burden H, Burgess R, Xie Y, Yang T, Massa SM, Longo FM, Lu Q (2008) Anti-cancer drug induced neurotoxicity and identification of Rho pathway signaling modulators as potential neuroprotectants. Neurotoxicology 29:605–612
Jowsey PA, Williams FM, Blain PG (2012) DNA damage responses in cells exposed to sulphur mustard. Toxicol Lett 209:1–10
Kim DO, Heo HJ, Kim YJ, Yang HS, Lee CY (2005) Sweet and sour cherry phenolics and their protective effects on neuronal cells. J Agric Food Chem 53:9921–9927
Kong JM, Chia LS, Goh NK, Chia TF, Brouillard R (2003) Analysis and biological activities of anthocyanins. Phytochemistry 64:923–933
Lee SK, Zhang W, Sanderson BJ (2008) Selective growth inhibition of human leukemia and human lymphoblastoid cells by resveratrol via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. J Agric Food Chem 56:7572–7577
McWhinney SR, Goldberg RM, McLeod HL (2009) Platinum neurotoxicity pharmacogenetics. Mol Cancer Ther 8:10–16
Orhan B, Yalcin S, Nurlu G, Zeybek D, Muftuoglu S (2004) Erythropoietin against cisplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in rats. Med Oncol 21:197–203
Pavlica S, Gebhardt R (2005) Protective effects of ellagic and chlorogenic acids against oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Free Radic Res 39:1377–1390
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA (2005) Ototoxicity: therapeutic opportunities. Drug Discov Today 10:1313–1321
Servais H, Ortiz A, Devuyst O, Denamur S, Tulkens PM, Mingeot-Leclercq MP (2008) Renal cell apoptosis induced by nephrotoxic drugs: cellular and molecular mechanisms and potential approaches to modulation. Apoptosis 13:11–32
Staat K, Segatore M (2005) The phenomenon of chemo brain. Clin J Oncol Nurs 9:713–721
Tuncer S, Dalkilic N, Akif Dunbar M, Keles B (2010) Comparative effects of alpha lipoic acid and melatonin on cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity. Int J Neurosci 120:655–663
Vogt W (1995) Oxidation of methionyl residues in proteins: tools, targets, and reversal. Free Radic Biol Med 18:93–105
Waseem M, Parvez S (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated cisplatin induced toxicity: modulatory role of curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol 53:334–342
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 81471212, 81271275, 81070947, 30770759 to B.-L. Sun, No. ZR2010HM101, Y2008C124 to M.-J. Zhu; Science and Technology Research Fund of Shandong No. 2007GGWZ02056 to M.-J. Zhu; Science and Technology Development Plans of Jinan No. 201202053 to M.-J. Zhu; and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong No. ZR2012HZ006 to B.-L. Sun.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests for all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Da-wei Li and Jing-yi Sun have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Dw., Sun, Jy., Wang, K. et al. Attenuation of Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity by Cyanidin, a Natural Inhibitor of ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in PC12 Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 995–1001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0194-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0194-6