Abstract
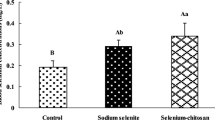
This study examined the effect of dietary (200 μg/d for 8 wk) supplementation with selenium (as sodium selenite) on the ability of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to respond to stimulation with alloantigen, develop into cytotoxic lymphocytes, and to destroy tumor cells, and on the activity of natural killer cells. The participants in the study were randomized for age, sex, weight, height, and nutritional habits and given selenite or placebo tablets; all participants had a selenium replete status as indicated by their plasma Se levels prior to supplementation. The data indicated that the supplementation regimen resulted in 118% increase in cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated tumor cytotoxicity and 82.3% increase in natural killer cell activity as compared to baseline values. This apparently was related to the ability of the nutrient to enhance the expression of receptors for the growth regulatory lymphokine interleukin-2, and consequently, the rate of cell proliferation and differentiation into cytotoxic cells. The supplementation regimen did not produce significant changes in the plasma Se levels of the participants. The results indicated that the immunoenhancing effects of selenium in humans require supplementation above the replete levels produced by normal dietary intake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Beilstein, P. D. Whanger, and I. Wong,Selenium in Biology and Medicine, Part A, G. F. Combs, J. E. Spallholz, O. H. Levander, and J. E. Oldfield, eds., Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1987, pp. 197–212.
W. C. Willet, B. V. Polk, J. S. Morris, M. J. Stampler, S. Pressil, B. Rosner, and J. Taylor,Lancet 2, 130–134 (1983).
G. N. Schrauzer, D. A. White, and C. J. Schneider,Bioinorg. Chem. 7, 35–56 (977).
D. Medina and D. G. Morrison,Pathol. Immunopathol. Rev. 7, 187–198 (1988).
L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher and G. Stotzky,Environ. Res. 42, 277–303 (1987).
M. Roy, L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 193, 143–148 (1990).
L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, M. Roy, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,J. Nutr. Immunol. 1, 65–67 (1992).
M. Roy, L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 200, 36–43 (1992).
M. Roy, L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 202, 295–301 (1993).
L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, M. Roy, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 33, 23–35 (1992).
Committee on Dietary Allowances, Food and Nutrition Board, National Research Council. Recommended dietary allowances. 9th ed. Washington, DC., National Academy Press (1980).
J. E. Spallholz, G. F. Collins, and K. A. Schwartz,Bioinorg. Chem. 9, 453–459 (1978).
S. J. Bol, H. J. Rosdorff, C. P. Ronteltap, and L. A. Hennen,J. Immunol. Meth. 90, 15–23 (1986).
M. H. Julius, E. Simpson, and L. A. Herzenberg,Eur. J. Immunol. 3, 645–649 (1973).
M. G. Roncarolo, M. Bigler, J. B. Haanen, H. Yssel, R. Bacchetta, J. E. de Vries, and H. Spits,J. Immunol. 147, 781–787 (1991).
B. G. Brenner, G. Friedman, and R. G. Margolese,Cancer 56, 1543–1548 (1985).
L. Olmsted, G. N. Schrauzer, M. F. Arce, and J. Dowd,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 20, 59–65 (1989).
G. N. Schrauzer, and D. A. White,Bioinorg. Chem. 8, 303–318 (1978).
H. M. Meltzer, G. Norheim, E. G. Loken, and H. Holm,Br. J. Nutr. 67, 287–294 (1992).
H. M. Meltzer, G. Norheim, K. Bibow, K. Myhre, and H. Holm,Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 44, 435–446 (1990).
A. E. Chang and S. Shu,Cancer Invest. 10, 357–369 (1992).
H. Umehara and E. T. Bloom,Immunol. 70, 111–115 (1990).
T. A. Waldman,Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58, 875–911 (1989).
K. A. Smith,Science 240, 1169–1176 (1988).
M. Roy, L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. this issue (1994).
K. Ullman, J. B. Northrop, C. L. Verweij, and G. R. Grabtree,Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8, 421–452 (1990).
D. A. Cantrell and K. A. Smith,J. Exp. Med. 158, 1985–1911 (1983).
K. J. Einspahr, R. T. Abraham, C. J. Dick, and P. J. Leibson,J. Leuk. Biol. 52, 565–571 (1992).
A. Nagler, L. L. Lanier, and J. H. Phillips,J. Exp. Med. 171, 1527–1533 (1990).
G. Trinchieri, M. Matsumoto-Koboyashi, S. G. Clark, J. Sheehra, L. London, and B. Perussia,J. Exp. Med. 160, 1147–1169 (1989).
C. S. Henney, K. Kuribayashi, D. E. Kern, and S. Gillis,Nature 291, 335–338 (1981).
L. Kiremidjian-Schumacher, M. Roy, H. I. Wishe, M. W. Cohen, and G. Stotzky,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 193, 136–142 (1990).
G. H. Schranzer,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 33, 51–62 (1992).
R. F. Burk,J. Nutr. 116, 1584–1586 (1986).
M. Janghorbani, R. F. Martin, L. J. Kasper, X. F. Sun, and V. R. Young,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1, 670–677 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiremidjian-Schumacher, L., Roy, M., Wishe, H.I. et al. Supplementation with selenium and human immune cell functions. Biol Trace Elem Res 41, 115–127 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917222
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02917222