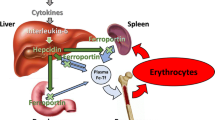
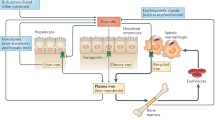
Abstract
Iron deficiency is the most common micronutrient deficiency in the world. Children, particularly infants living in developing countries are highly vulnerable to infectious diseases. Therefore, understanding the relationship between iron deficiency and infection is of great importance. Iron deficiency is associated with impairment of innate (natural) immunity and cell mediated immunity, thereby contributing to increased risk of infections. The iron acquisition by the microbes and their virulence is determined by various host and microbial mechanisms. Altering these mechanisms might provide modes of future therapy for infectious diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham-Rundles S. Effects of nutritional status on immunological function. Am J Clin Nutr 1982; 35:S1202–S1210.
Chandra RK. Reduced bactericidal capacity of polymorphs in iron deficiency. Arch Dis Child 1973; 48:864–866.
Bhaskaram C, Reddy V. Cell mediated immunity in iron- and vitamin- deficient children. Br Med J 1975; 3:522–522.
Kochan I. The role of iron in bacterial infections with special consideration of host-tubercle bacillus interaction. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1973; 60:1–30.
Beard JL. Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J Nutr 2001; 131:568S–580S.
Spear AT, Sherman AR. Iron deficiency alters DMBA-induced tumor burden and natural killer cell cytotoxicity in rats. J Nutr 1992; 122:46–55.
Oppenheimer SJ. Iron and its relation to immunity and infectious disease. J Nutr 2001; 131:616S–635S.
Markel TA, Crisotomo PR, Wang M et al. The struggle for iron: gastrointestinal microbes modulate the host immune response during infection. J Leukoc Biol 2007; 81:393–400.
Hallquist NA, McNeil LK, Lockwood JF, Sherman AR. Maternal-iron-deficiency effects on peritoneal macrophage and peritoneal natural-killer-cell cytotoxicity in rat pups. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55:741–746.
Bagchi K, Mohanram M, Reddy V. Humoral immune response in children with iron-deficiency anaemia. Br Med J 1980; 280:1249–1251.
Svoboda M, Nechvatalova K, Krejci J, Drabek J, Ficek R, Faldyna M. The absence of iron deficiency effect on the humoral immune response of piglets to tetanus toxoid. Veterinarni Medicina 2007; 52:179–185.
Murray MJ, Murray AB, Murray MB, Murray CJ. The adverse effect of iron repletion on the course of certain infections. Br Med J 1978; 2:1113–1115.
Oppenheimer SJ, Gibson FD, Macfarlane SB et al. Iron supplementation increases prevalence and effects of malaria: report on clinical studies in Papua New Guinea. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1986; 80:603–612.
Bullen J, Griffiths E, Rogers H, Ward G. Sepsis: the critical role of iron. Microbes Infect 2000; 2:409–415.
Ahluwalia N, Sun J, Krause D, Mastro A, Handte G. Immune function is impaired in iron-deficient, homebound, older women. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79:516–521.
Ekiz C, Agaoglu L, Karakas Z, Gurel N, Yalcin I. The effect of iron deficiency anemia on the function of immune system. Hematol J 2005; 5:579–583.
Snow RW, Byass P, Shenton FC, Greenwood BM. The relationship between anthropometric measurements and measurements of iron status and susceptibility to malaria in Gambian children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1991; 85:584–589.
Oppenheimer SJ, Hill AV, Gibson FD, Macfarlane SB, Moody JB, Pringle J. The interaction of alpha thalassaemia with malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1987; 81:322–326.
Higgs JM, Wells RS. Chronic muco-cutaneous candidiasis: new approaches to treatment. Br J Dermatol 1973; 89:179–190.
Weijmer MC, Neering H, Welten C. Preliminary report: furunculosis and hyporferraemia. Lancet 1990; 336:464–466.
Harju E. Empty iron stores as a significant risk factor in abdominal surgery. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1988; 12:282–285.
MacKay HM. Anaemia in infancy; its prevalence and prevention. Arch Dis Child 1928; 3:117–147.
Andelman MB, Sered BR. Utilization of dietary iron by term infants. A study of 1,048 infants from a low socioeconomic population. Am J Dis Child 1966; 111:45–55.
Cantwell RJ. Iron deficiency anemia of infancy: some clinical principles illustrated by the response of Maori infants to neonatal parenteral iron administration. Clin Pediatr 1972; 11:443–449.
Barry DM, Reeve AW. Increased incidence of gram-negative neonatal sepsis with intramuscular iron administration. Pediatrics 1977; 60:908–912.
James JA, Combes M. Iron deficiency in the premature infant: Significance and prevention by the intramuscular administration of iron-dextran. Pediatrics 1960; 26:368–374.
Berger J, Dyck JL, Galan P et al. Effect of daily iron supplementation on iron status, cell-mediated immunity, and incidence of infections in 6–36 month old Togolese children. Eur J Clin Nutr 2000; 54:29–35.
Gera T, Sachdev HP. Effect of iron supplementation on incidence of infectious illness in children: systematic review. Br Med J 2002; 325:1142–1144.
Tielsch JM, Khatry S, Stoltzfus RJ et al. Effect of routine prophylactic supplementation with iron and folic acid on preschool child mortality in southern Nepal: community-based, cluster-randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2006; 367:144–152.
Sazawal S, Black RE, Ramsan M et al. Effect of routine prophylactic supplementation with iron and folic acid on admission to hospital and mortality in preschool children in a high malaria transmission setting: community-based, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2006; 367:133–143.
Weinberg ED. Iron availability and infection. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1790:600–605.
Beaumont C, Delaby C. Recycling iron in normal and pathological states. Semin Hematol 2009; 46:328–338.
Ganz T, Nemeth E. Iron sequestration and anemia of inflammation. Semin Hematol 2009; 46:387–393.
Jurado RL. Iron, infections, and anemia of inflammation. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25:888–895.
Nishimoto N, Kanakura Y, Aozasa K et al. Humanized antiinterleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease. Blood 2005; 106: 2627–2632.
Kawabata H, Tomosugi N, Kanda J, Tanaka Y, Yoshizaki K, Uchiyama T. Anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody tocilizumab reduces the level of serum hepcidin in patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease. Haematologica 2007; 92:857–858.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Choudhry, V.P. Iron deficiency and infection. Indian J Pediatr 77, 789–793 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0120-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0120-3