Abstract
Purpose
The increase in endothelin-1 (ET-1) and the decrease in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) both induce vasoconstriction and lead to molecular changes associated with diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) activation stimulates insulin secretion and may prevent atherosclerosis by increasing eNOS synthesis. However, there is paucity of information on the effect of GLP-1 activation on ET-1 expression. This study was conducted to address this issue.
Methods and Results
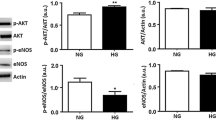
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were incubated with different concentrations of liraglutide, a GLP-1 agonist, and the expression of ET-1 and eNOS and activity of NF-κB were measured. Liraglutide, in a concentration-dependent manner, was observed to promote eNOS expression and to inhibit ET-1 expression both at mRNA and protein levels. Liraglutide also inhibited NF-κB phosphorylation and its translocation from cytoplasm to the nucleus. To ascertain the role of NF-κB activation in the altered expression of ET-1 and eNOS, we treated HUVECs with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). PMA activated NF-κB and reversed the effects of liraglutide on eNOS and ET-1 expression. The effects of PMA on eNOS and ET-1 expression were reproduced in experiments wherein cells were treated with TNF-α. Further, we measured the generation of IL-6, apowerful pro-inflammatory molecule released by endothelial cells, as a measure of cellular function. PMA increased IL-6 generation, and this effect was blocked by liraglutide.
Conclusions
Our observations suggest liraglutide suppresses ET-1 expression by inhibiting the phosphorylation of NF-κB. This mechanism may underlie the potential anti-atherosclerotic effects of GLP-1 agonists. Of note, these effects of liraglutide were seen in an in vitro setting wherein cellular glucose concentrations were elevated.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLP-1R:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-KappaB
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMA:
-
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- DPP4:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
- IκBα:
-
Inhibitor of kappa B alpha
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
References
Gibbons GW, Shaw PM. Diabetic vascular disease: characteristics of vascular disease unique to the diabetic patient. Semin Vasc Surg. 2012;25:89–92.
Madden JA. Role of the vascular endothelium and plaque in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2012;79:S58–62.
Toda N, Nakanishi-Toda M. How mental stress affects endothelial function. Pflugers Arch. 2011;462:779–94.
Hattori Y, Jojima T, Tomizawa A, et al. A glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue, liraglutide, upregulates nitric oxide production and exerts anti-inflammatory action in endothelial cells. Diabetologia. 2010;53:2256–63.
Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptides. Diabetes. 1998;47:159–69.
Montanya E. A comparison of currently available GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012;13:1451–67.
Ban K, Noyan-Ashraf MH, Hoefer J, Bolz SS, Drucker DJ, Husain M. Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation. 2008;117:2340–50.
Nyström T, Gutniak MK, Zhang Q, et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes patients with stable coronary artery disease. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;287:E1209–15.
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Shikatani EA, SchuikiI, et al. A glucagon-like Peptide-1 analog reverses the molecular pathology and cardiac dysfunction of a mouse model of obesity. Circulation. 2013;127:74–85.
Wang X, Khaidakov M, Ding Z, et al. Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) and cardiac fibroblast growth. Hypertension. 2012;60:1437–42.
Lu J, Mitra S, Wang X, Khaidakov M, Mehta JL. Oxidative stress and lectin-like ox-LDL-receptor LOX-1 in atherogenesis and tumorigenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15:2301–33.
Erdogdu O, Nathanson D, Sjöholm A, Nyström T, Zhang Q. Exendin-4 stimulates proliferation of human coronary artery endothelial cells through eNOS-, PKA- and PI3K/Akt-dependent pathways and requires GLP-1 receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;325:26–35.
Shiraki A, Oyama J, Komoda H, et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2012;221:375–82.
Chang MS, Chen BC, Yu MT, Sheu JR, Chen TF, Lin CH. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells via Ras, Raf-1, ERK, and NF-kappaB, but not p38 MAPK, pathways. Cell Signal. 2005;17:299–310.
Kampoli AM, Tousoulis D, Briasoulis A, Latsios G, Papageorgiou N, Stefanadis C. Potential pathogenic inflammatory mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:4147–58.
Oh YC, Kang OH, Kim SB, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of sinomenine by inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators in PMA plus A23187-stimulated HMC-1 Cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16:1184–91.
Davidson KW, Burg M, Shimbo D. Endothelin-1 release and stimulation of the inflammatory cascade: is acute coronary syndrome triggered by watching spectator sports? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:643–4.
Calles-Escandon J, Cipolla M. Diabetes and endothelial dysfunction: a clinical perspective. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:36–52.
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Momen MA, Ban K, et al. GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in mice. Diabetes. 2009;58:975–83.
Gaspari T, Liu H, Welungoda I, et al. A GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelial cell dysfunction and vascular adhesion molecule expression in an ApoE−/− mouse model. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2011;8:117–24.
Quehenberger P, Bierhaus A, Fasching P, et al. Endothelin 1 transcription is controlled by nuclear factor-kappaB in AGE-stimulated cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2000;49:1561–70.
Rajapurohitam V, Kilic A, Javadov S, Karmazyn M. Role of NF-κB and p38 MAPK activation in mediating angiotensin II and endothelin-1-induced stimulation in leptin production and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;366:287–97.
Piechota A, Goraca A. Influence of nuclear factor-κB inhibition on endothelin-1 induced lung edema and oxidative stress in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;62:183–8.
Hattori Y, Hattori S, Sato N, Kasai K. High-glucose-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;46:188–97.
Yang WS, Seo JW, Han NJ, et al. High glucose-induced NF-kappaB activation occurs via tyrosine phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha in human glomerular endothelial cells: involvement of Syk tyrosine kinase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F1065–75.
Suzuki J, Ogawa M, Muto S, et al. Novel IkB kinase inhibitors for treatment of nuclear factor-kB-related diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011;20:395–405.
Grumbach IM, Chen W, Mertens SA, Harrison DG. A negative feedback mechanism involving nitric oxide and nuclear factor kappa-B modulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase transcription. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;39:595–603.
Katsuyama K, Shichiri M, Marumo F, Hirata Y. NO inhibits cytokine-induced iNOS expression and NF-kappaB activation by interfering with phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB-alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18:1796–802.
Mohan S, Hamuro M, Sorescu GP, et al. IkappaBalpha-dependent regulation of low-shear flow-induced NF-kappa B activity: role of nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284:C1039–47.
Okayasu T, Tomizawa A, Suzuki K, Manaka K, Hattori Y. PPARalpha activators upregulate eNOS activity and inhibit cytokine-induced NF-kappaB activation through AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Life Sci. 2008;82:884–91.
Bonavida B, Baritaki S. Dual role of NO donors in the reversal of tumor cell resistance and EMT: Downregulation of the NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP circuitry. Nitric Oxide. 2011;24:1–7.
Romeo G, Liu WH, Asnaghi V, Kern TS, Lorenzi M. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB induced by diabetes and high glucose regulates a proapoptotic program in retinal pericytes. Diabetes. 2002;51:2241–8.
Ho FM, Lin WW, Chen BC, et al. High glucose-induced apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells is mediated through NF-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway and prevented by PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. 2006;18:391–9.
Abeywardena MY, Leifert WR, Warnes KE, Varghese JN, Head RJ. Cardiovascular biology of interleukin-6. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15:1809–21.
Clapp BR, Hirschfield GM, Storry C, et al. Inflammation and endothelial function: direct vascular effects of human C-reactive protein on nitric oxide bioavailability. Circulation. 2005;111:1530–6.
Arakawa M, Mita T, Azuma K, et al. Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4. Diabetes. 2010;59:1030–7.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development, Washington, DC. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Mehta, J.L. & Chen, M. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Inhibits Endothelin-1 in Endothelial Cell by Repressing Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Activation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 27, 371–380 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6463-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6463-z